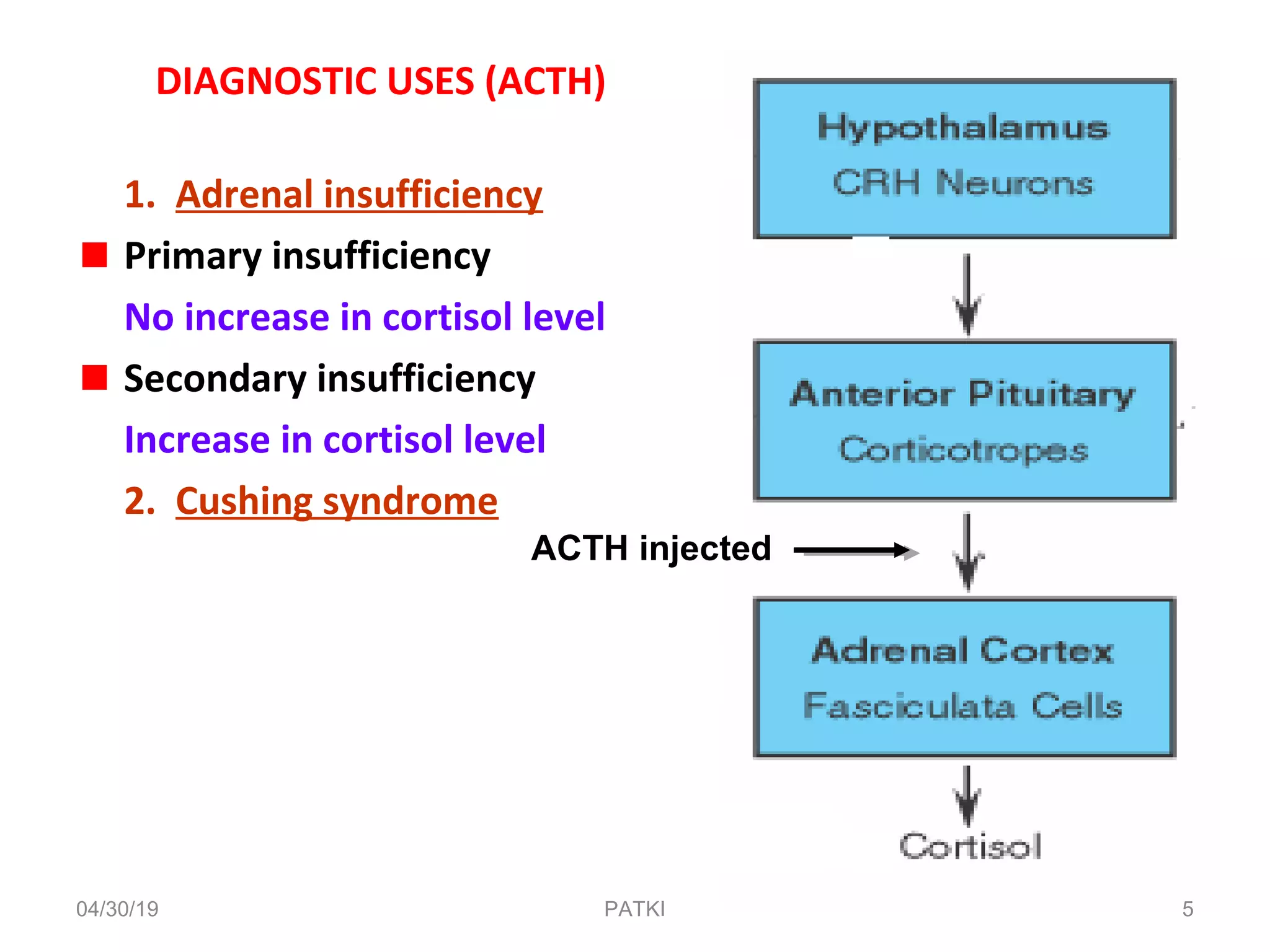
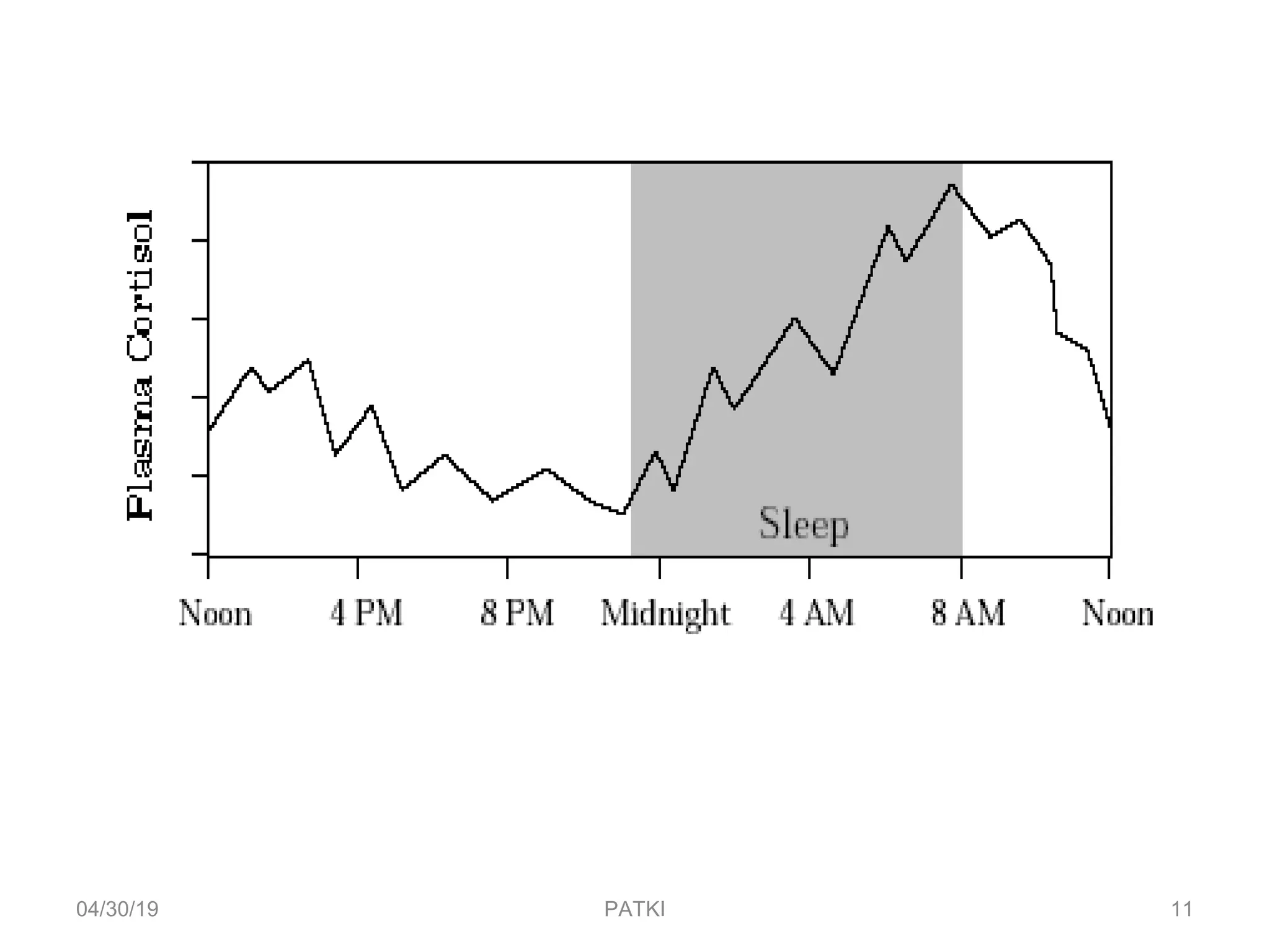
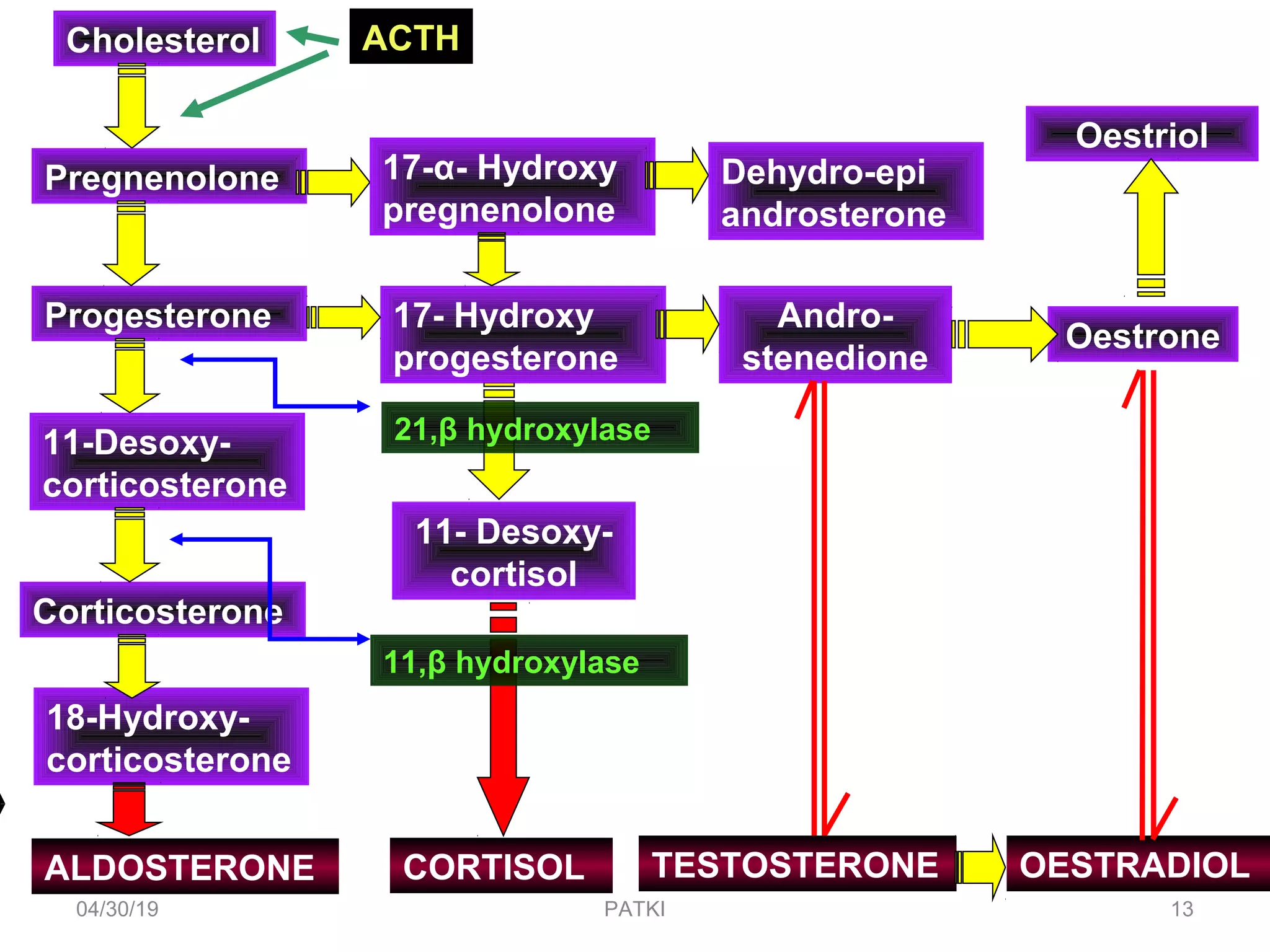
