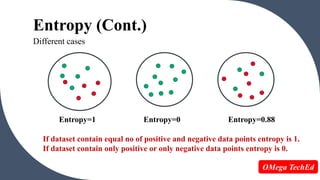
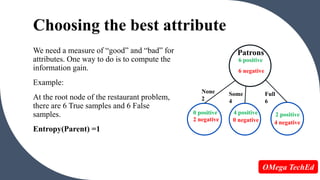
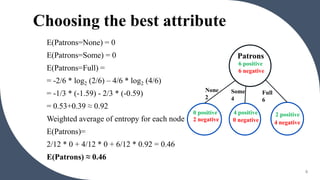
Entropy is a measure of unpredictability or impurity in a data set. It is used in decision trees to determine the best way to split data at each node. High entropy means low purity with an equal mix of classes, while low entropy means high purity with mostly one class. Information gain is the reduction in entropy when splitting on an attribute, with the attribute with the highest information gain chosen as the split. For example, in a data set on restaurant patrons, splitting on the "patrons" attribute results in a higher information gain than splitting on "type of food" so "patrons" would be chosen as the root node.







![Choosing the best attribute
E(Type=French) = 1
E(Type=Italian) = 1
E(Type=Thai) = 1
E(Type=Burger) =1
Weighted average of entropy for each node
E(Type)=
[2/12 * 1 + 2/12 * 1 + 4/12 * 1 + 4/12 *1]
= 1
E(Type) ≈ 1
11
6 positive
6 negative
2 positive
2 negative
French
2
Italian
2
Thai
4
1 negative
1 positive
1 positive
1 negative
Burger
4
2 positive
2 negative
Type
OMega TechEd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-231203160515-80cb685b/85/Entropy-and-information-gain-in-decision-tree-11-320.jpg)

