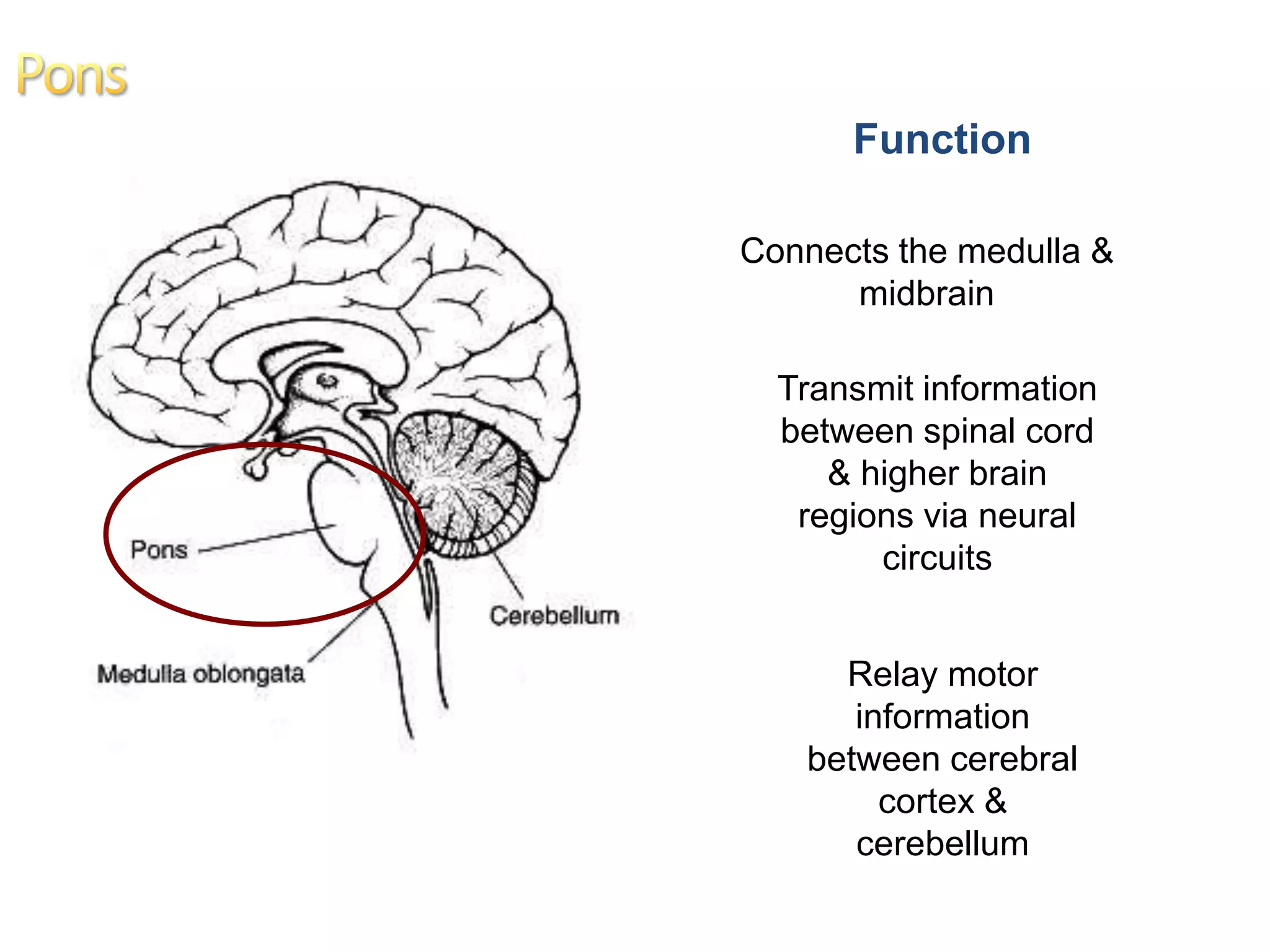
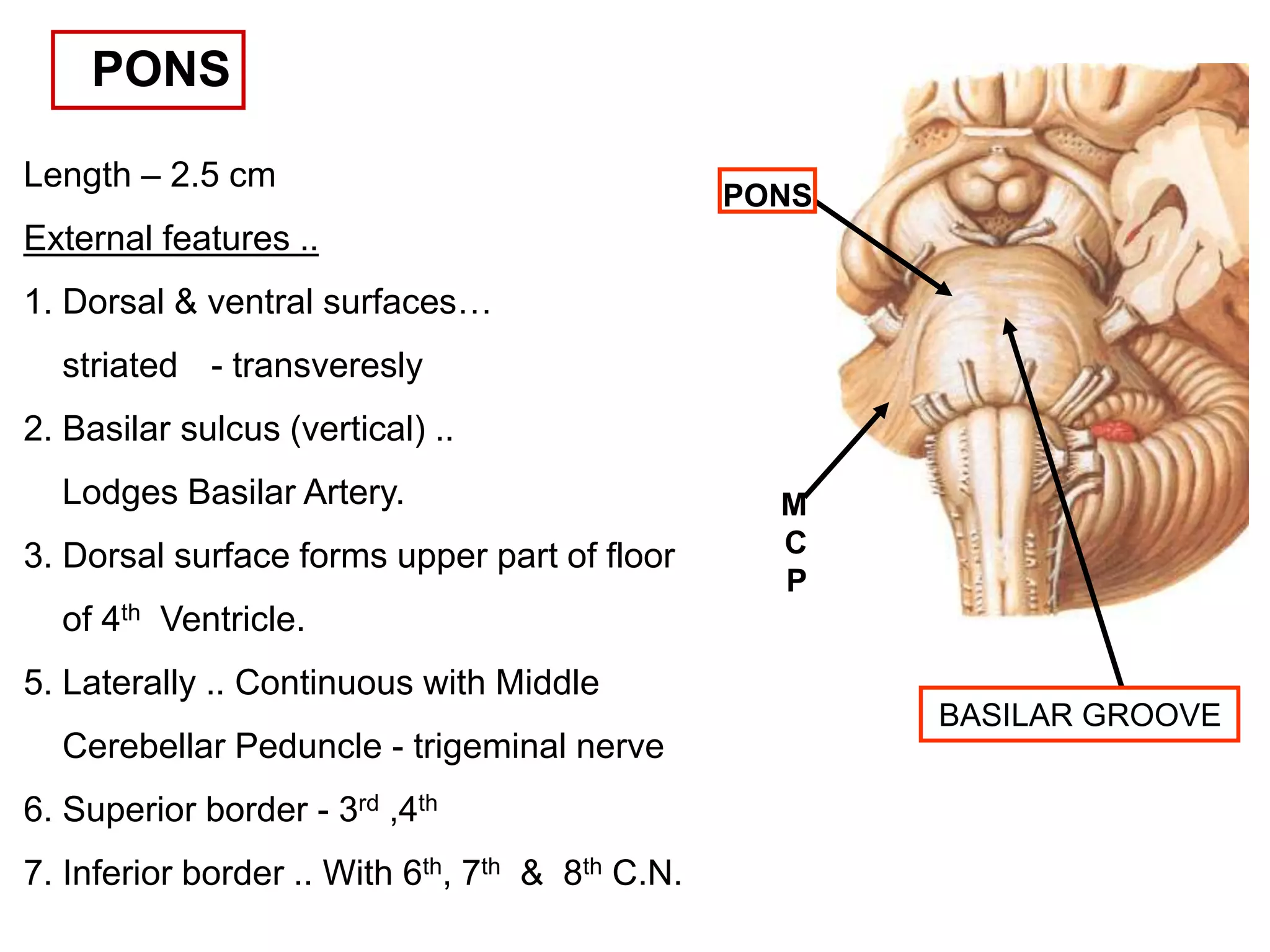
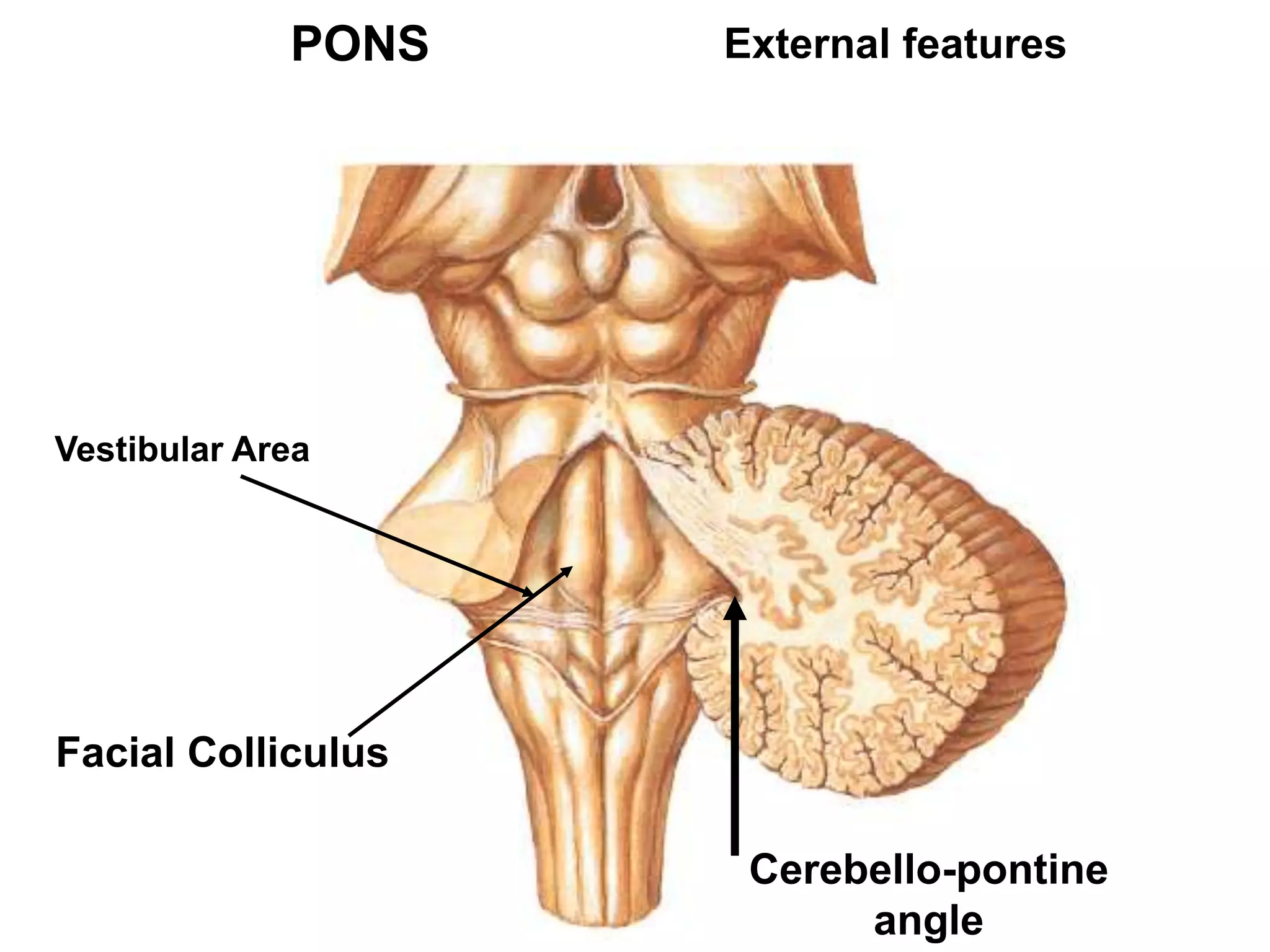