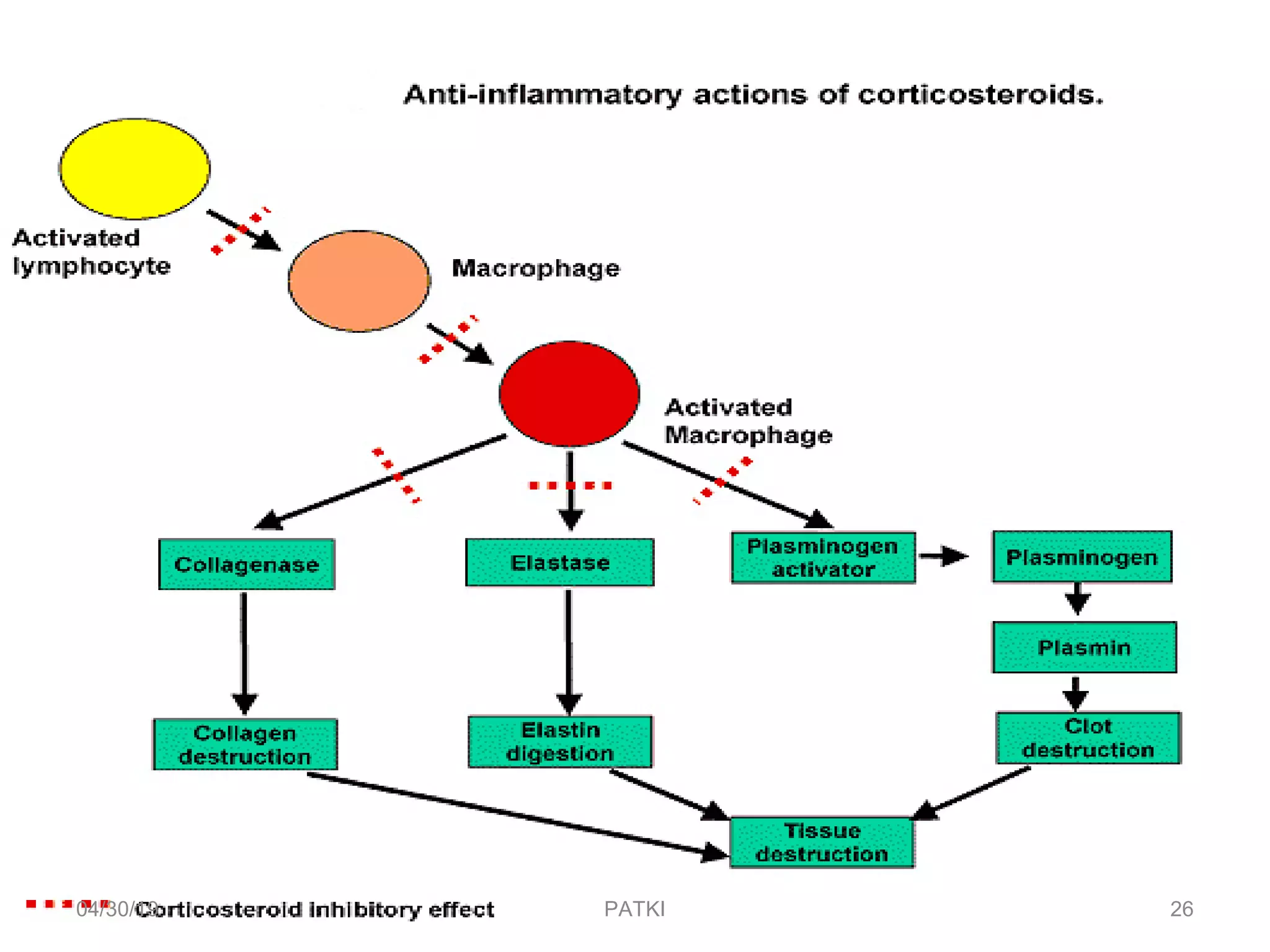
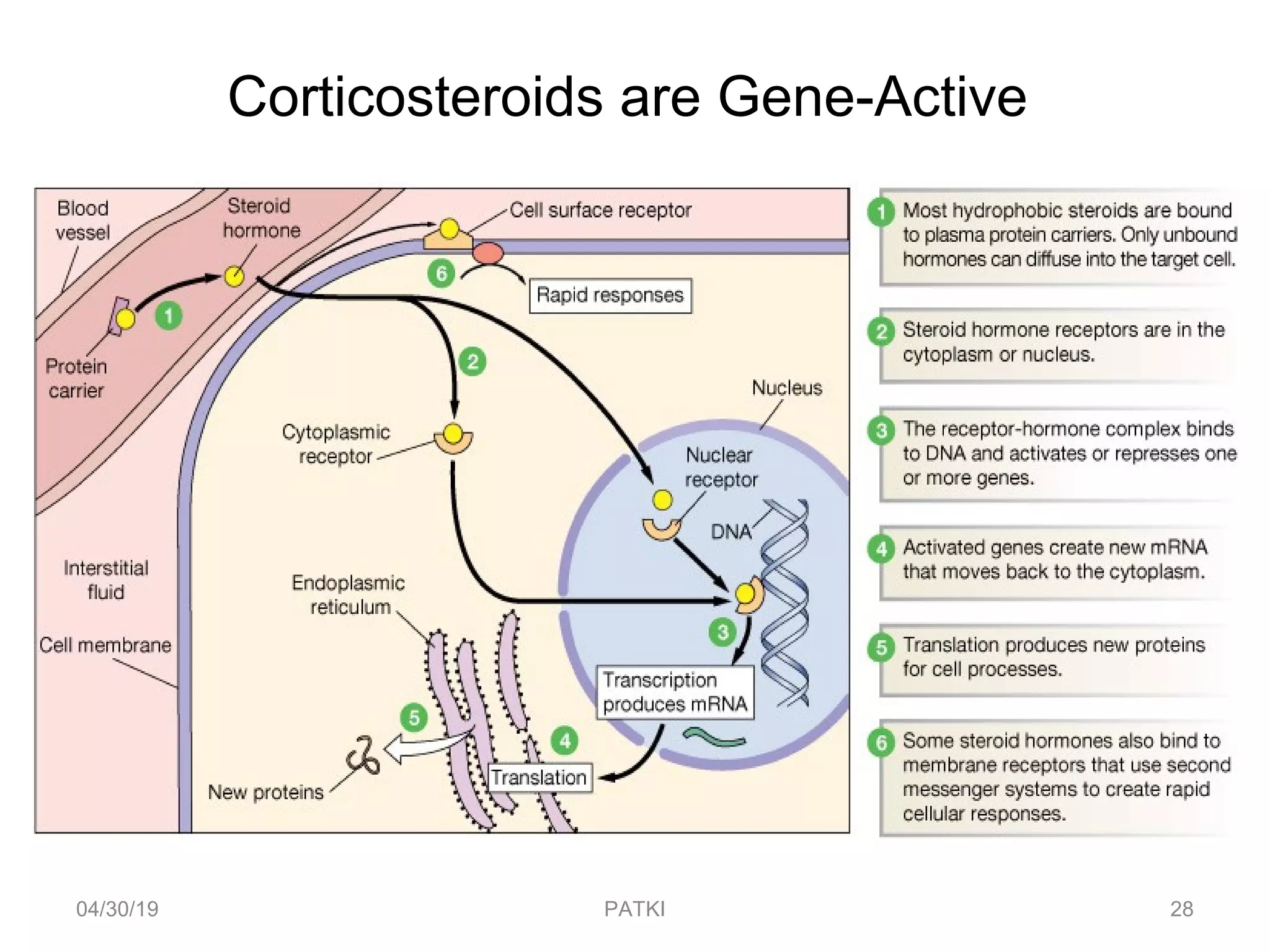
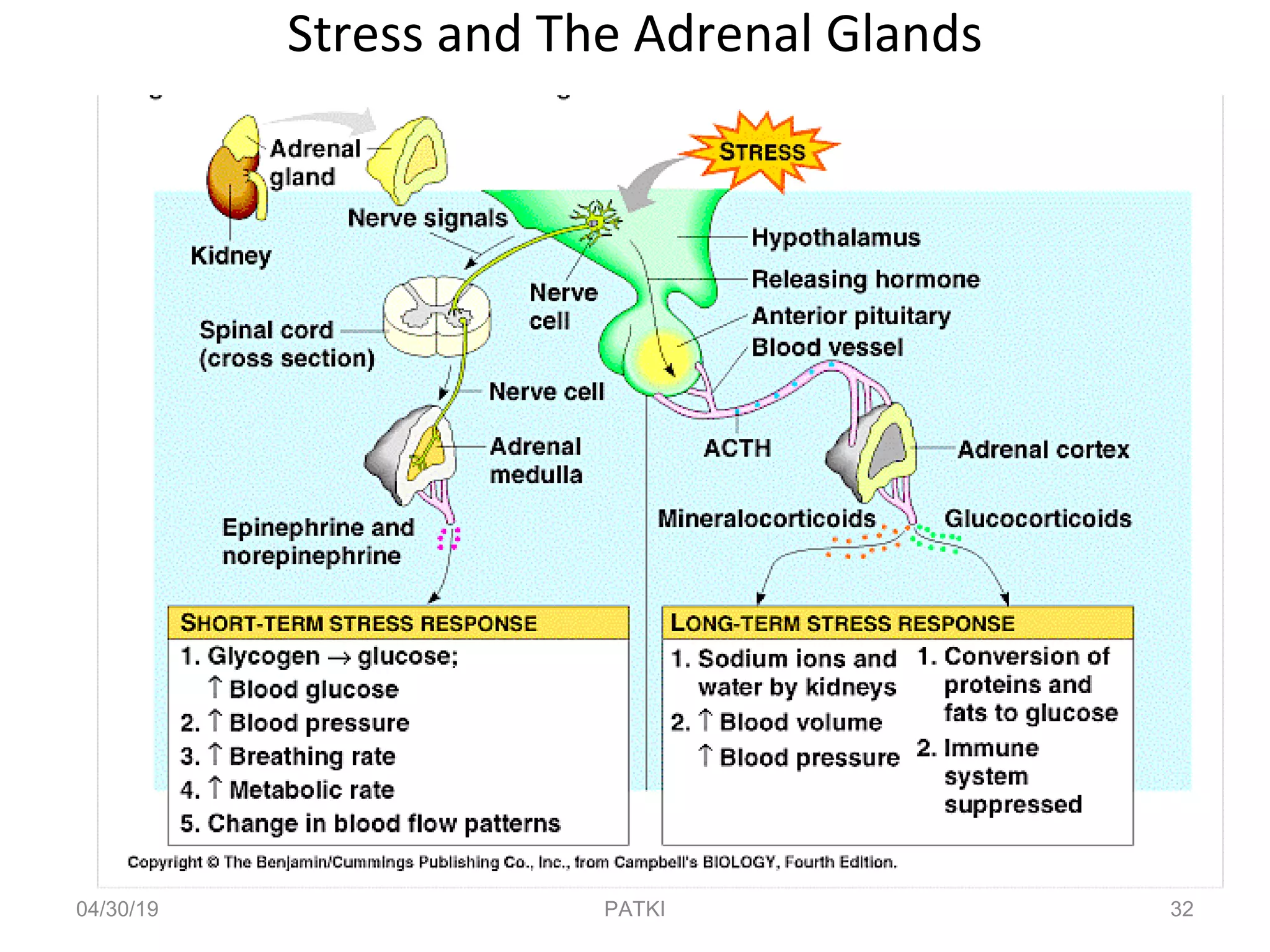
