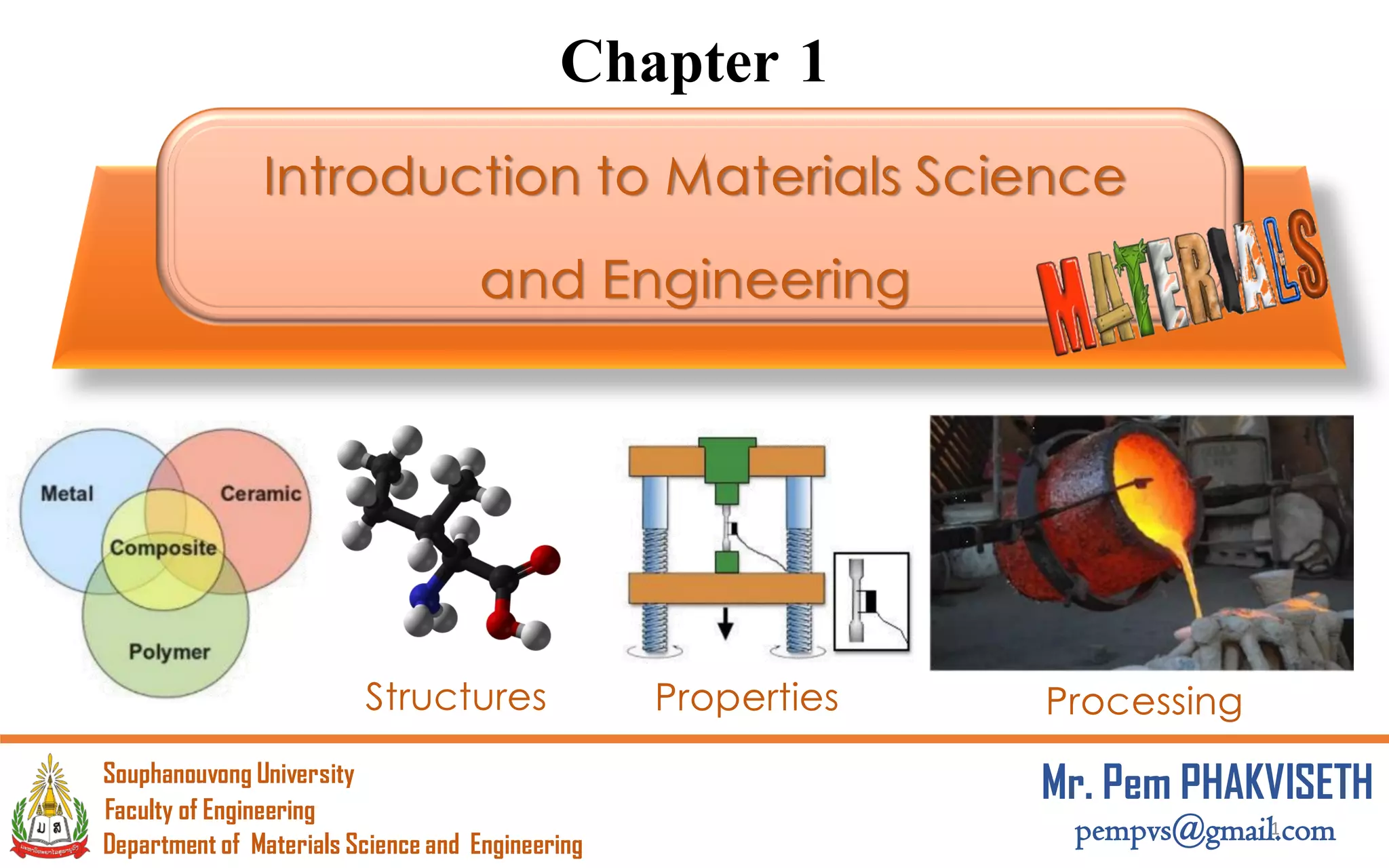
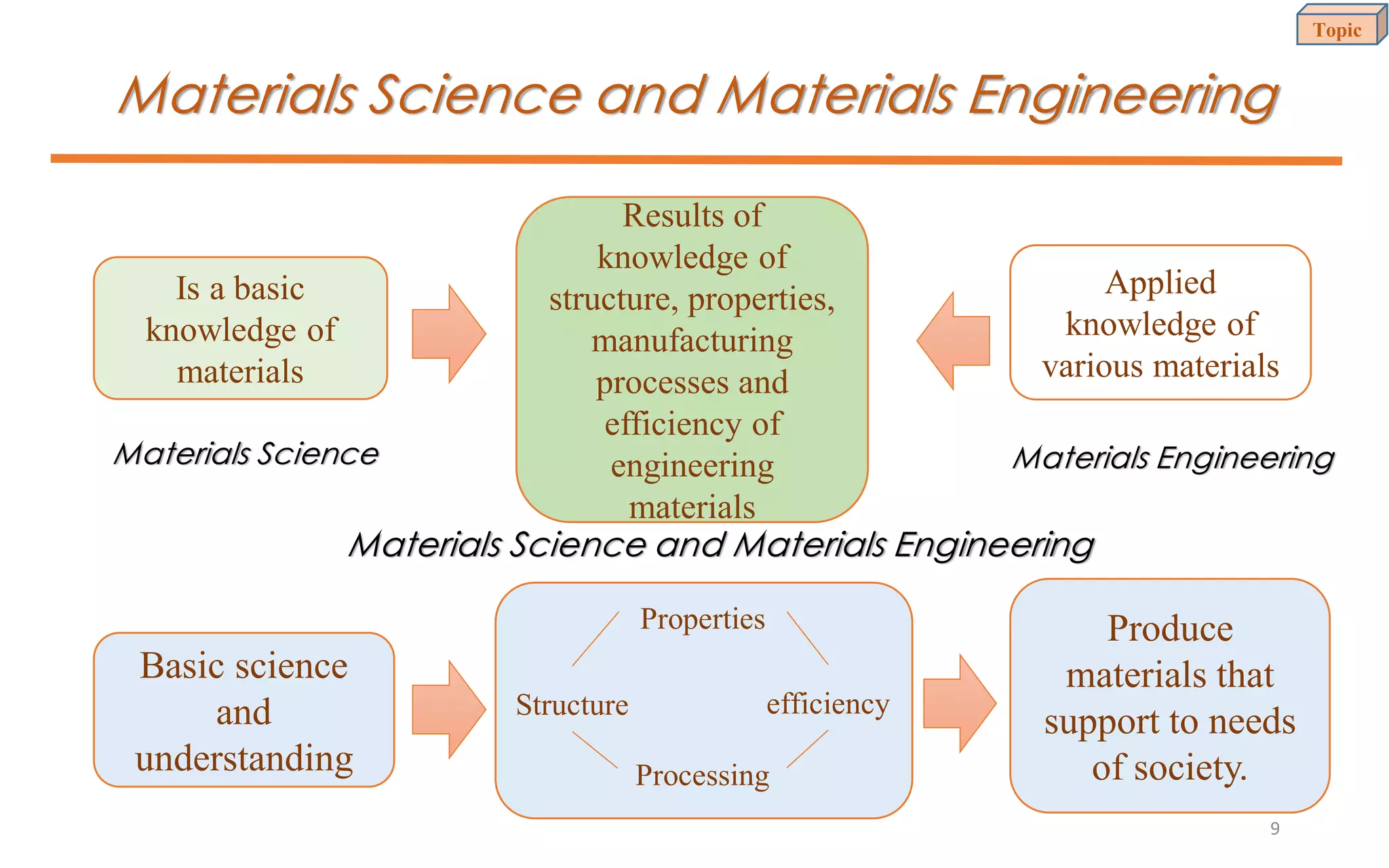
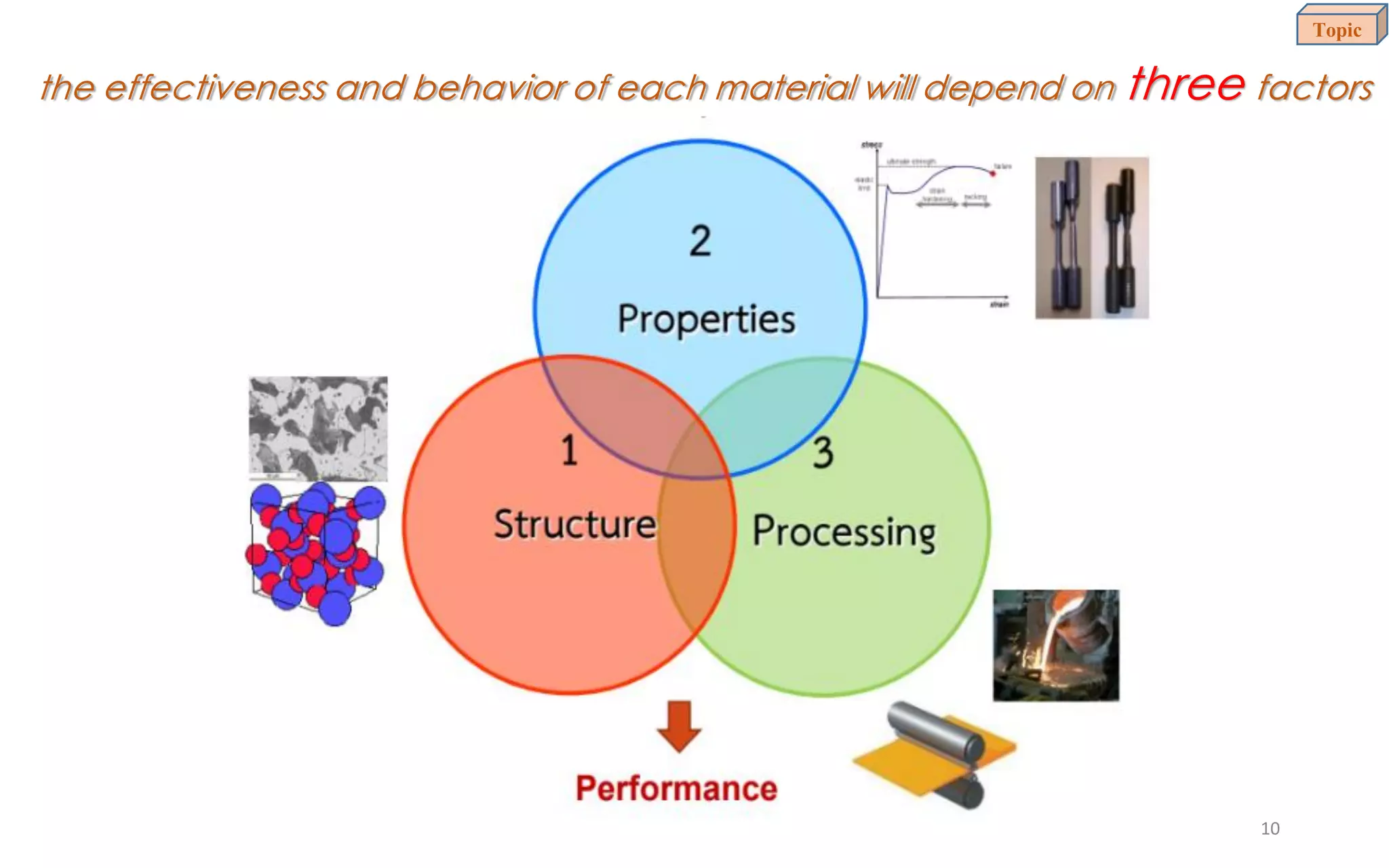
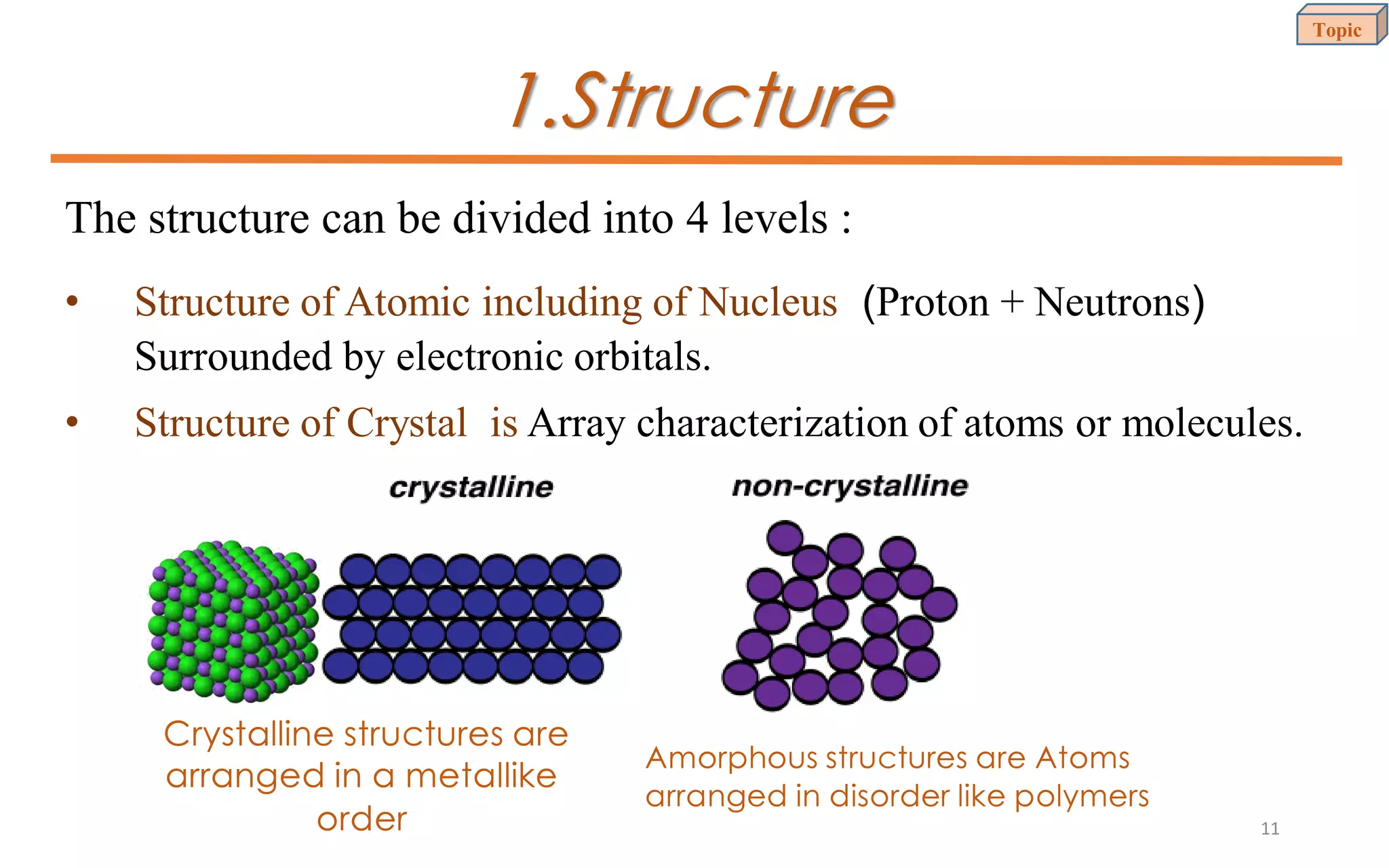
