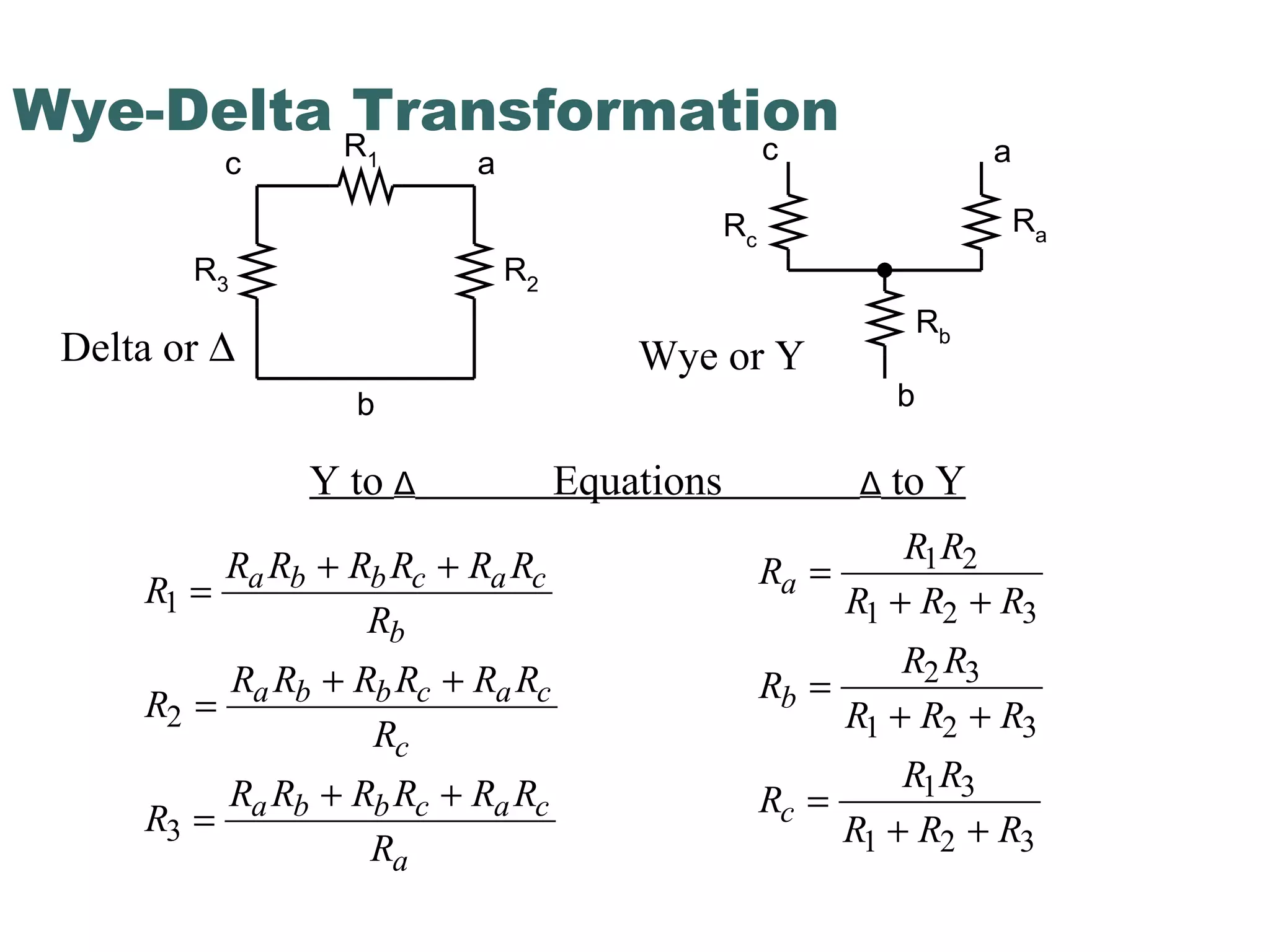
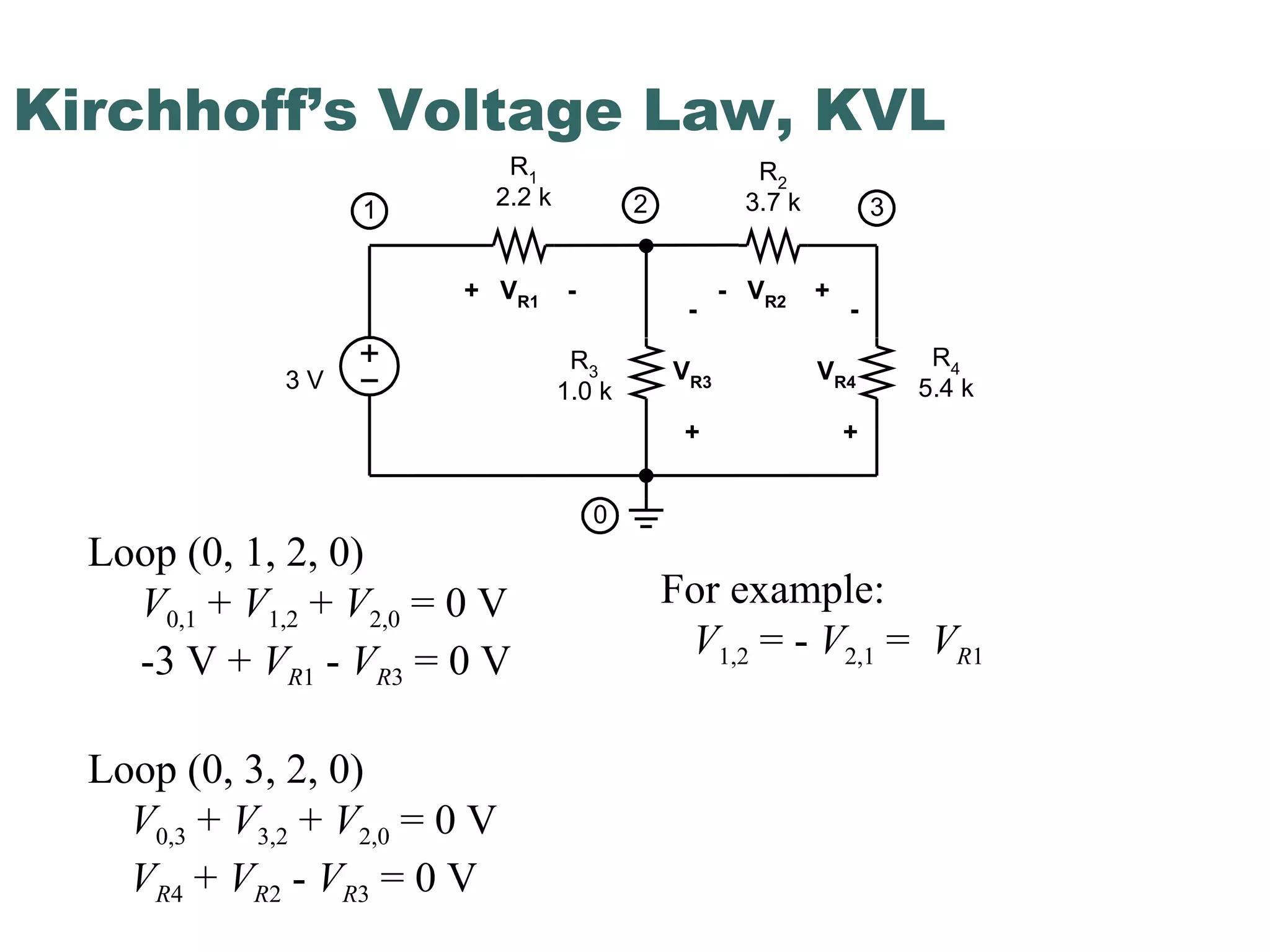
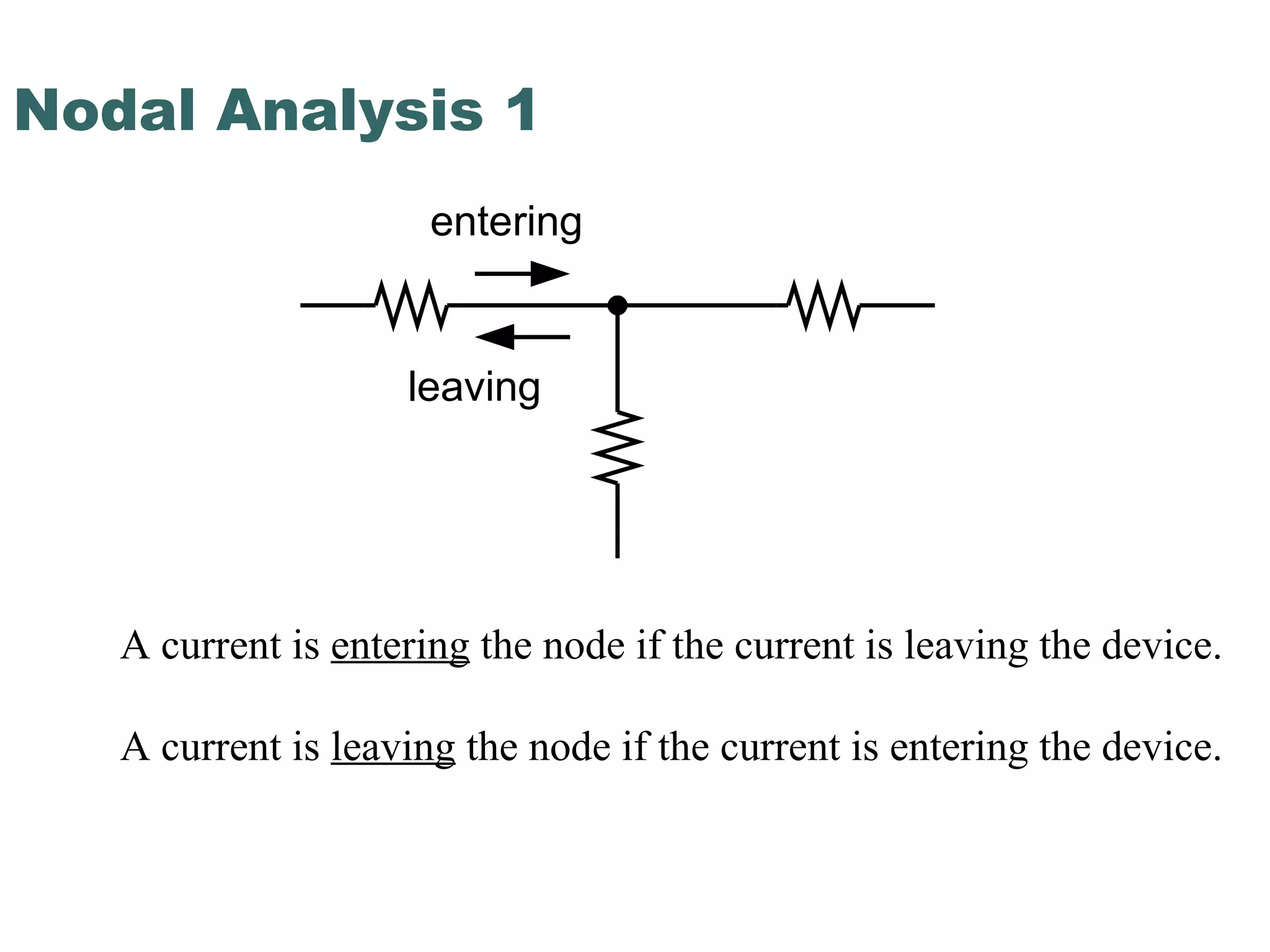
