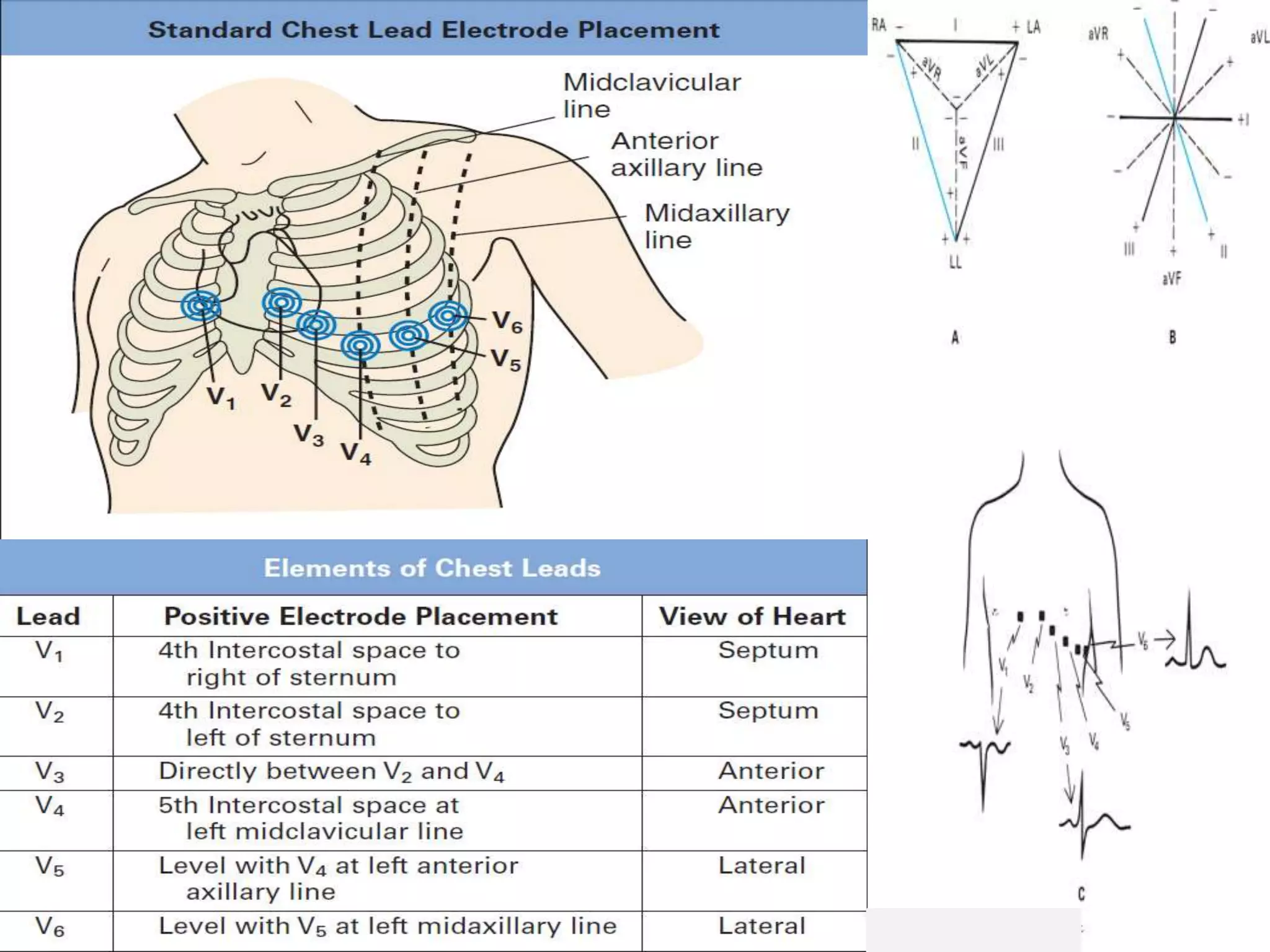
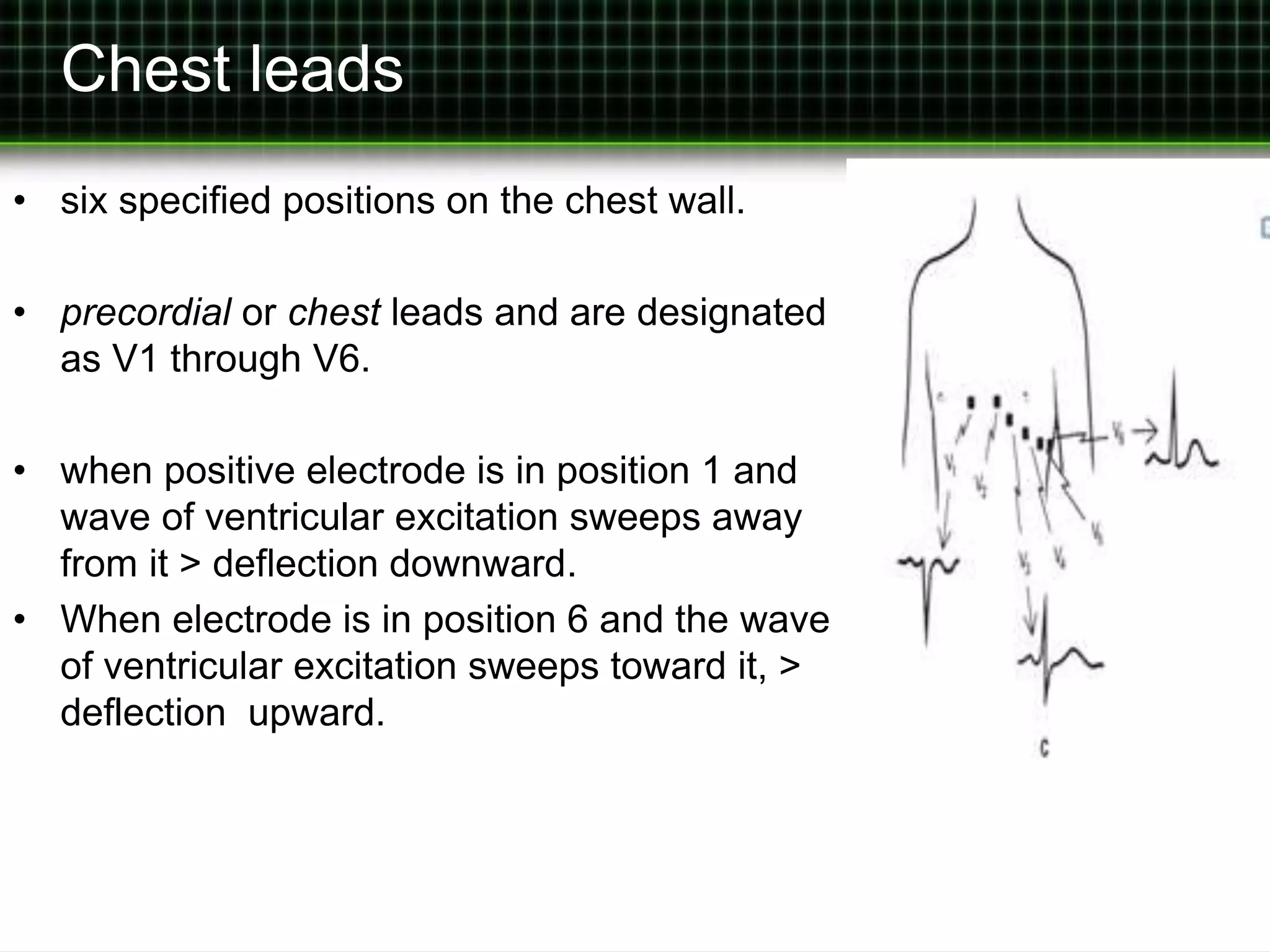
An electrocardiogram uses electrical conductors placed on the arms and legs to detect cardiac potential differences between sites. The standard 12-lead electrocardiogram records voltage changes from 12 different leads, including bipolar limb leads and unipolar chest leads. It provides a record of voltage changes occurring on the body surface as the heart's electrical impulse propagates through the cardiac cycle, following standardized conventions.






![The Standard 12-Lead Electrocardiogram
• Recorded from 12 different leads.
