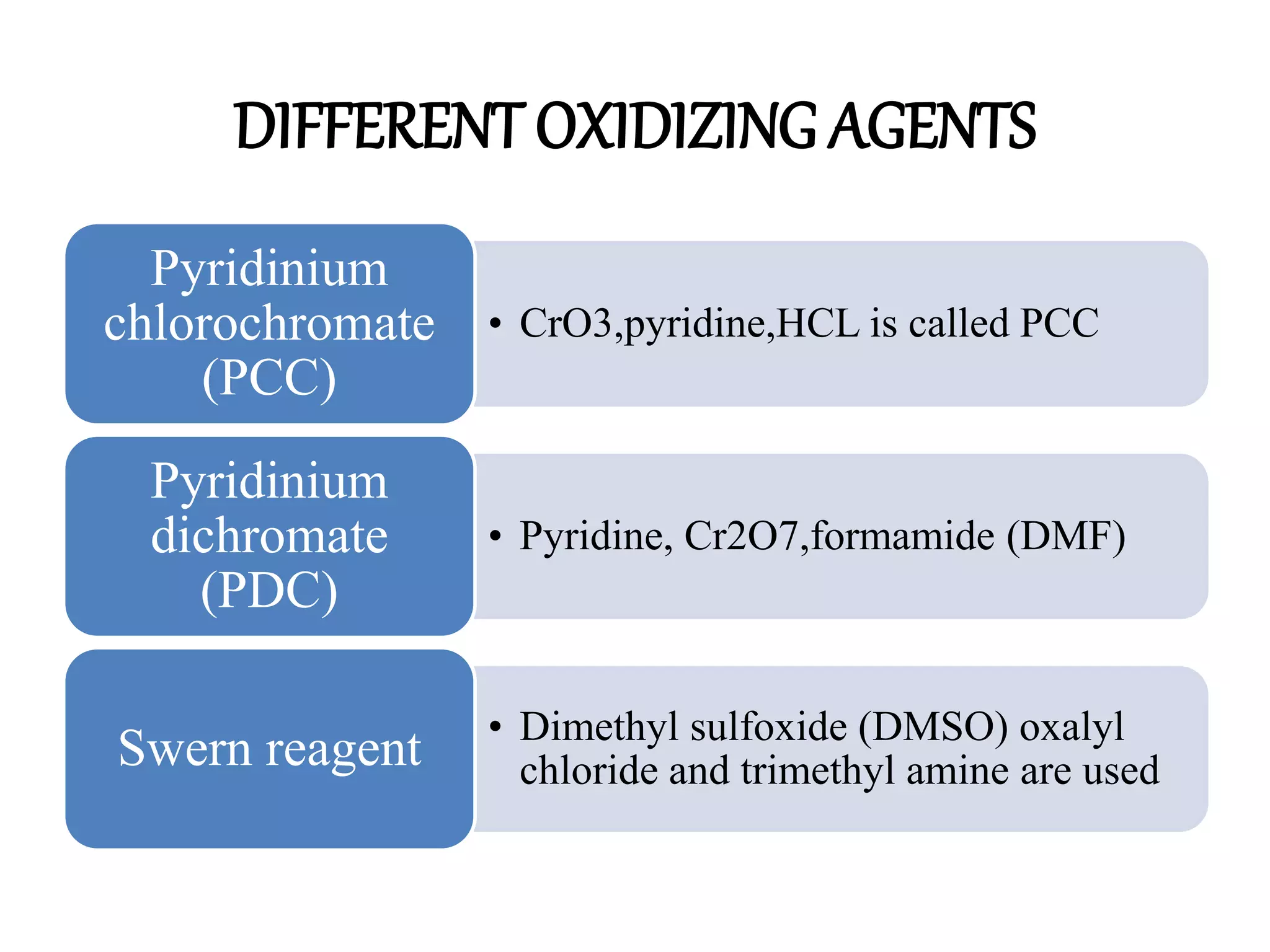
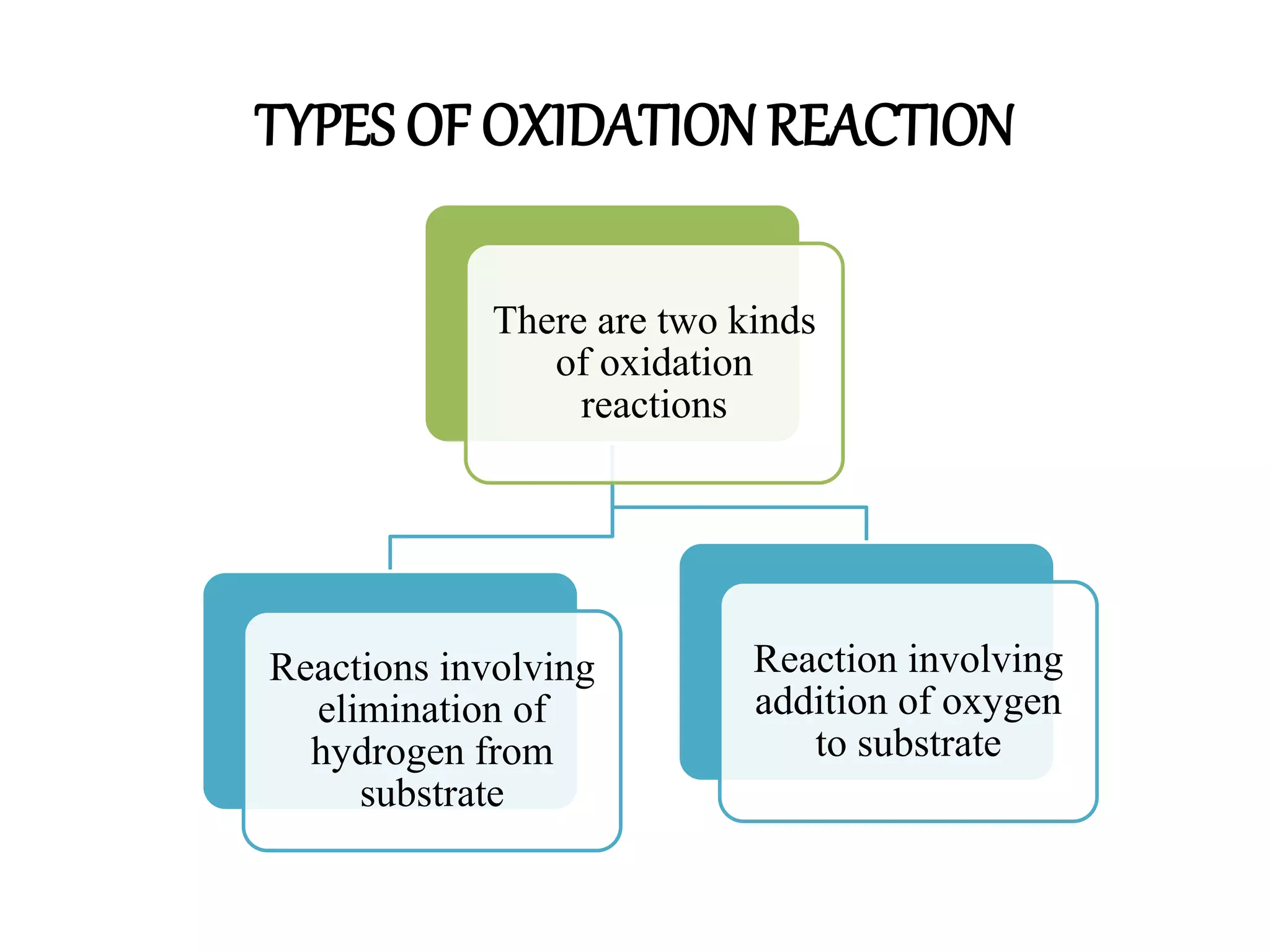
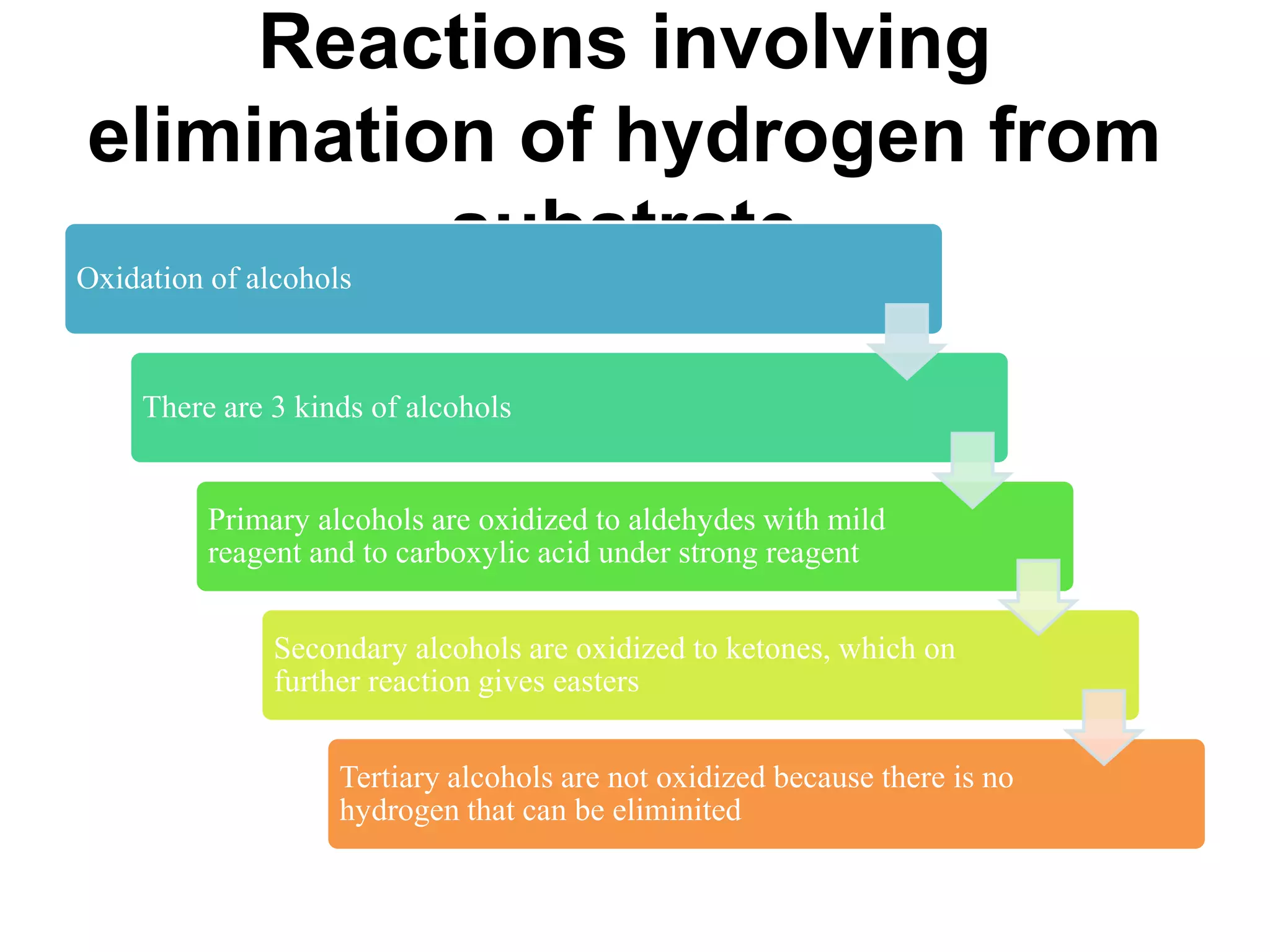
