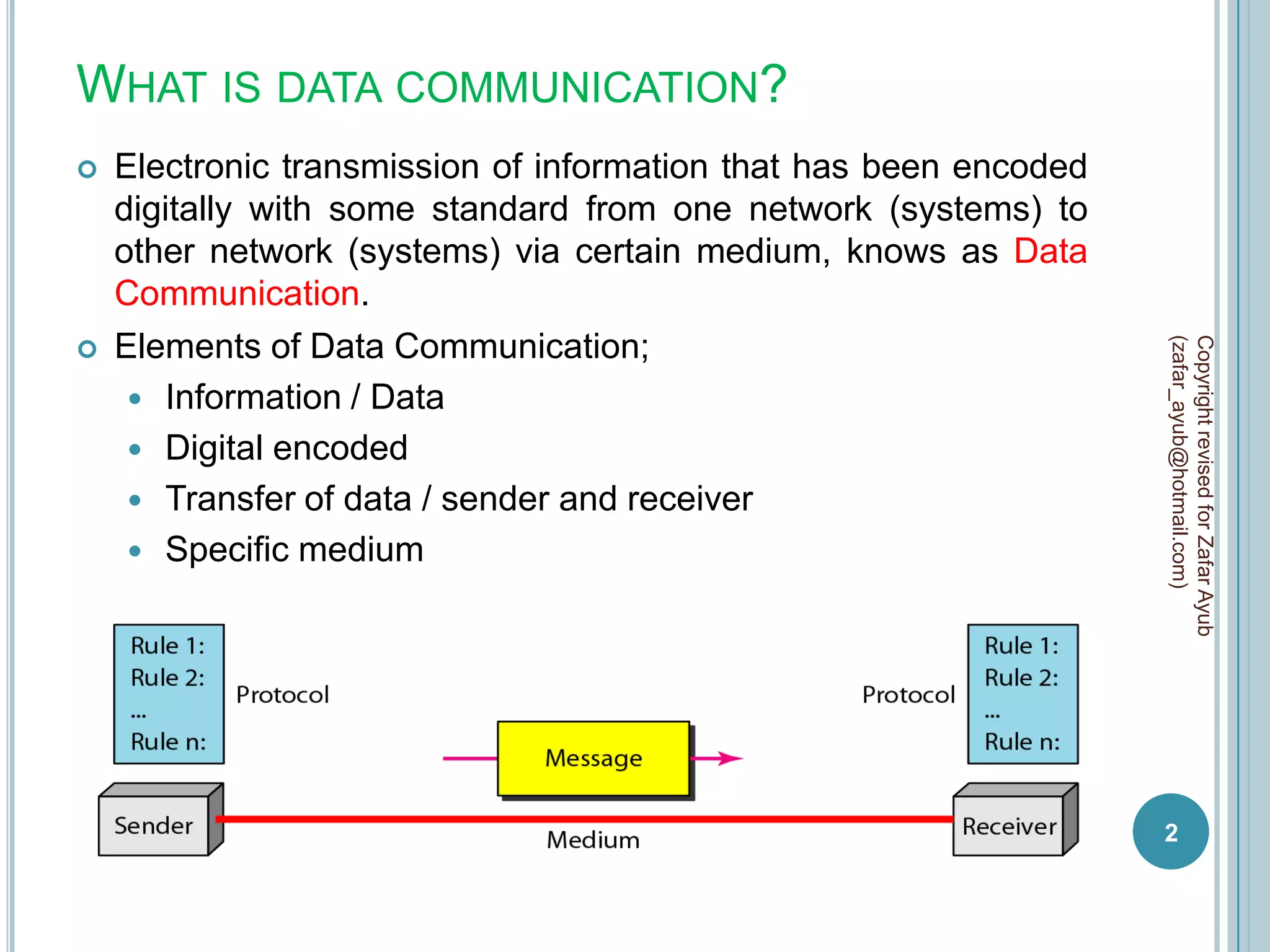
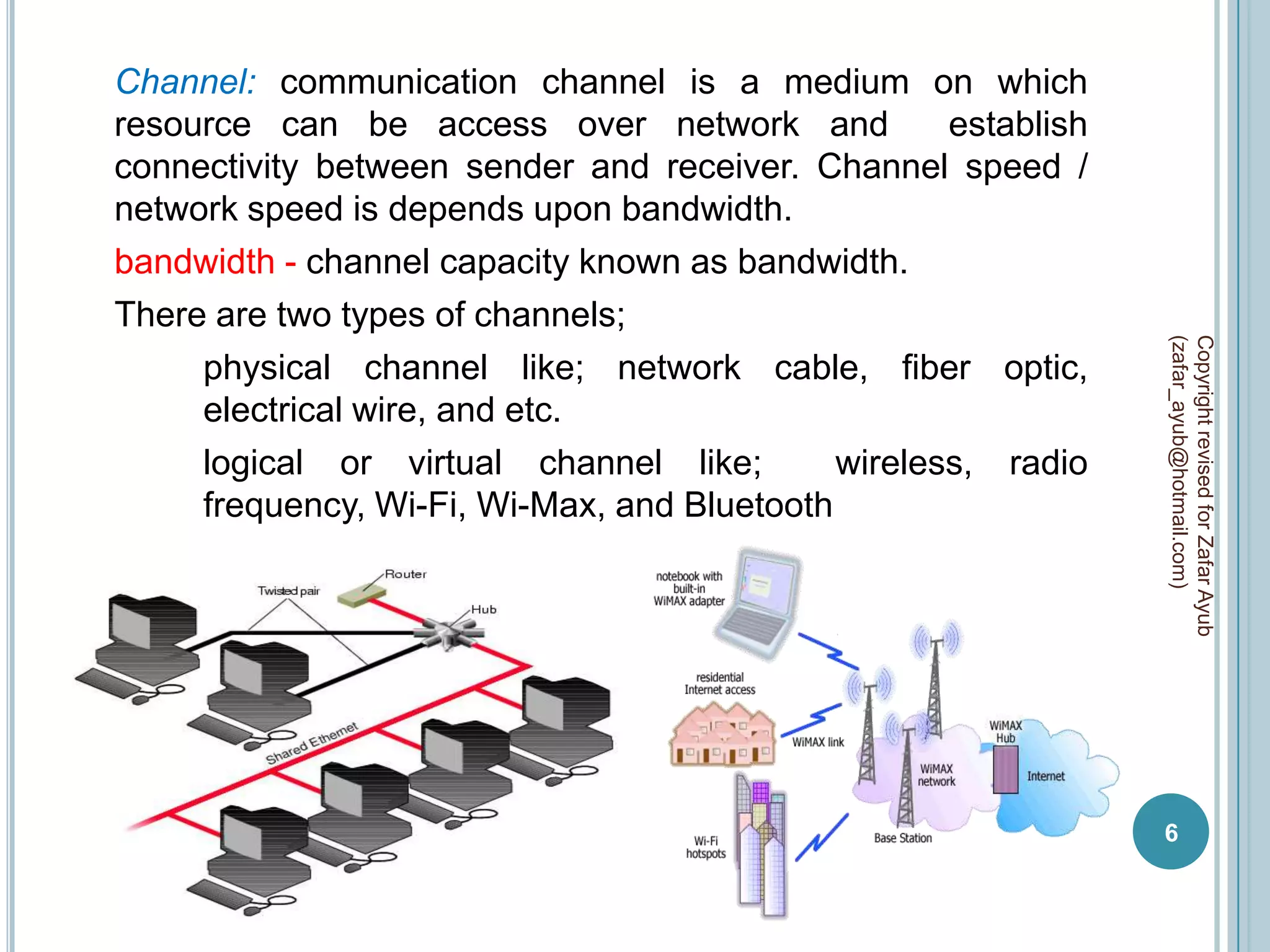
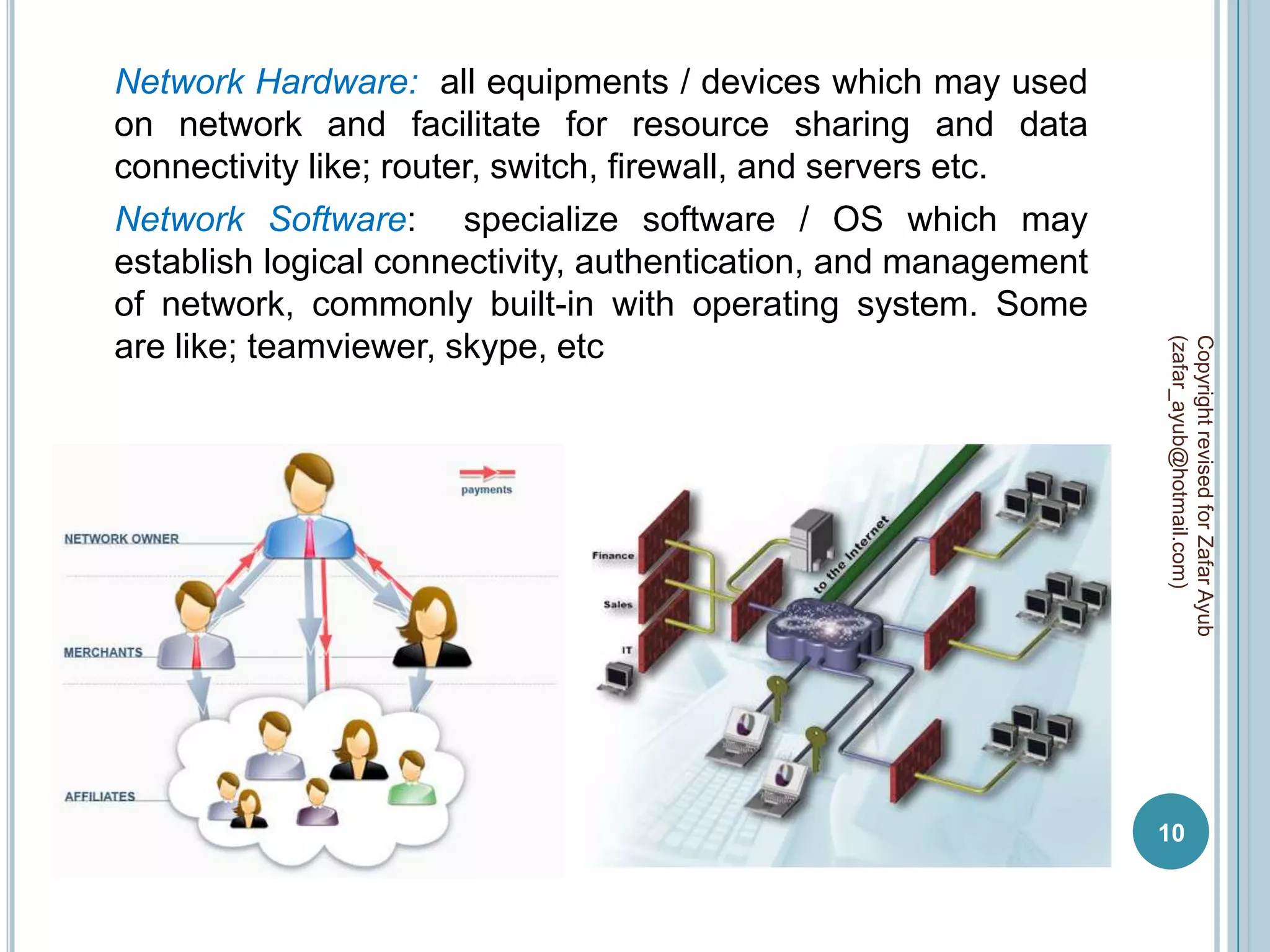
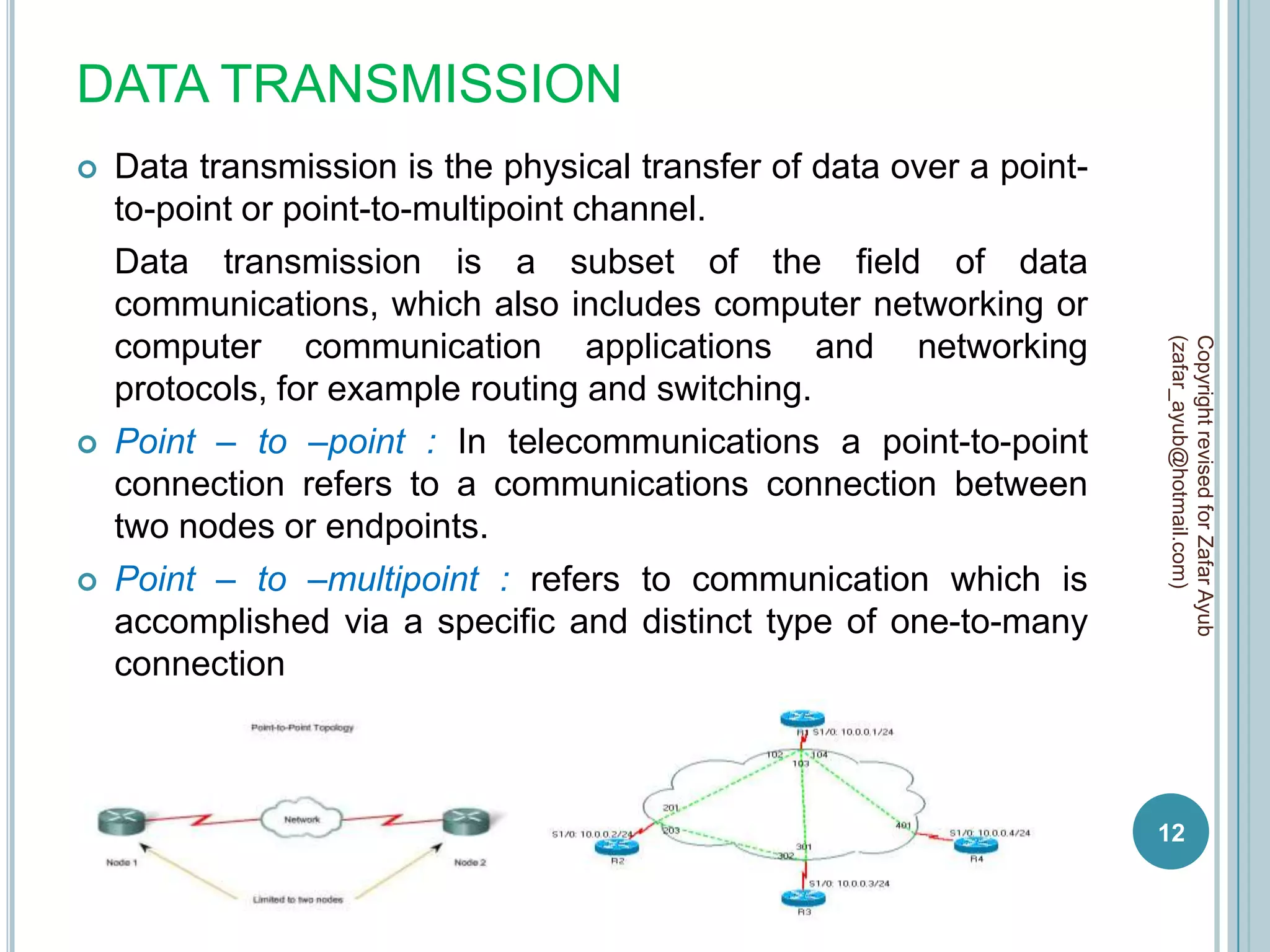
