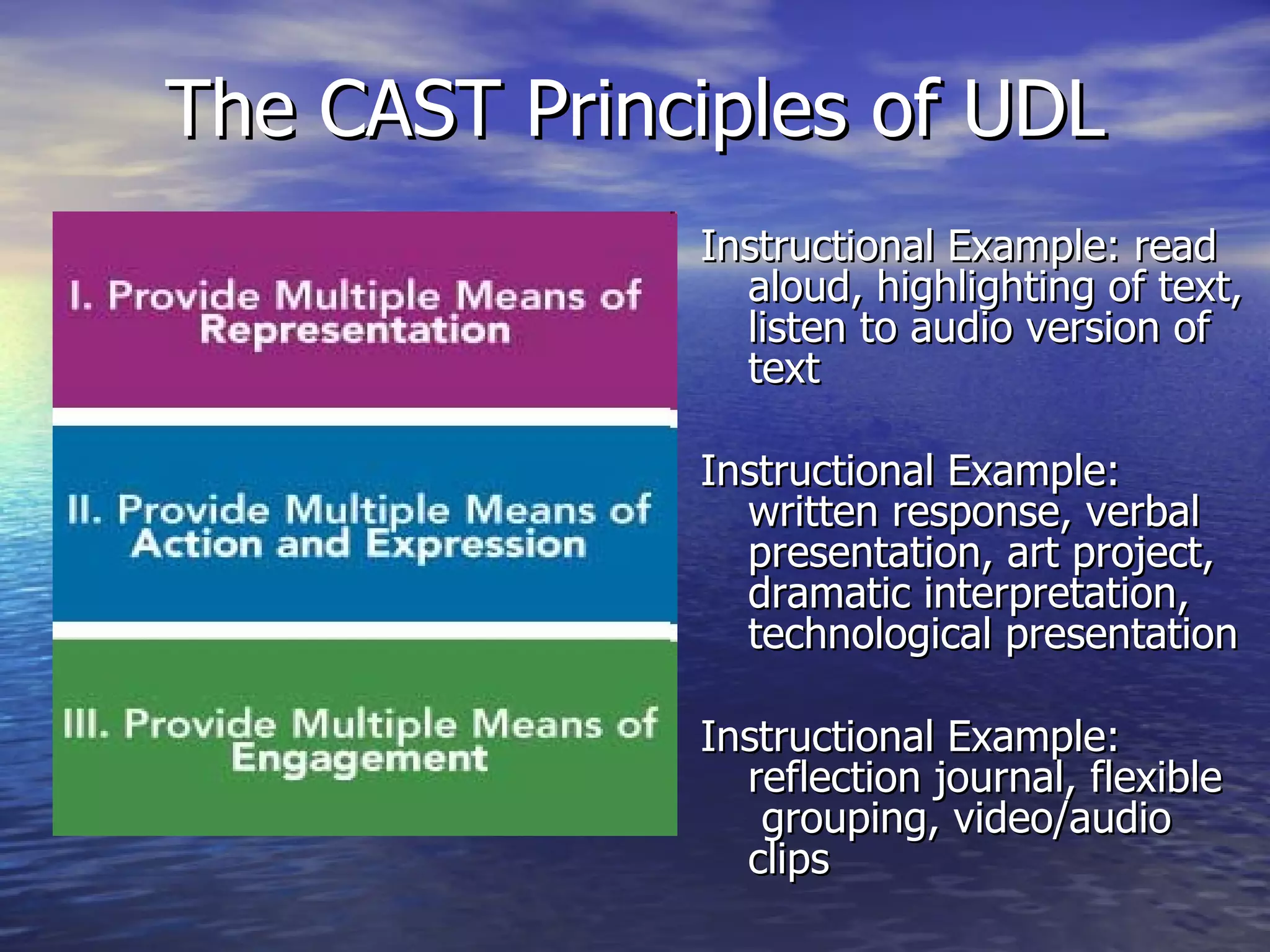
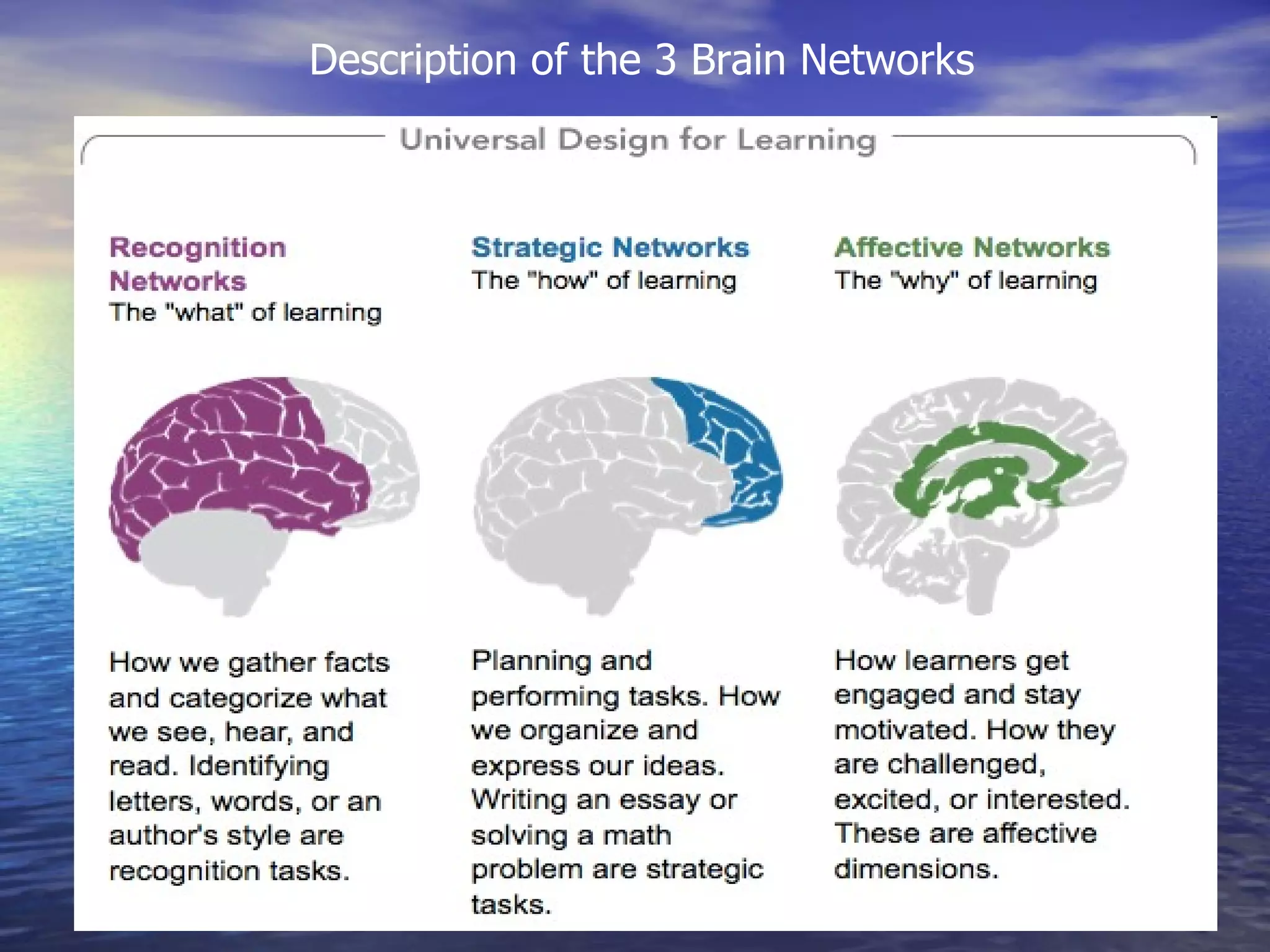
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is an educational framework that provides flexibility in how information is presented, how students respond or demonstrate their knowledge, and how students are engaged. UDL aims to reduce barriers in instruction and provide appropriate support to meet the needs of all learners. UDL is based on research about how the brain functions and individual differences in learners. Technology plays a central role in UDL by allowing for flexible presentation of content in multiple formats.