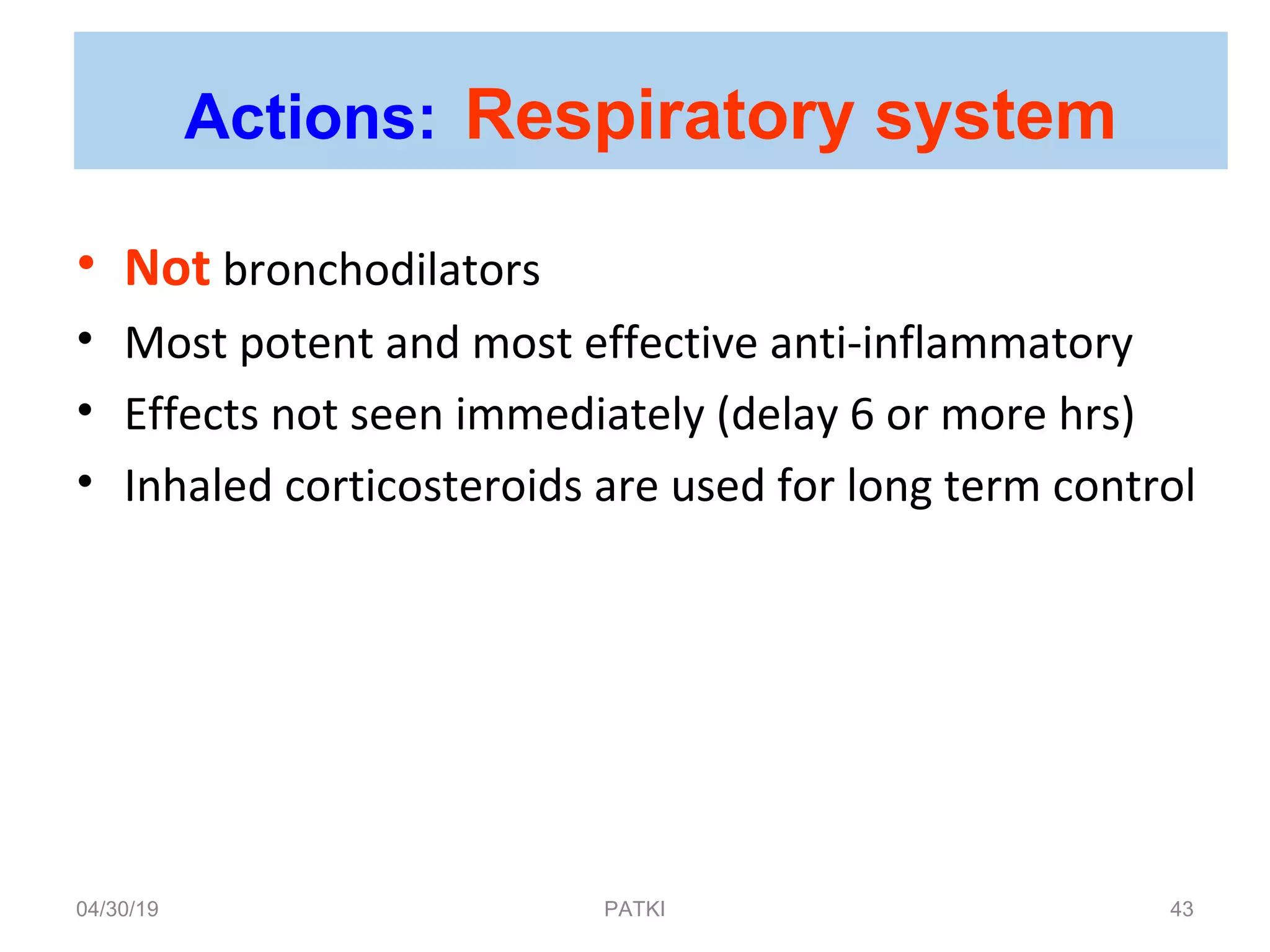
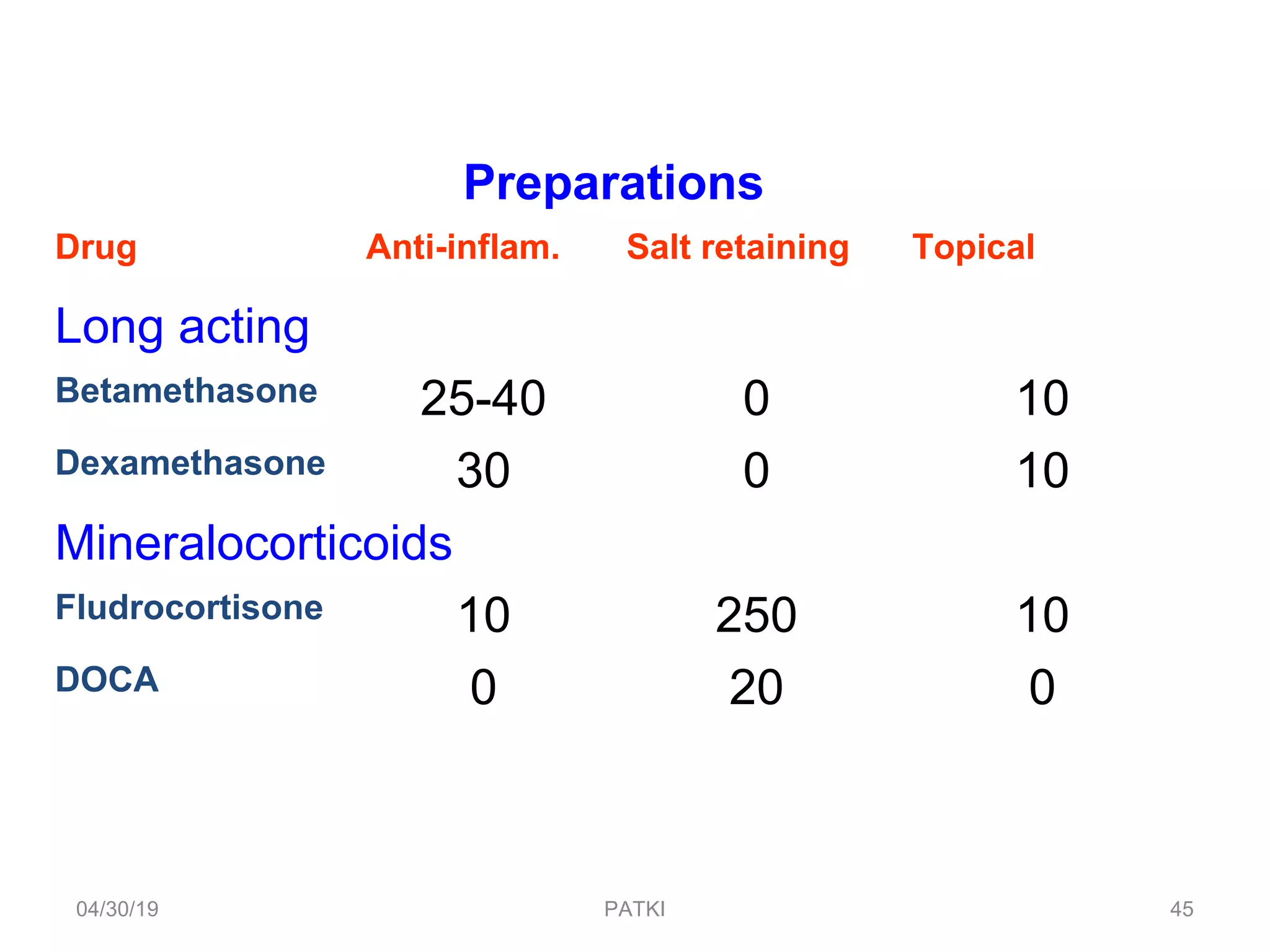
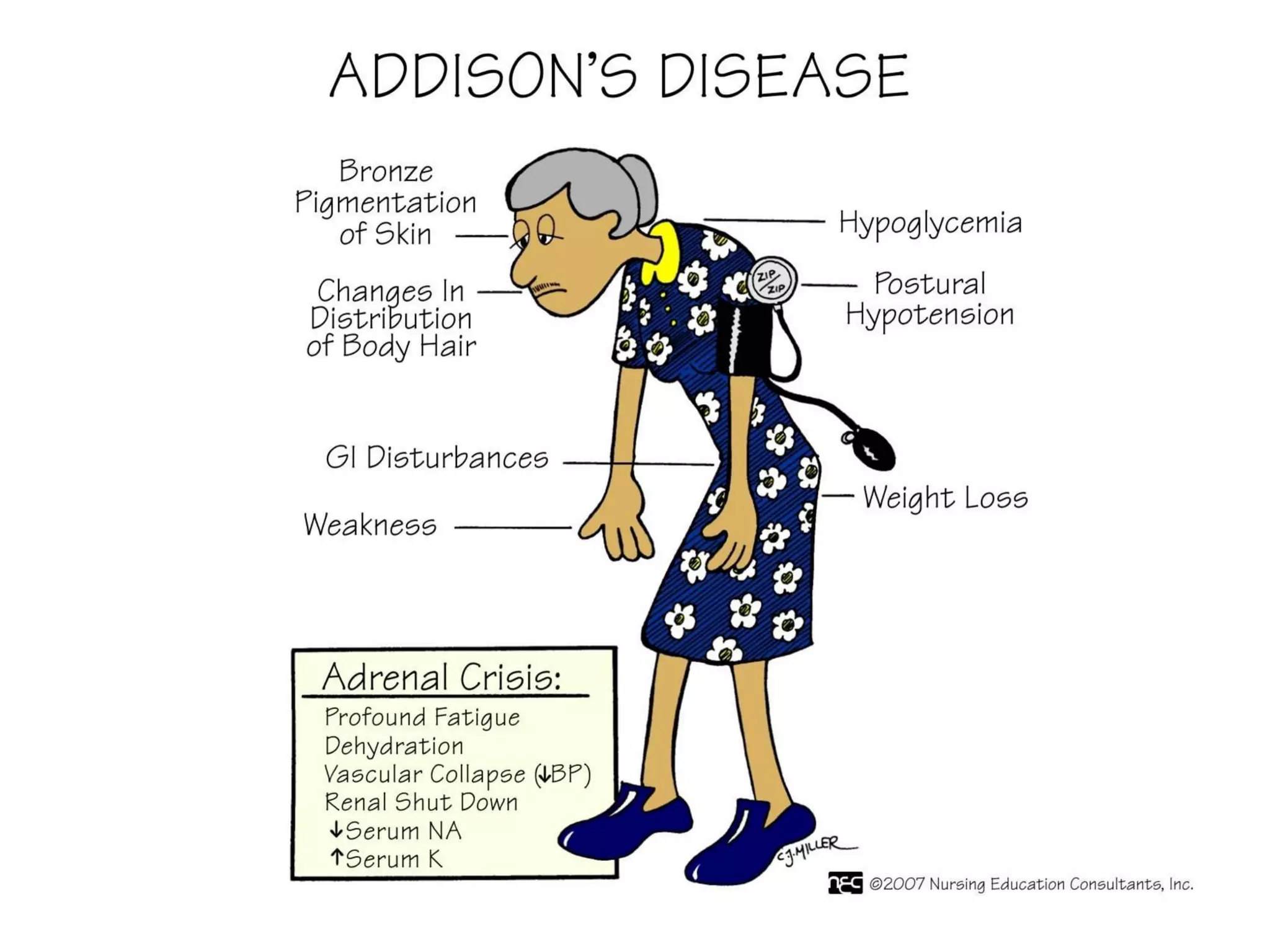