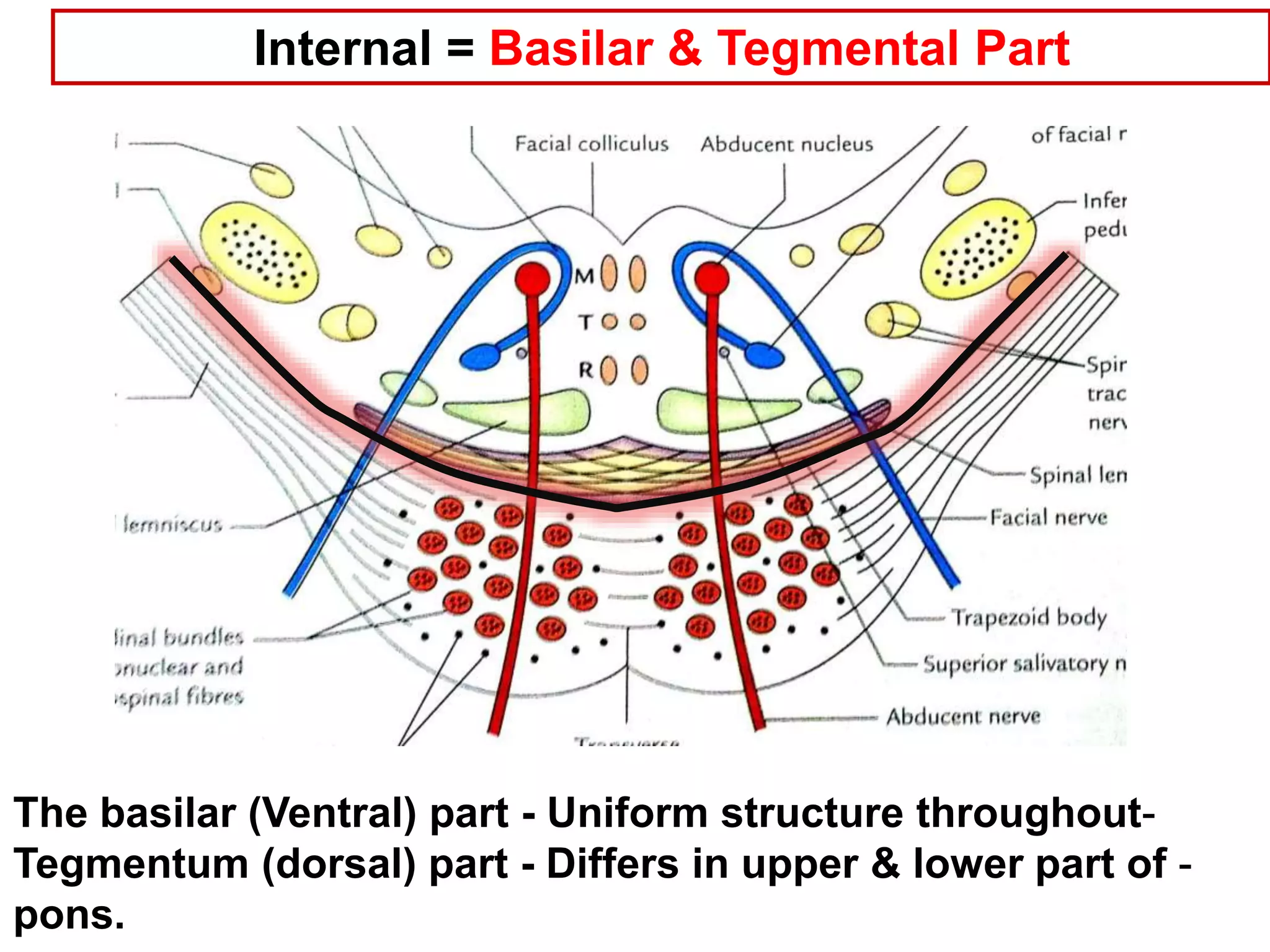
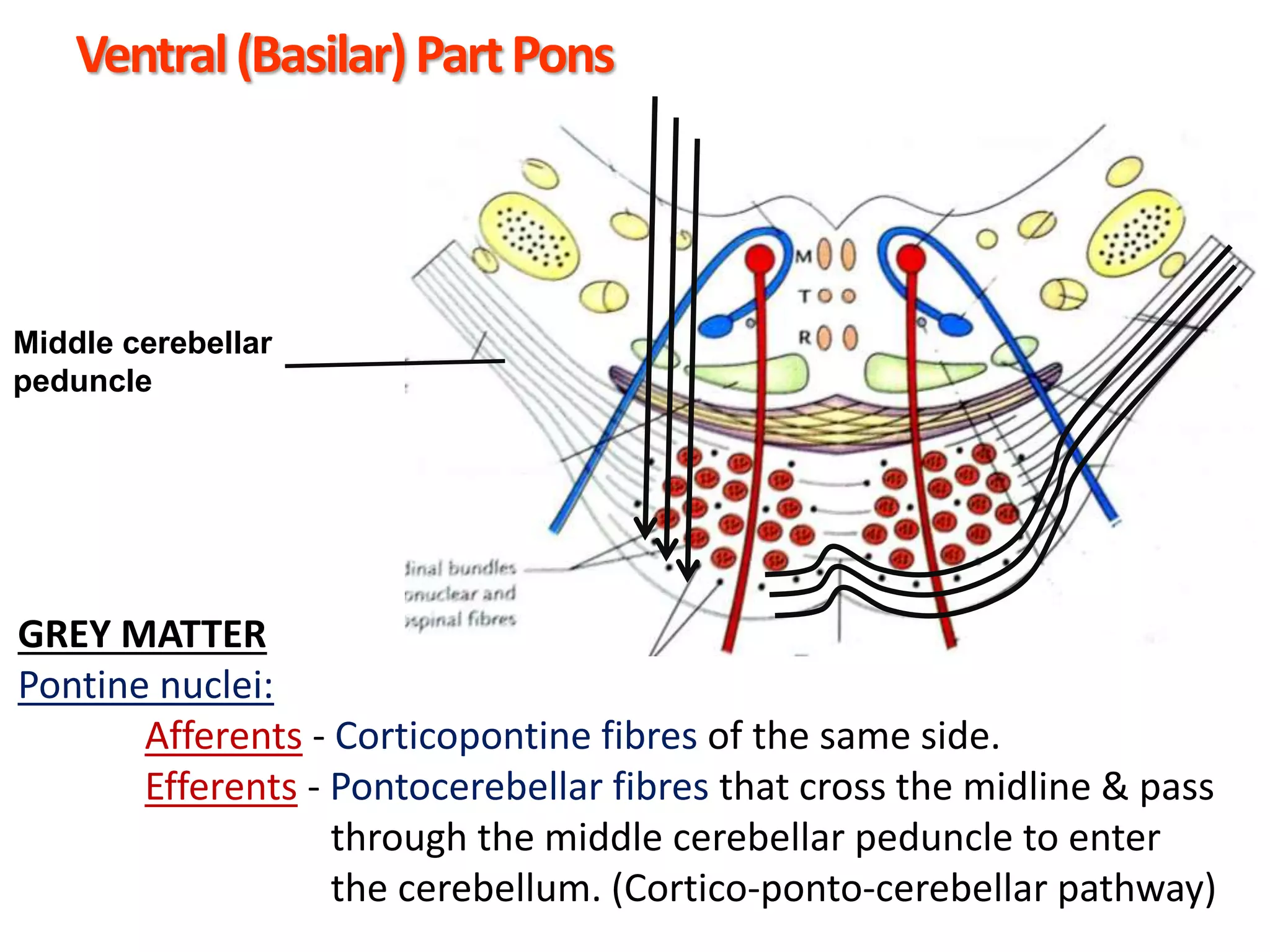
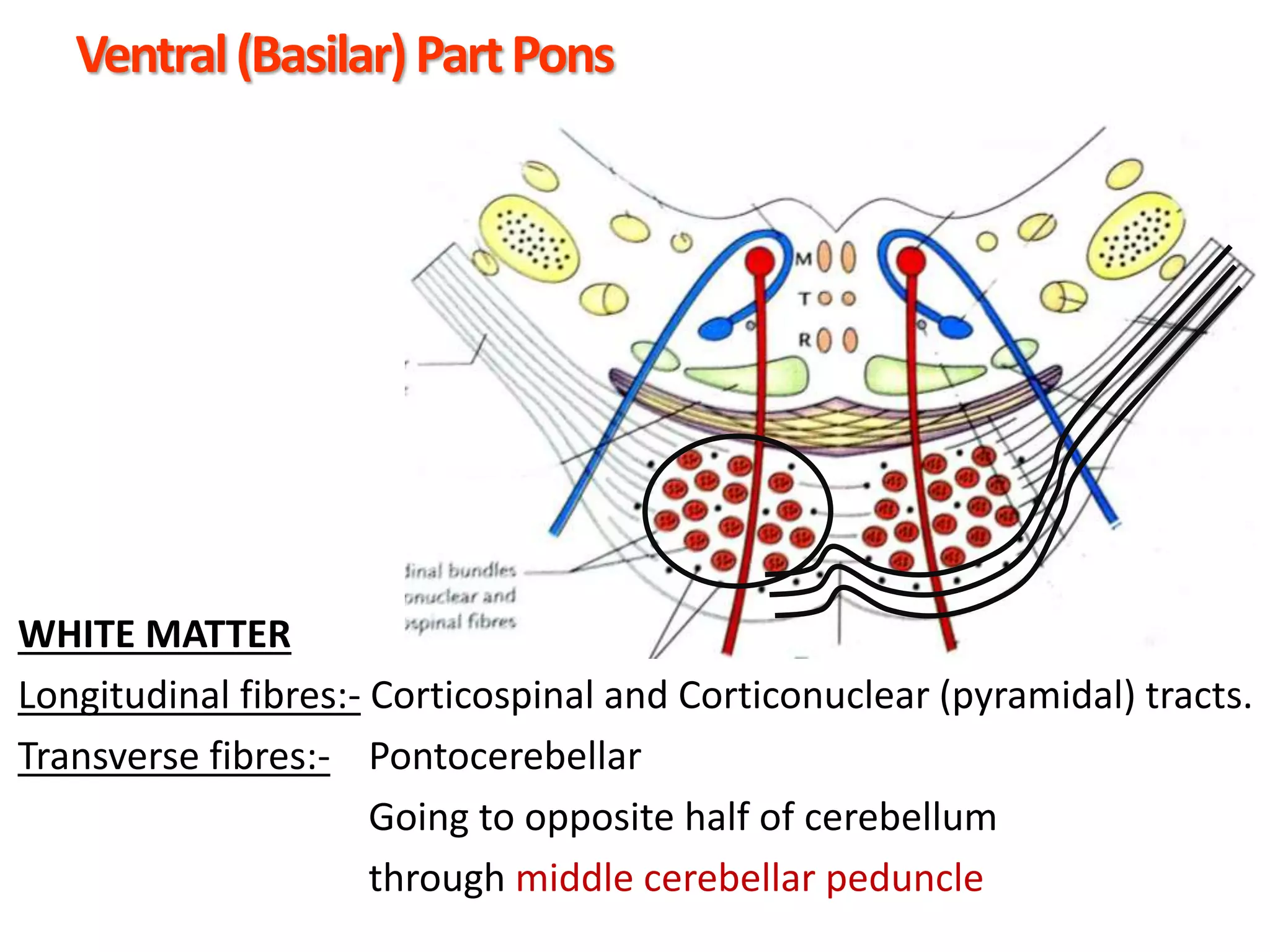
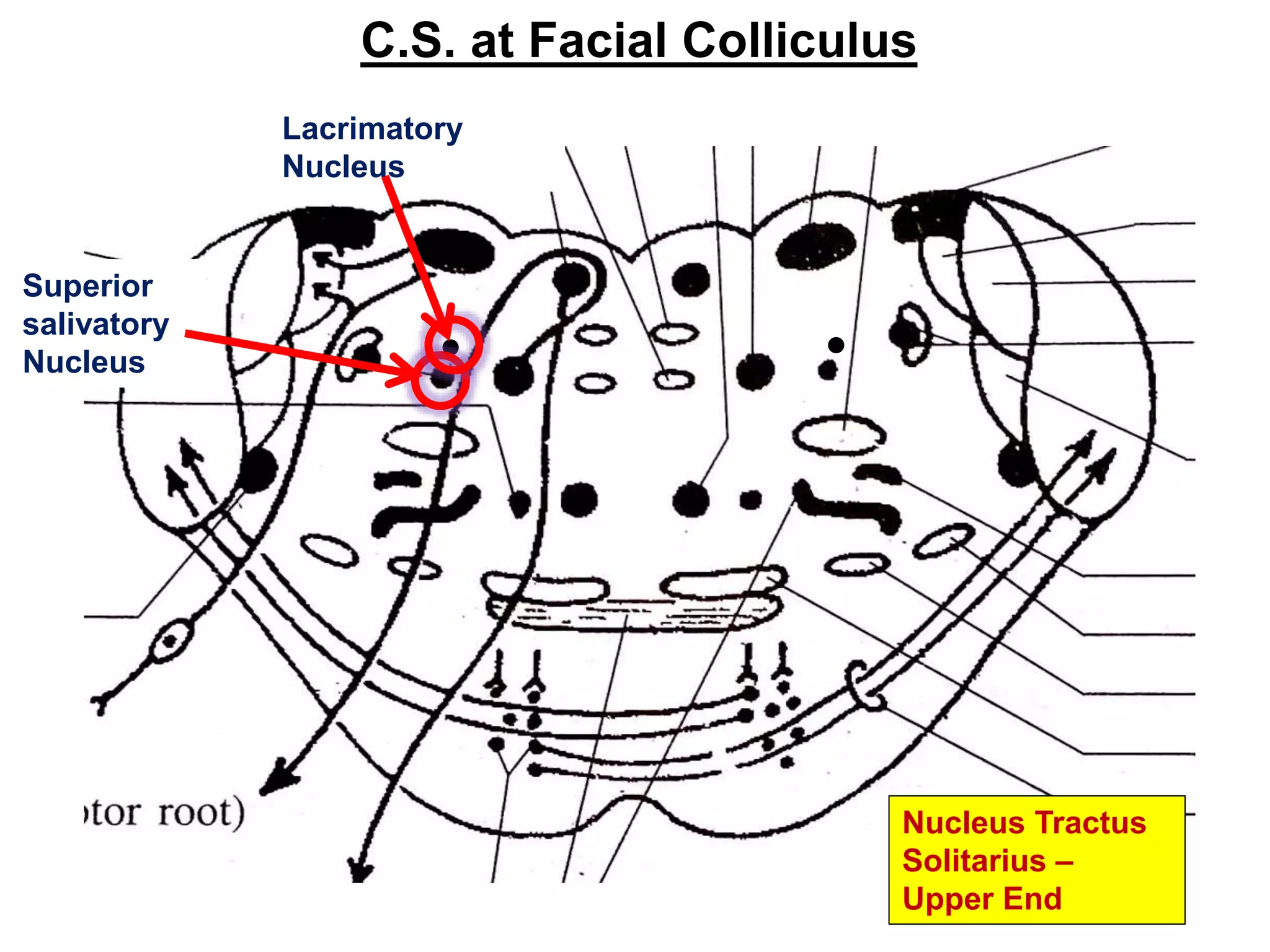