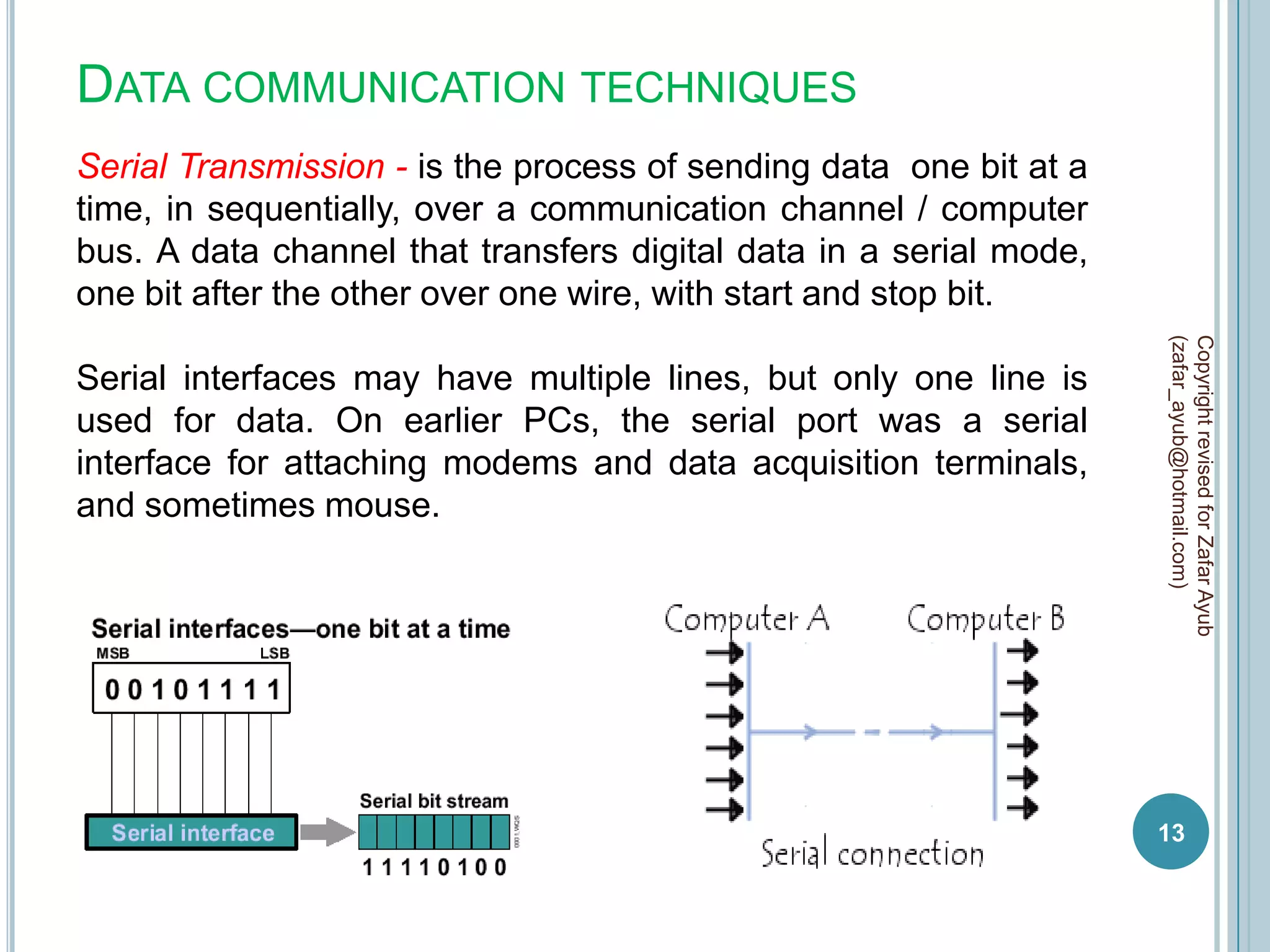
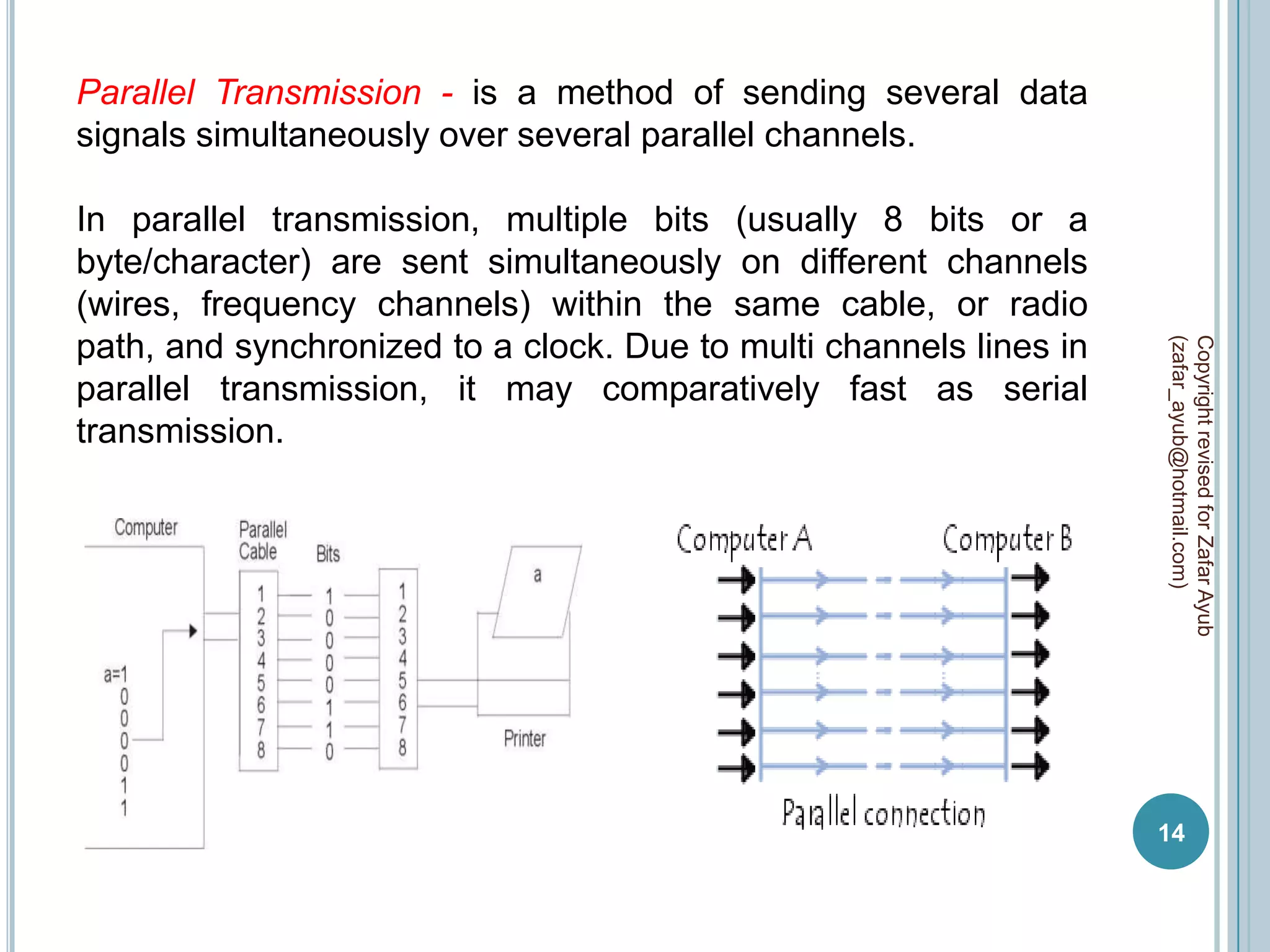
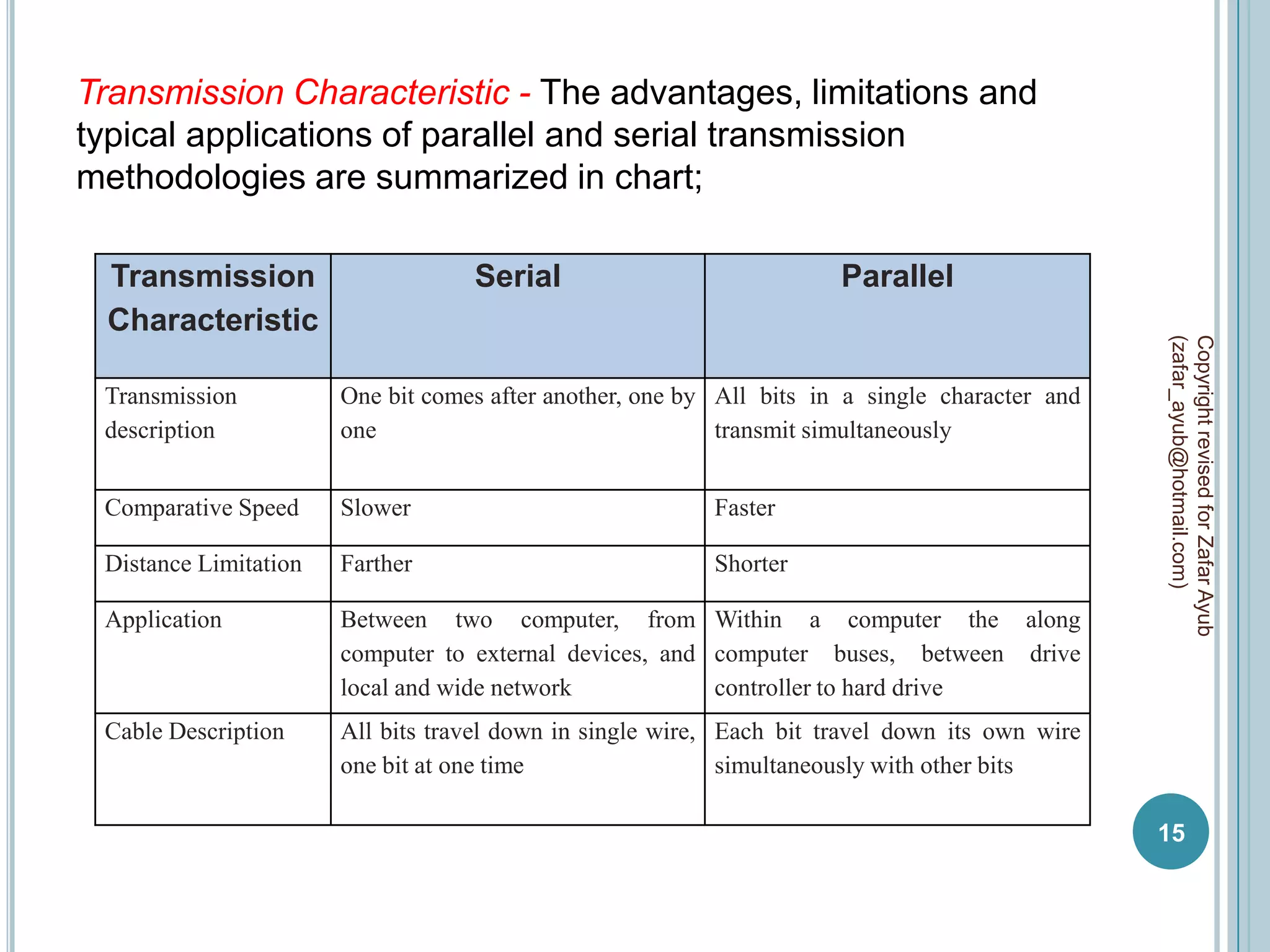
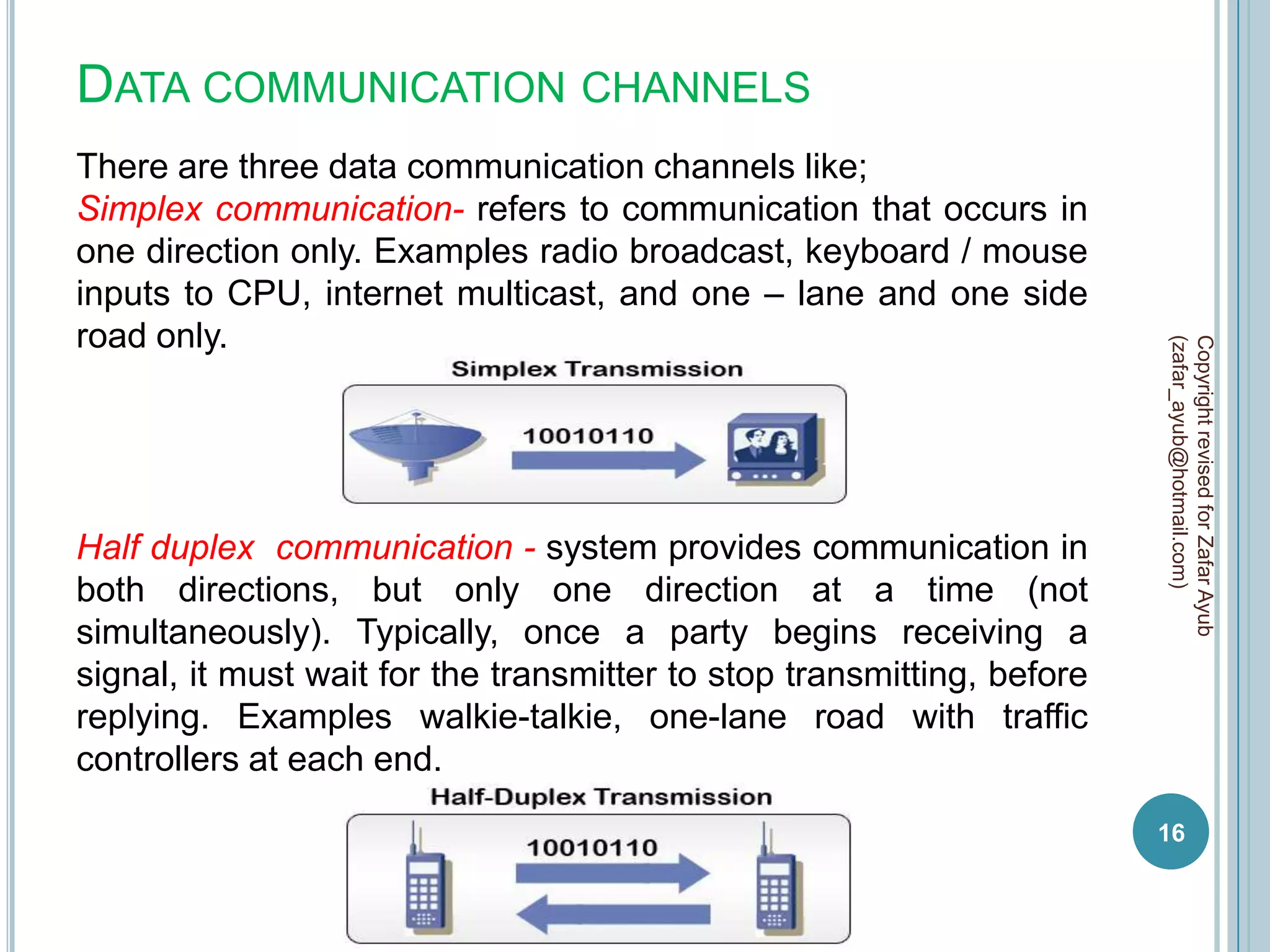
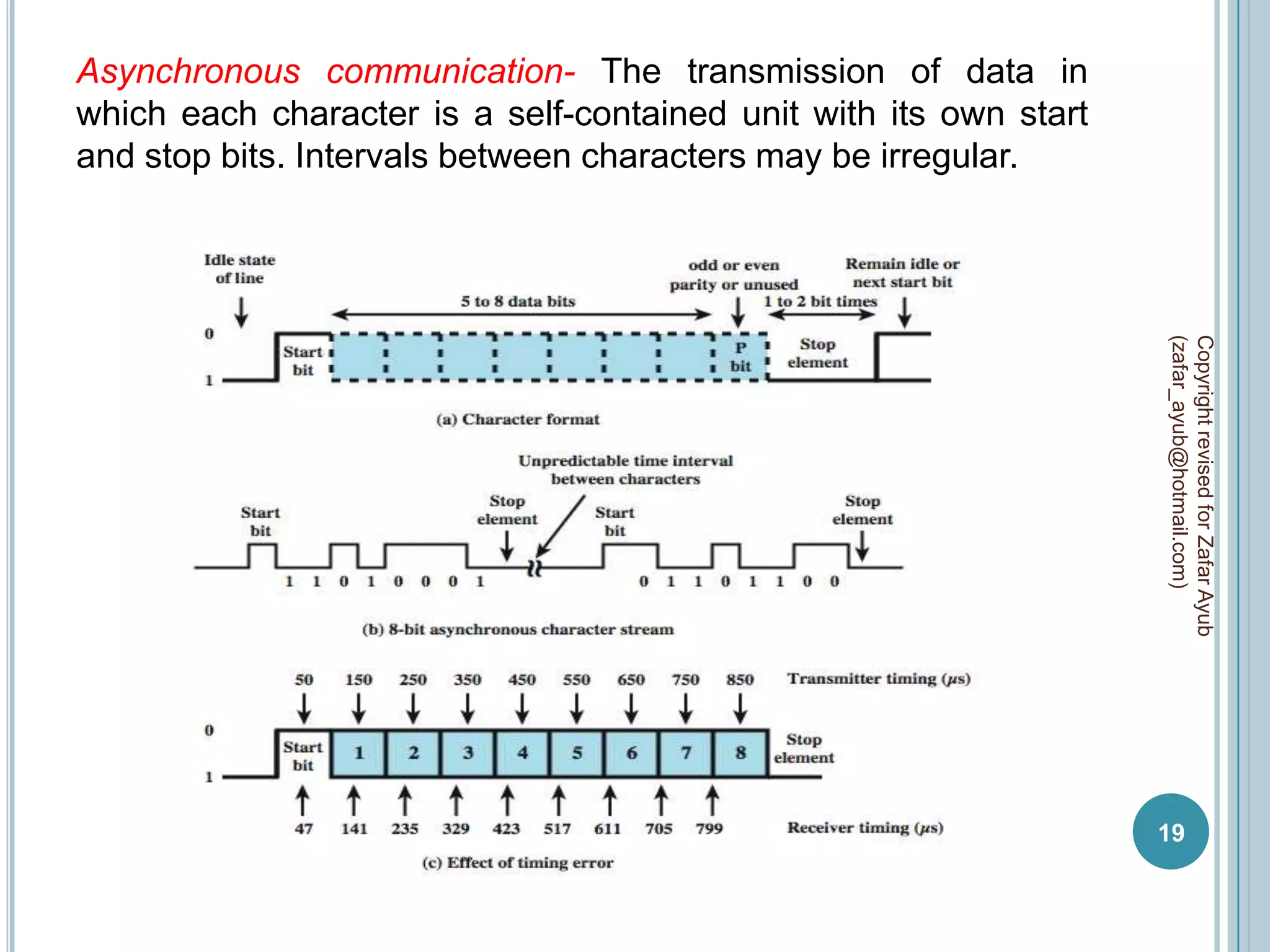
