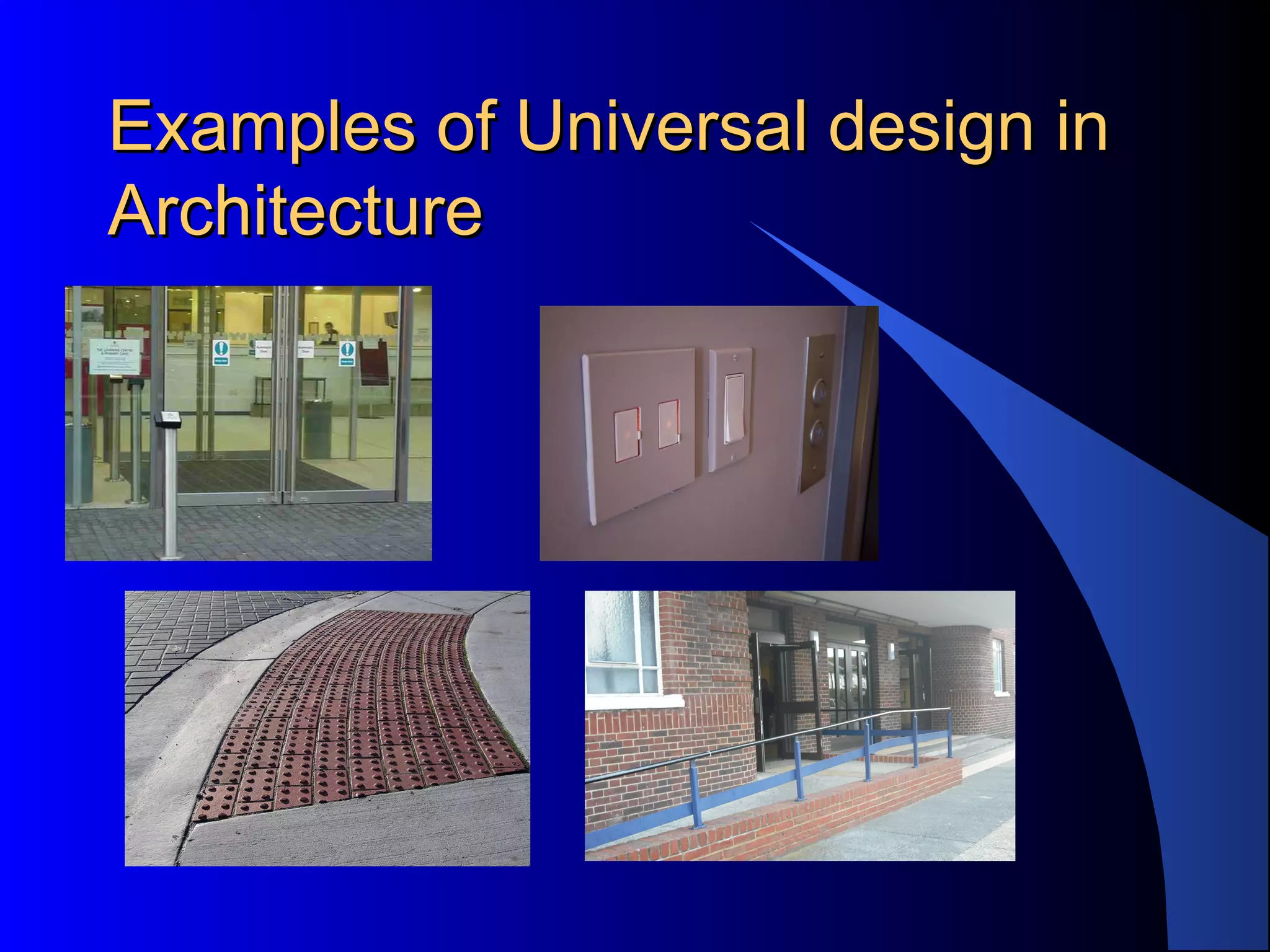
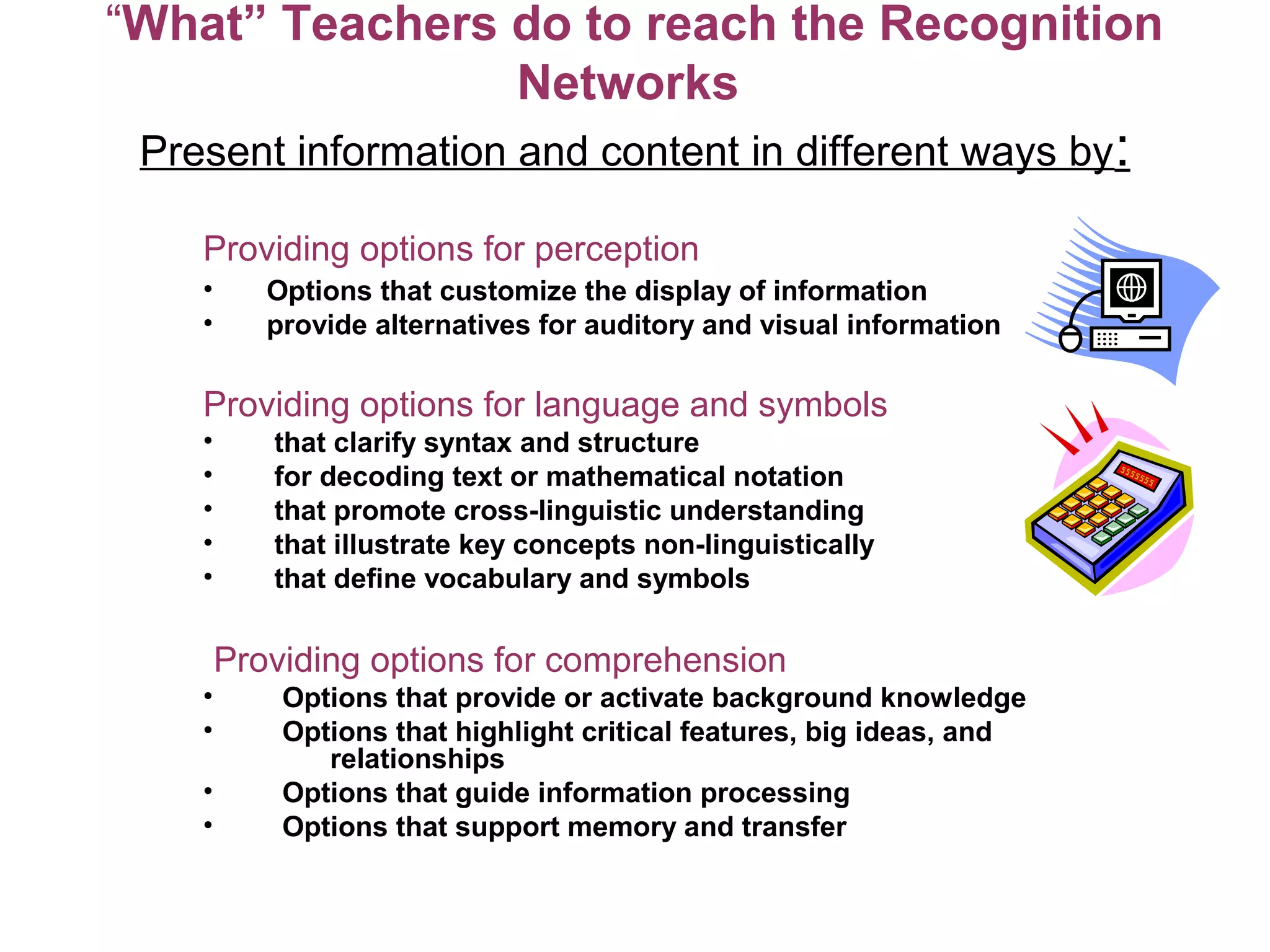
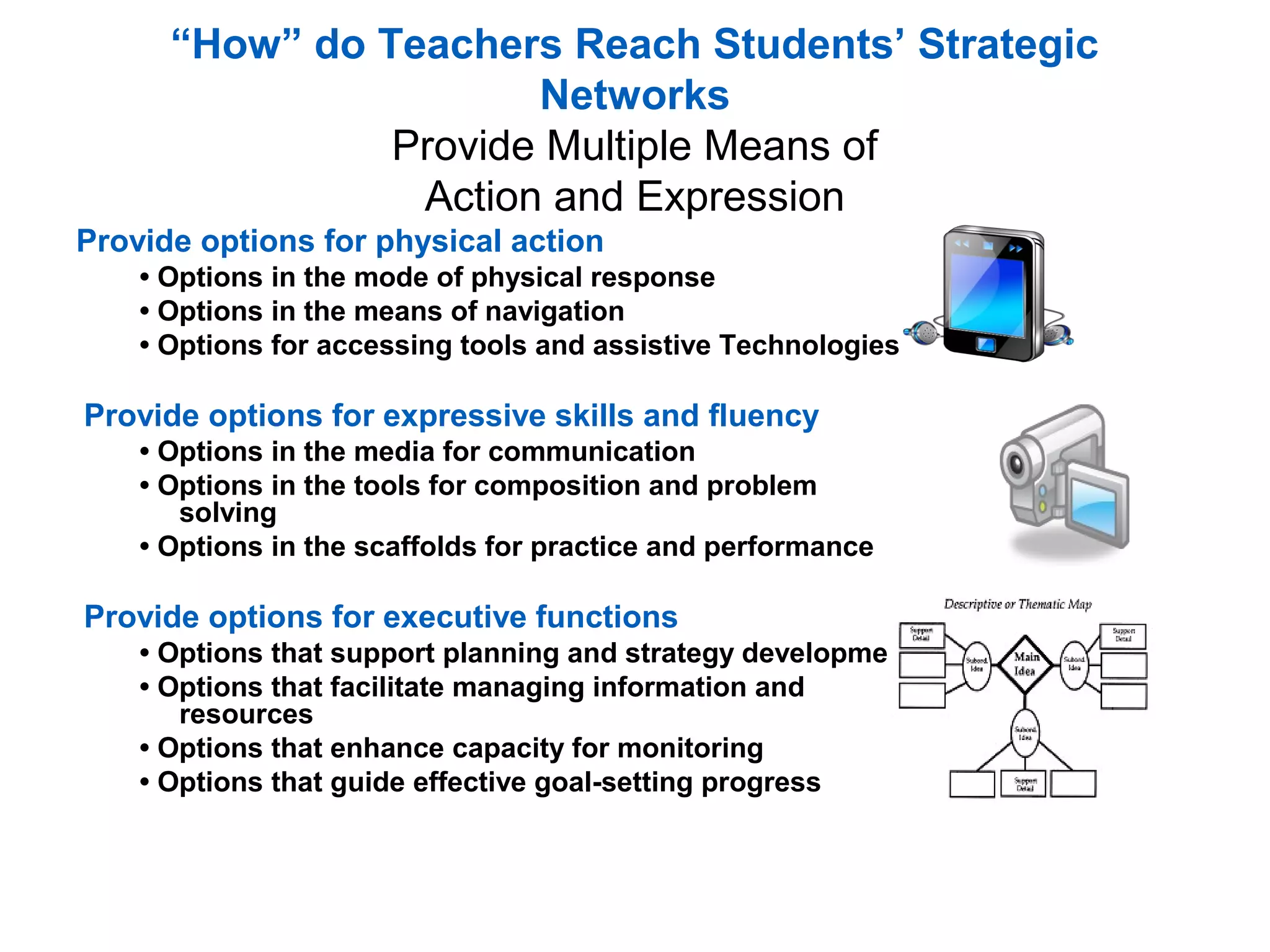
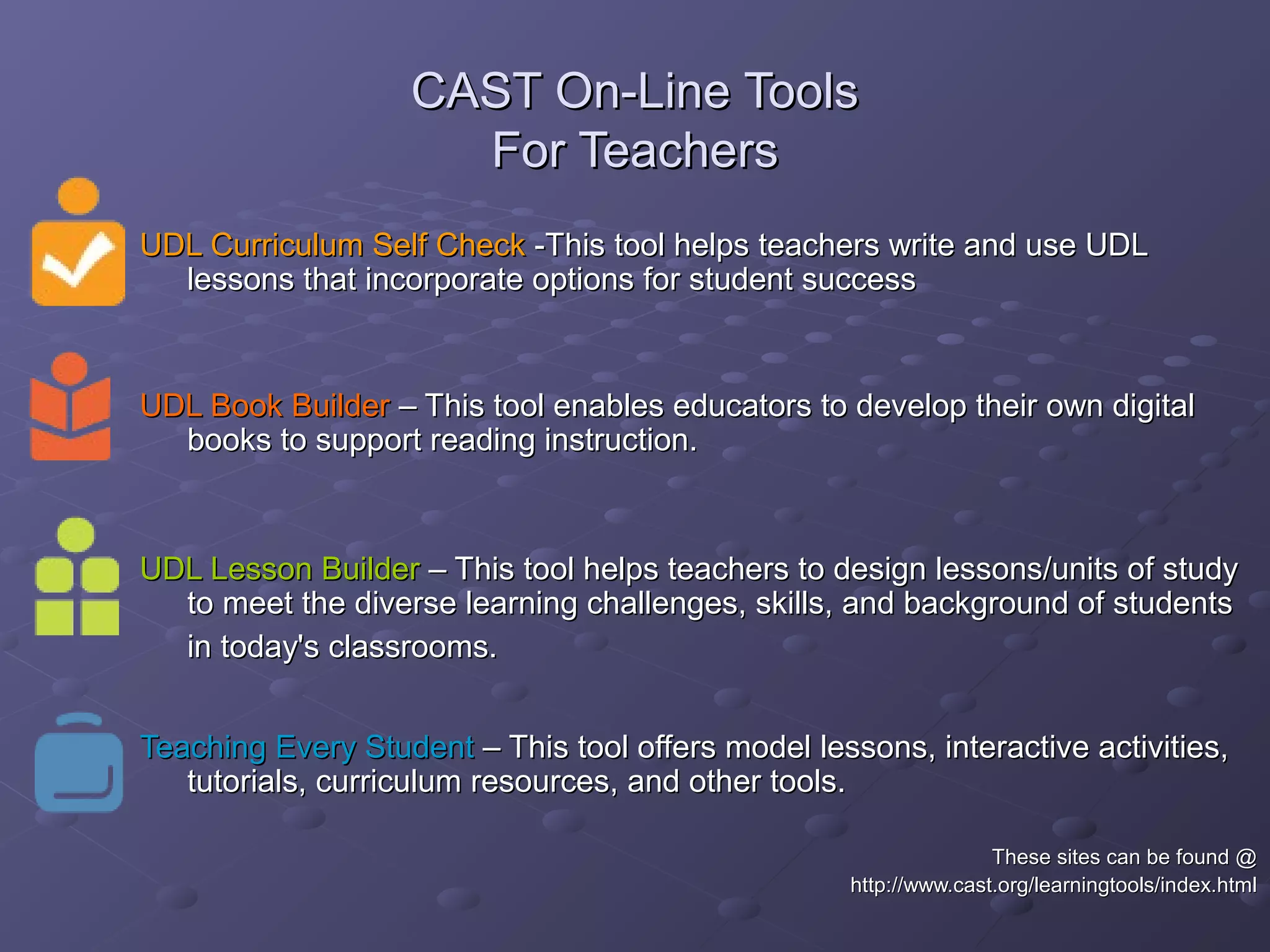
