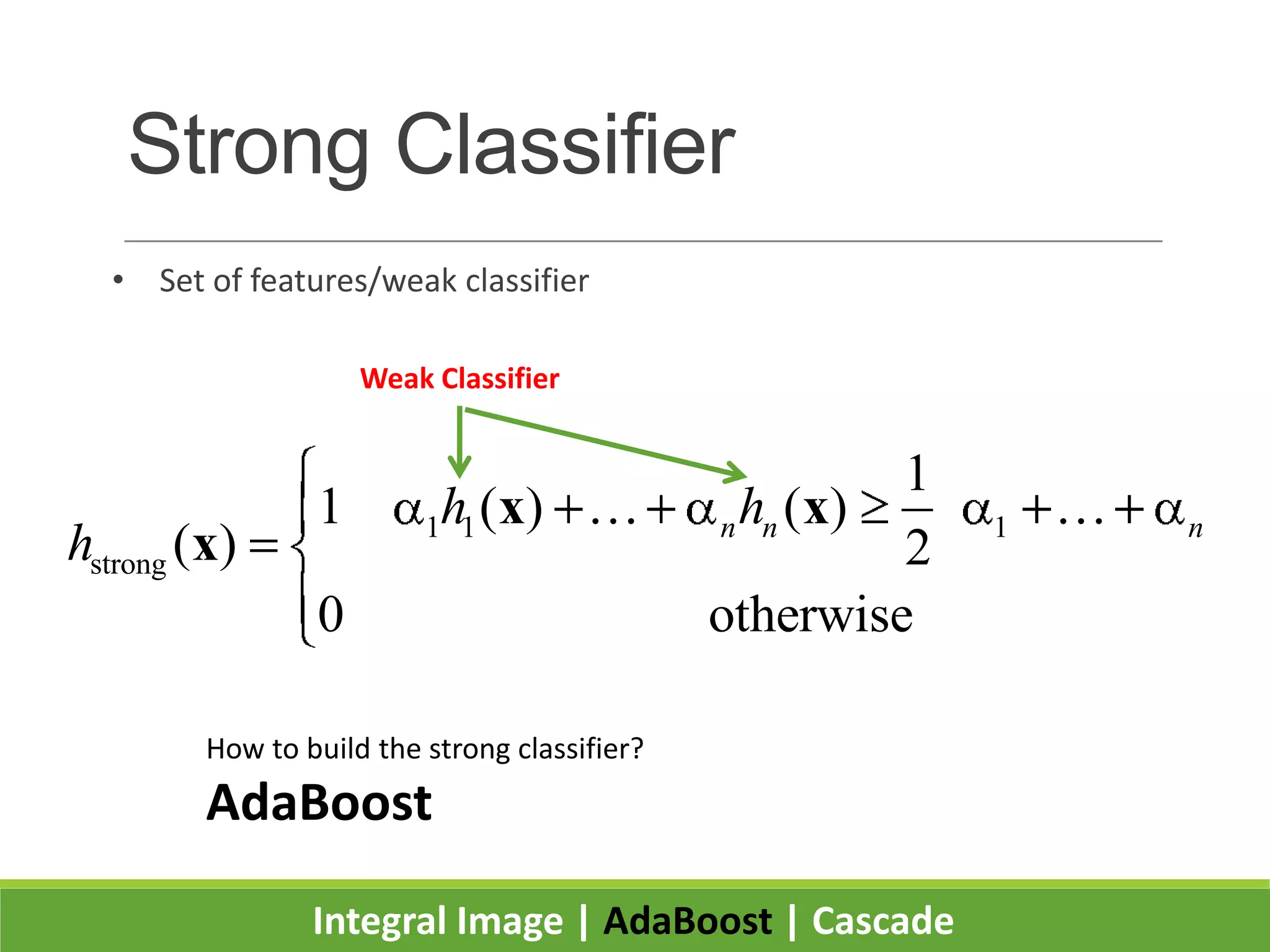
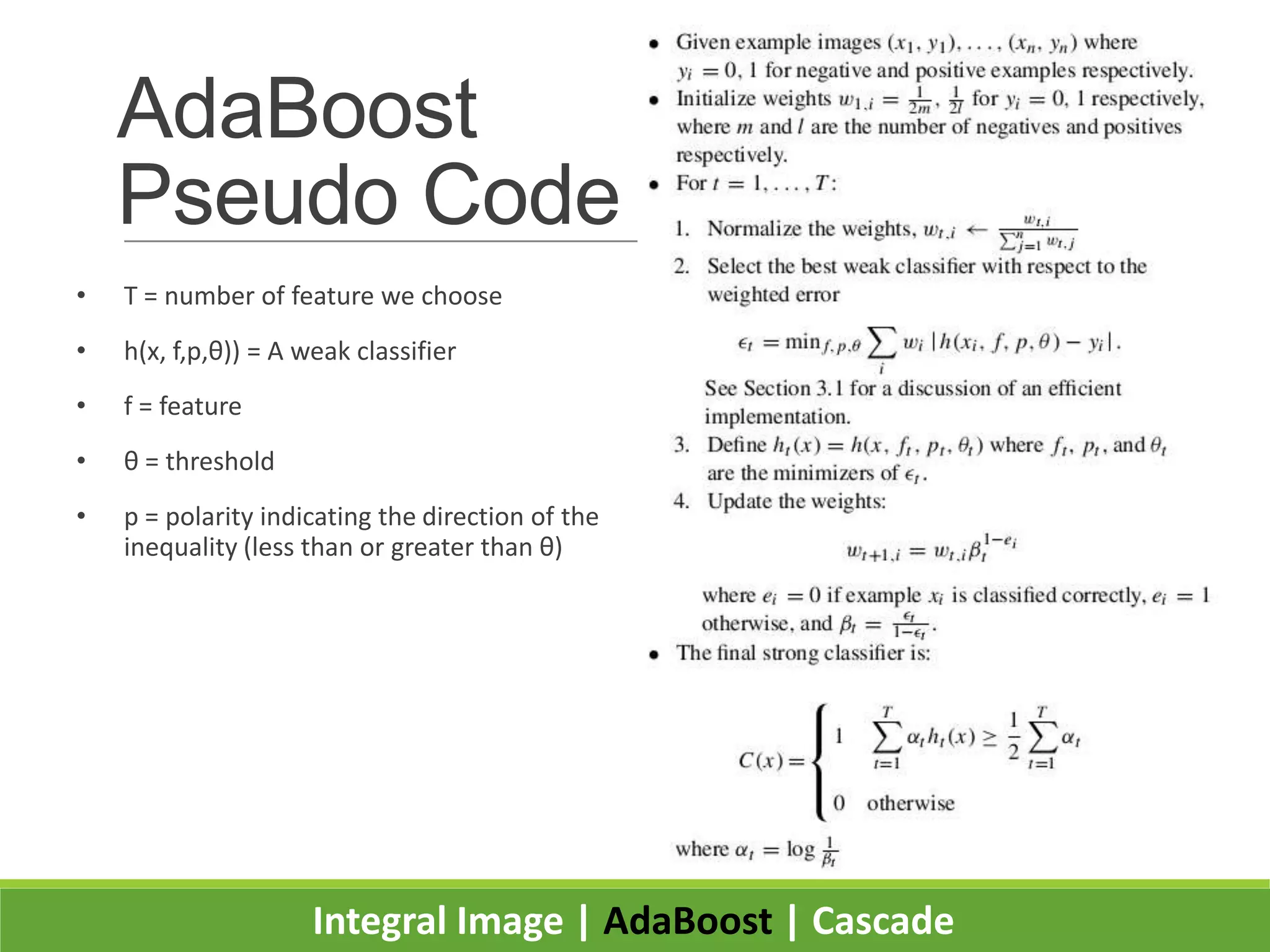
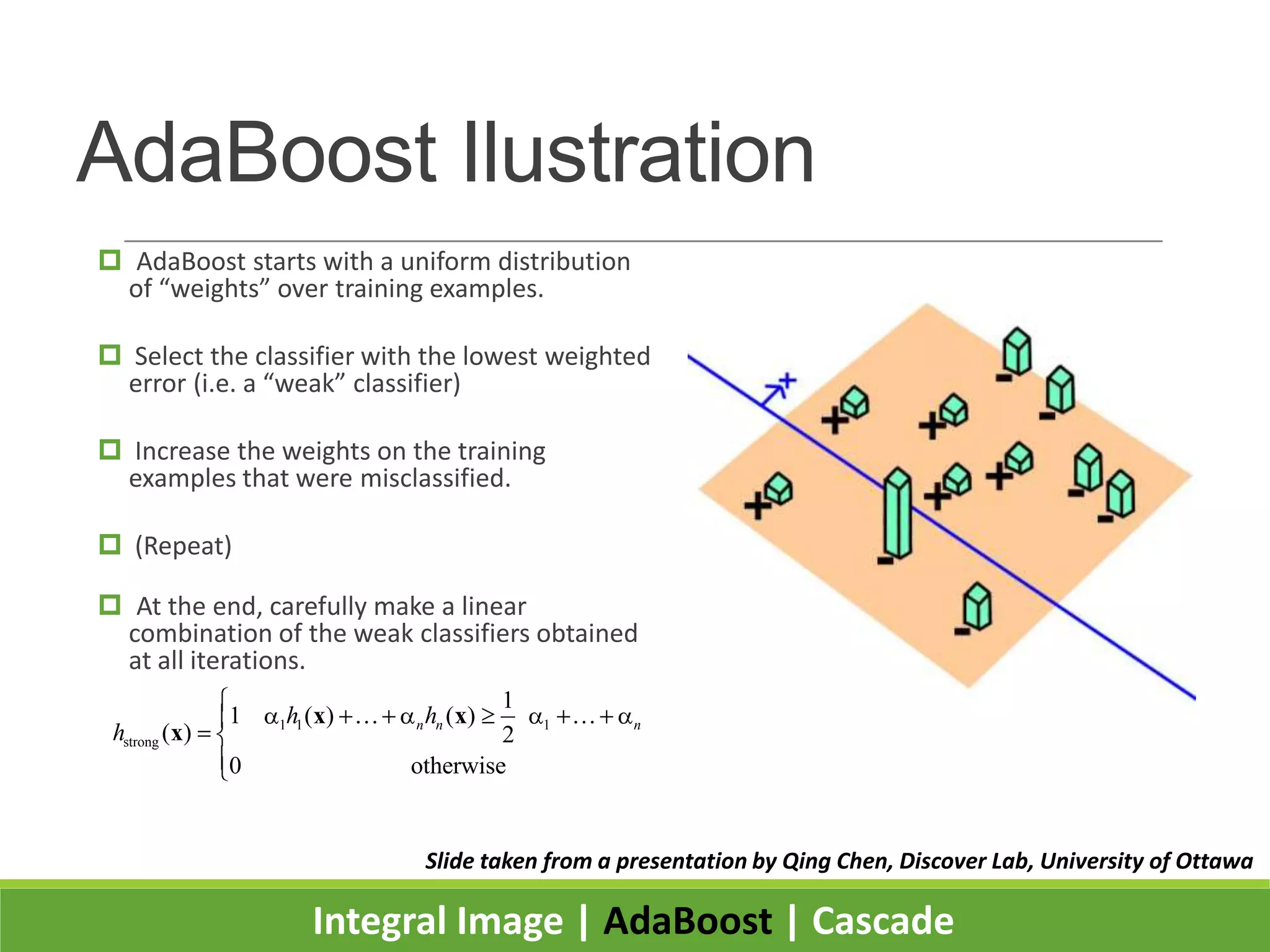
1. The document presents the Viola-Jones object detection framework which uses integral images, AdaBoost learning, and a cascade classifier structure for real-time object detection, such as face detection.
