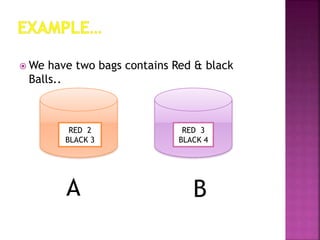
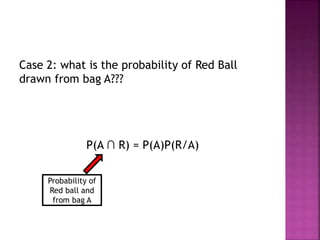
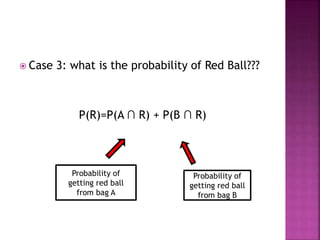
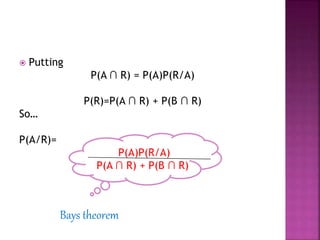
Bayes' theorem describes the probability of an event based on prior knowledge of conditions related to the event. For example, a person's age can make the probability of them having cancer more accurate than without knowing their age. Bayesian inference applies Bayes' theorem to statistical analysis by updating probabilities based on new evidence. The example problem calculates probabilities of drawing a red ball from two bags with different numbers of red and black balls using Bayes' theorem. It finds the probability of a red ball being from bag A given that a red ball was drawn is 2/5 divided by the total probability of drawing a red ball from either bag.