Seed formation, apomixsis, polyembrony
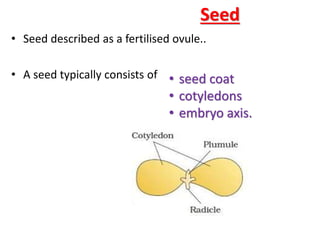
- 1. Seed • Seed described as a fertilised ovule.. • A seed typically consists of • seed coat • cotyledons • embryo axis.
- 2. To download power point : Pay: 20 US $ or RS : 400 and send pay receipt to mail (biohari14@gmail.com). I will send power point to your mail id. Name: Harinatha Reddy Bank name: HDFC Account number: 50100203661752 IFC code: HDFC0000514 Bangalore Karnataka.
- 3. Non-albuminous and albuminous seeds. Mature seeds Non-albuminous: Albuminous • Seeds have no residual endosperm. • Endosperm completely consumed during embryo development.. • (e.g., pea, groundnut). • Albuminous seeds retain a part of endosperm. • Endosperm is not completely used up during embryo development .. • (e.g., wheat, maize, barley, castor
- 4. Perisperm. • In some seeds such as black pepper and beet, remnants of nucellus are also persistent. • This residual, persistent nucellus is the perisperm.
- 5. Seed The cotyledons of the embryo are simple structures, generally thick and swollen due to storage of food reserves (as in legumes).
- 6. • Integuments of ovules Protective seed coats. • The micropyle remains as a small pore in the seed coat. • Micropyle facilitates entry of oxygen and water into the seed during germination. Castor seeds AFTER FERTILIZATOIN PROCESS
- 7. SEED DORMANCY. • As the seed matures, its water content is reduced and seeds become relatively dry (10-15 % moisture by mass). • The general metabolic activity of the embryo slows down.
- 8. SEED DORMANCY. • The embryo may enter a state of inactivity called dormancy. • If favourable conditions are available (adequate moisture, oxygen and suitable temperature), they germinate…
- 9. • Endosperm is persistent in cereals – wheat, rice and maize.
- 10. • ovules mature seeds. • The ovary fruit. • The wall of the ovary wall of fruit Pericarp. • Fleshy fruits: Guava, orange, mango, etc., • Dry fruits : groundnut, and mustard, etc. AFTER FERTILIZATOIN PROCESS
- 12. True fruits • Most fruits however develop only from the ovary and are called true fruits. • Eg: Mango, Citrus, Orange etc.. • The other floral parts degenerate and fall off.
- 13. False fruits: • In a few species such as apple, strawberry, cashew, etc., the thalamus also contributes to fruit formation. The edible part in strawberry is thalamus. pedicel
- 14. Achenes • The strawberry is an aggregate of achenes (the true fruits which contain the seed). • Achenes attached in an orderly fashion to the epidermis of the thalamus …
- 15. Parthenocarpic fruits • In a few species fruits develop without fertilisation. • Banana and grape is one such example. • Auxins, gibberellins are used to induce parthenocarpy..
- 16. Seeds offer several advantages to angiosperms. • Reproductive processes such as pollination and fertilisation are independent of water, seed formation is more dependable. • Seeds have better adaptive strategies for dispersal to new habitats and help the species to colonise in other areas..
- 17. • Seeds have sufficient food reserves, young seedlings are nourished until they are capable of photosynthesis. • The hard seed coat provides protection to the young embryo. • Seeds are products of sexual reproduction, they generate new genetic combinations leading to variations.
- 18. Seed is the basis of our agriculture. • Dehydration and dormancy of mature seeds are crucial for storage of seeds.. • Stored seeds used as food throughout the year and also to raise crop in the next season…
- 19. How long seeds remain alive after they are dispersed? • In a few species the seeds lose viability within a few months. • Seeds of a large number of species live for several years. • Some seeds can remain alive for hundreds of years.
- 20. The oldest is that of a lupine seeds • Lupinus arcticus excavated from Arctic Tundra. • The seed germinated and flowered after an estimated record of 10,000 years of dormancy. Archeological digging
- 21. Date palm seed • A recent record of 2000 years old viable seed is of the date palm. • Phoenix dactylifera (Date palm) discovered during the archeological excavation at King Herod’s palace near the dead Sea.
