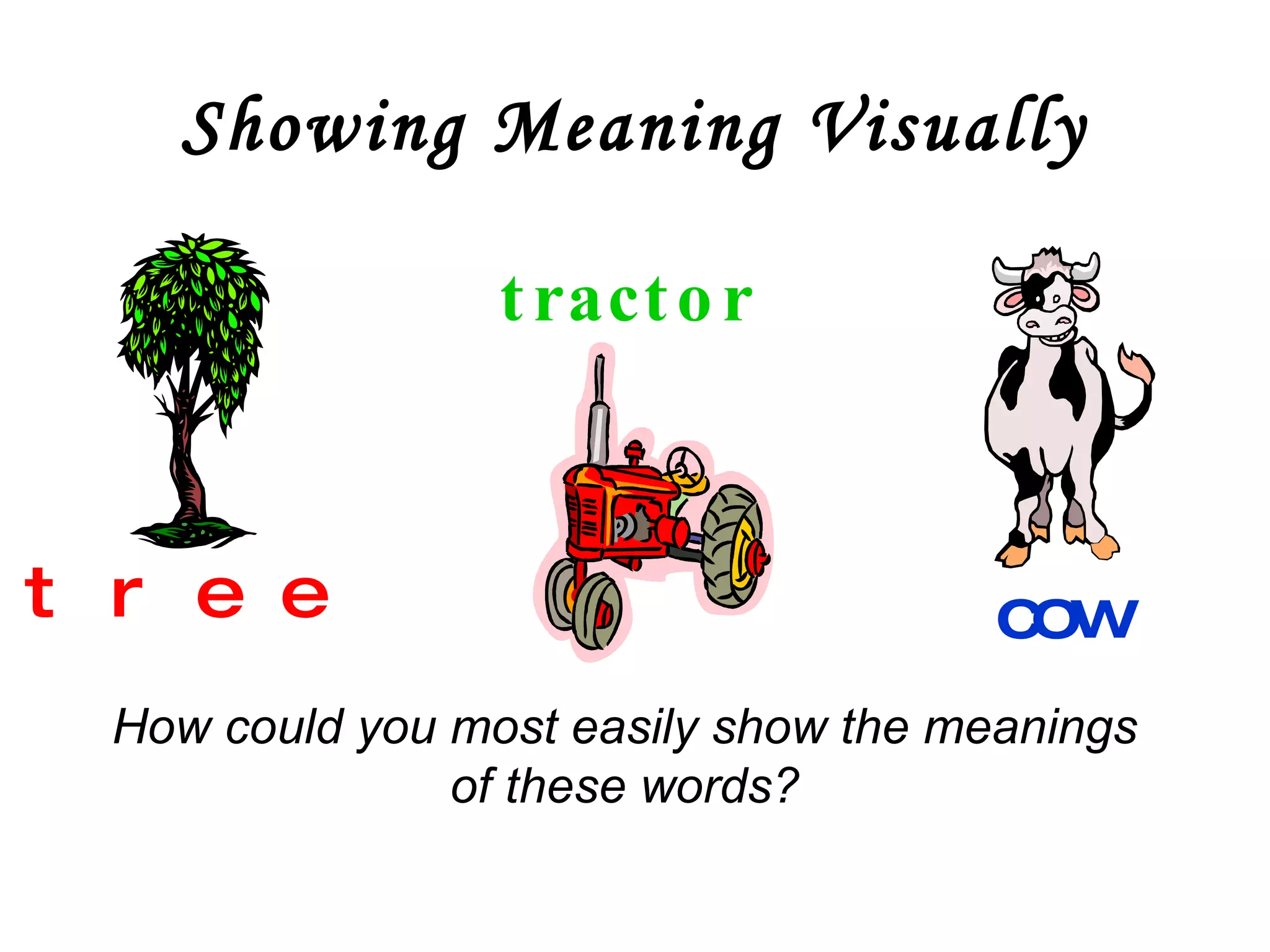
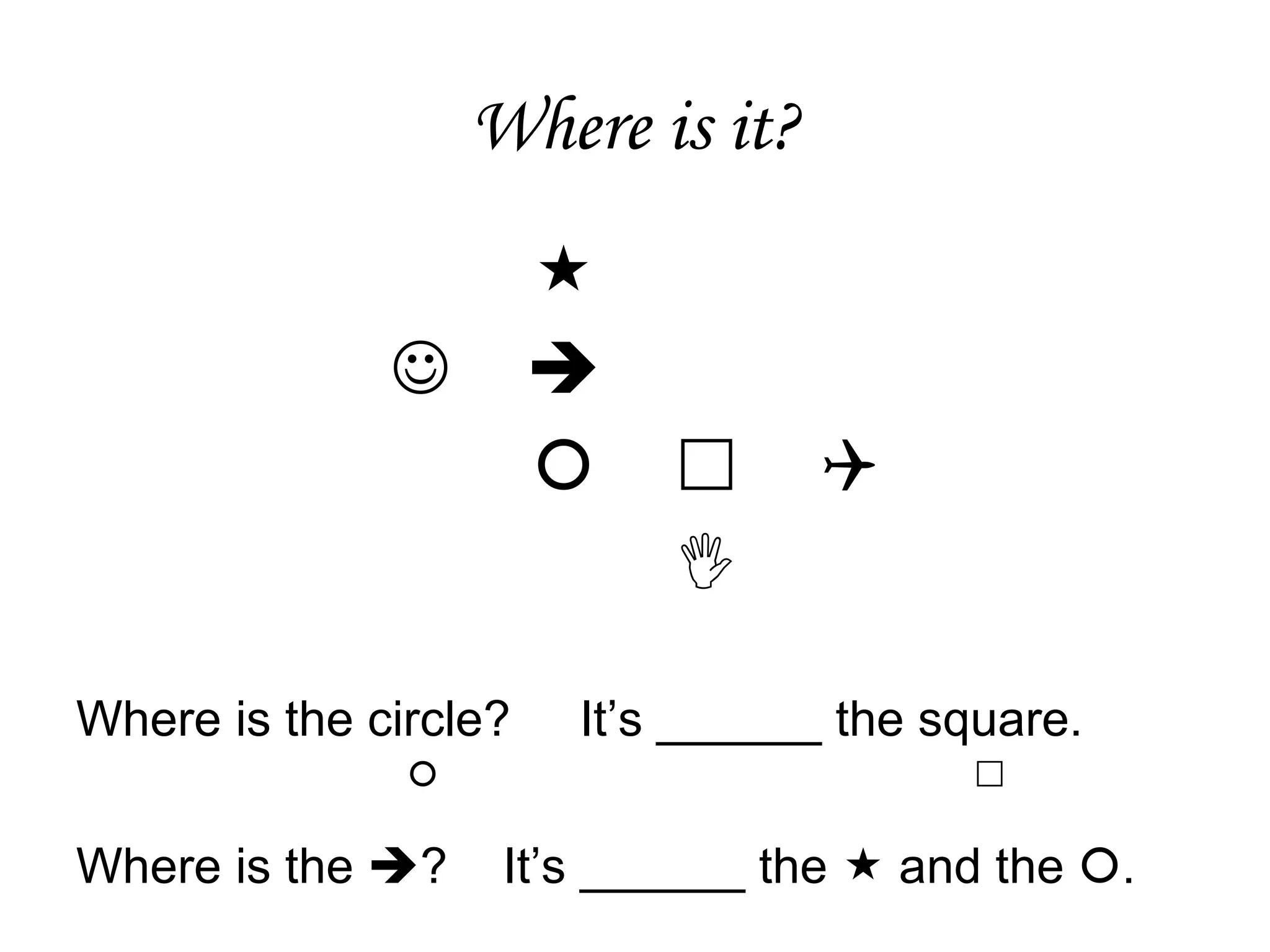
The document outlines effective strategies for teaching vocabulary and grammar within a contextual framework, emphasizing techniques such as scaffolding, elicitation, and interaction. It discusses the importance of simplifying language, utilizing visuals, and engaging students in active learning to enhance vocabulary retention. Additionally, the document highlights key vocabulary teaching principles, including the need for regular revision and motivation, along with various methods for presenting new words.