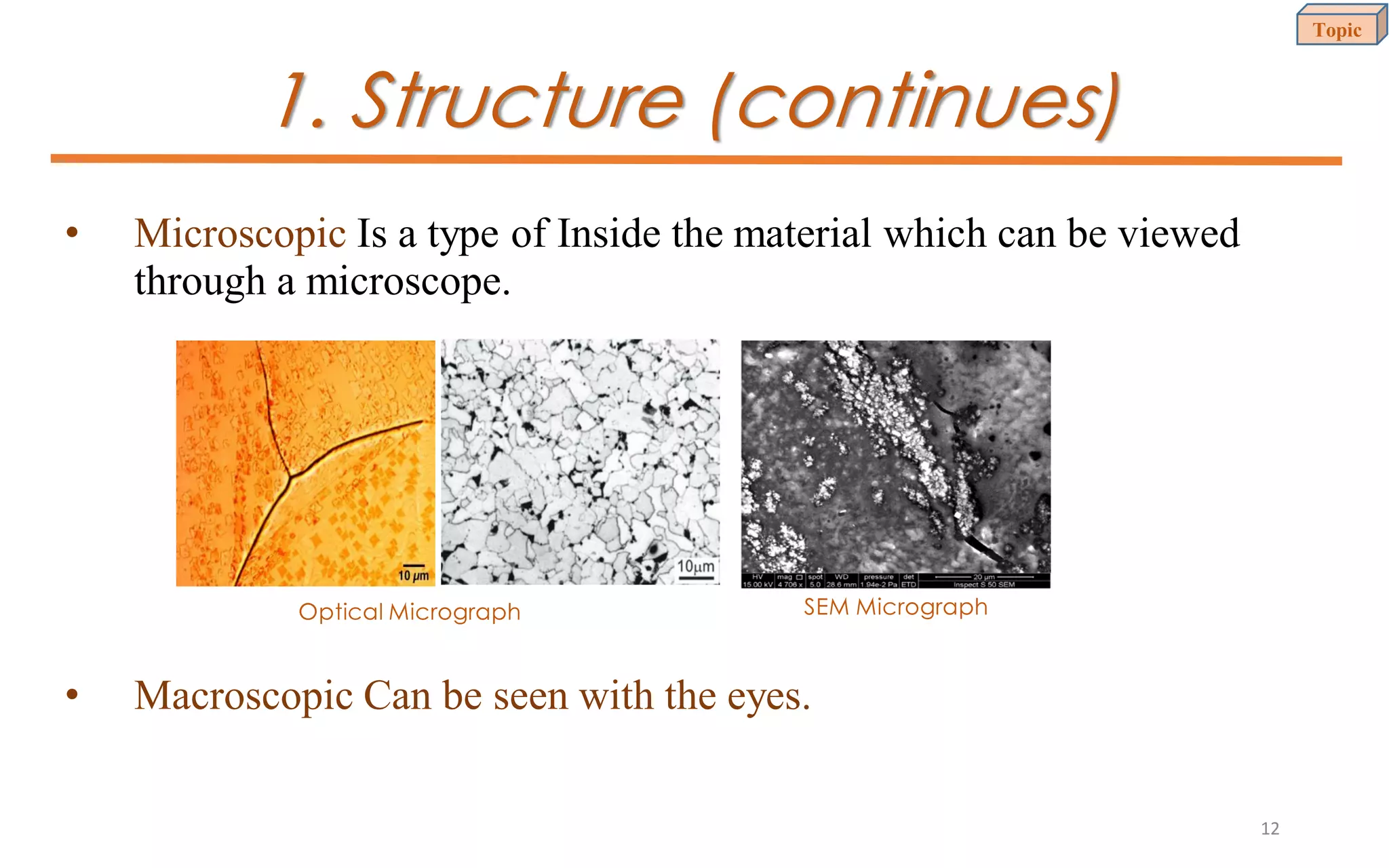
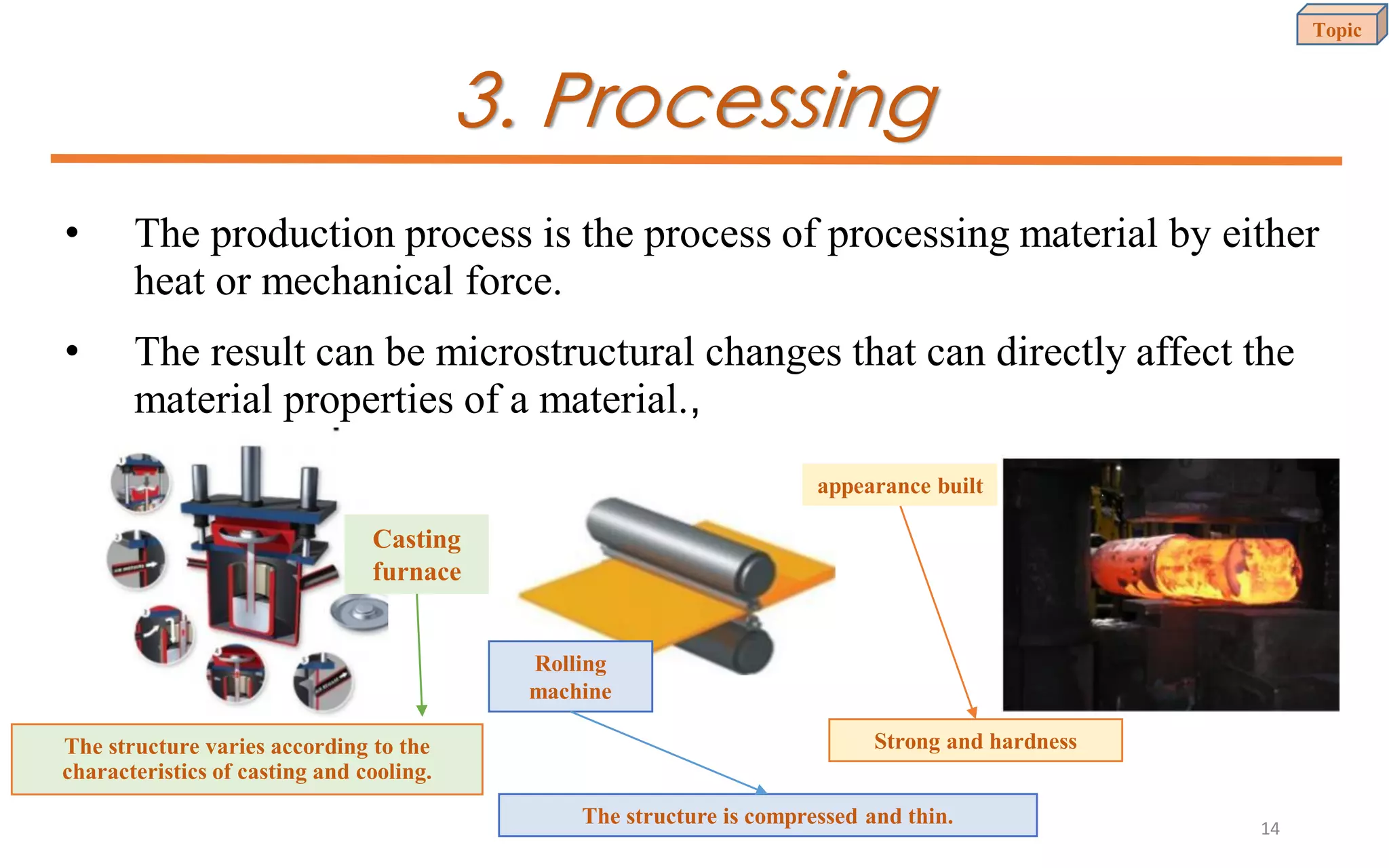
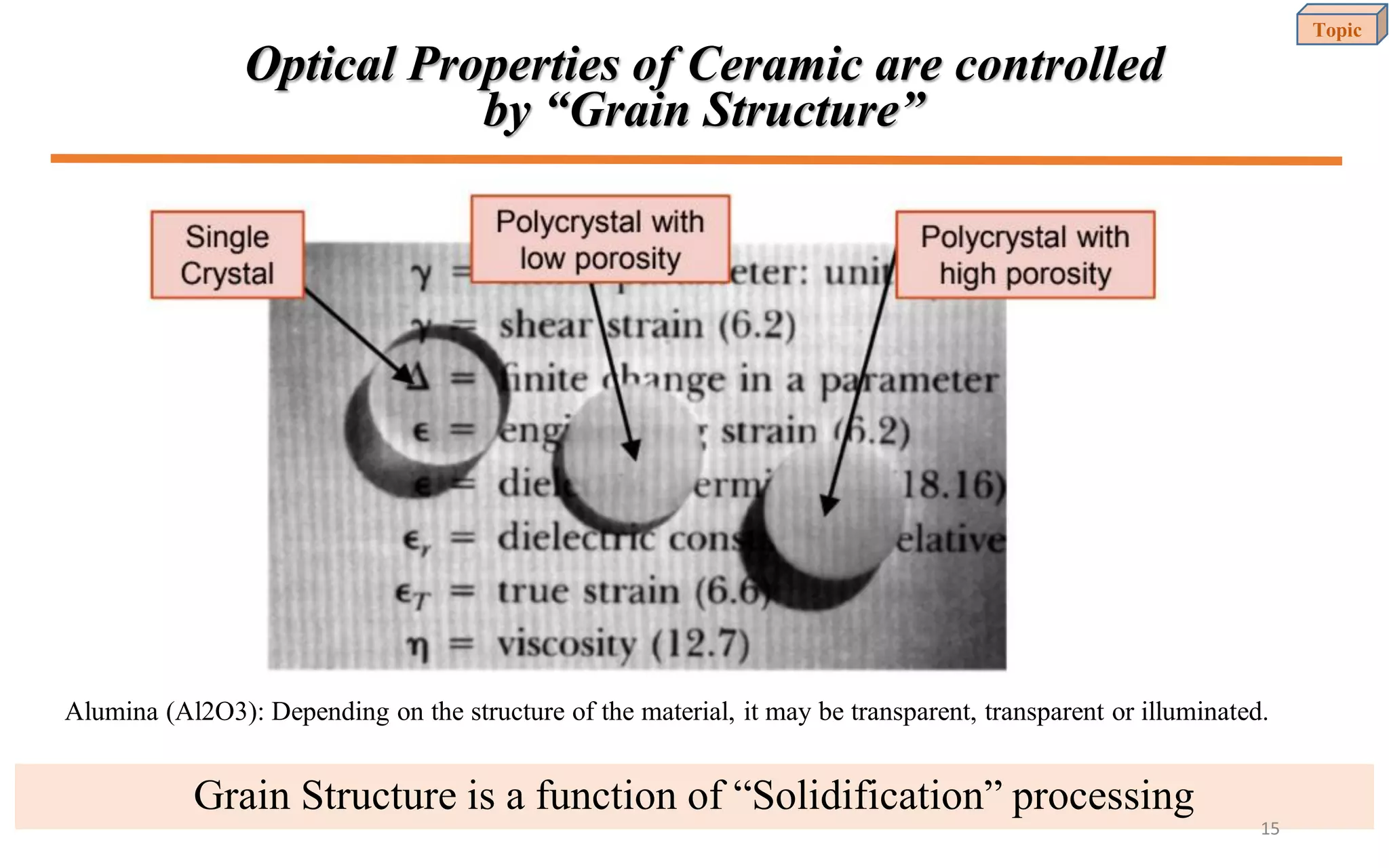
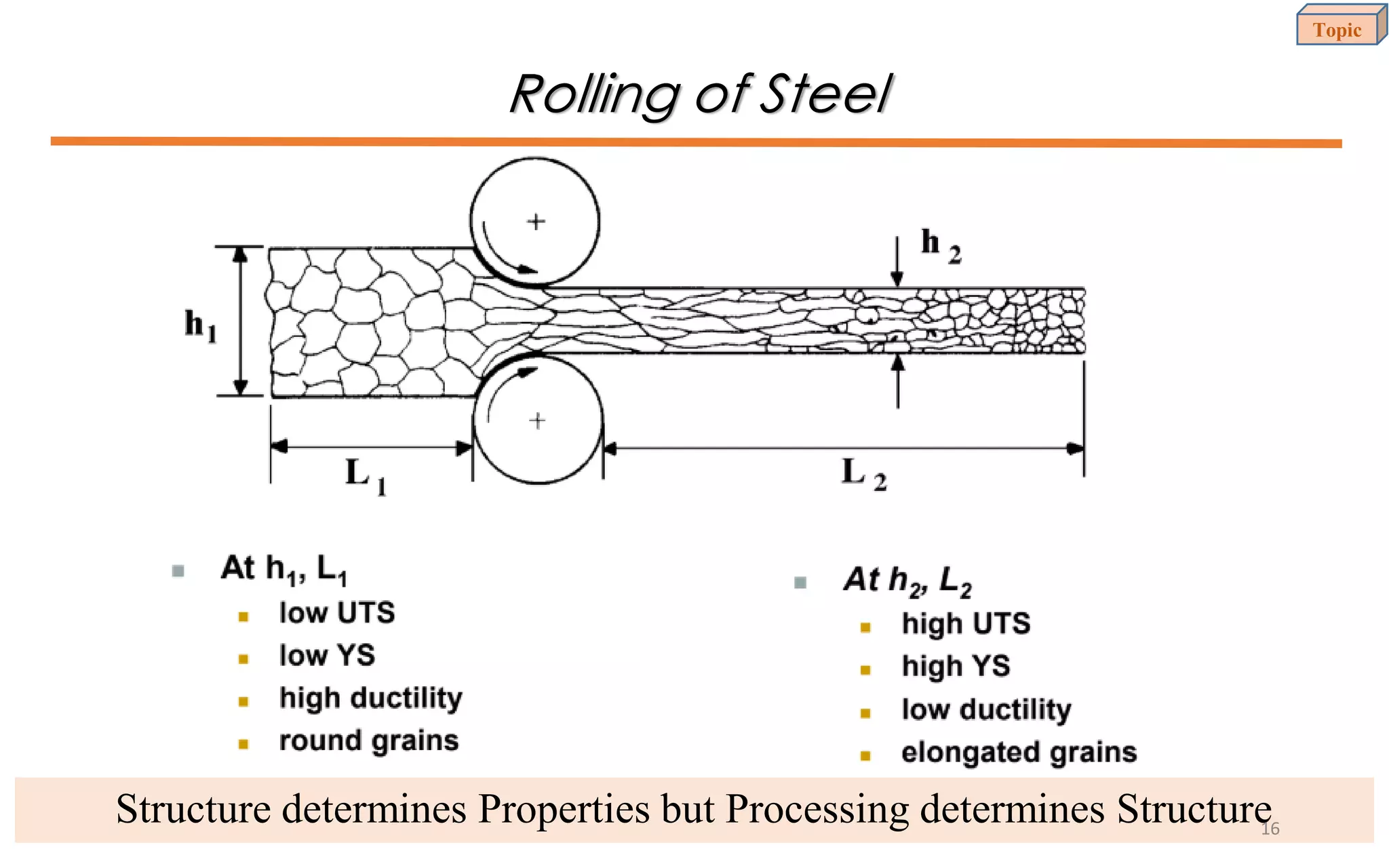