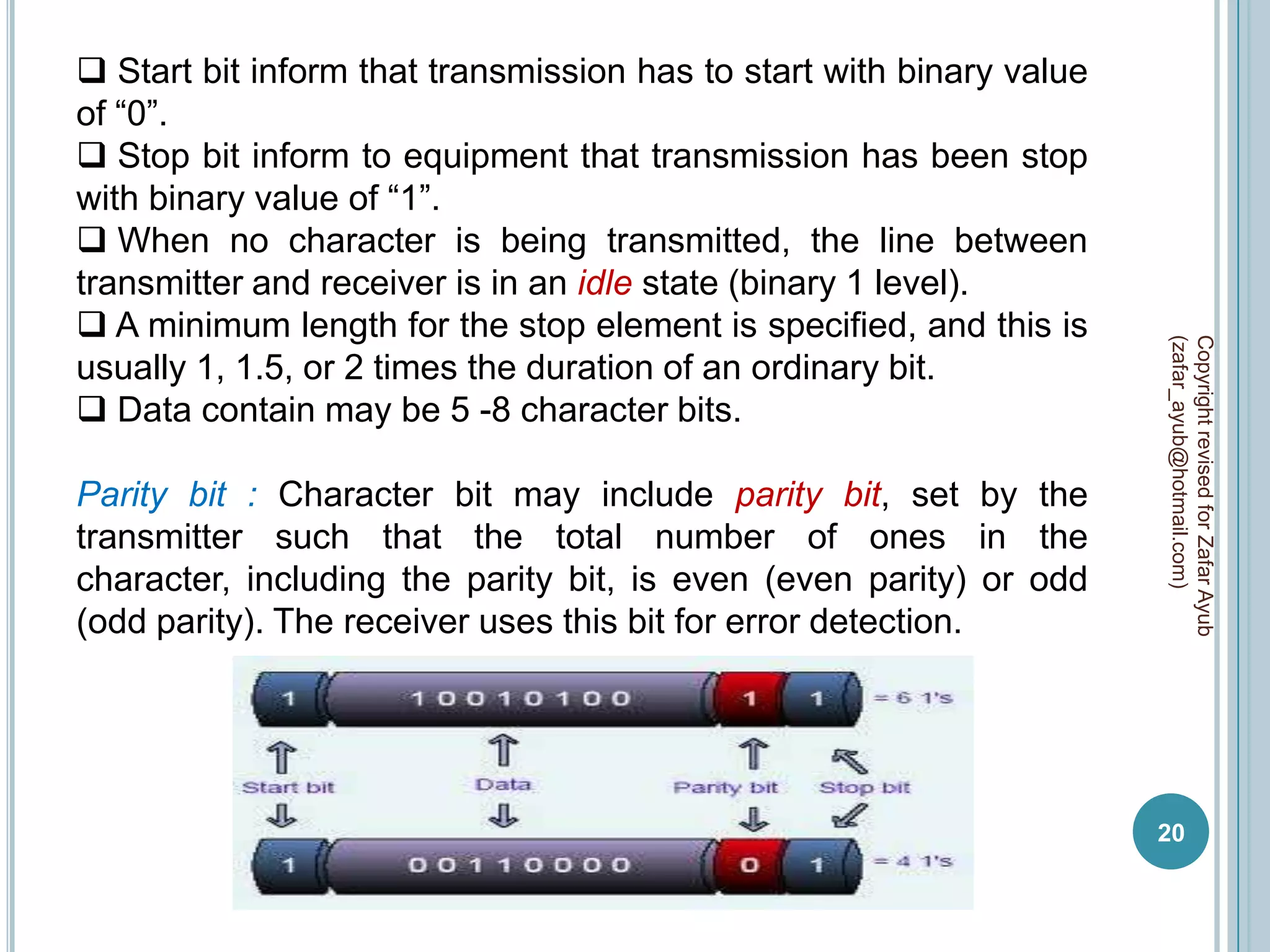
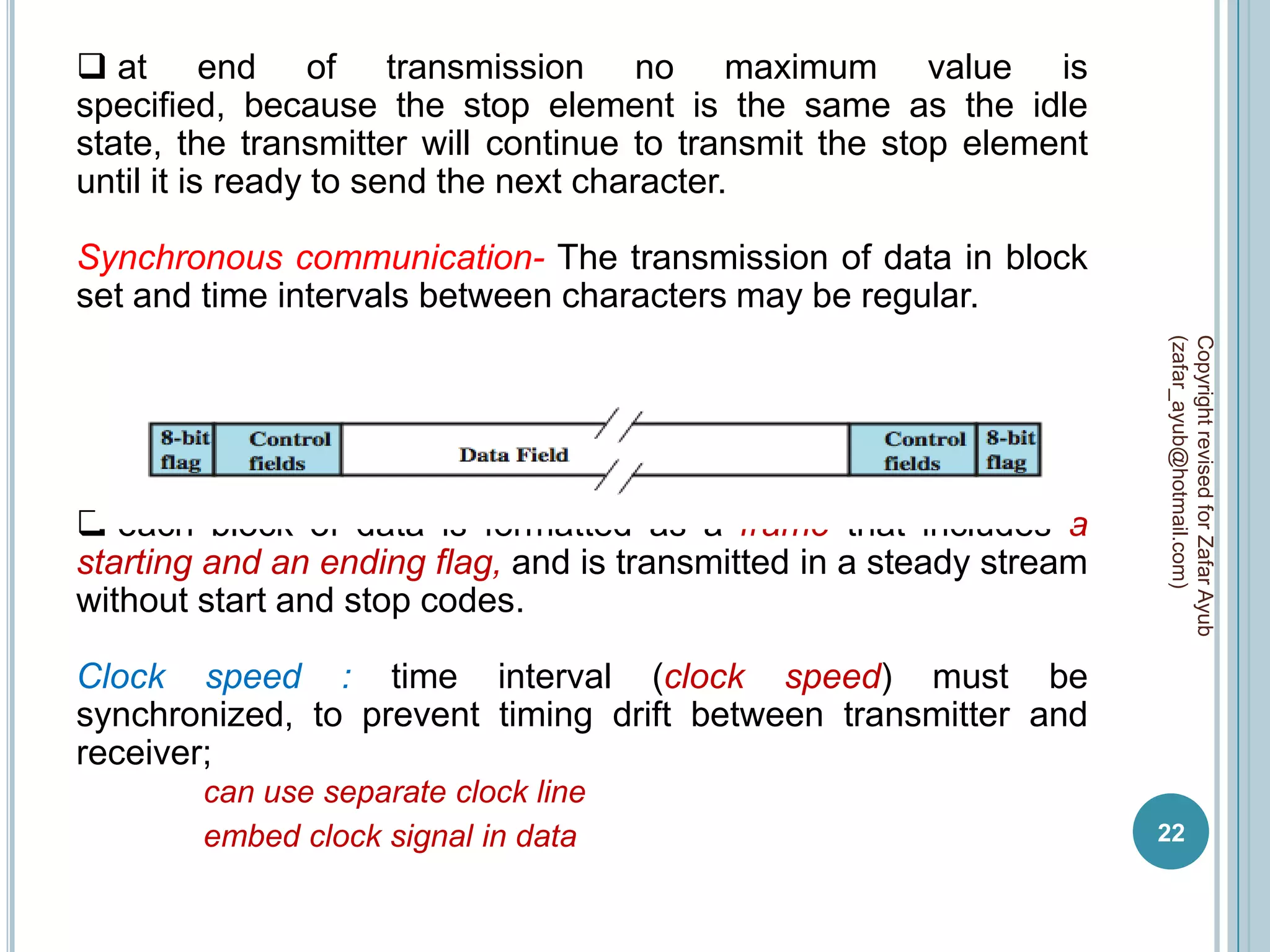
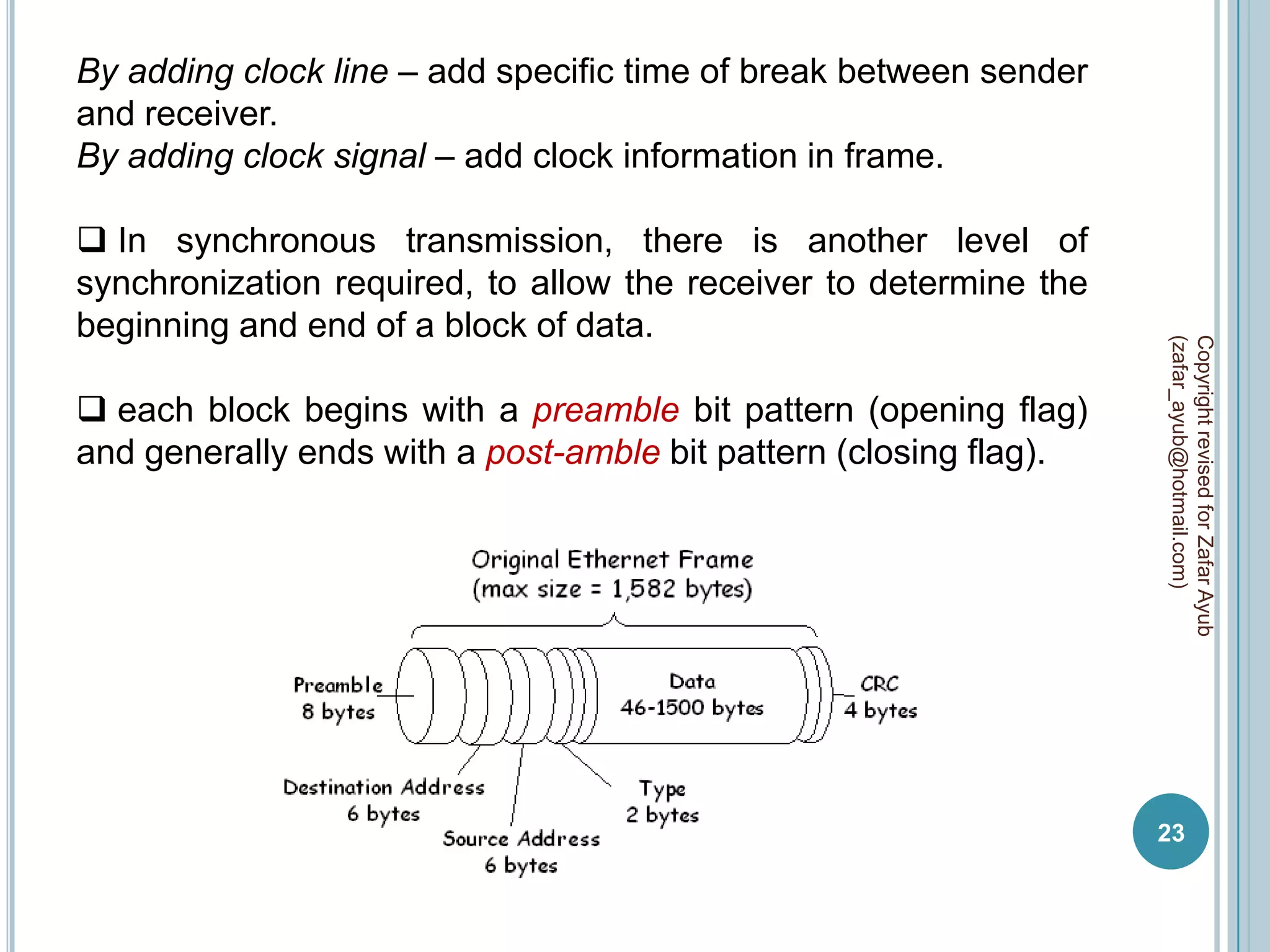
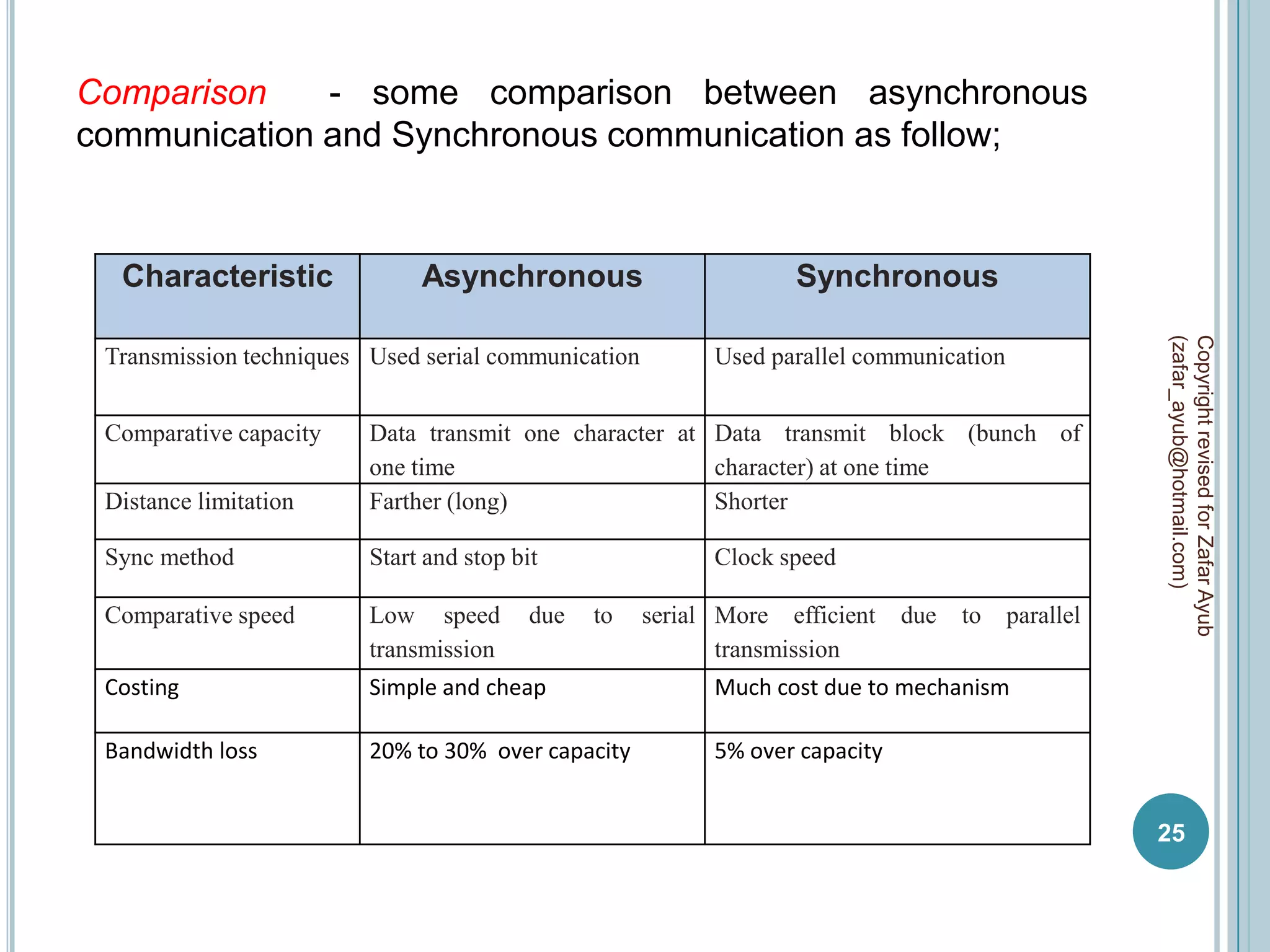