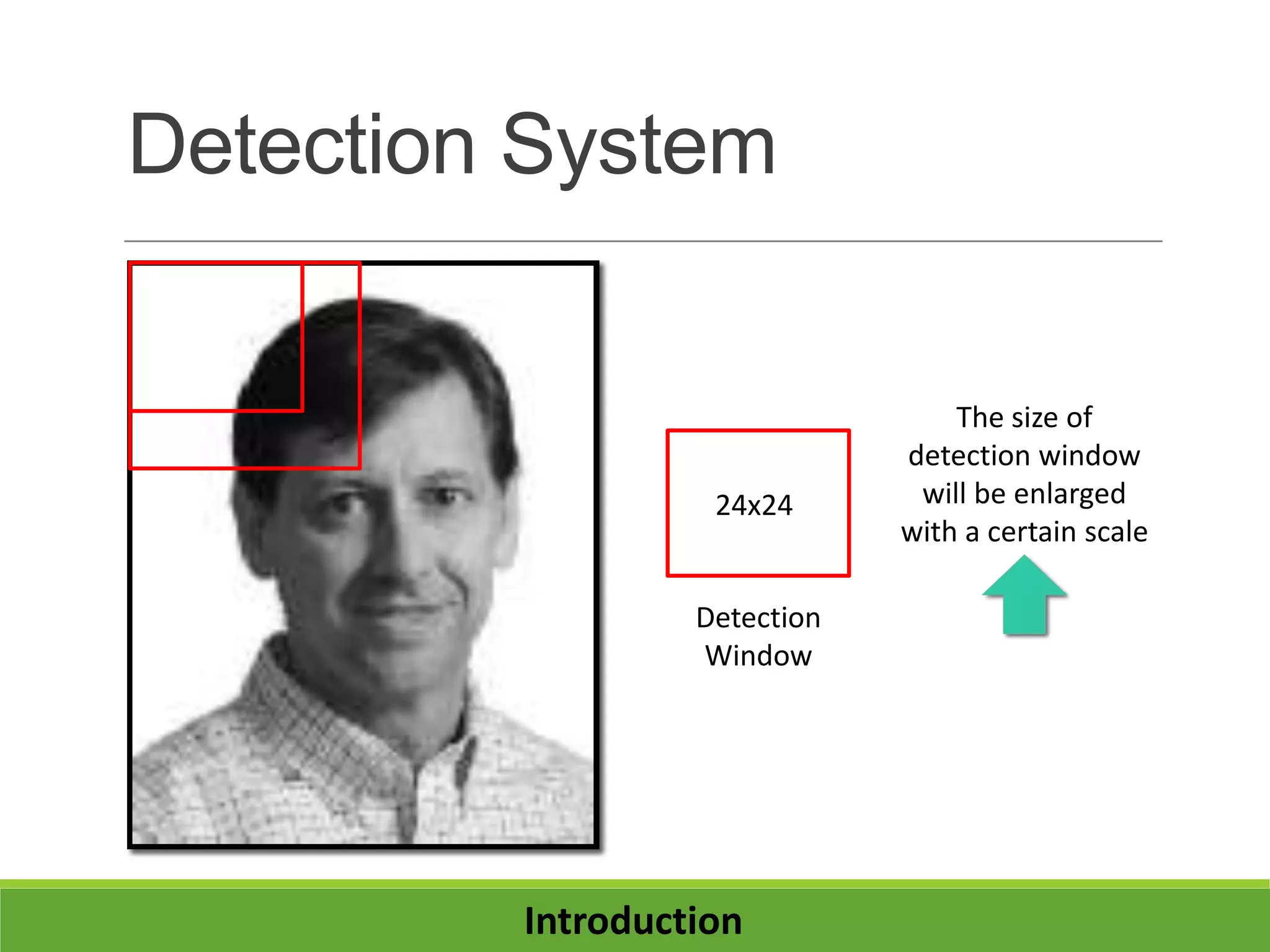
