Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times





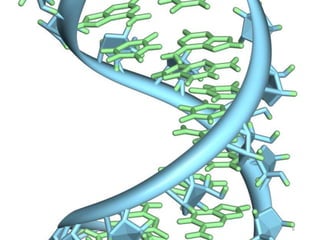
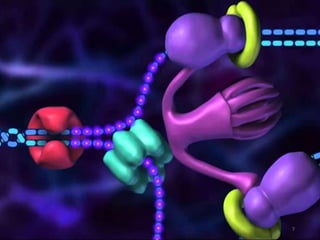




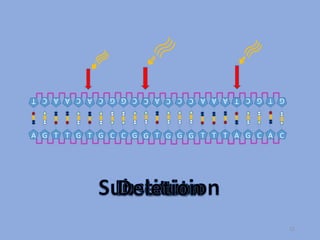



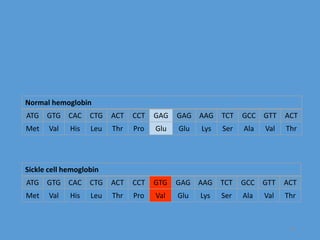
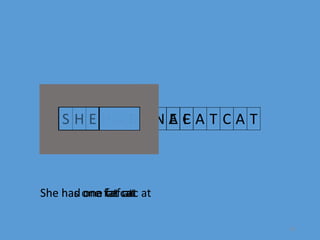

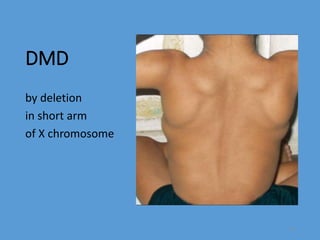



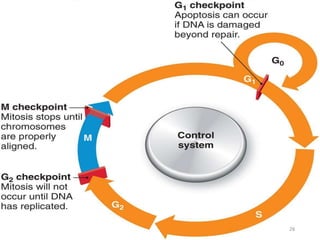





The document discusses mutations, defining them as permanent changes in the genome or extra-chromosomal elements. It outlines various causes and types of mutations, including deletion, insertion, and translocation, as well as their effects on conditions like sickle cell anemia and Down's syndrome. The key points also emphasize understanding the causes, types, effects, and prevention of mutations.