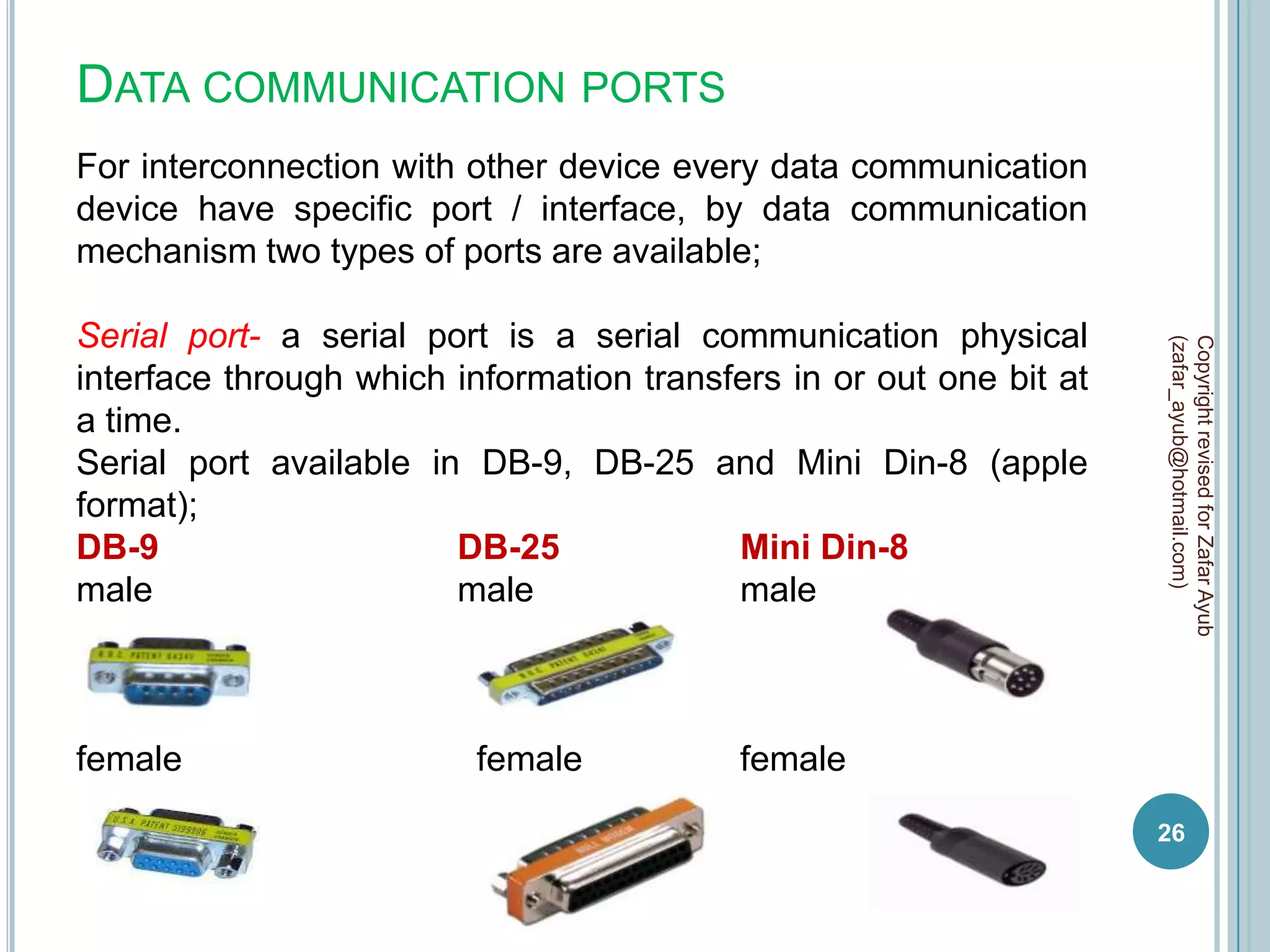
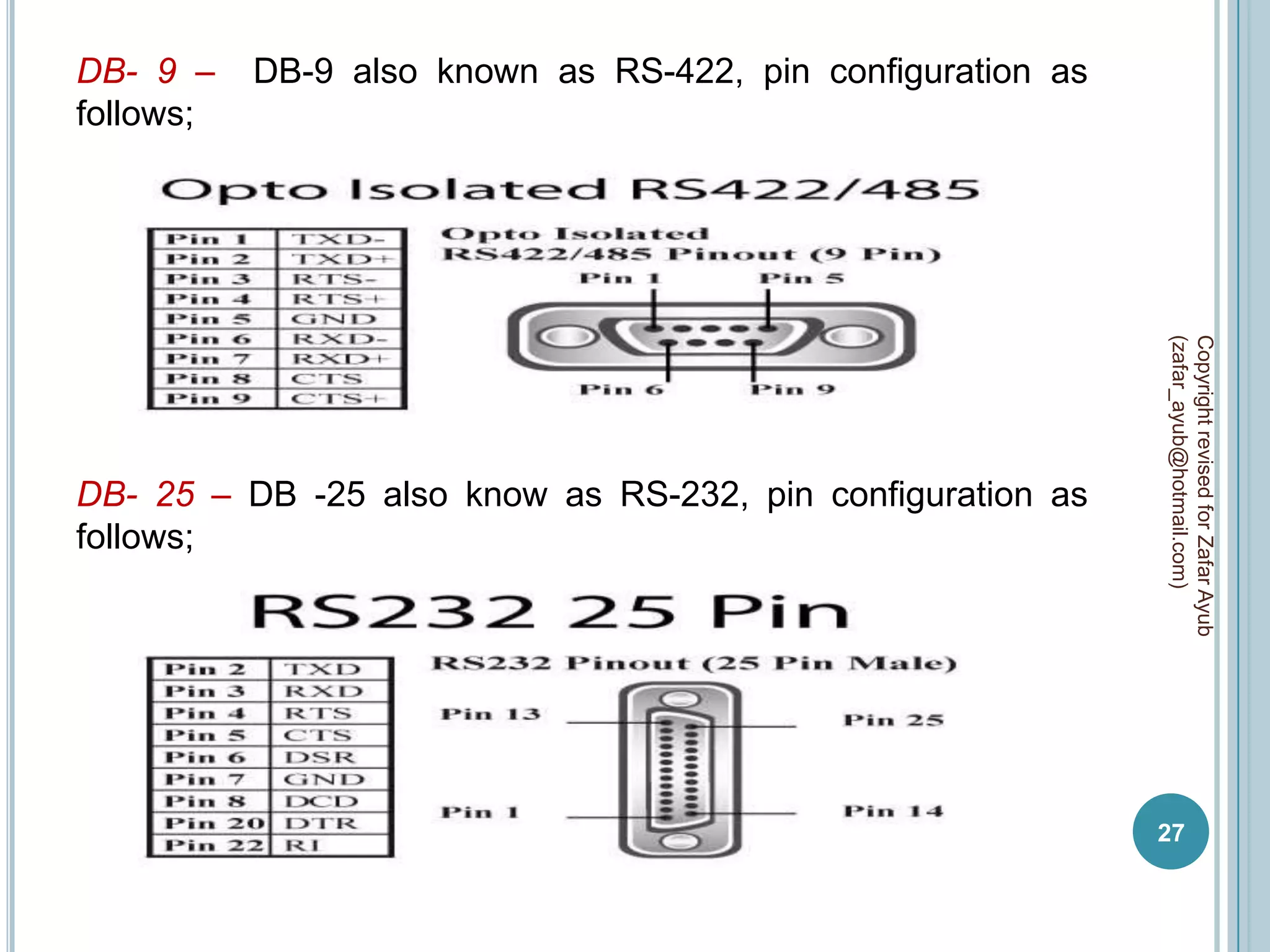
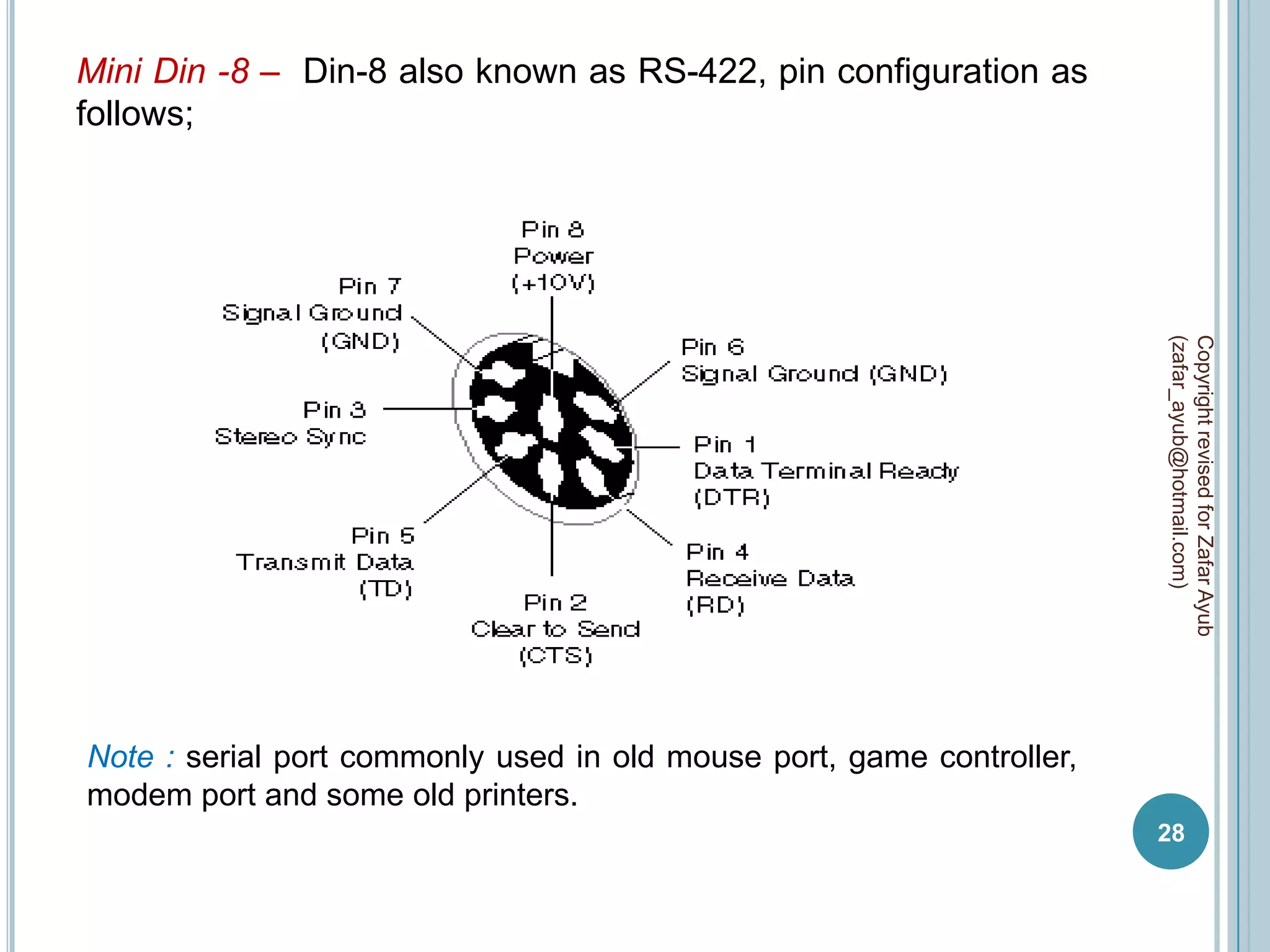
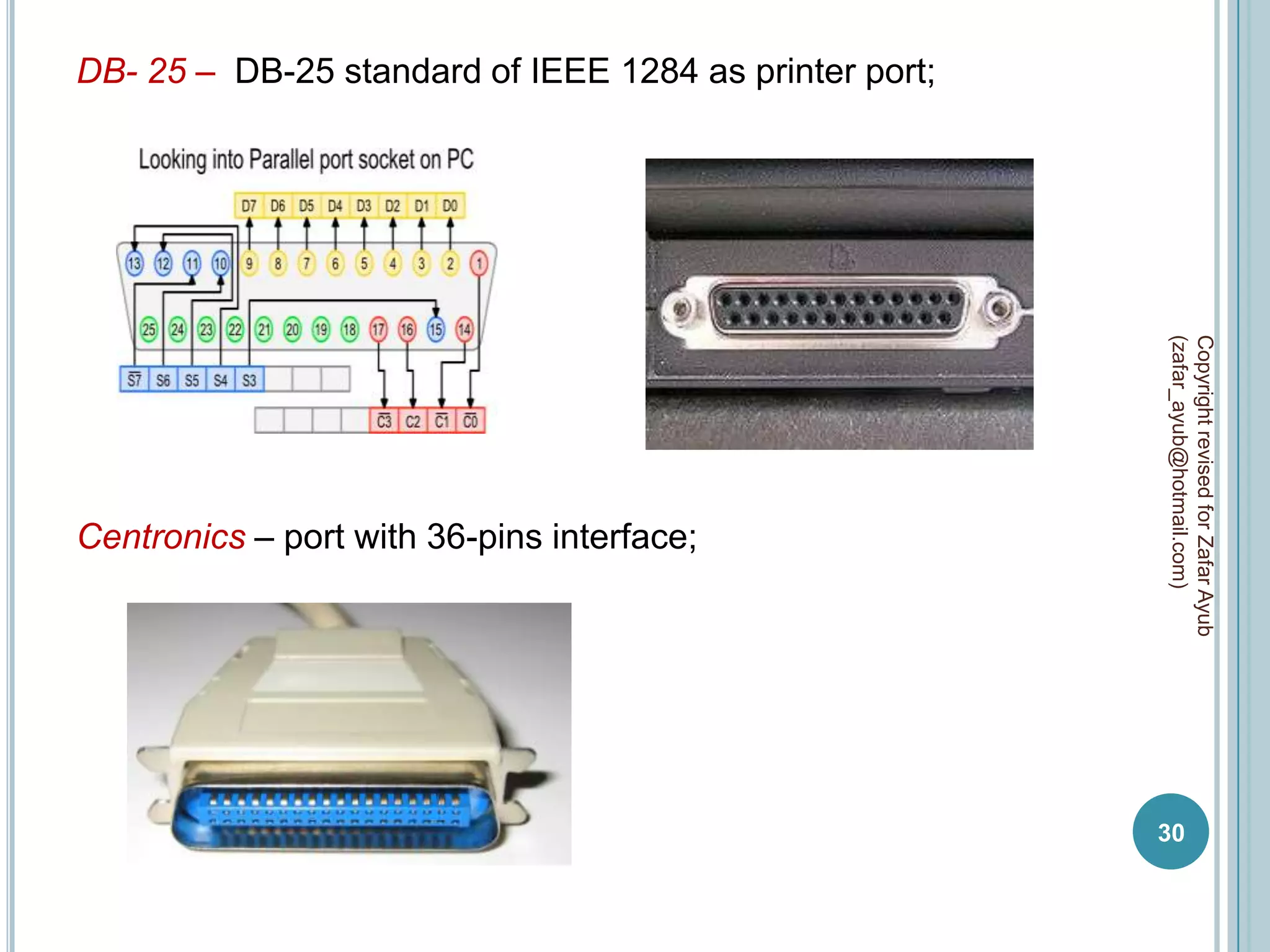
