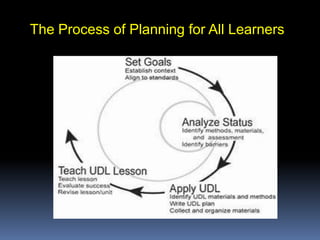
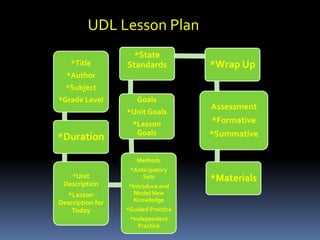
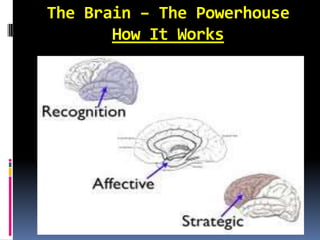
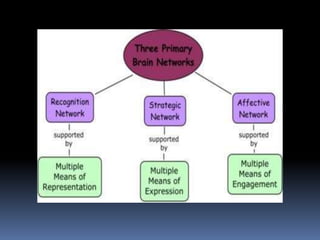
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework for curriculum design that fosters access to learning for all students. It aims to identify and remove barriers from teaching methods and curriculum materials to engage each student. UDL addresses unique learner needs, backgrounds, and interests by supporting customized methods, materials, and assessments. The framework is based on research about how the brain functions and learns best. It parallels the three brain networks of recognition, strategic, and affective learning. UDL provides flexibility in instruction and expands access to resources through technology to benefit diverse learners.