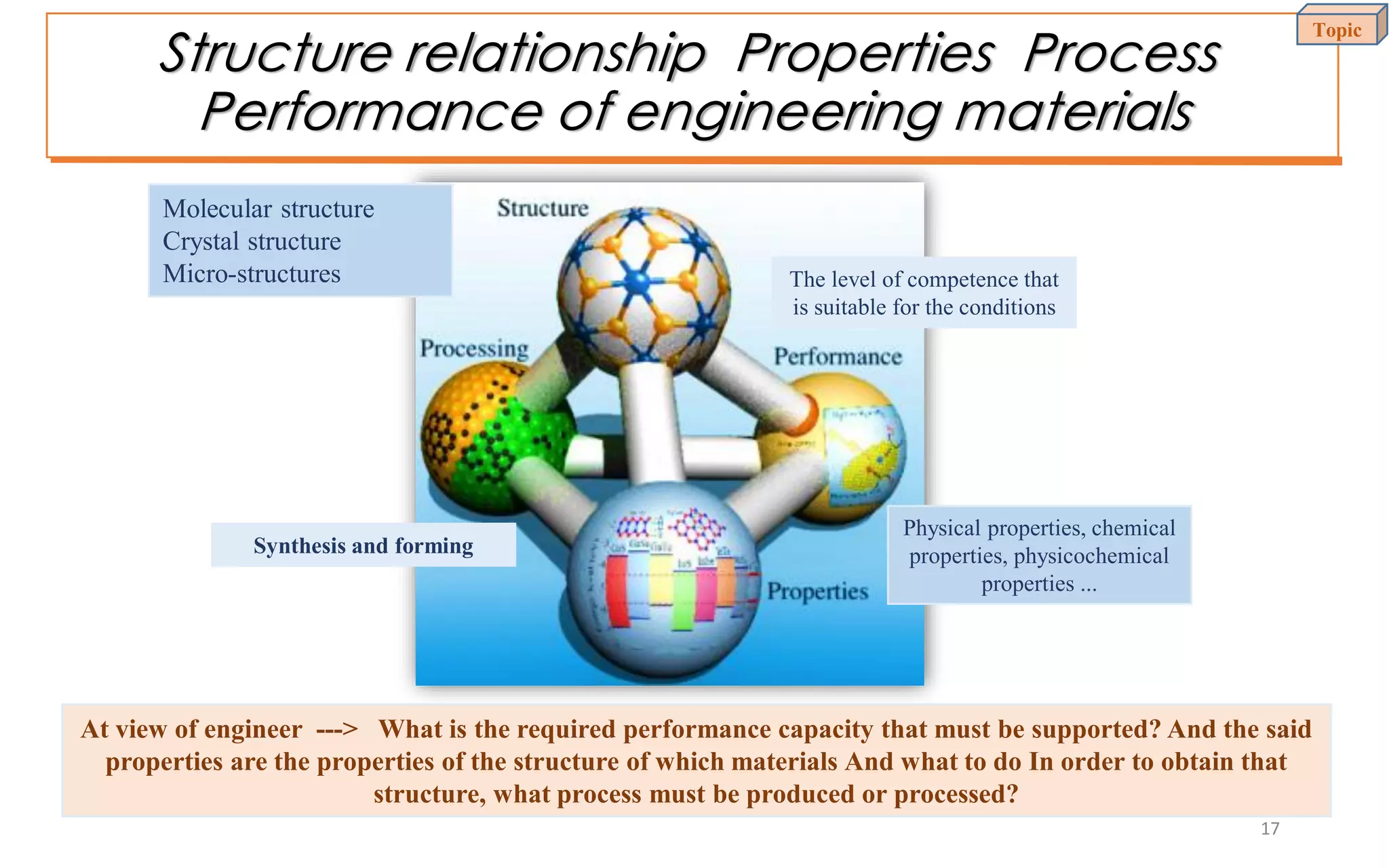
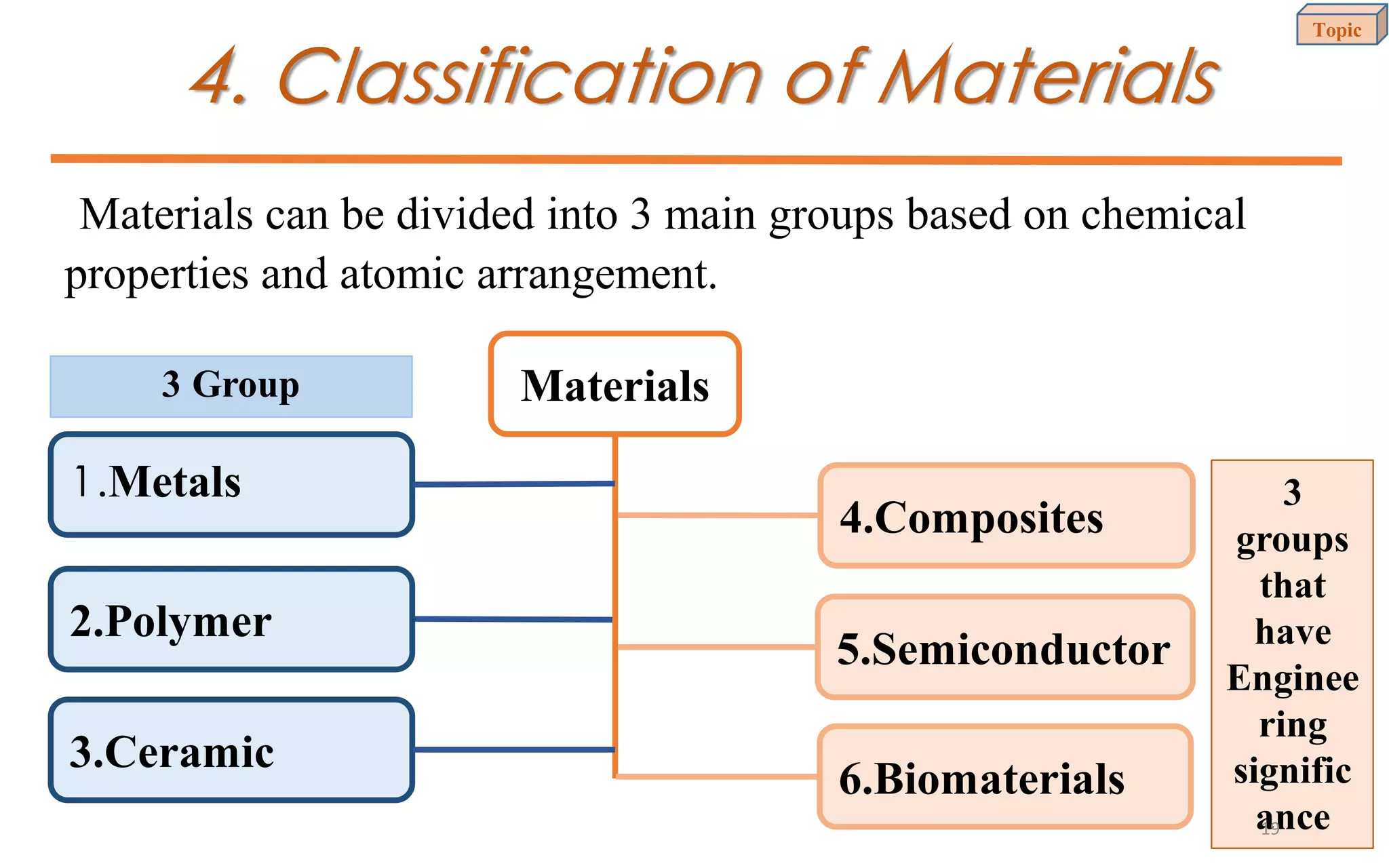
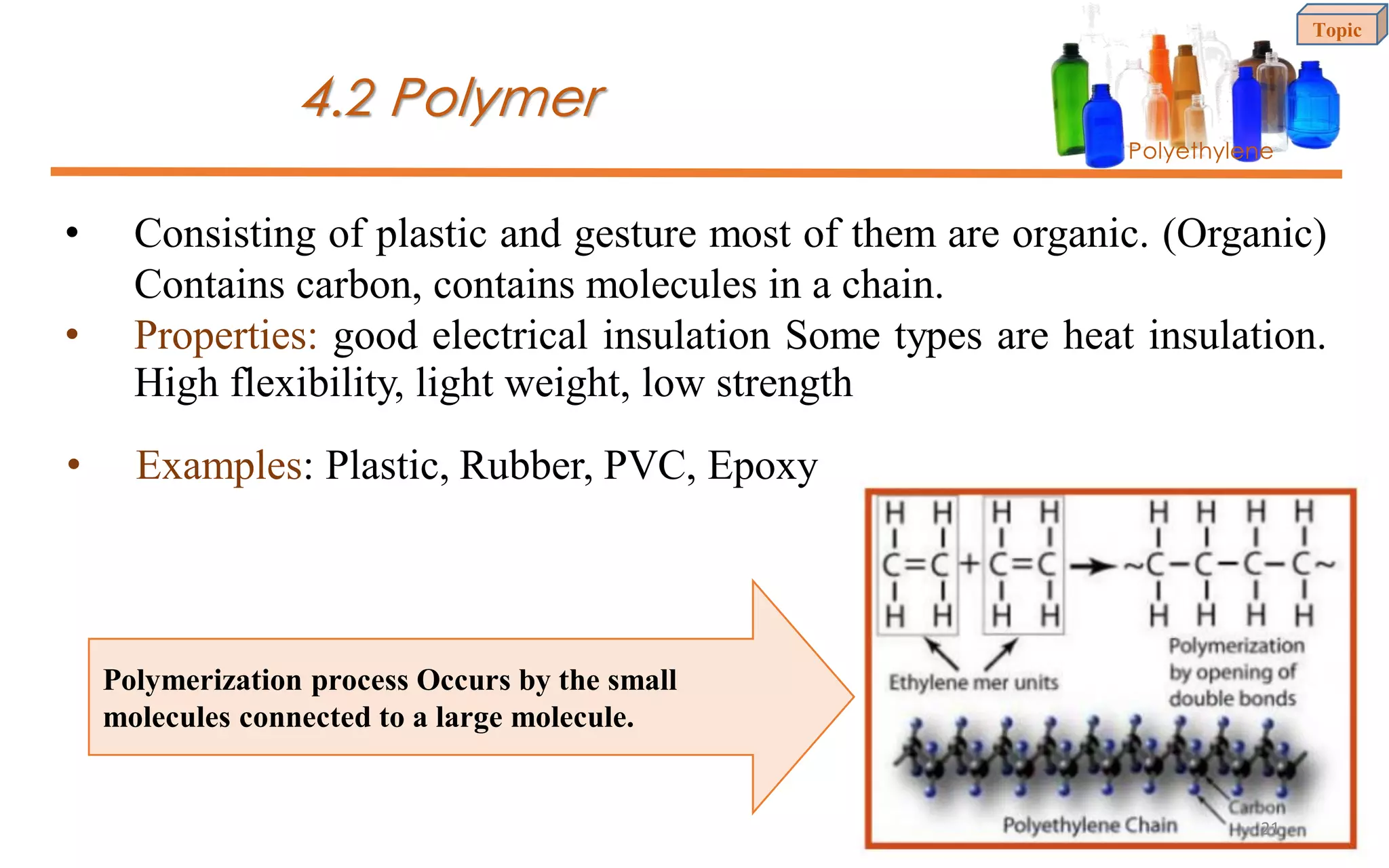
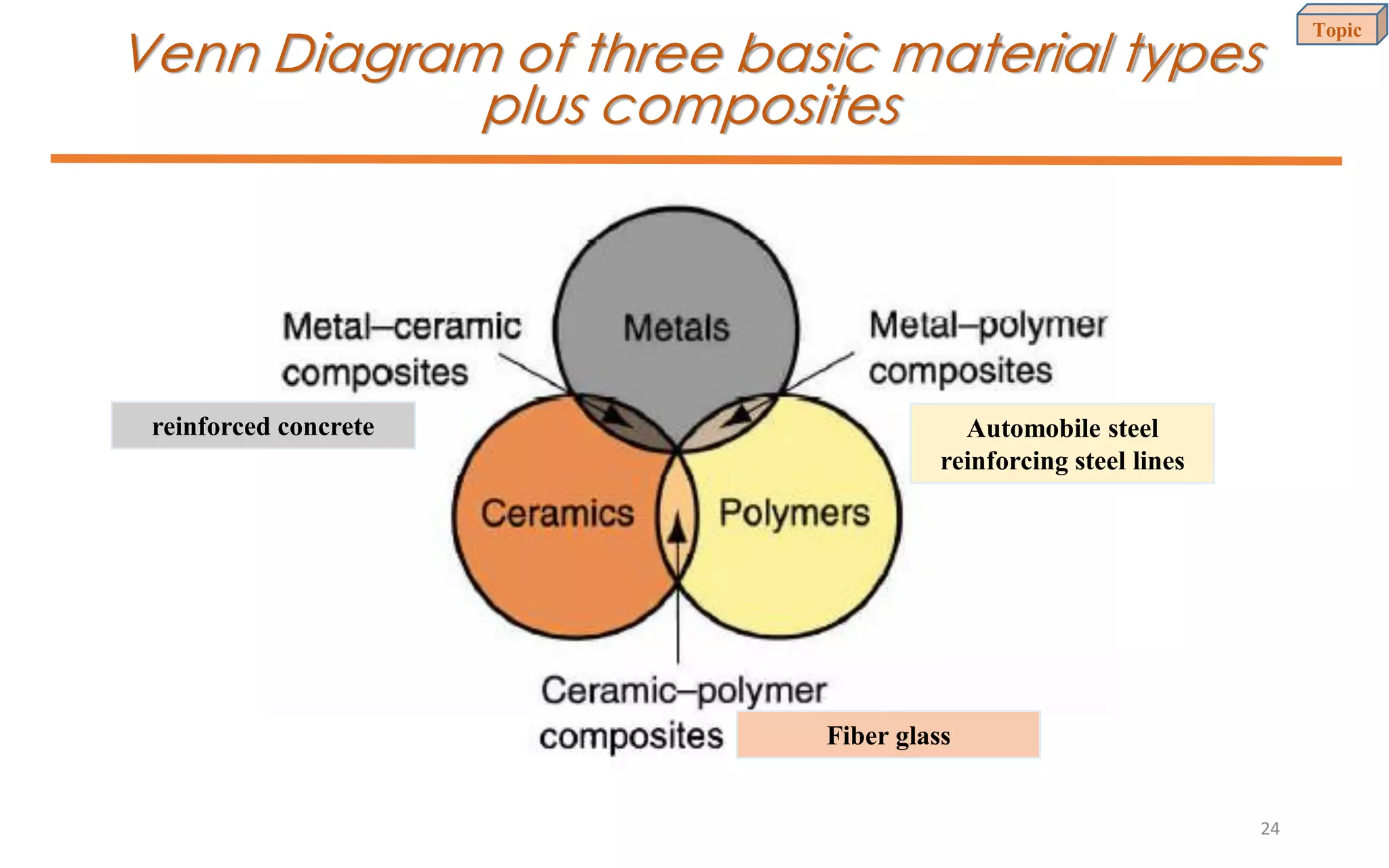