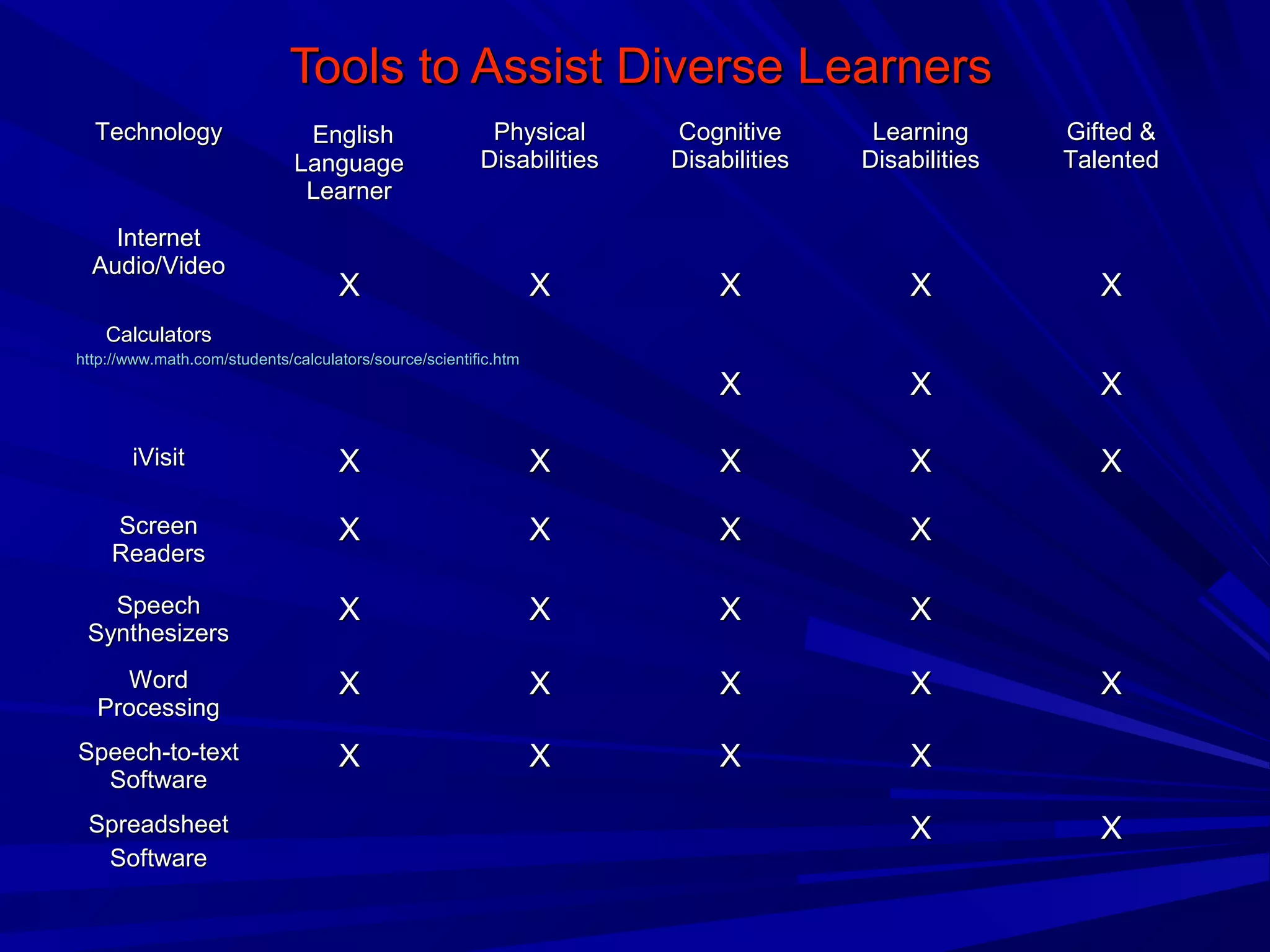
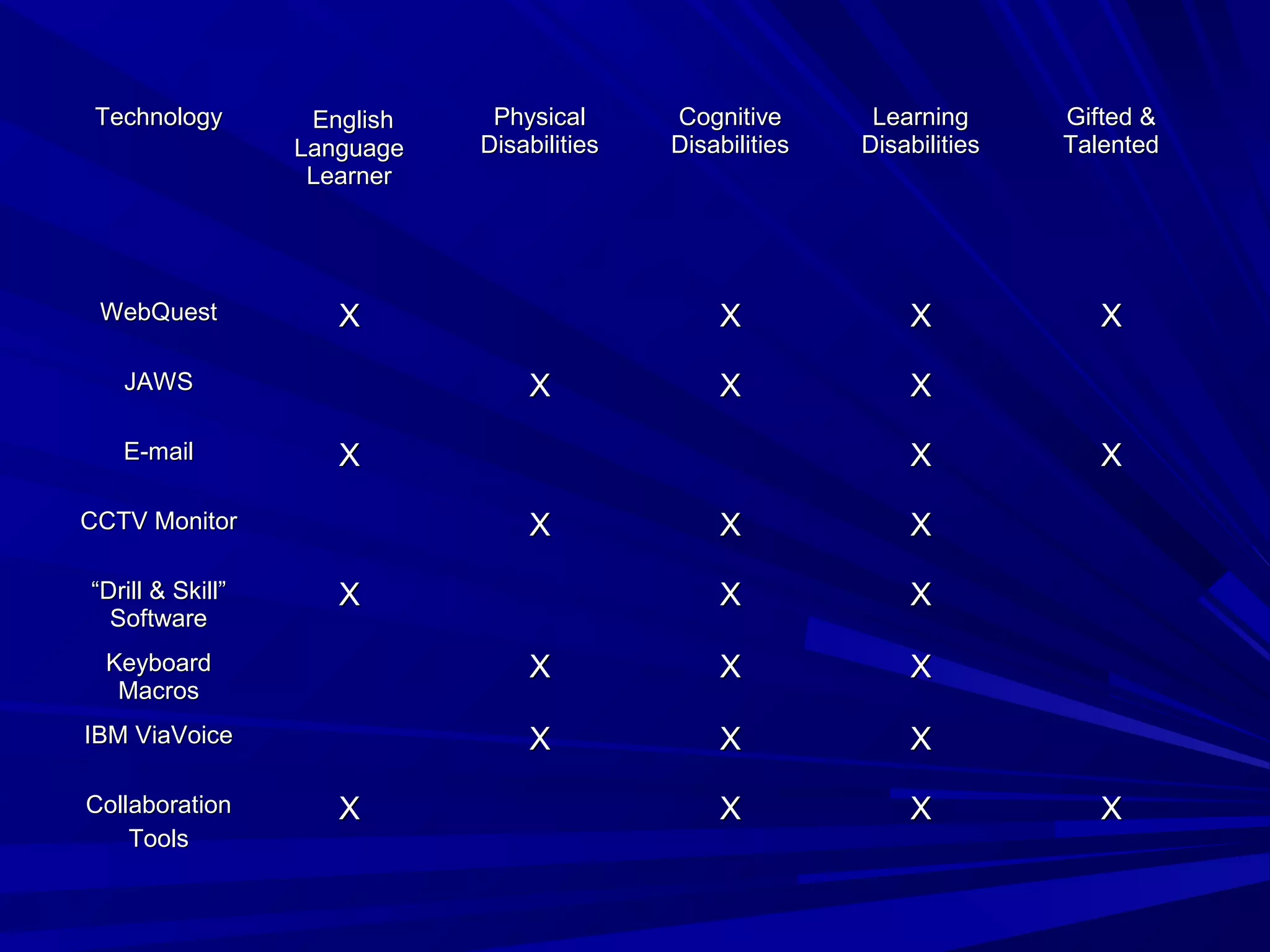
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework for curriculum development that provides equal opportunities for all students to learn. UDL aims to minimize barriers and maximize flexibility in how content is presented, how students respond or demonstrate knowledge, and student engagement. The three principles of UDL are providing multiple means of representation, action and expression, and engagement. UDL draws on research in cognitive neuroscience showing how students have varied skills, needs and interests that impact learning. Teachers can implement UDL by presenting information in varied formats, allowing for different modes of participation and expression, and fostering relevance, choice and motivation.