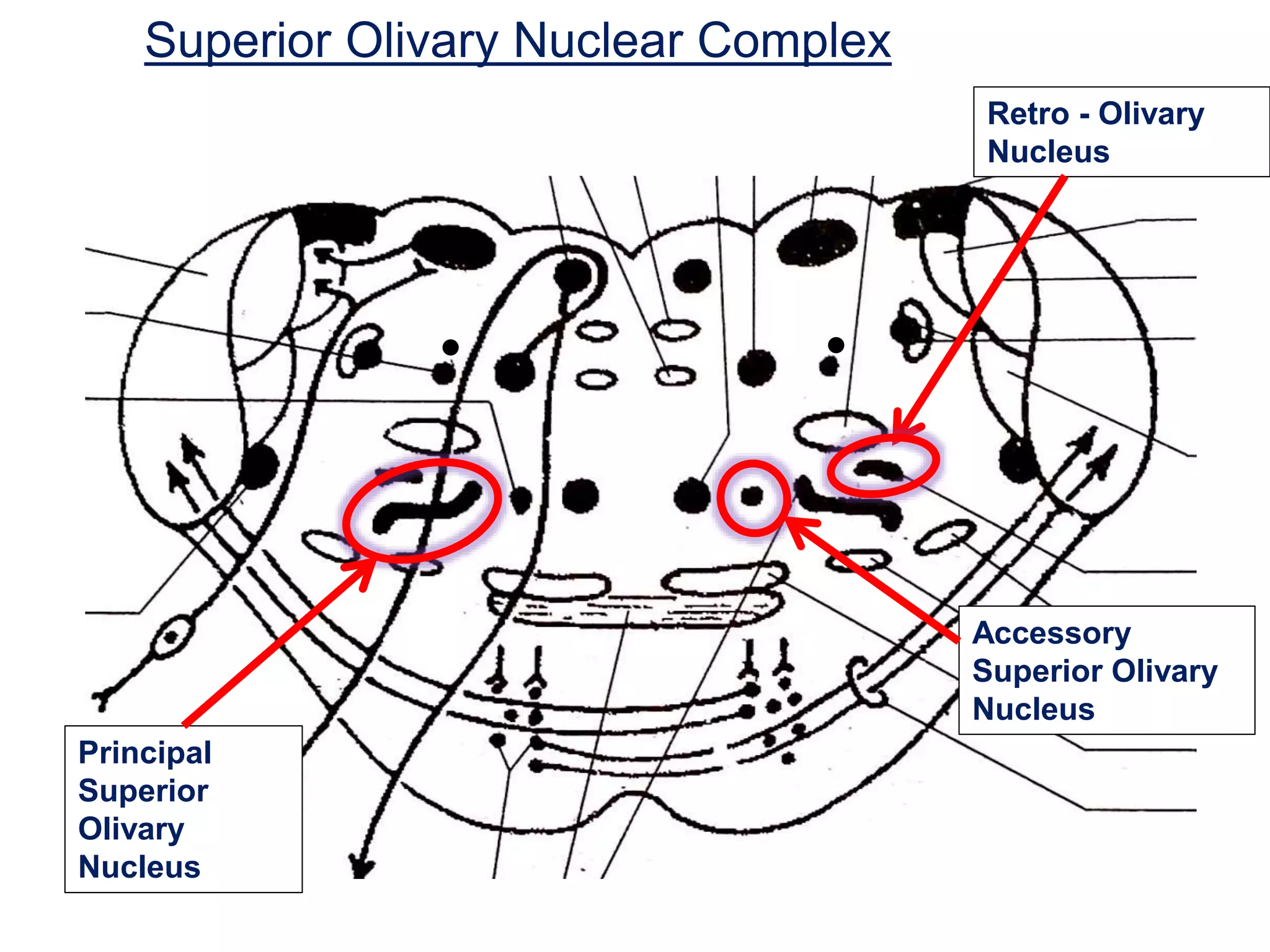
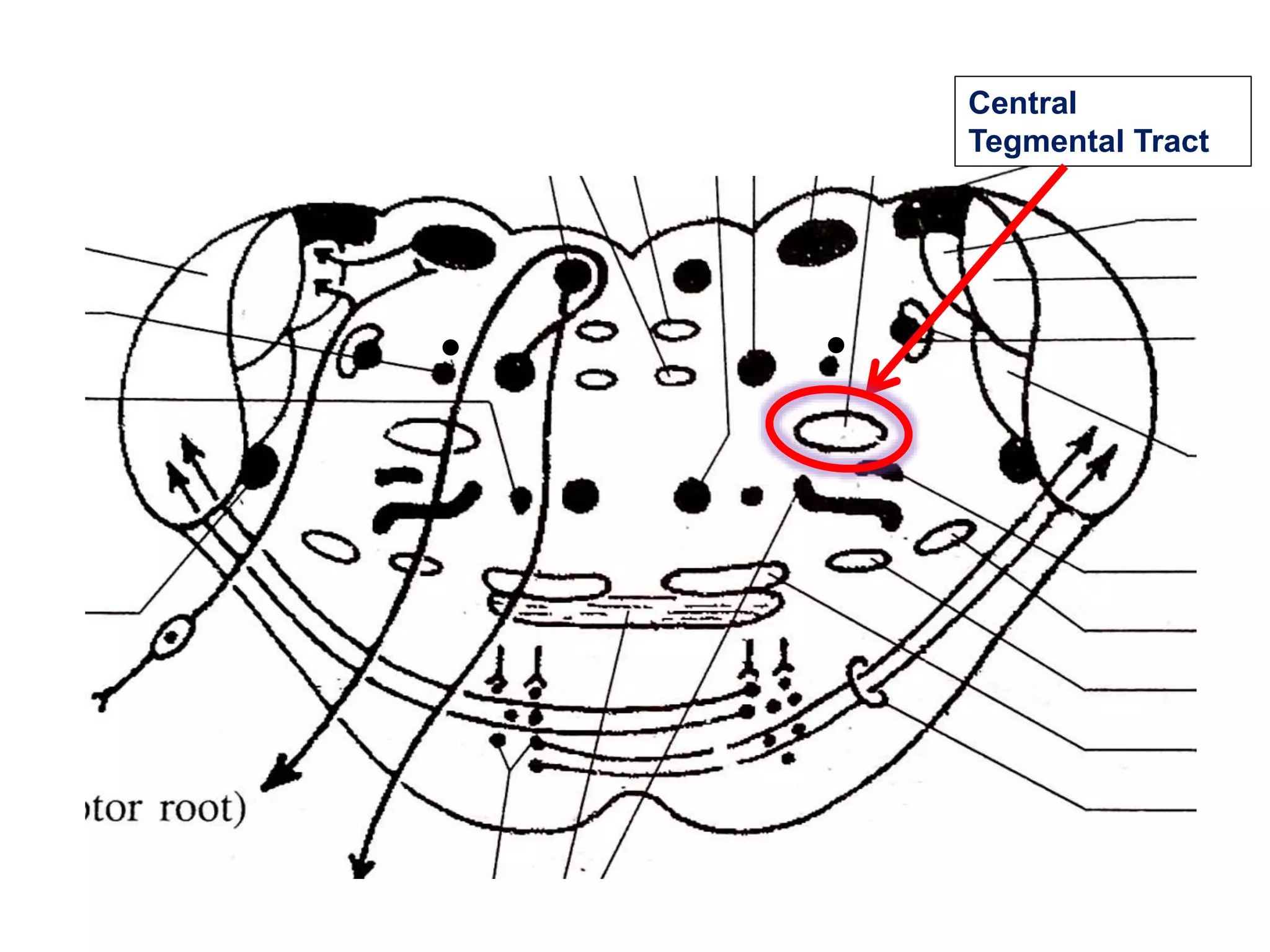
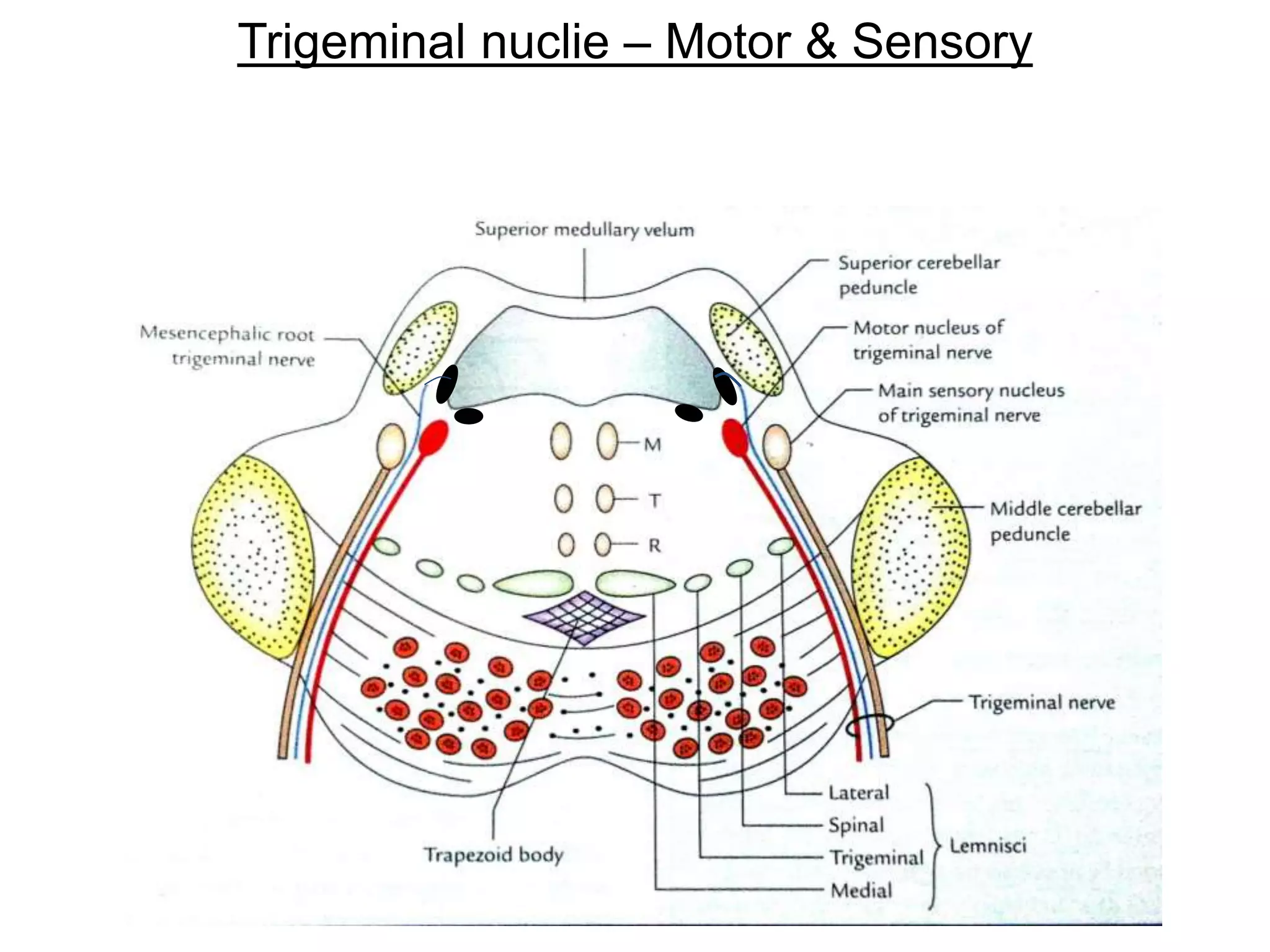