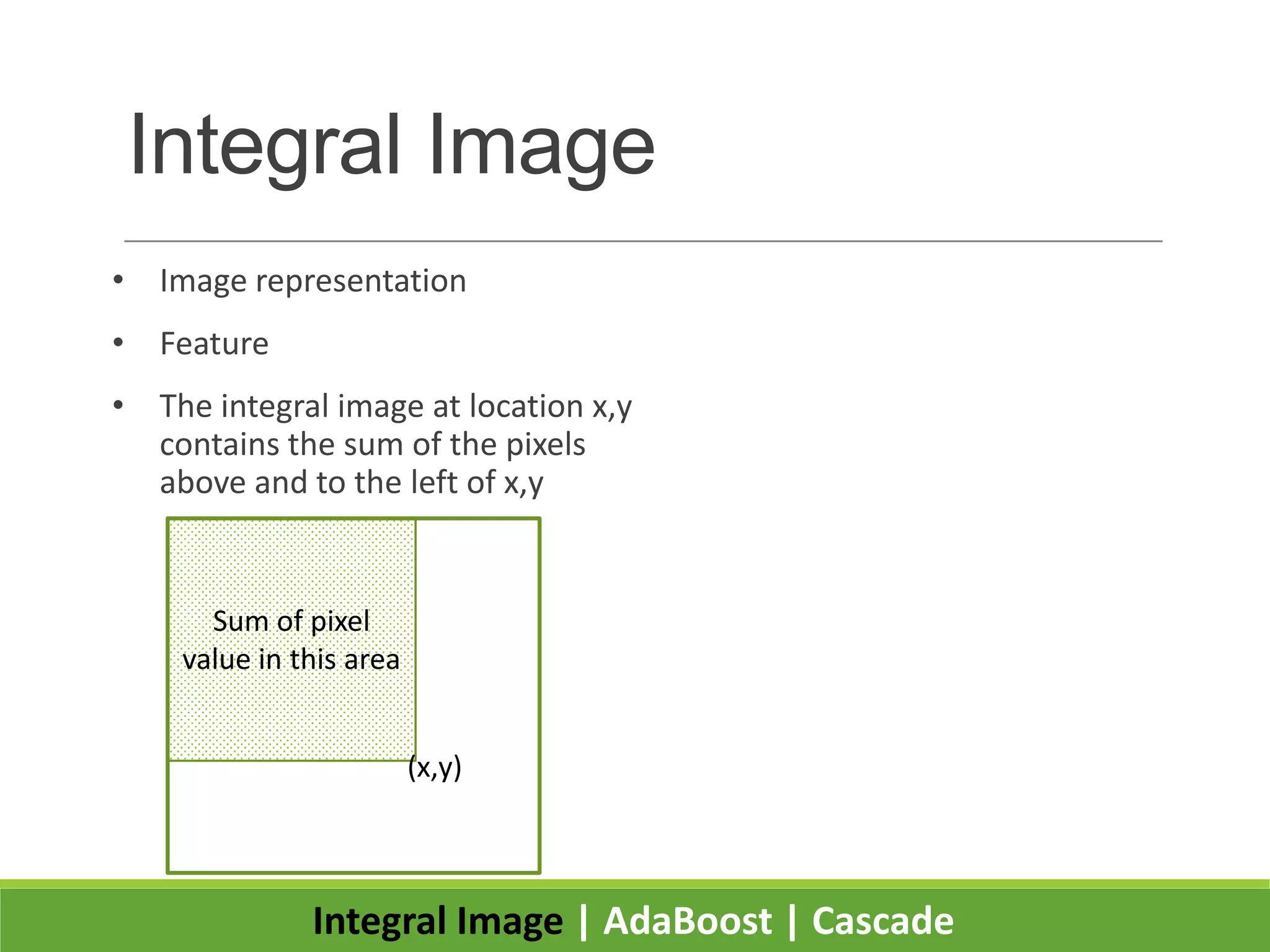