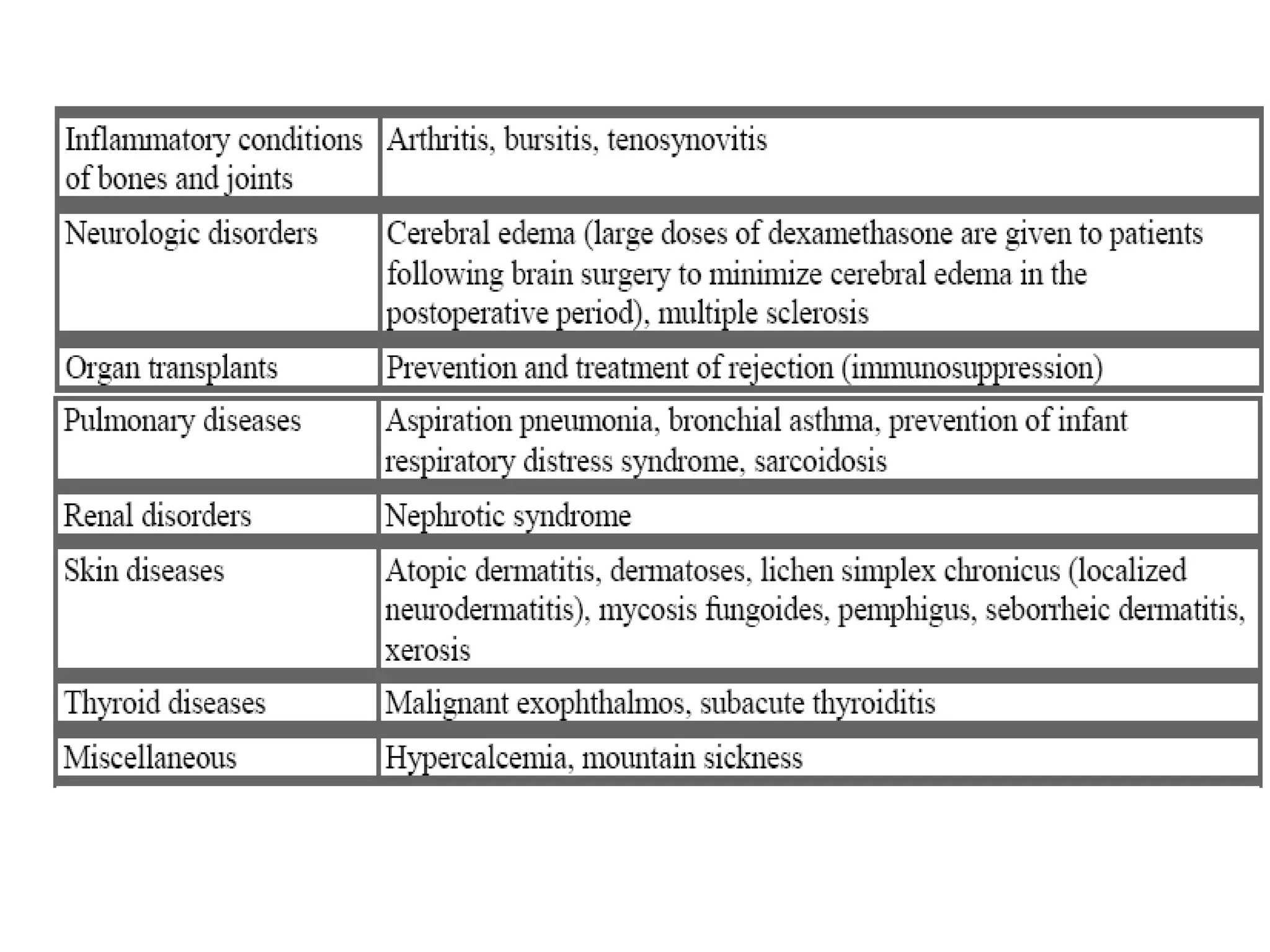
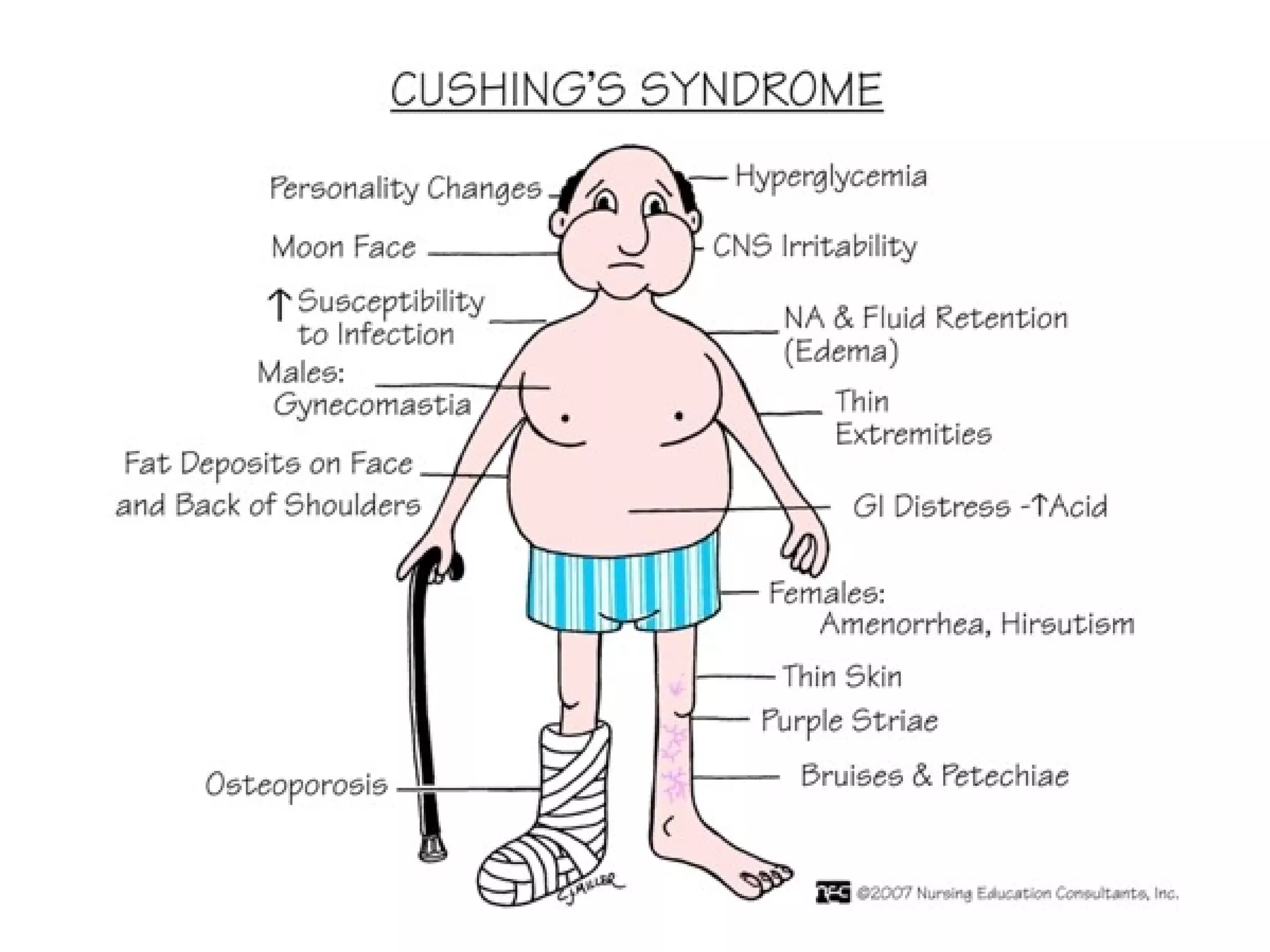
The document discusses corticosteroids, detailing their production from the adrenal cortex and medulla, and their physiological regulation via the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. It covers various physiological and pharmacological effects, therapeutic uses, side effects, and contraindications associated with corticosteroids, along with their classification into natural and synthetic forms. The document also highlights their application in treating conditions like Addison's disease, Cushing's syndrome, and various inflammatory and autoimmune disorders.