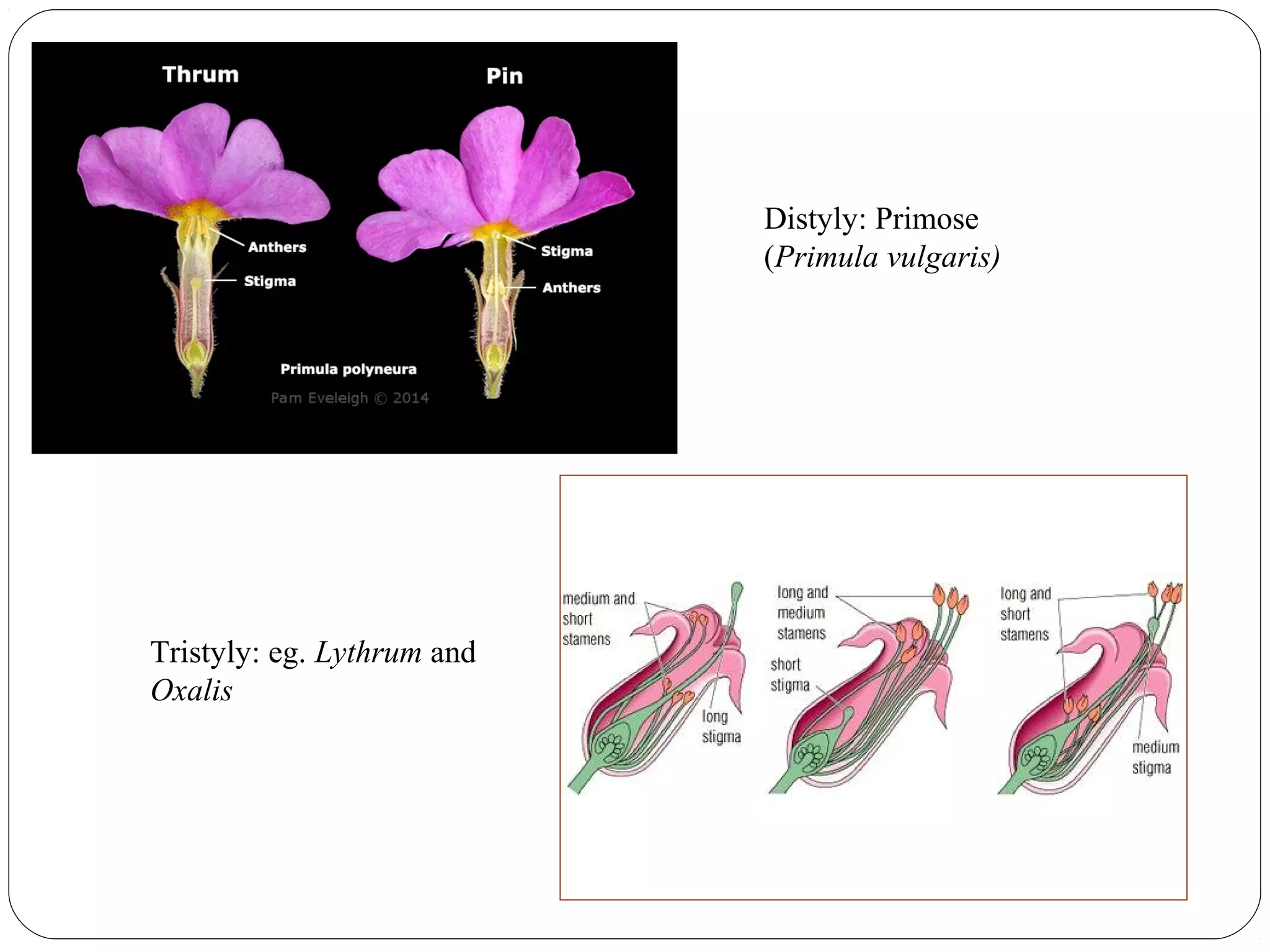
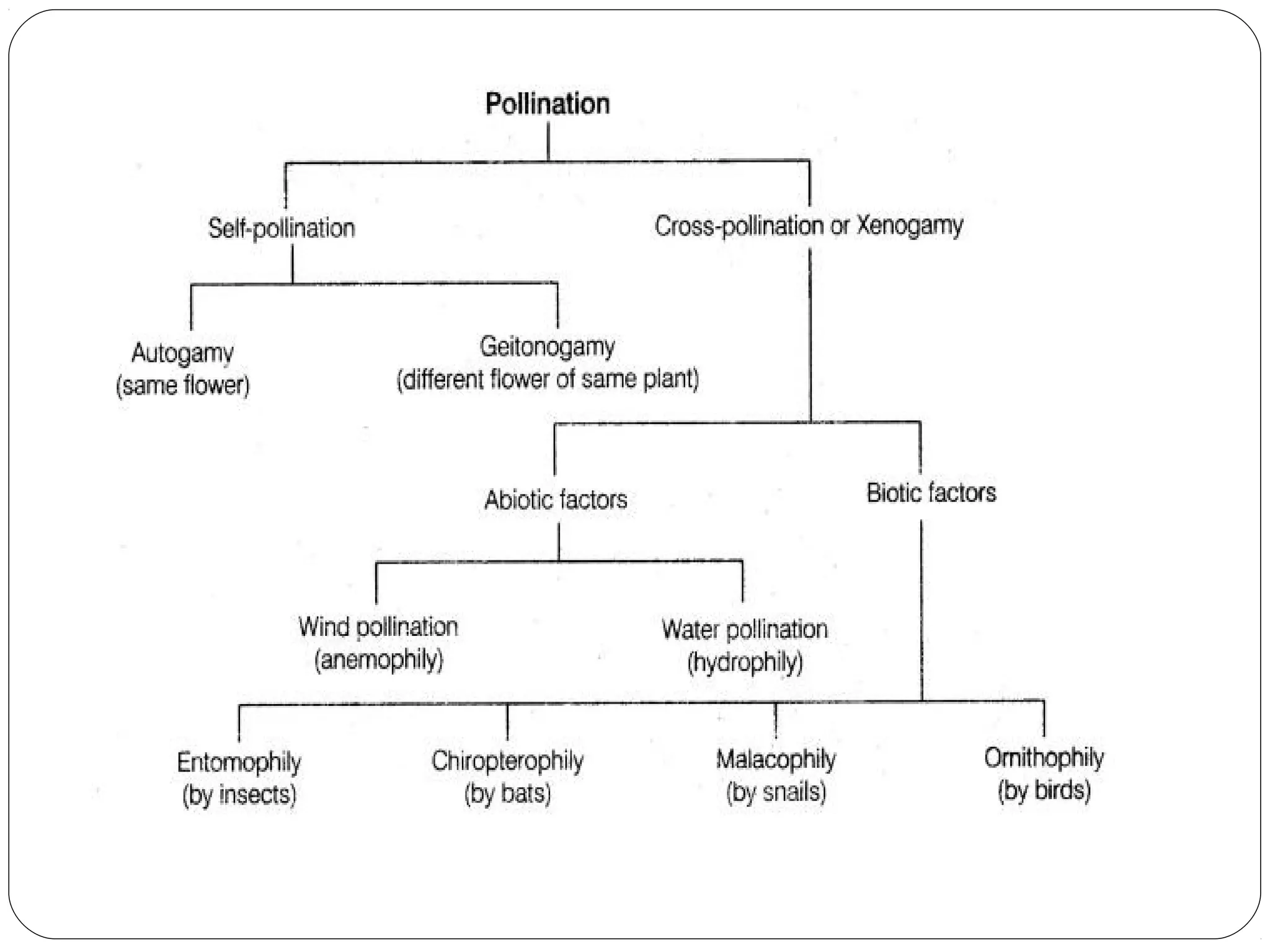
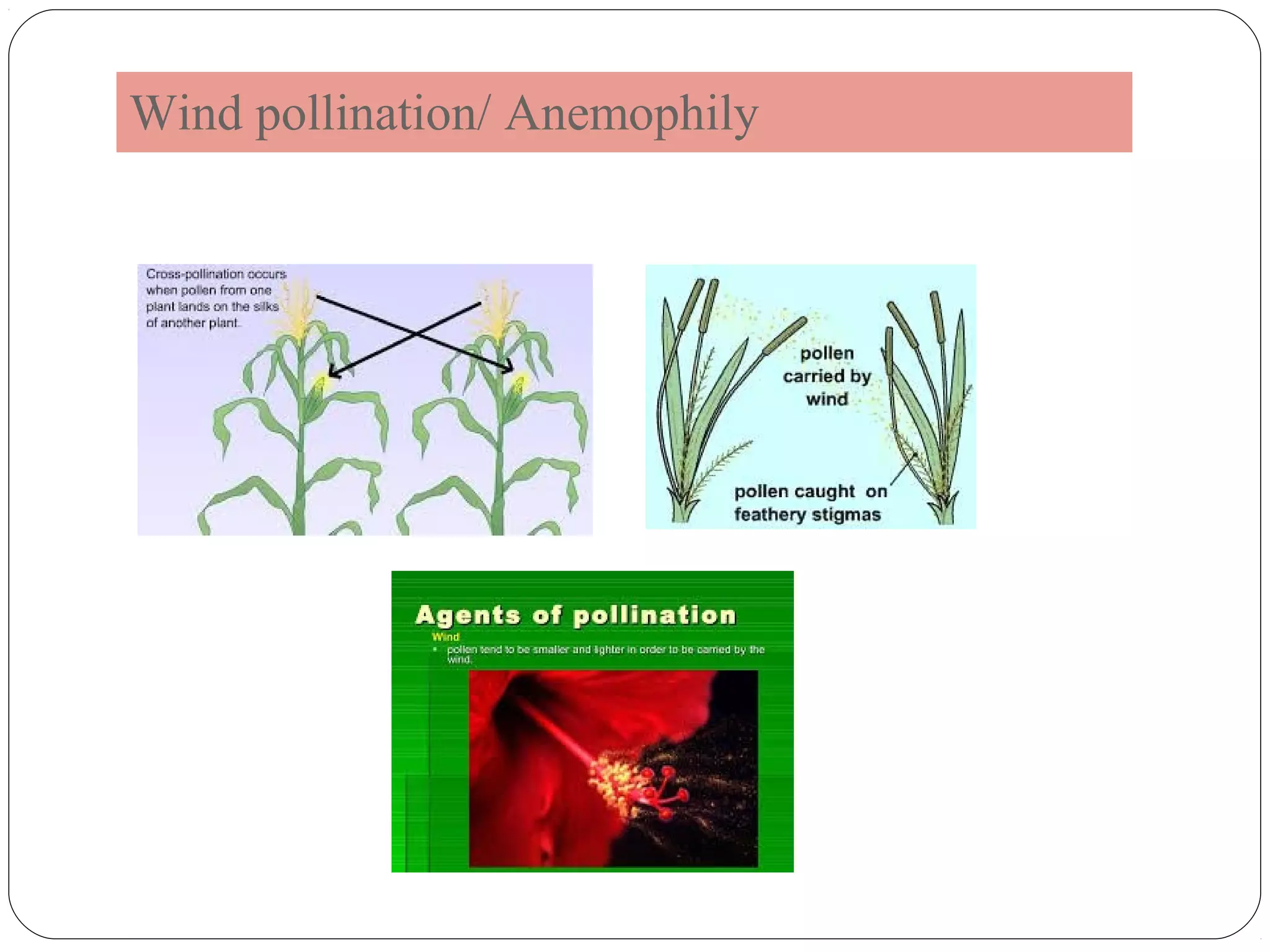
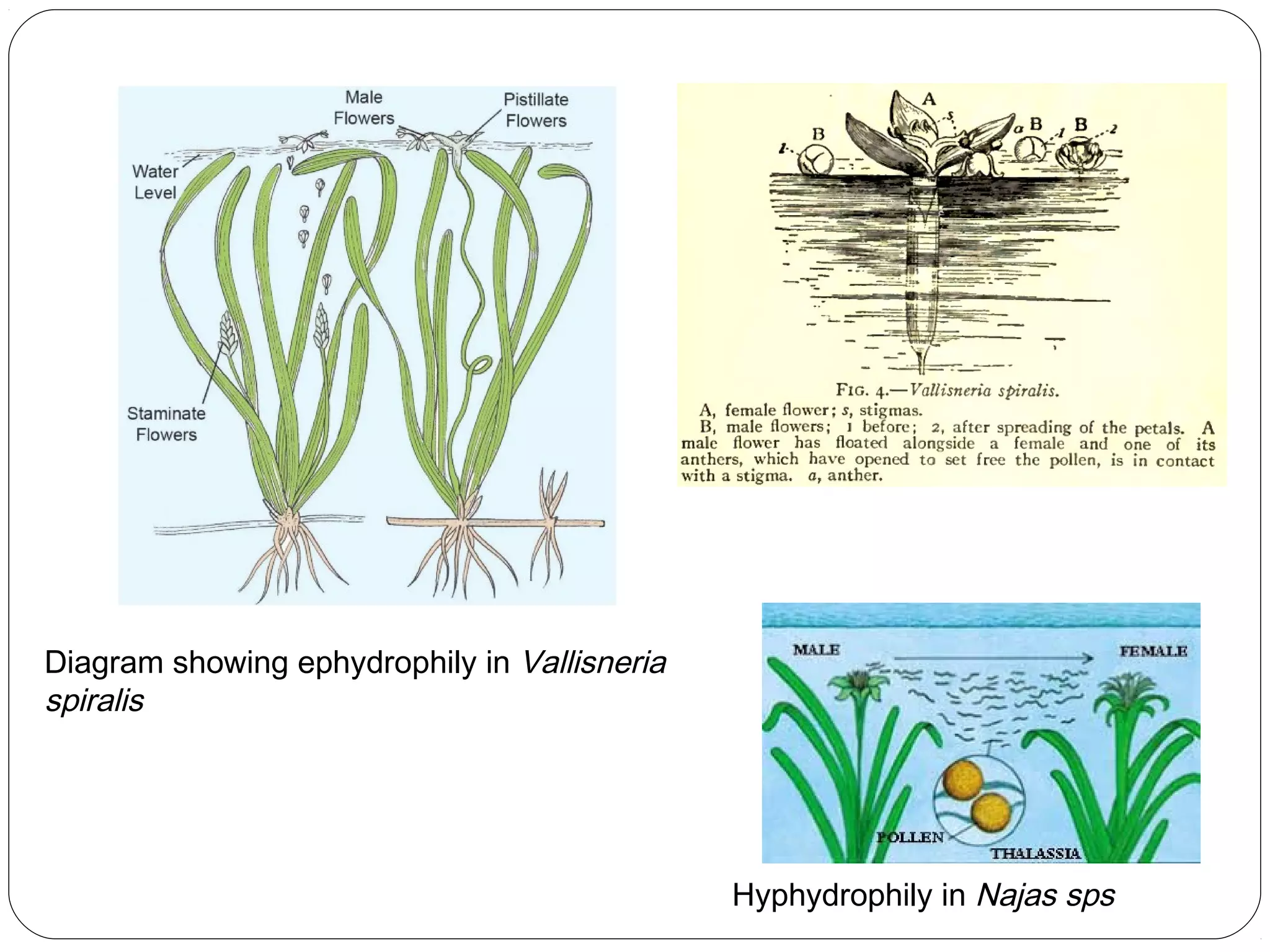
The document discusses two main types of pollination: autogamy (self-pollination) and allogamy (cross-pollination). Autogamy occurs when a pollen grain is transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower and is promoted by traits like bisexuality, homogamy, cleistogamy, and chasmogamy. Allogamy involves transfer of pollen between different plants and is encouraged by dicliny, dichogamy, heterostyly, herkogamy, and self-incompatibility. The mode of pollination influences plant breeding by affecting gene action, genetic constitution, adaptability, genetic purity, and gene transfer.