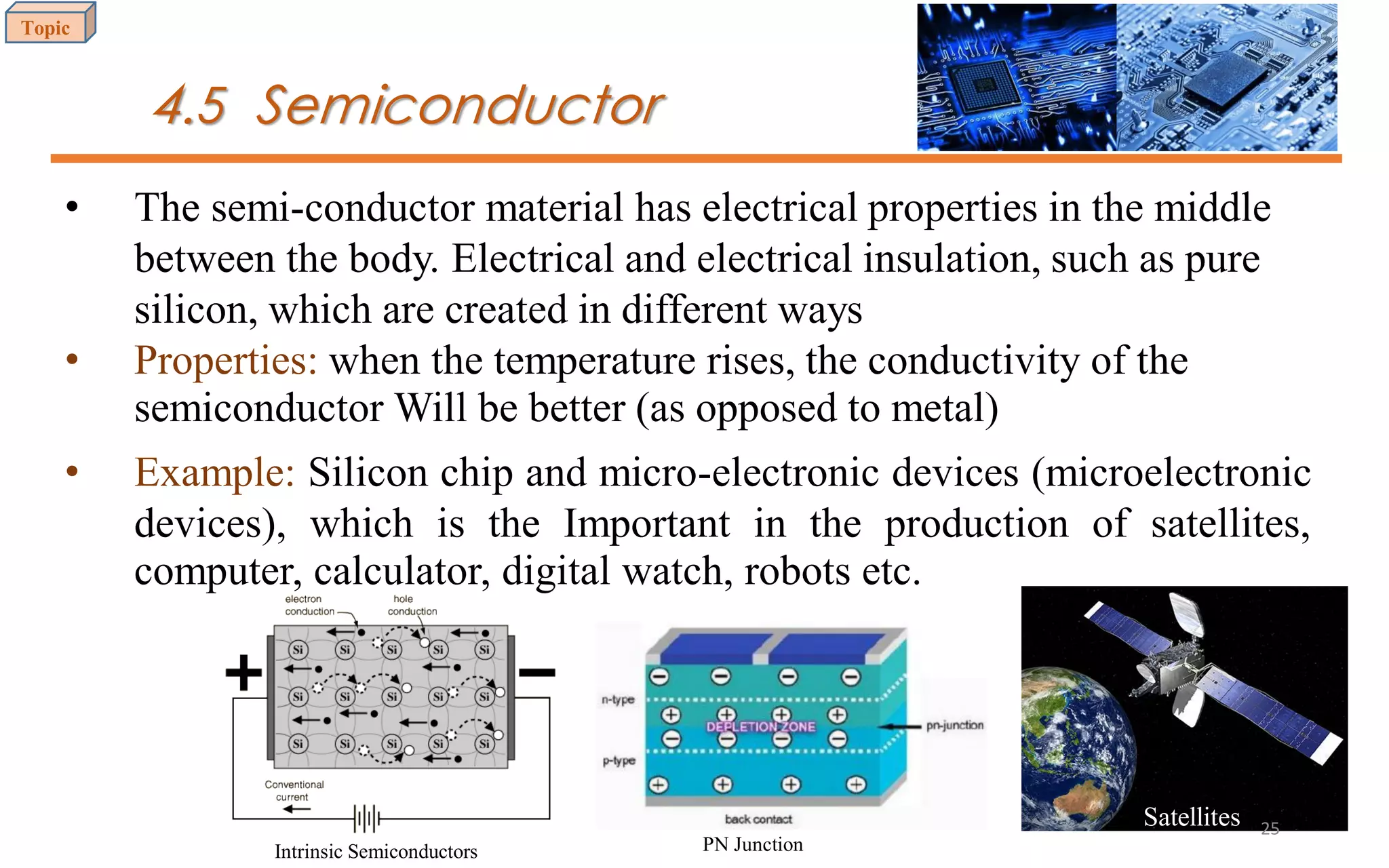
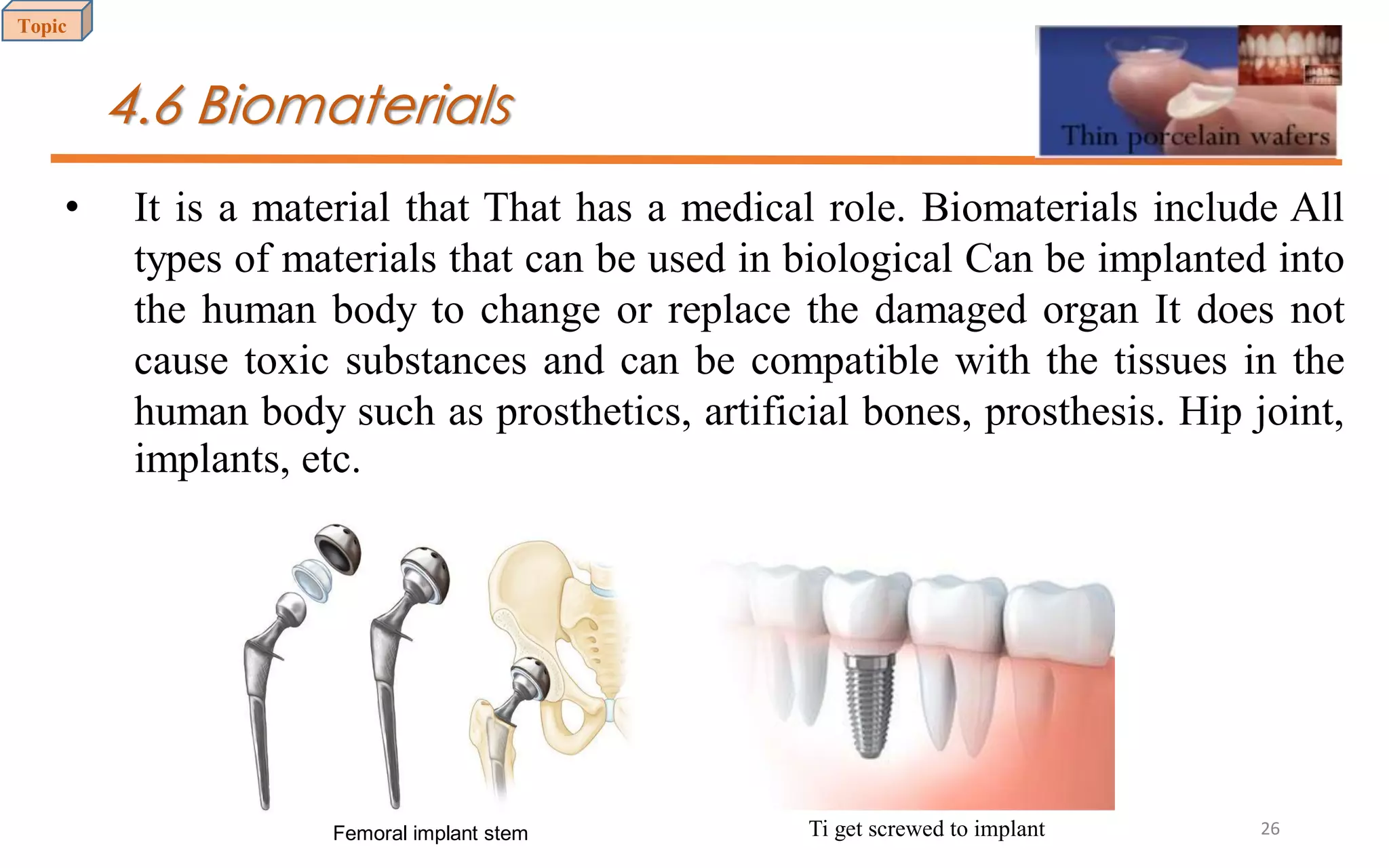
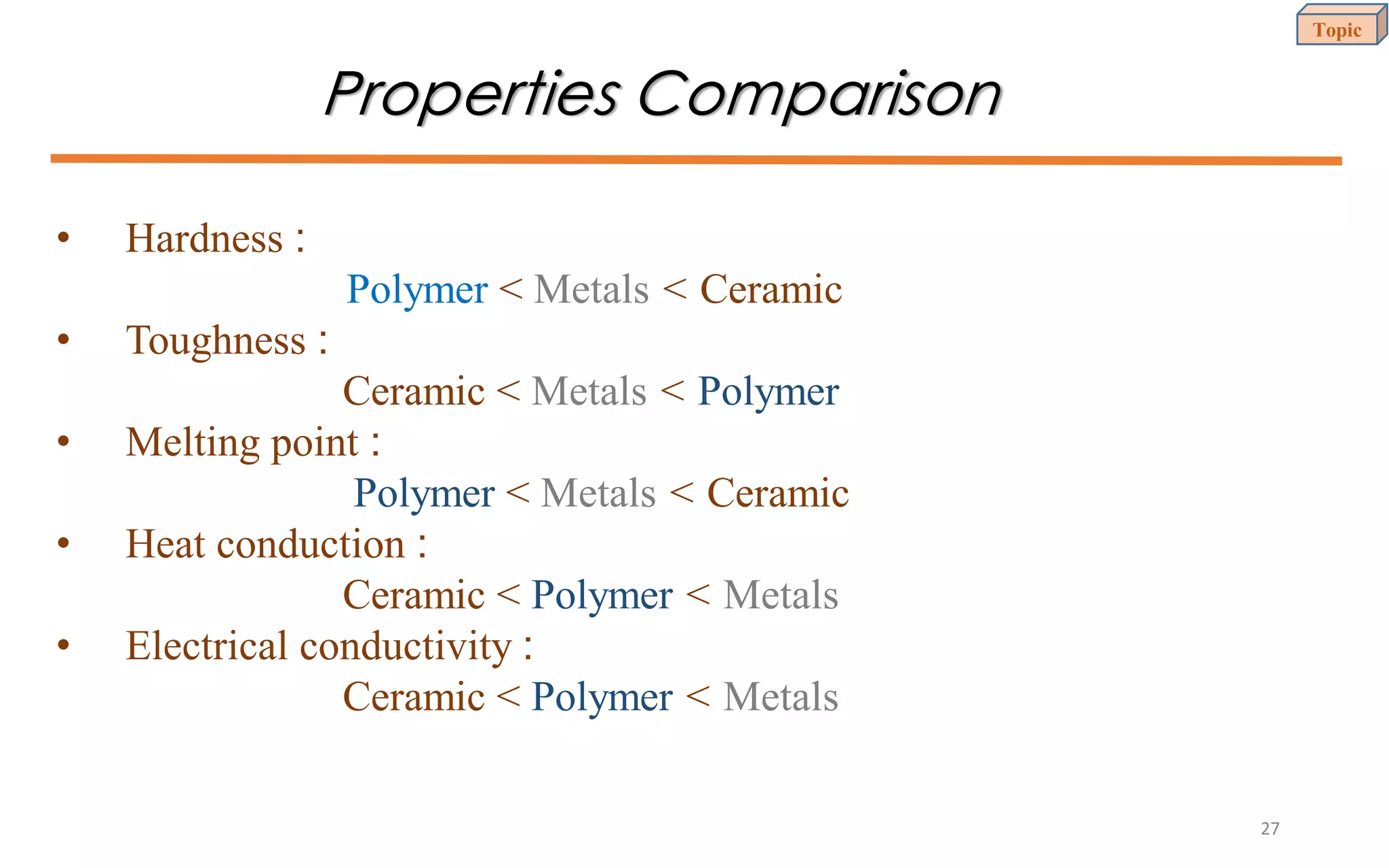