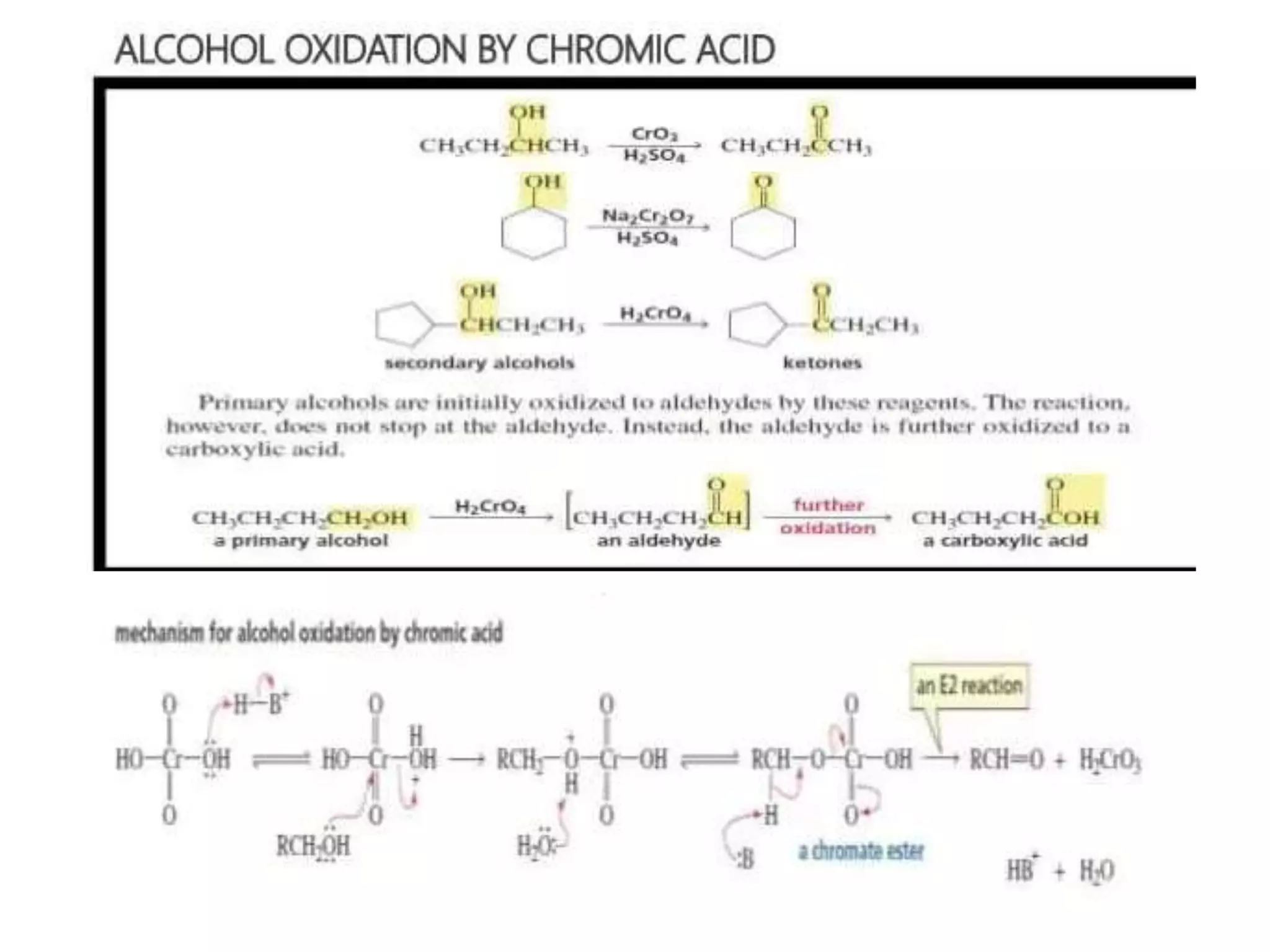
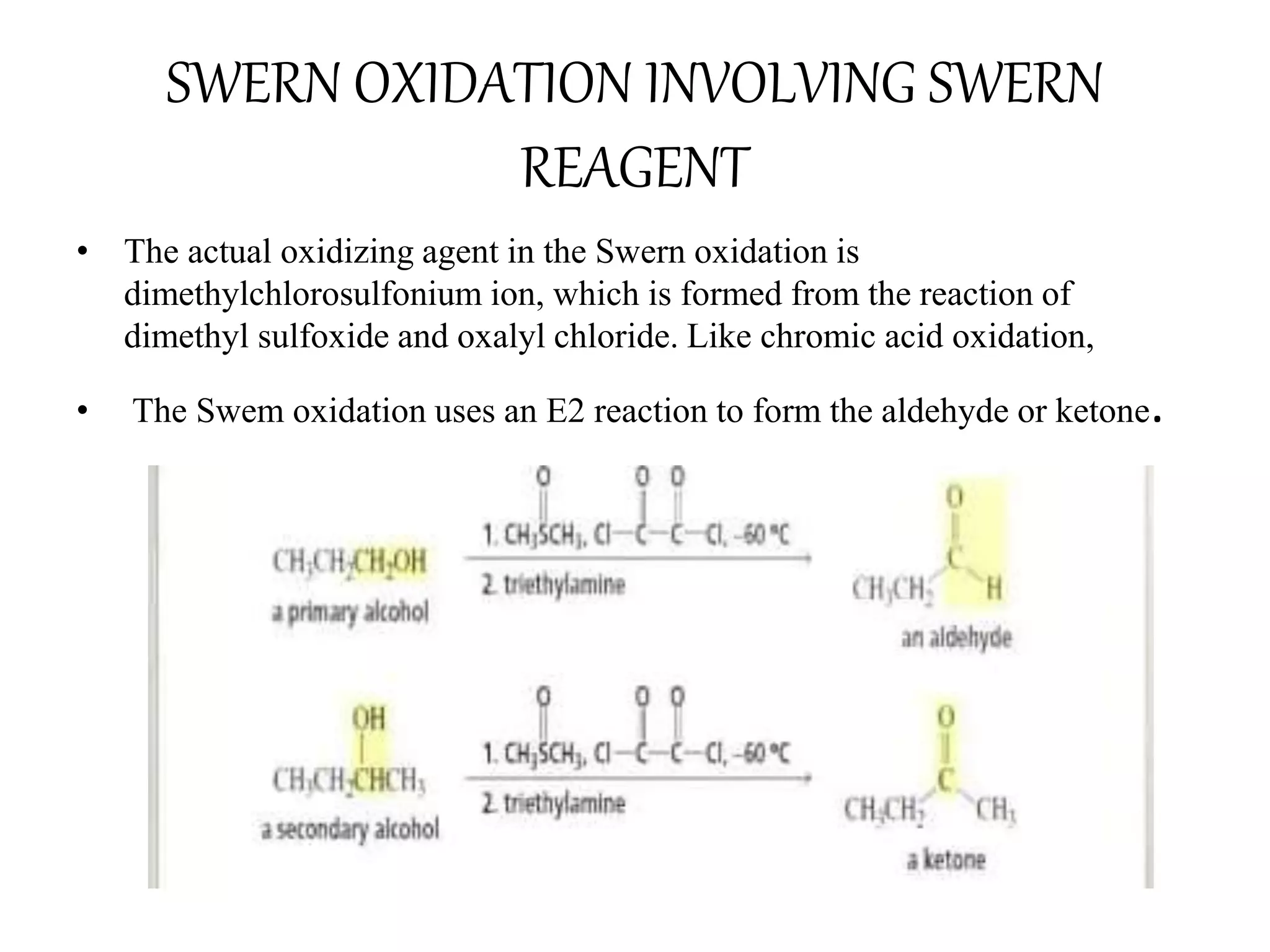
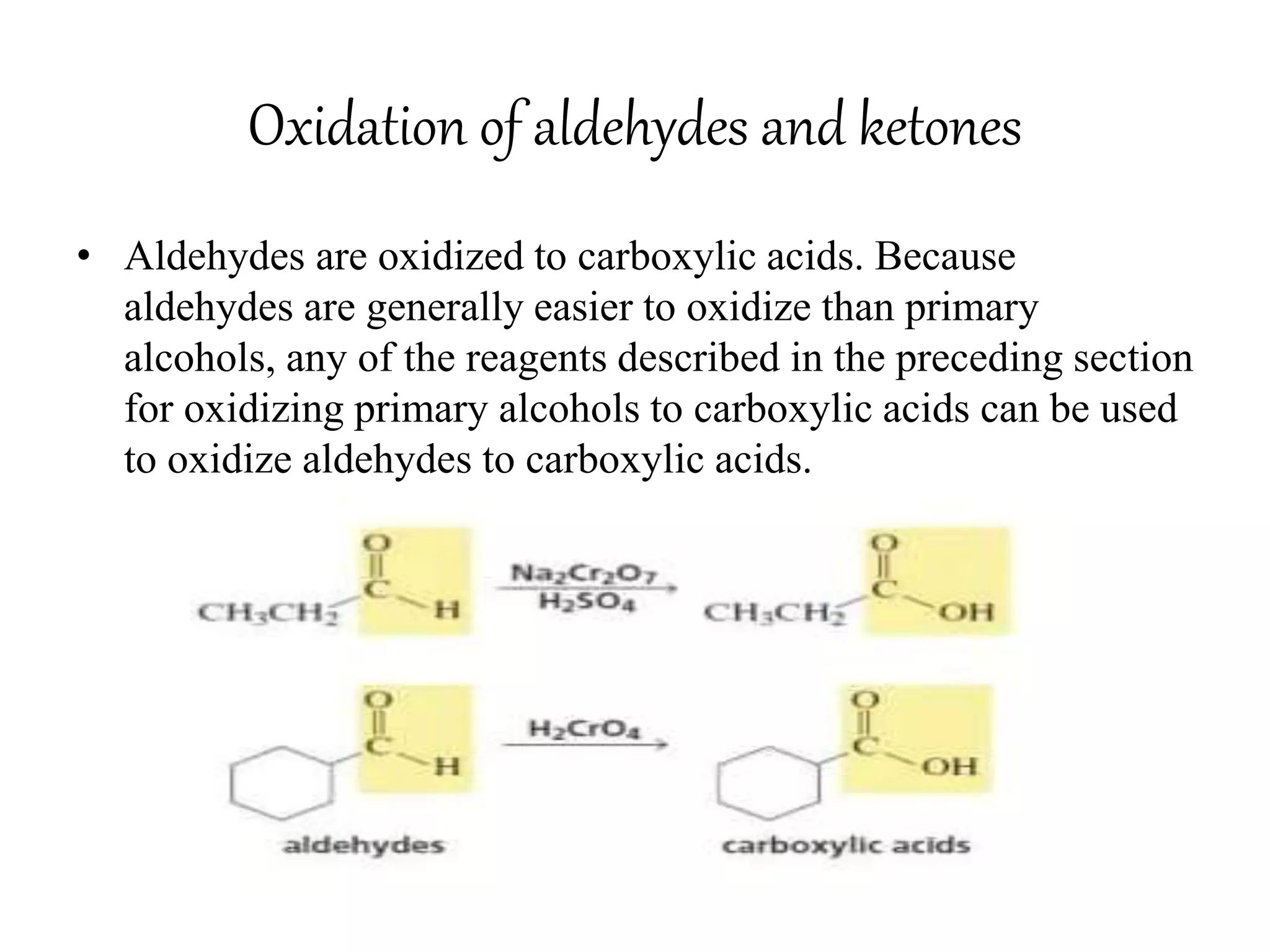
