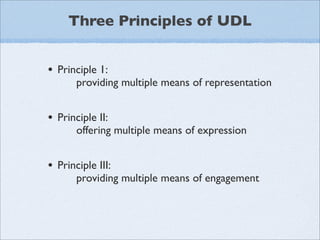
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework that provides flexibility in how information is presented, how students demonstrate knowledge, and how students are engaged. UDL principles include providing multiple means of representation, expression, and engagement. This flexibility benefits all learners by reducing barriers and maintaining high expectations. UDL is informed by research on how the brain learns and recognizes that there is diversity in how students learn. Technology can support UDL by providing flexible options to present content and for students to demonstrate understanding.