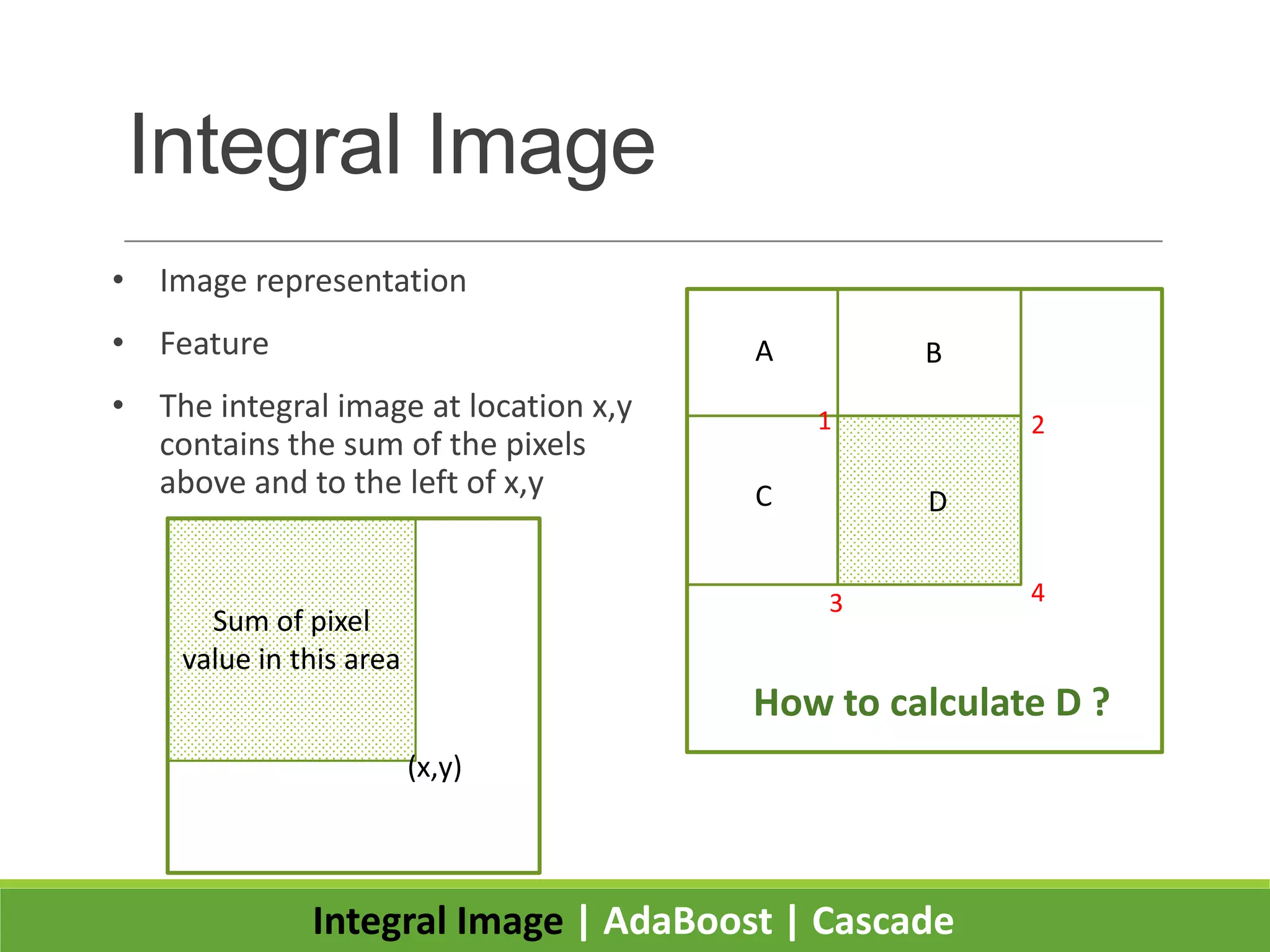
