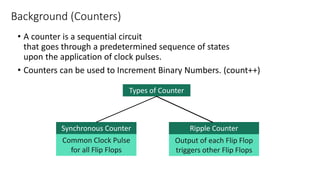
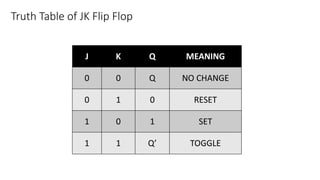
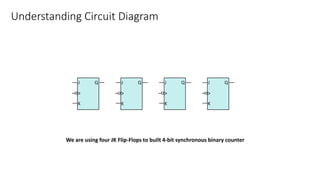
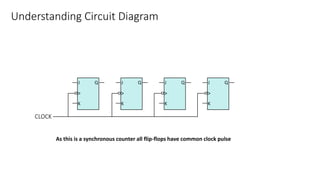
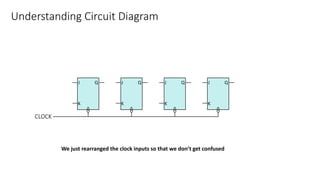
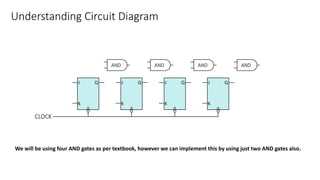
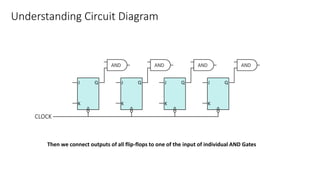
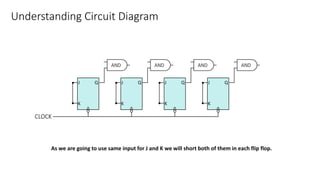
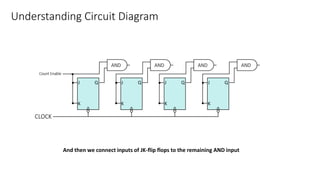
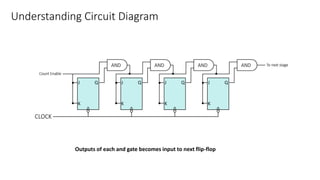
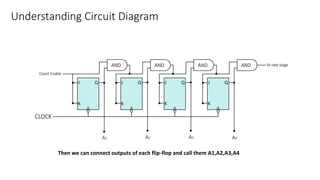
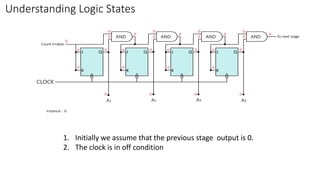
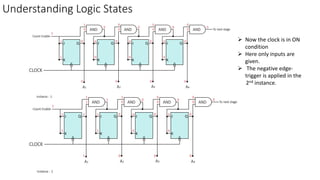
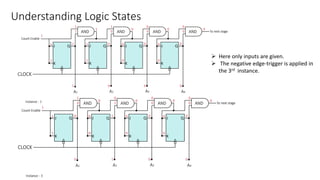
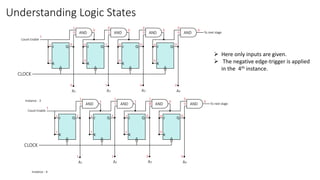
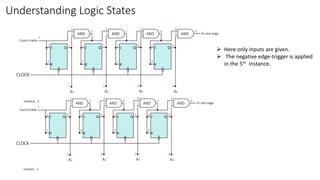
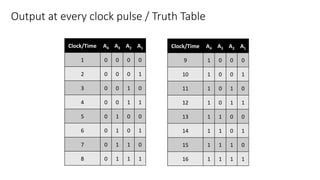
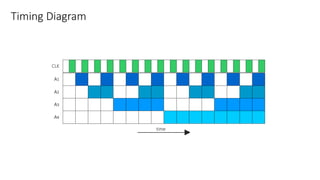
This document describes a 4-bit synchronous binary counter. It contains the truth table for a JK flip-flop, diagrams of the counter circuit using 4 JK flip-flops connected in series with a common clock, and tables showing the output logic states and timing diagram as the counter counts from 0 to 15 over 16 clock pulses.