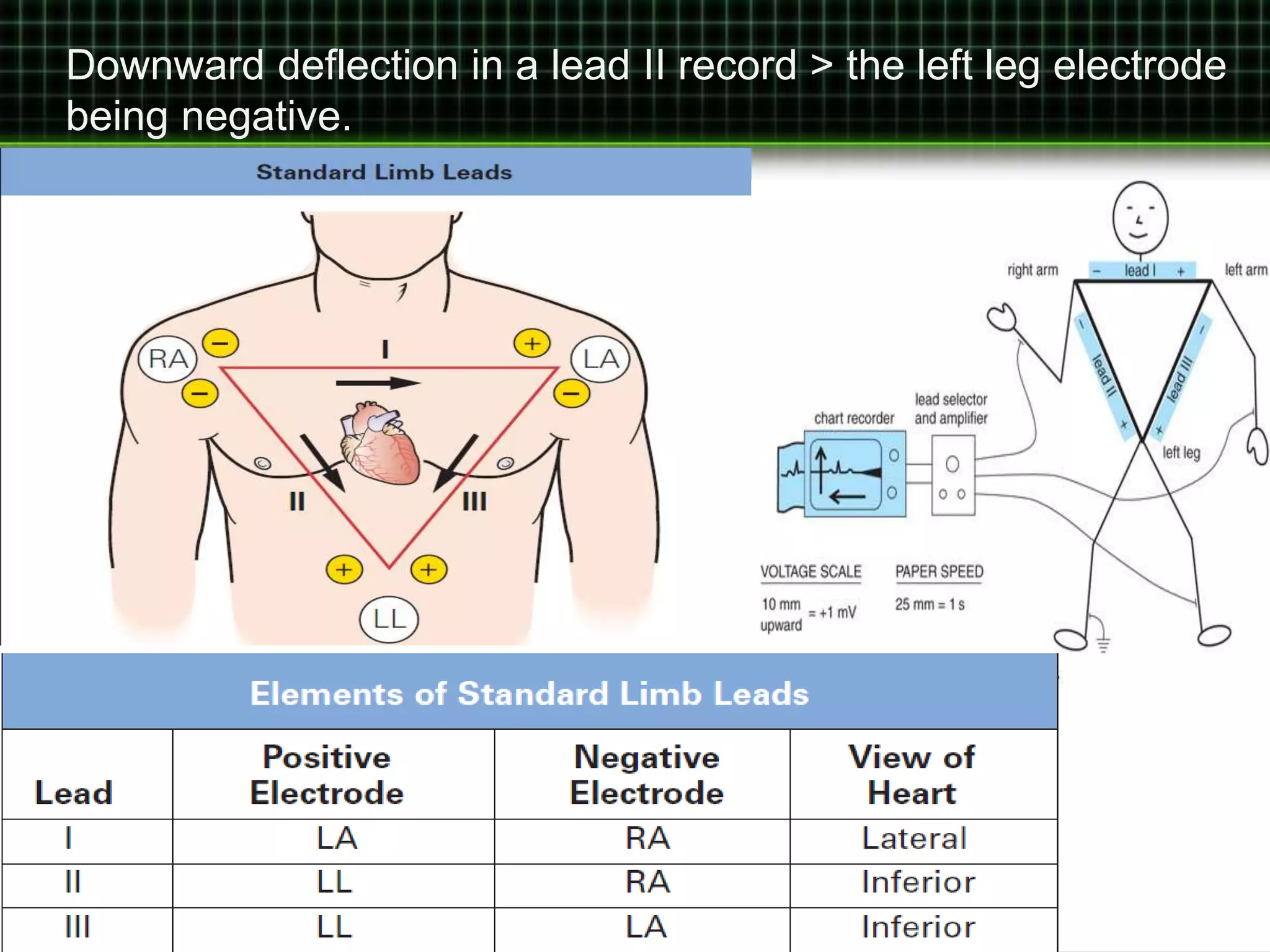
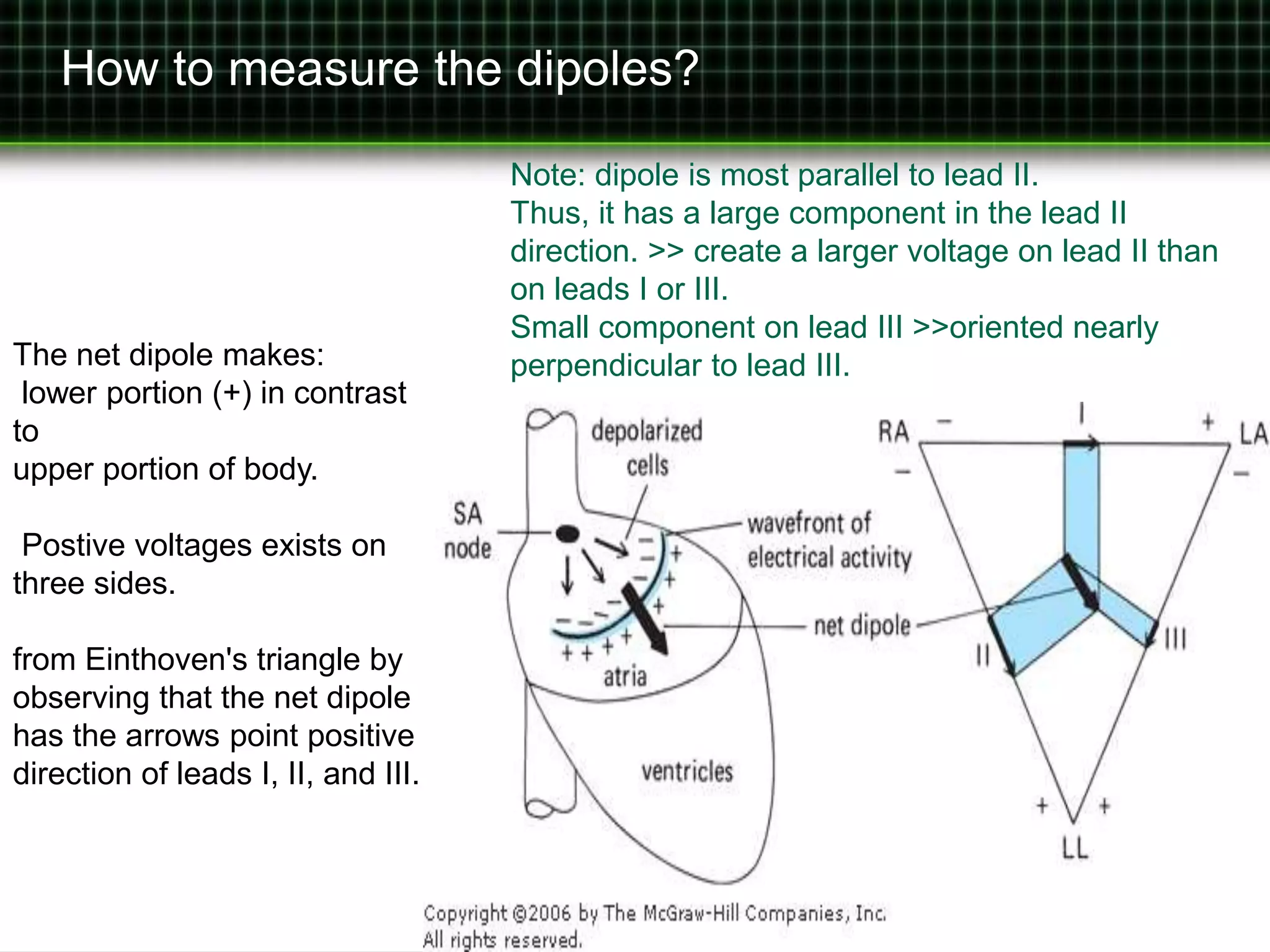
• leads I, II, and III > bipolar leads
• nine leads > unipolar leads.
• Three leads are generated by using the limb electrodes.
• Two electrodes > indifferent electrode.
• Third limb electrode is made the positive pole of the pair.
[augmented unipolar limb leads]
• The voltage record between the electrode at the right arm
and the indifferent electrode = aVR
• recorded on left arm and lead = aVL
• recorded from the electrode on left leg = aVF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/i3hdpvuqnmsptfz5jphx-signature-b530d64c6ff48986dc7ef925b8cd6317122c3680f0a4a747901d8f2cddb16017-poli-140825195020-phpapp01/75/ECG-Leads-9-2048.jpg)