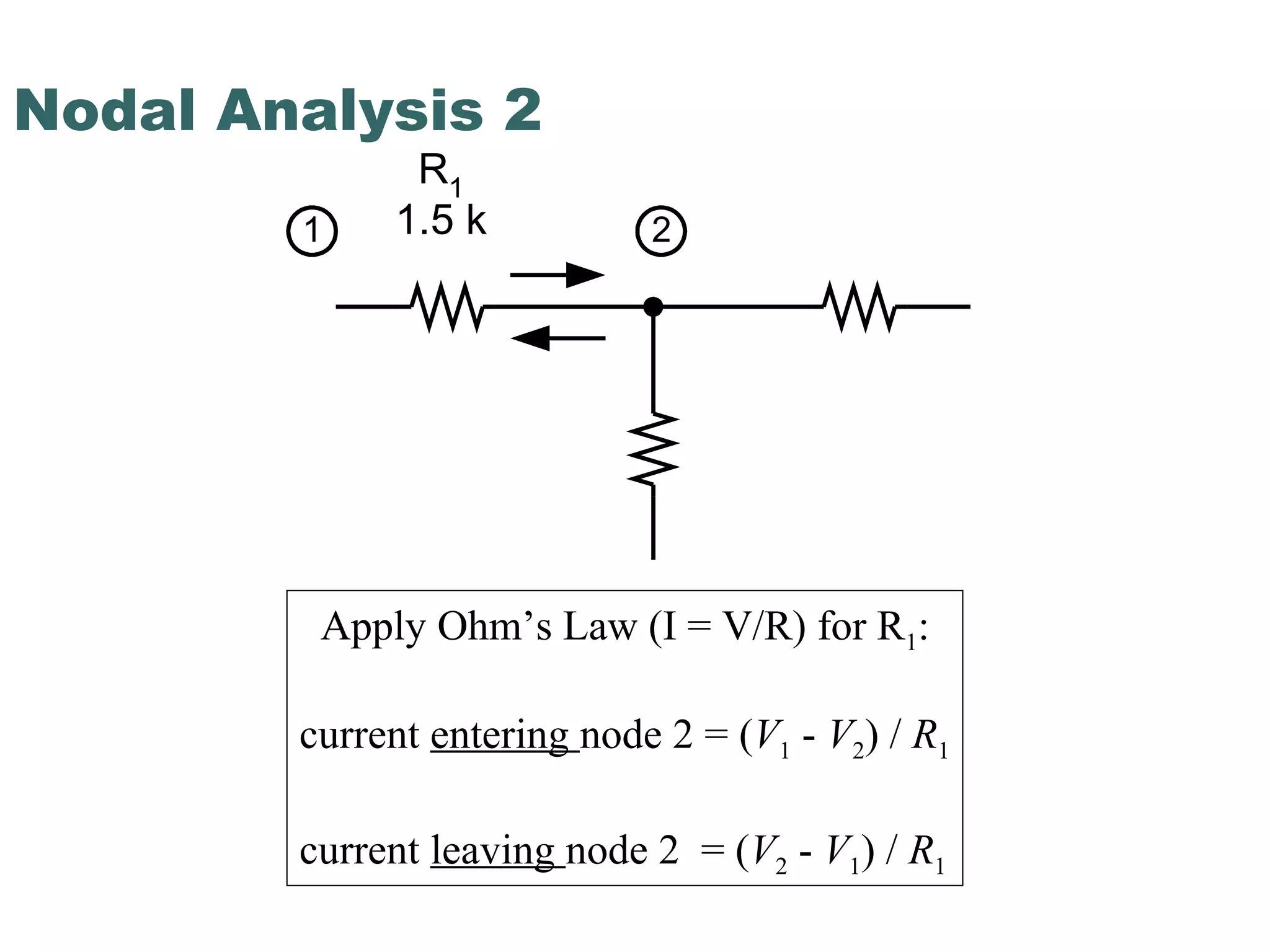
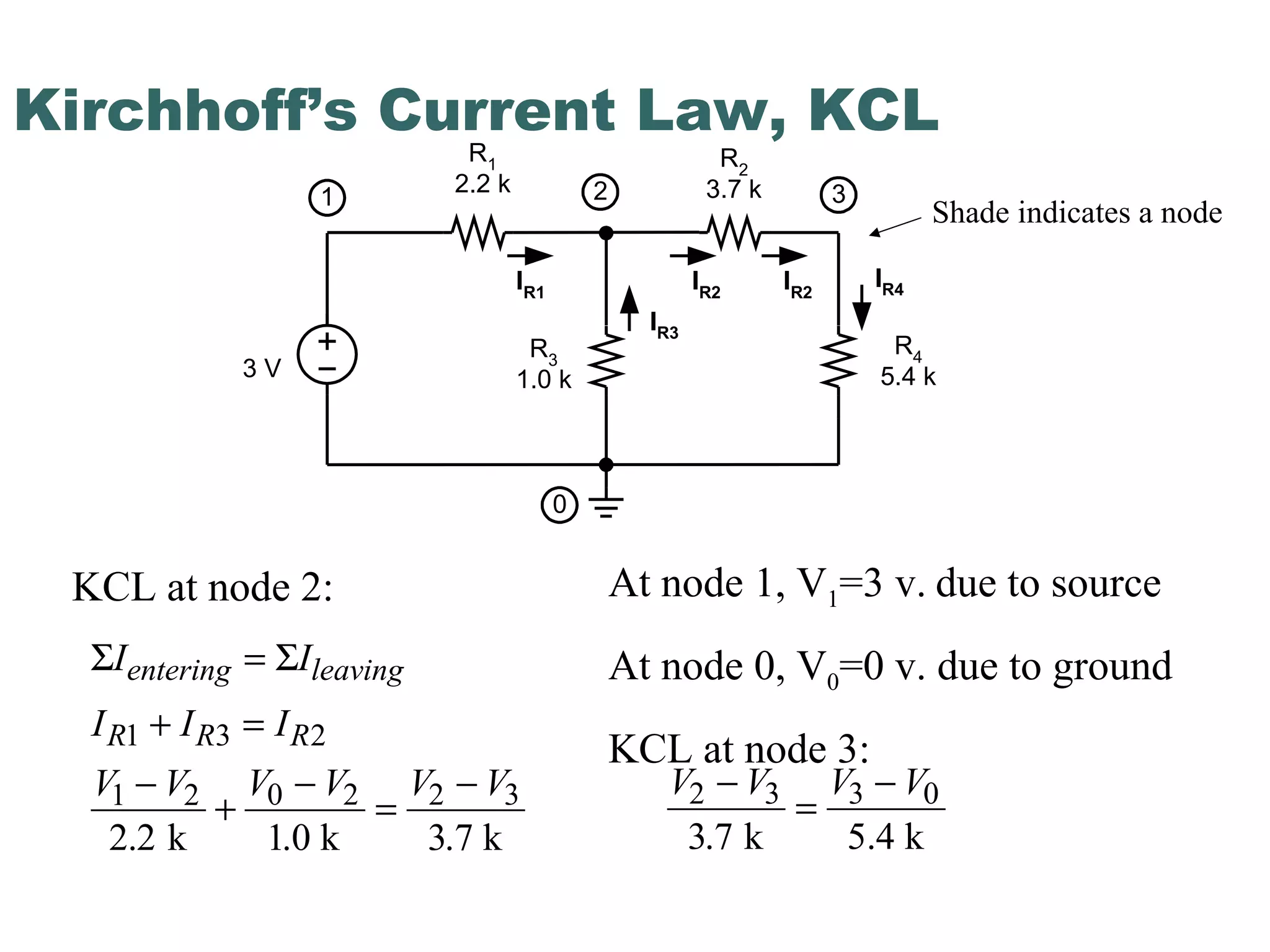
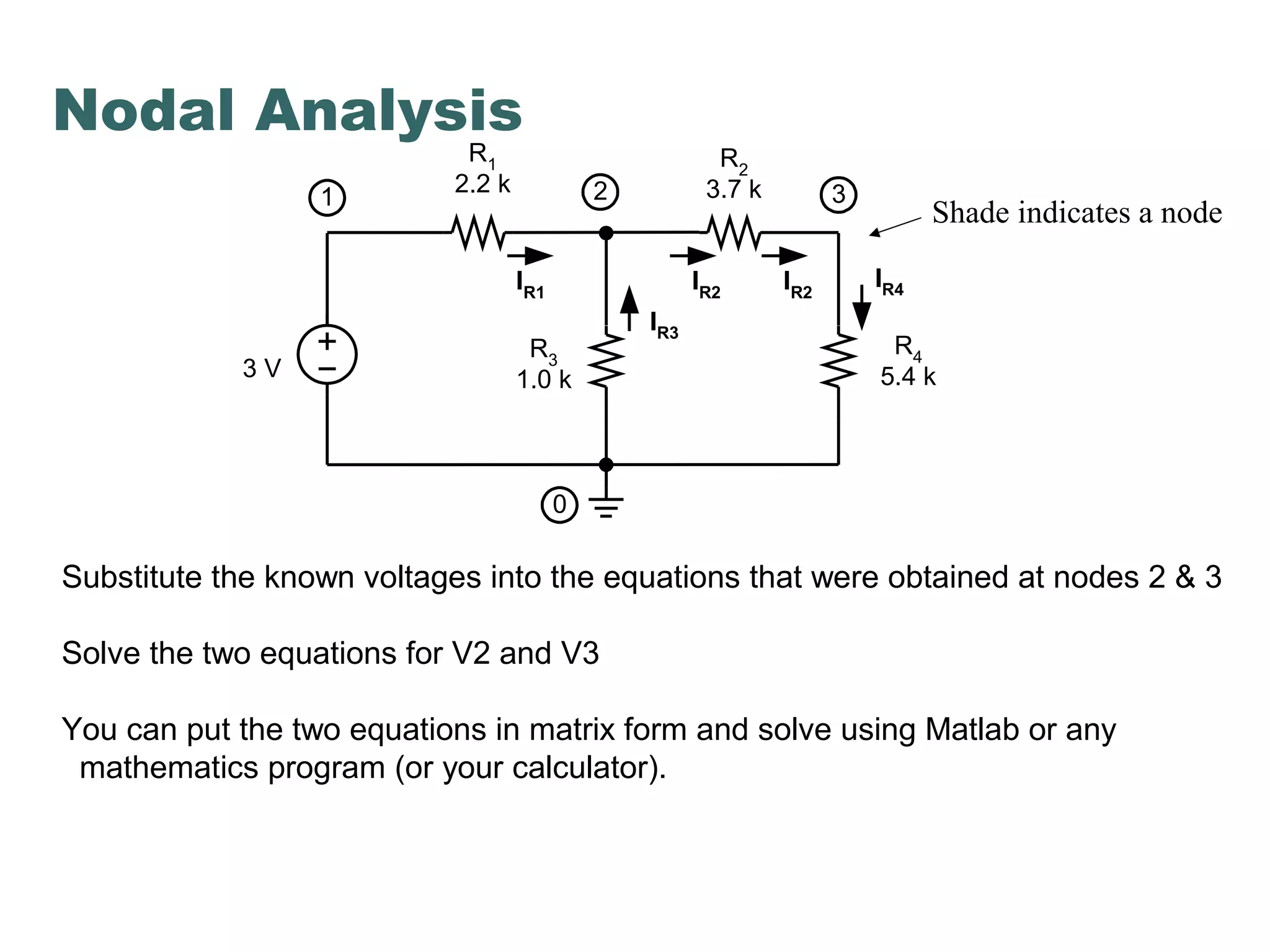
This document discusses nodal analysis, a technique for analyzing electrical circuits where the voltages at different nodes of the circuit are calculated. It provides examples of applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) to set up equations relating the currents and voltages in a circuit containing resistors connected in a mesh. The document explains how to use these equations to solve for the unknown voltages at each node of the circuit.