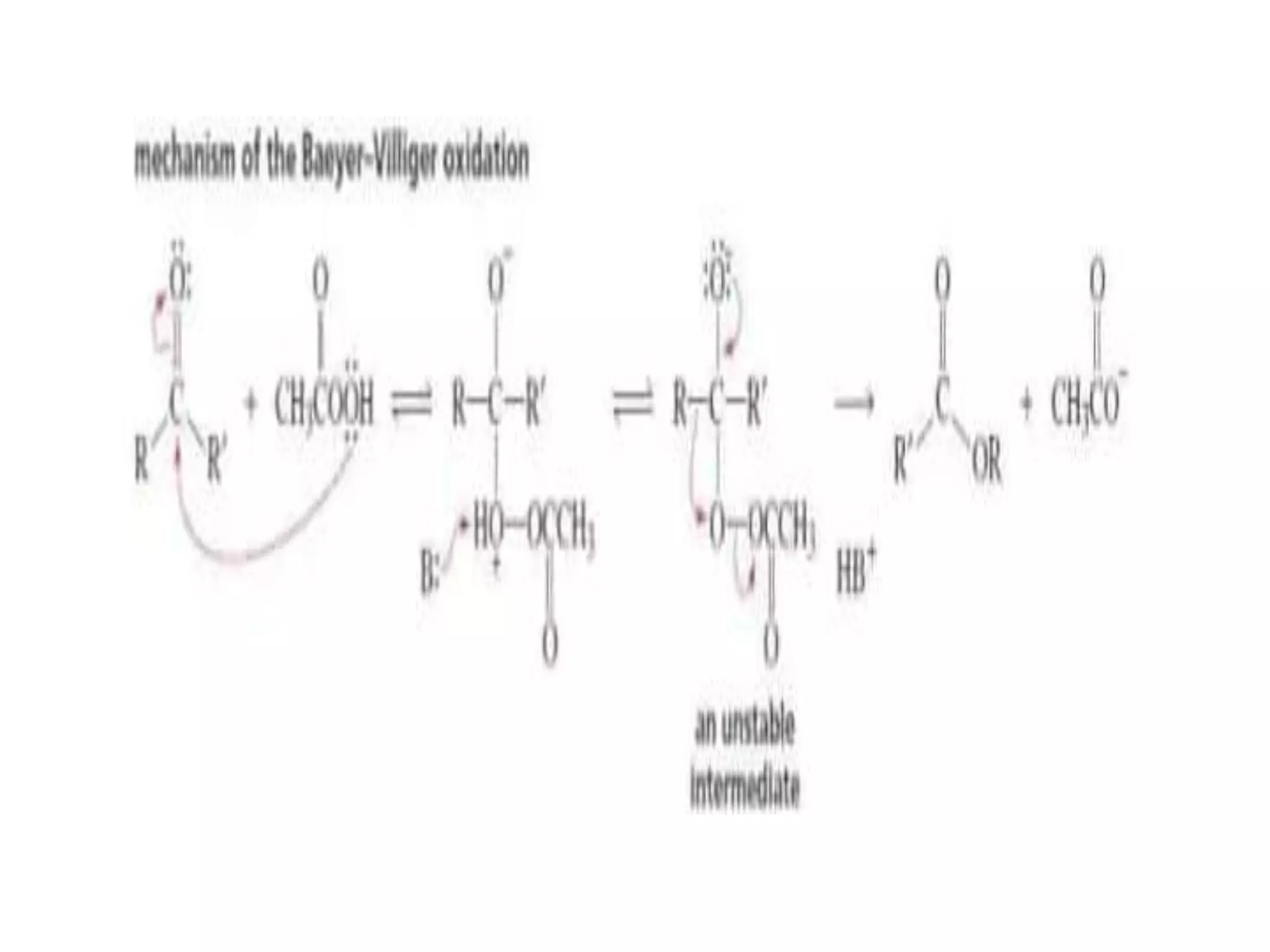
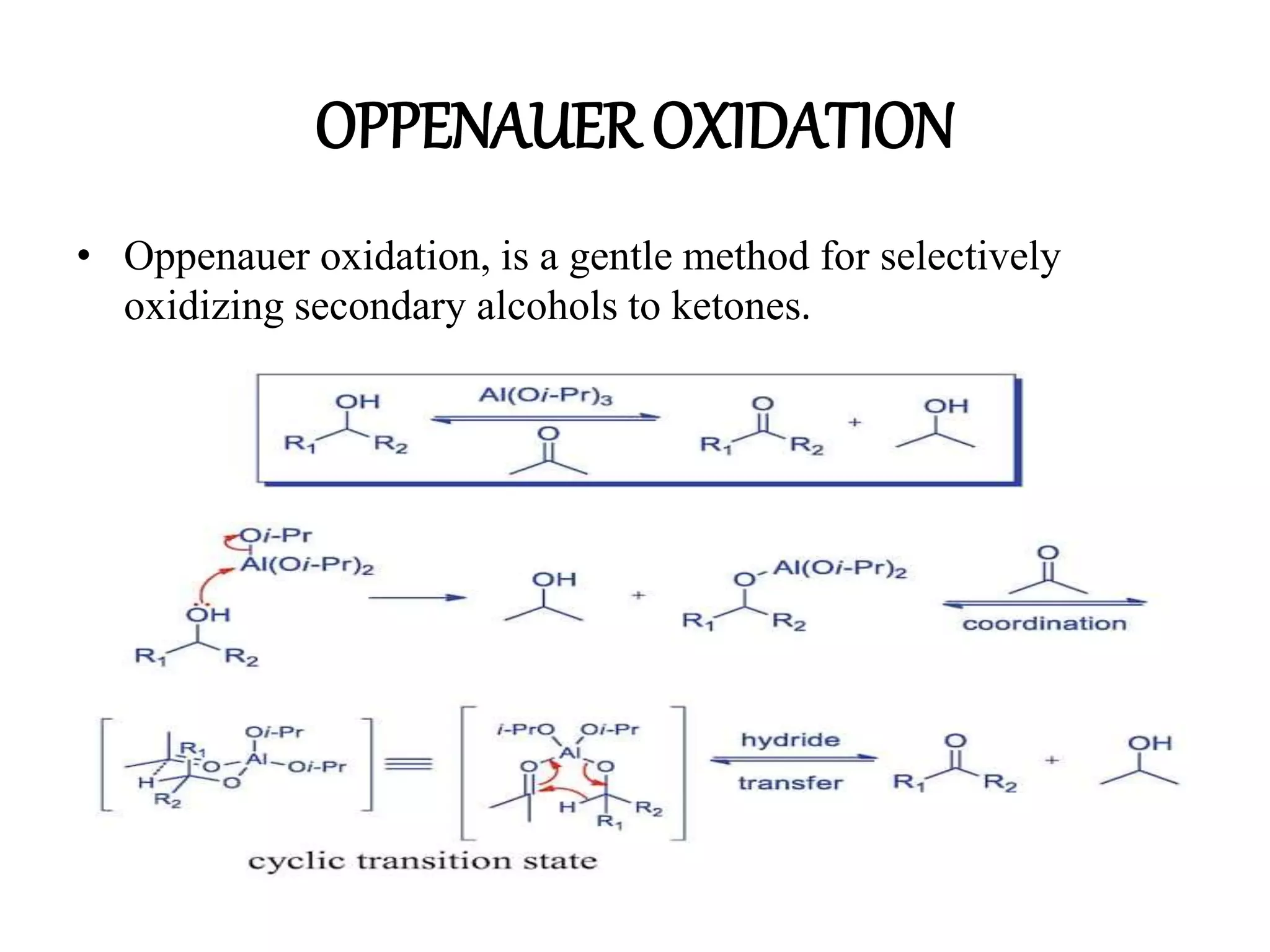
Oxidation is any chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons. There are two main types of oxidation reactions: reactions involving the elimination of hydrogen from a substrate, and reactions involving the addition of oxygen to a substrate. Common oxidizing agents include chromium trioxide, dichromate, permanganate, and halogens. Alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes and ketones, aldehydes to carboxylic acids, and alkenes can undergo permanganate cleavage. The document provides examples of oxidation reactions and multiple choice questions to test understanding.