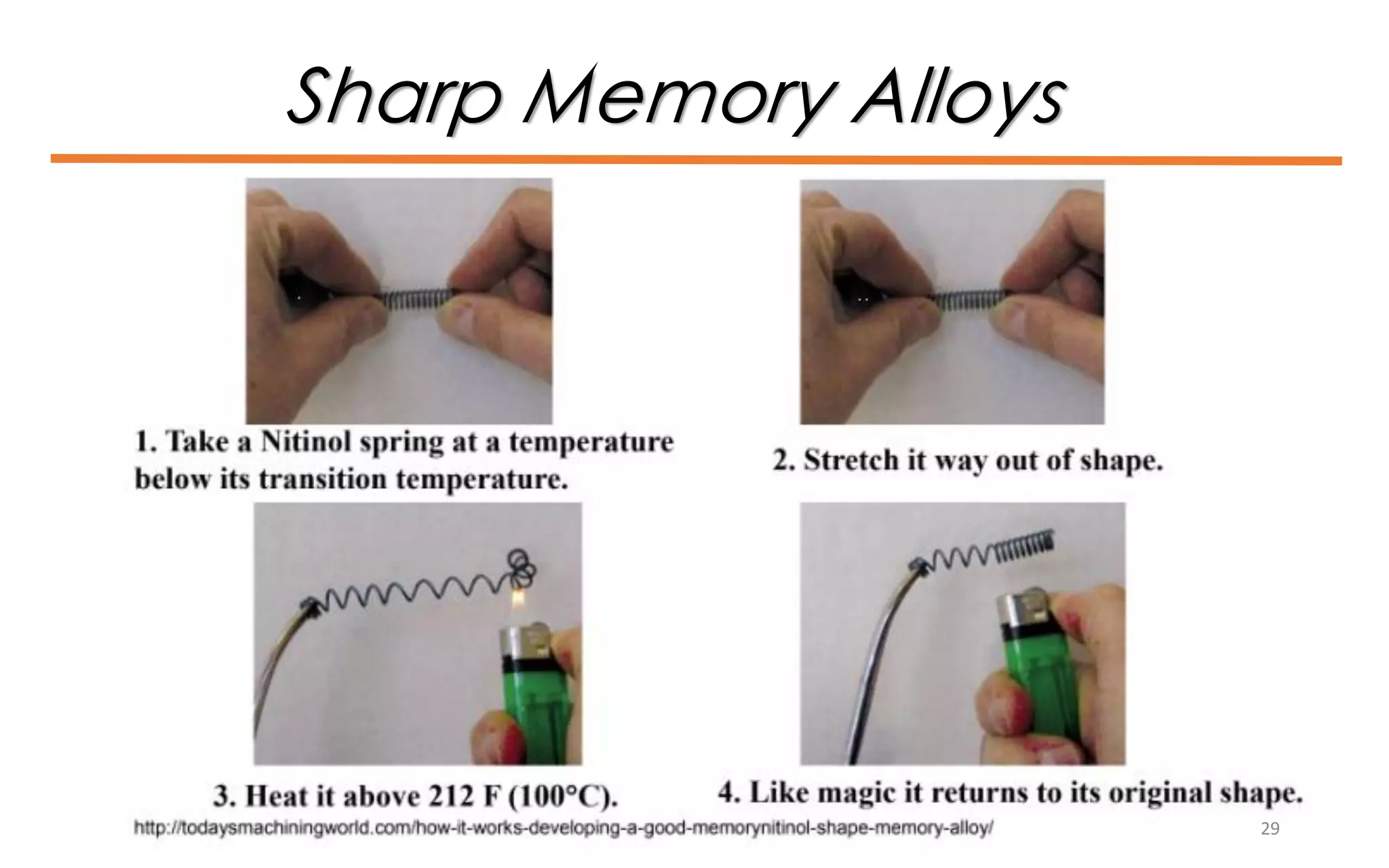
This document provides an introduction to materials science and engineering. It discusses key topics such as the structure, properties, and processing of materials, as well as how these factors influence a material's performance. The document also classifies common material types such as metals, polymers, ceramics, and composites. Emerging areas like smart materials and nanotechnology are introduced. Examples of materials used in applications like automotive, electronics, construction, and aerospace industries are provided to illustrate the relationship between materials selection and engineering design.