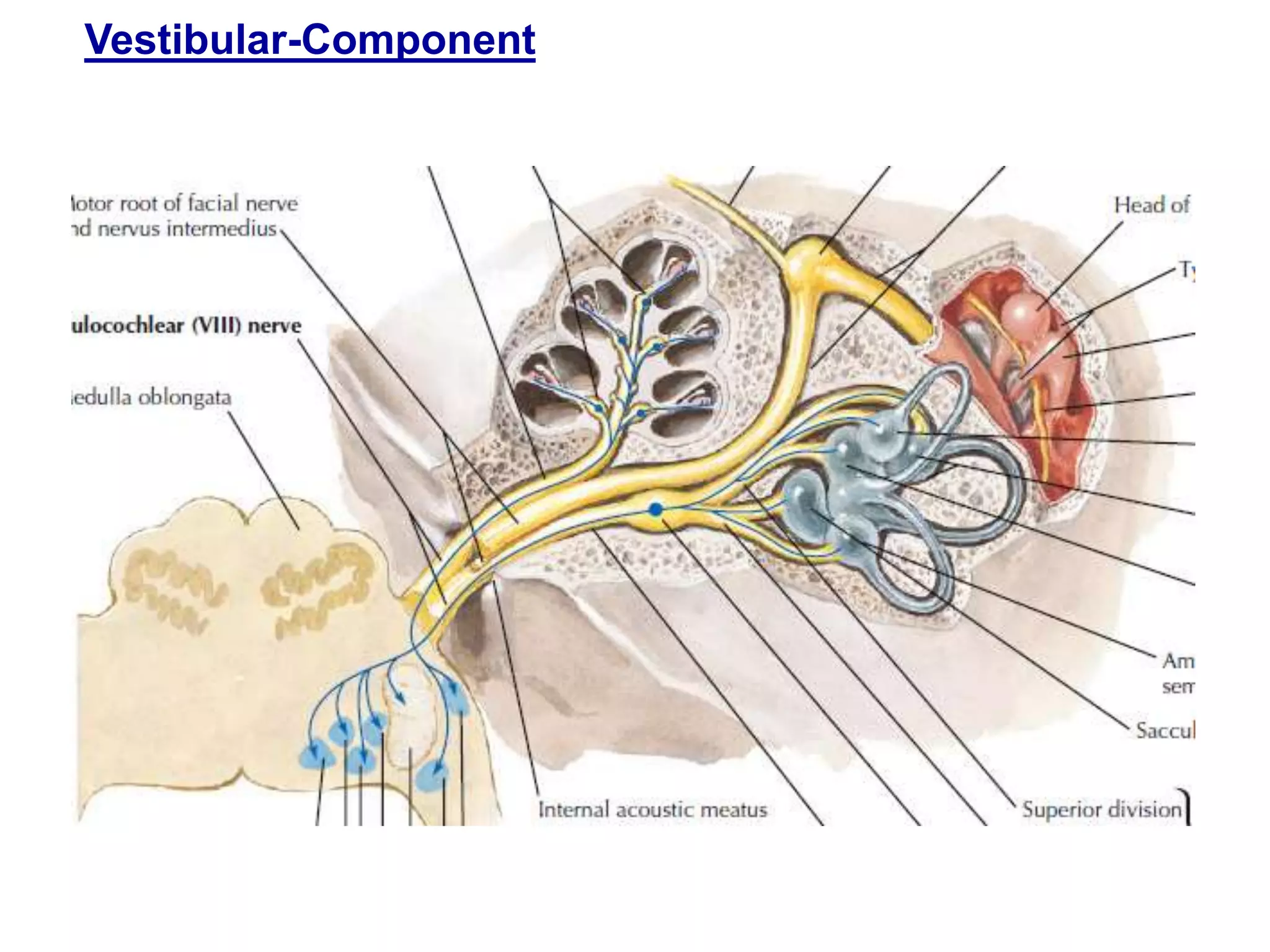
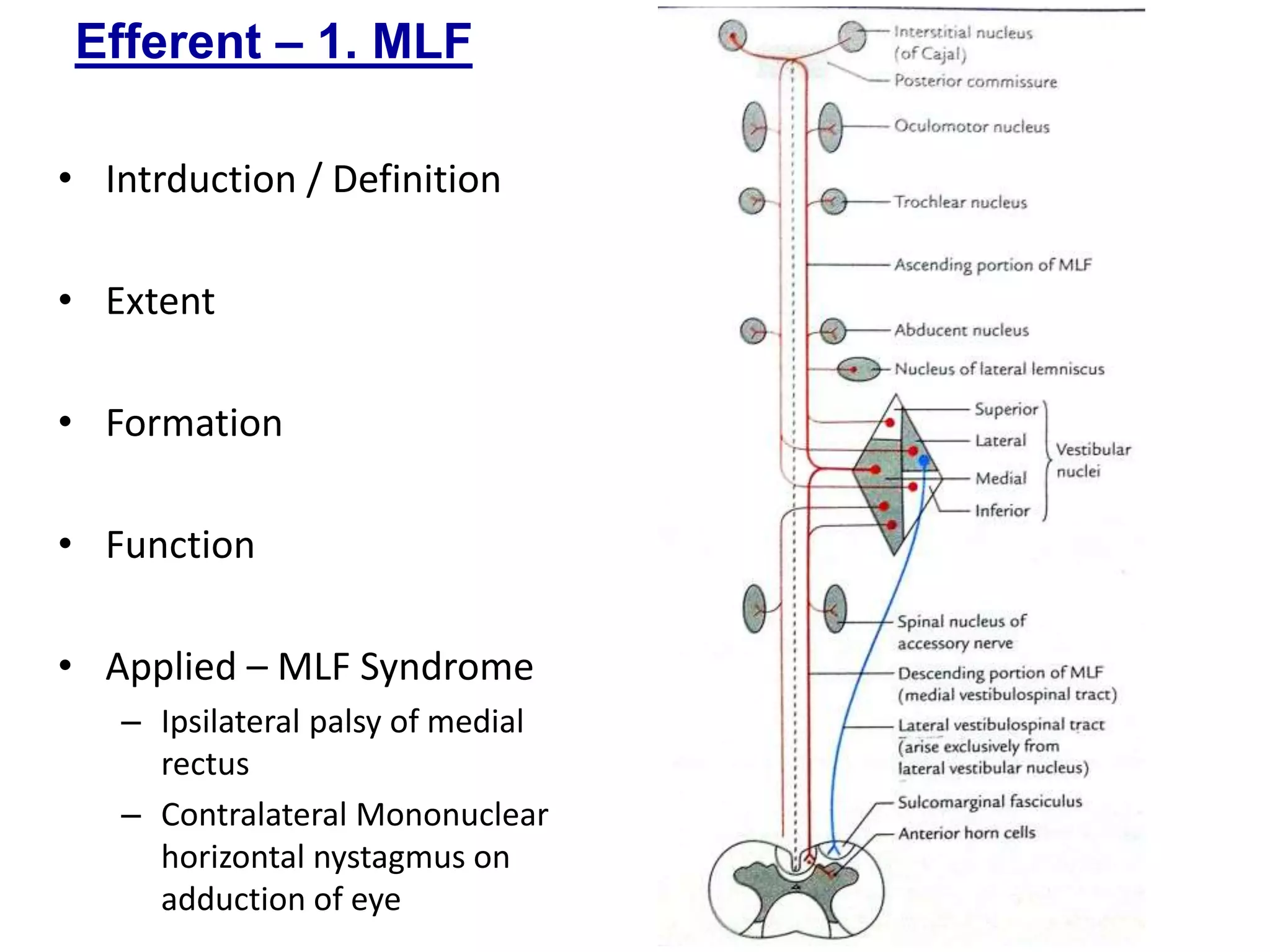
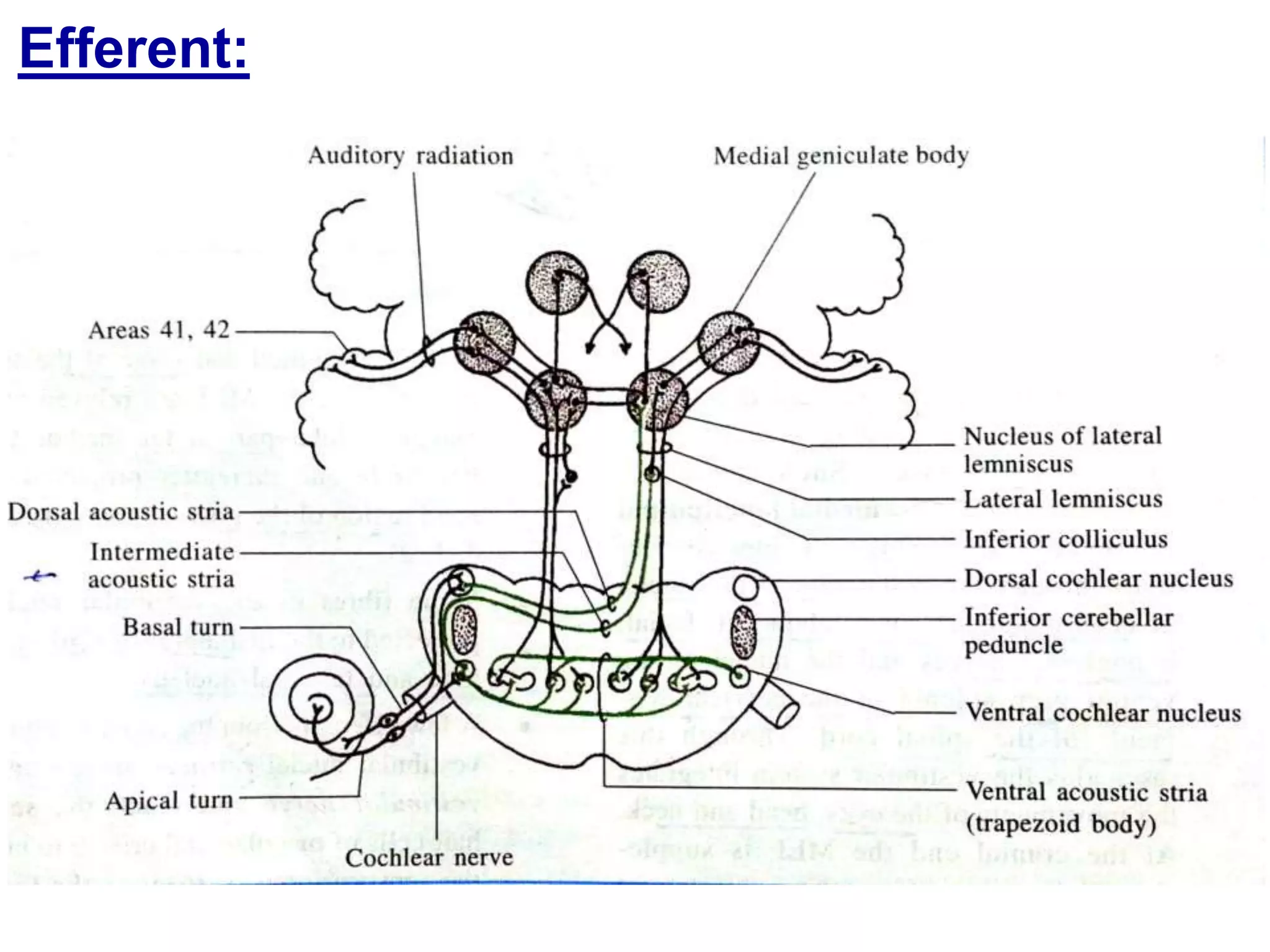
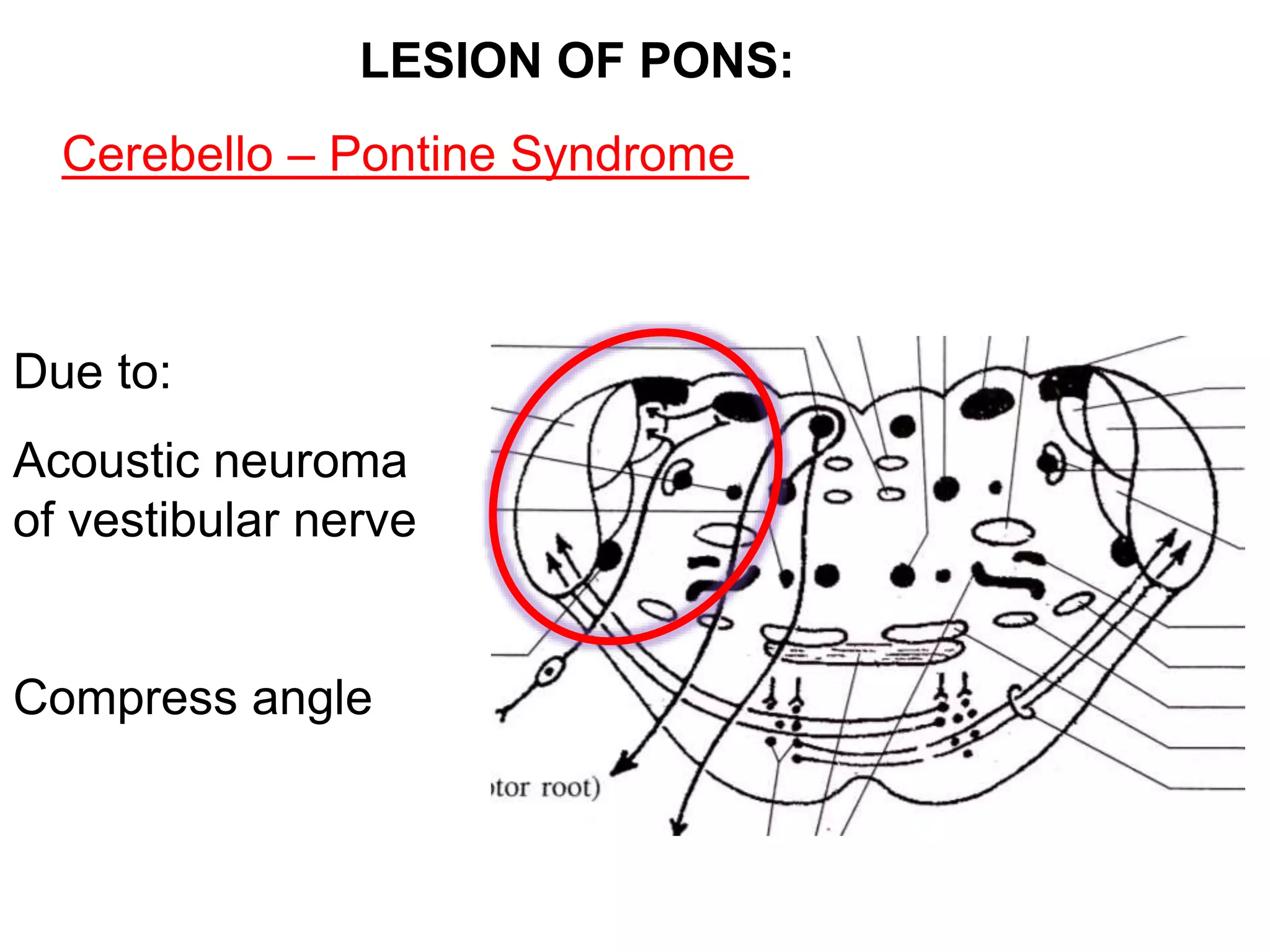