- 22. Tiny seeds • Some plants in which fruits contain very small and large number of seeds. • Orchid, Orobanche , striga, Ficus (Fig tree) each fruit contain thousands of tiny seeds. • Orobanche and Striga are parasitic plants. Cuscuta
- 23. Epiphyte • An epiphyte is an organism that grows on the surface of a plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air… e.g., Vanda
- 24. APOMIXIS • The process of formation of seeds without fertilisation, called apomixis. .. • Eg: Asteraceae and grasses. • Such seeds is called apomictic seeds…. • Apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction that mimics (to imitate closely) sexual reproduction..
- 25. Apomictic seeds • There are several ways of development of apomictic seeds. • In some species, the diploid egg cell is formed without reduction division and develops into the embryo without fertilisation.
- 26. Polyembryony. • Occurrence of more than one embryo in a seed is referred to as polyembryony.. • Example : Citrus and Mango..
- 27. Polyembryony. • More often, as in many Citrus and Mango varieties some of the nucellar cells surrounding the embryo sac.. • Nucellar cells start dividing, protrude (extend) into the embryo sac and develop into the embryos. Nucellar cells
- 28. Importance of apomixis in hybrid seed industry, • Hybrid varieties of several of our food and vegetable crops are being extensively cultivated.
- 29. Importance of apomixis in hybrid seed industry, • The seeds collected from hybrids do not maintain hybrid characters (Because of segregation). • Production of hybrid seeds is costly and hence the cost of hybrid seeds become too expensive for the farmers..
- 30. • If these hybrids are made into apomicts, there is no segregation of characters in the hybrid progeny. • Then the farmers can keep on using the hybrid seeds to raise new crop year after year.
- 33. DNA and RNA are Genetic materials • Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic acid (RNA) are the two types of nucleic acids found in living systems… • DNA acts as the genetic material in most of the organisms. • RNA also acts as a genetic material in some viruses….
- 34. RNA also acts as a genetic material in some viruses….
- 35. RNA has additional roles.. • Mostly RNA functions as a messenger RNA (m-RNA). • RNA functions as adapter (t-RNA/transfer RNA). • RNA functions as Structural RNA (r-RNA/ Ribosomal RNA). • In some cases function as a catalytic molecule (Enzyme/Ribozyme).
- 36. • Nucleotides DNA DNA+ Histone proteins Nucleosomes Chromatin Chromosomes Genome
- 37. Nucleic acids (DNA/RNA) are polymers nucleotides • DNA is a long polymer of deoxyribonucleotides. • RNA is a long polymer of ribonucleotides.
- 38. THE DNA • DNA is a long polymer of deoxyribonucleotides. A nucleotide has three components: • (ribose in case of RNA, and deoxyribose for DNA), Nitrogenous base, Pentose (or) Ribose sugar Phosphate group
- 39. The length of the DNA • The length of DNA is usually defined as number of nucleotides.. • or a pair of nucleotide referred to as base pairs present in it.
- 40. Single strand DNA • The length of ss DNA is usually defined as number of nucleotides..
- 41. • The length of ds DNA is usually defined as number of nucleotides..
- 42. A Bacteriophage known as φ ×174 has 5386 nucleotides Bacteriophage lambda has 48502 base pairs (bp)
- 43. Haploid content of human DNA is 3.3 × 109 bp. Escherichia coli has 4.6 × 106 bp
- 44. Structure of Polynucleotide Chain • DNA is a polynucleotide chain. • A nucleotide has three components: 1. a nitrogenous base, 2. a pentose sugar (ribose in case of RNA, and deoxyribose for DNA), 3. A phosphate group.
- 45. There are two types of nitrogenous bases • Thymine is present in DNA. Uracil is present in RNA at the place of Thymine. Purines: (Adenine and Guanine): Pyrimidines (Cytosine, Uracil and Thymine).
- 46. • In DNA • A=T • G=C • In RNA • A=U • G=C • Thymine also called as 5-methyl uracil…
- 47. Deoxyribose sugar and Ribose sugar
- 48. N-glycosidic linkage Phosphate group is linked to 5' -OH of a nucleoside through phosphoester linkage,
- 49. Uracil Uridine Uridylic acid Nitogen base +Sugar +Phosphate
- 50. • Two nucleotides are linked through 3'-5' phosphodiester linkage to form a dinucleotide. • More nucleotides can be joined in such a manner to form a polynucleotide chain..
- 51. • One end of polymer is called 5’-end contain free phosphate moiety at 5' -end of ribose sugar. • The other end of the polymer the ribose has a free 3' -OH group which is referred to as 3'-end of the polynucleotide chain.
- 52. • The backbone in a polynucleotide chain is formed due to sugar and phosphates.
- 53. Dr. HarinathaReddy Aswartha Assistant professor Department of Microbiology biohari14@gmail.com