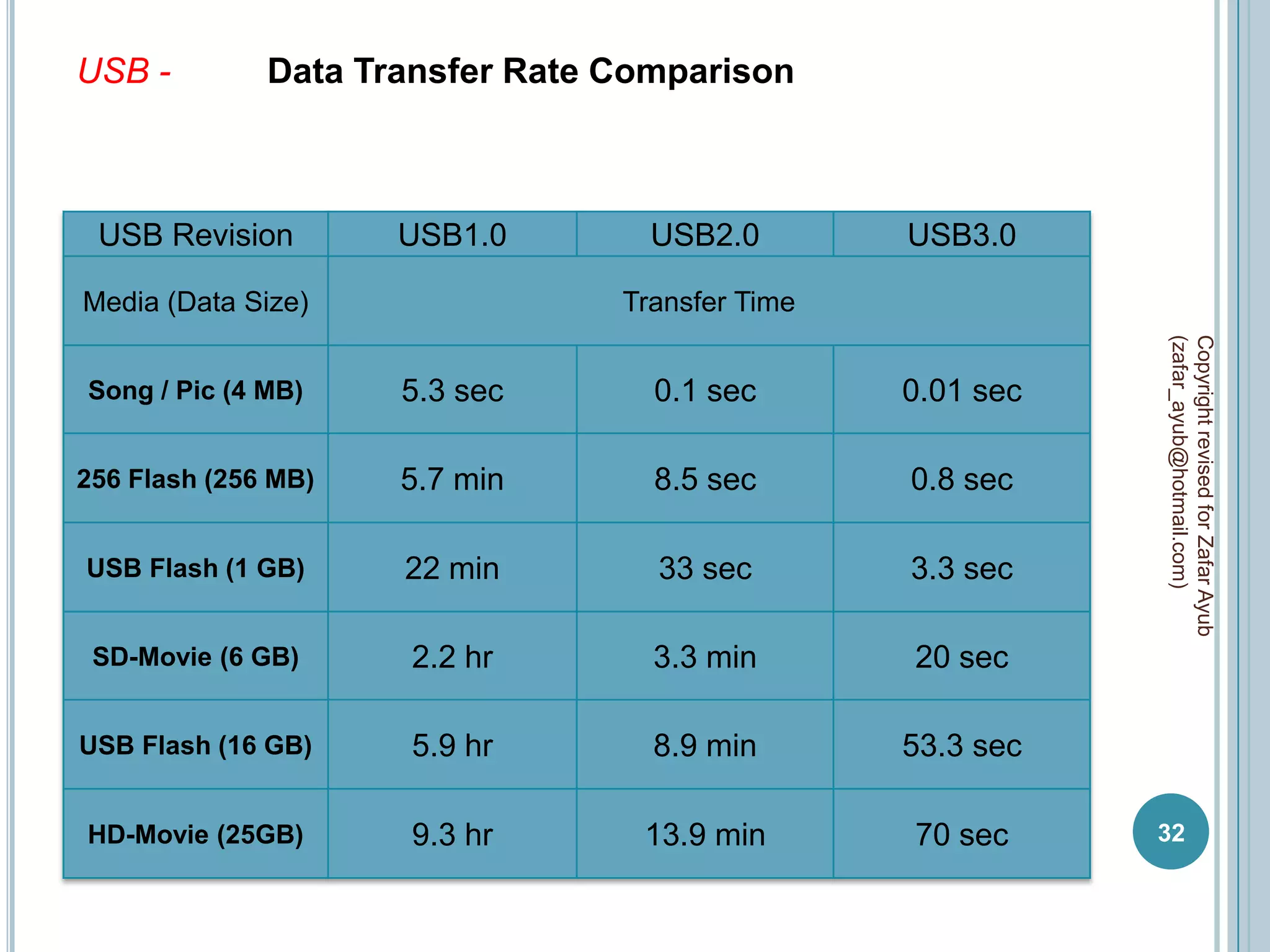
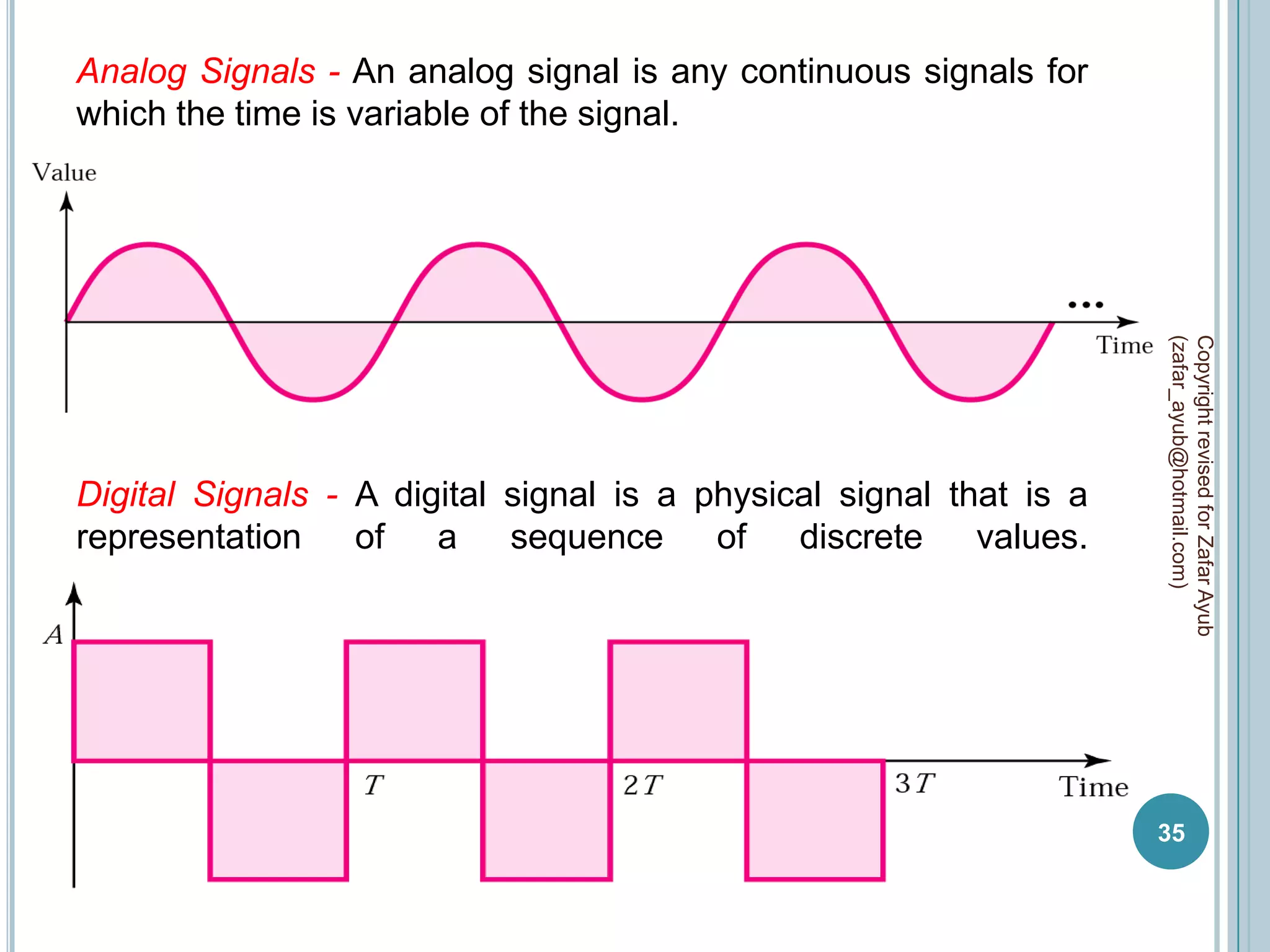
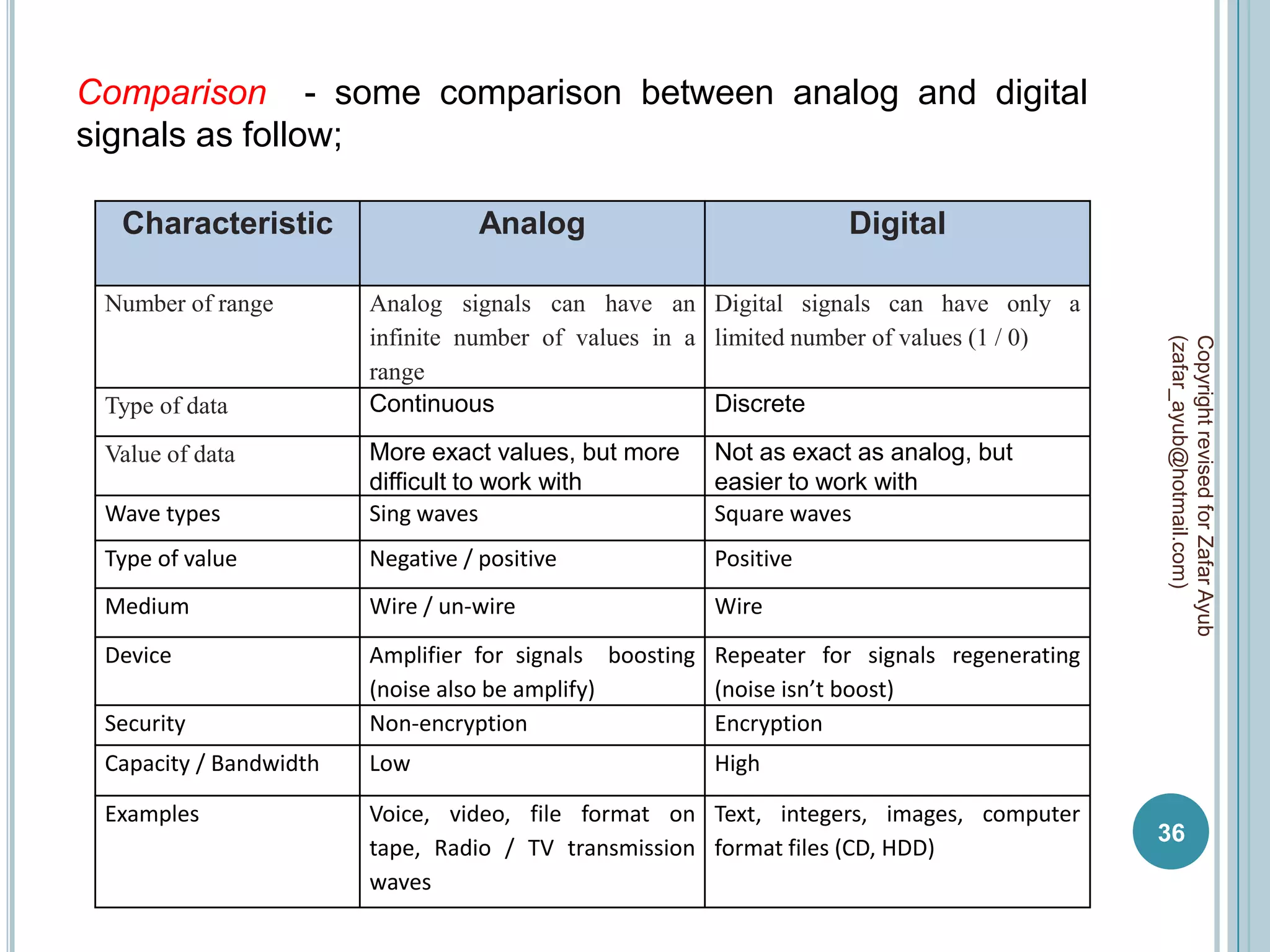
This document discusses data communication and networks. It defines data communication as the electronic transmission of digitally encoded information between networks via a medium. A network is defined as hardware, software, and protocols that allow sharing of resources and information according to set rules. The document also defines several key terms related to data communication and networks such as data, resources, channels, protocols, encryption, network hardware and software, senders, and receivers. It describes methods of data transmission including serial and parallel transmission.