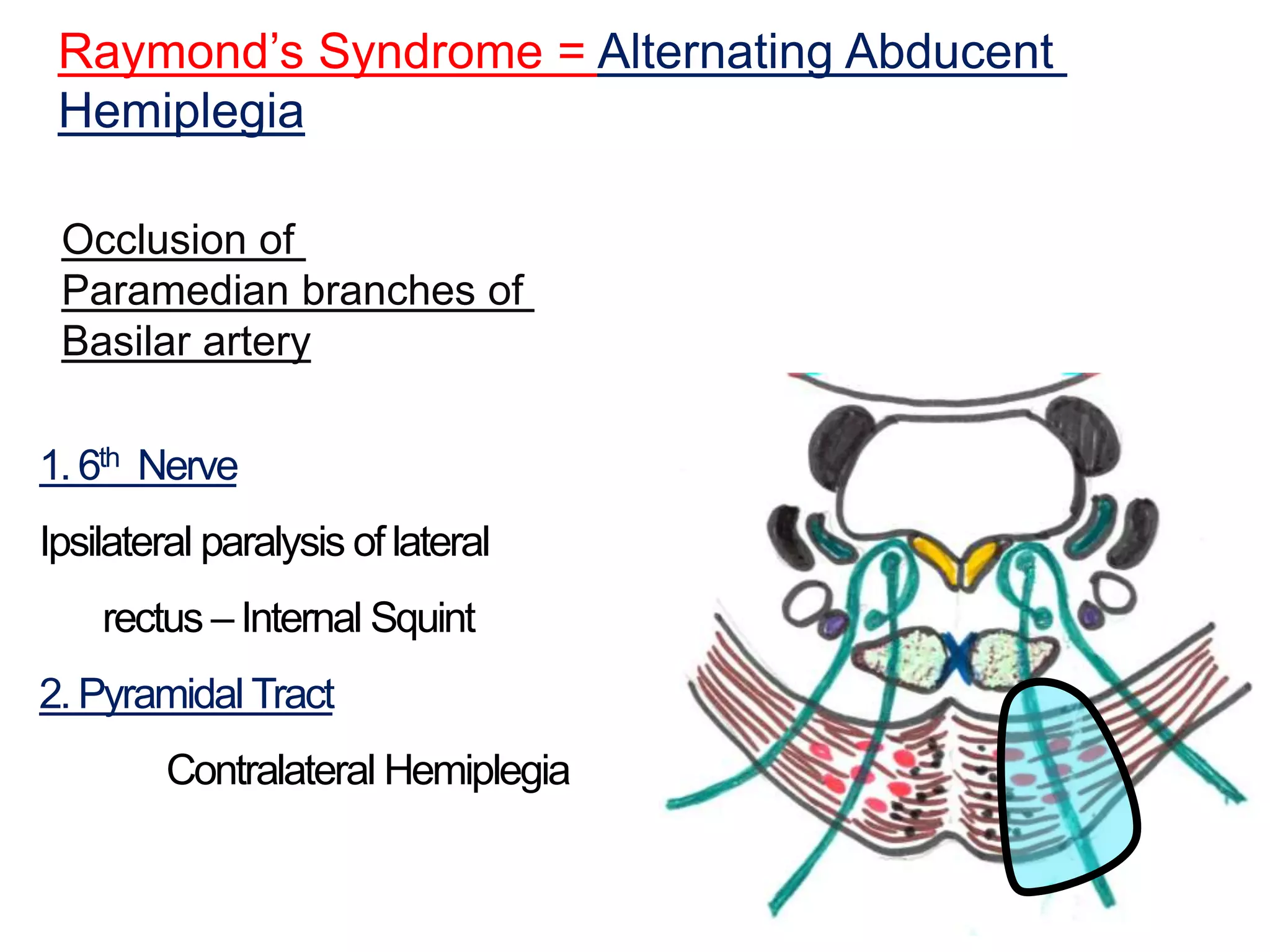
The document outlines the structure and functions of the pons, including its external and internal features, blood supply, and connections to various cranial nerves and the cerebellum. It details the roles of distinct parts of the pons, such as the basilar and tegmentum areas, as well as the pathways for sensory and motor information transmission. It also discusses conditions associated with pons lesions, such as cerebello-pontine syndrome, with specific symptoms resulting from various neural injuries.