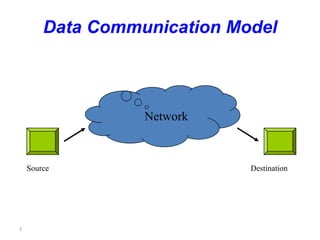
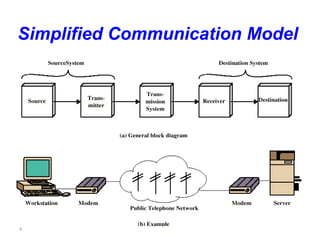
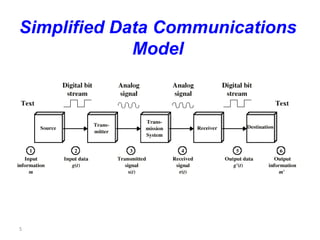
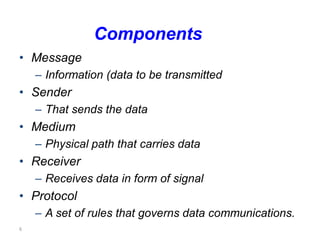
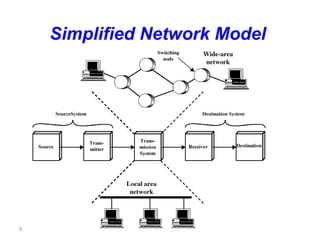
This document provides an introduction to computer networks. It defines data communication as the exchange of data between two devices via transmission medium. It presents a simplified data communication model including the message, sender, medium, receiver, and protocol. It explains that point-to-point communication is not practical for distant or large sets of devices, so a communications network is used instead. Networks allow for better connectivity, communication, sharing of resources, and overcome geographic limits to access remote data with the goal of universal communication between any devices. Networks can also be classified based on transmission media, size, management method, and topology.