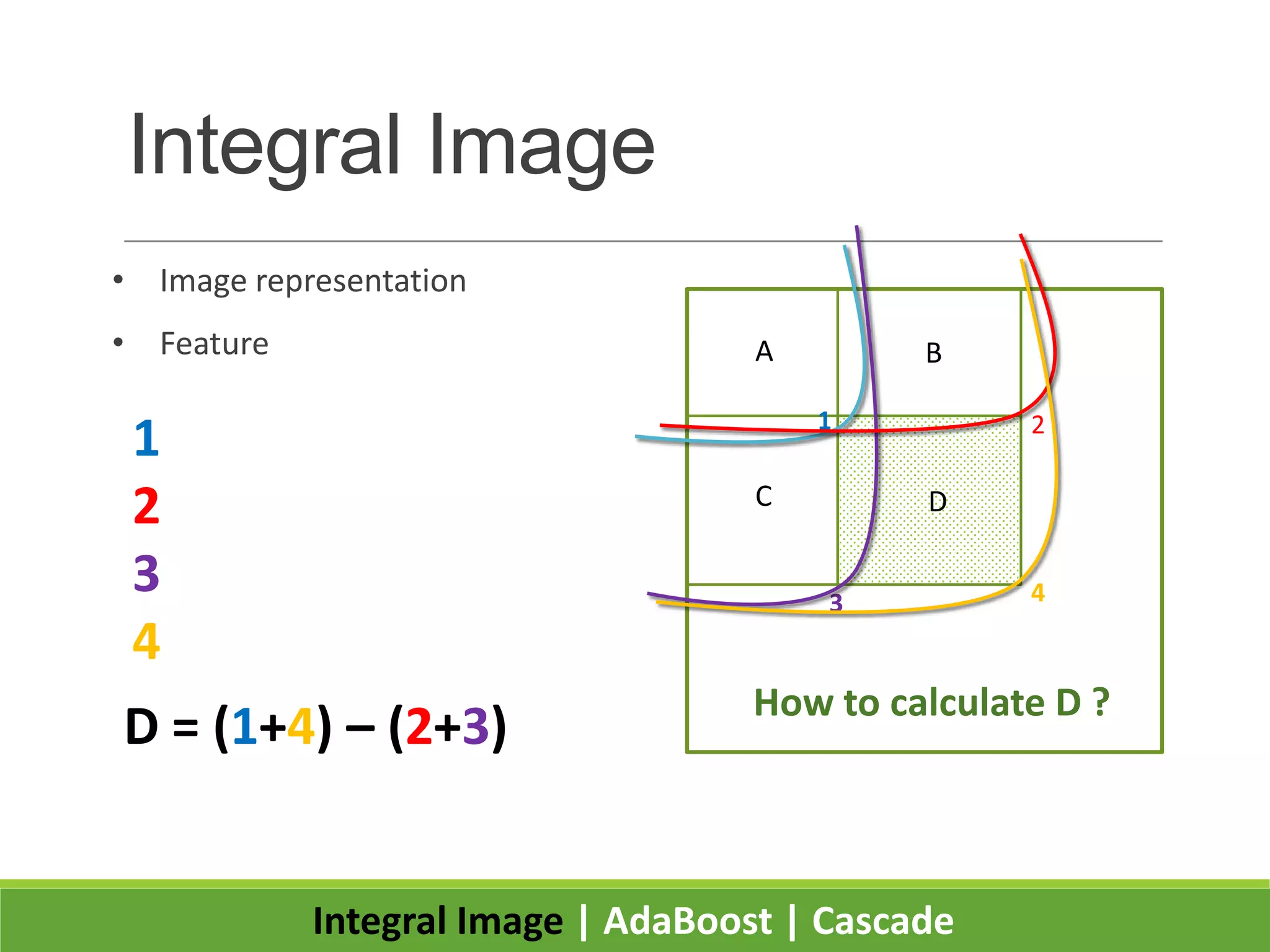
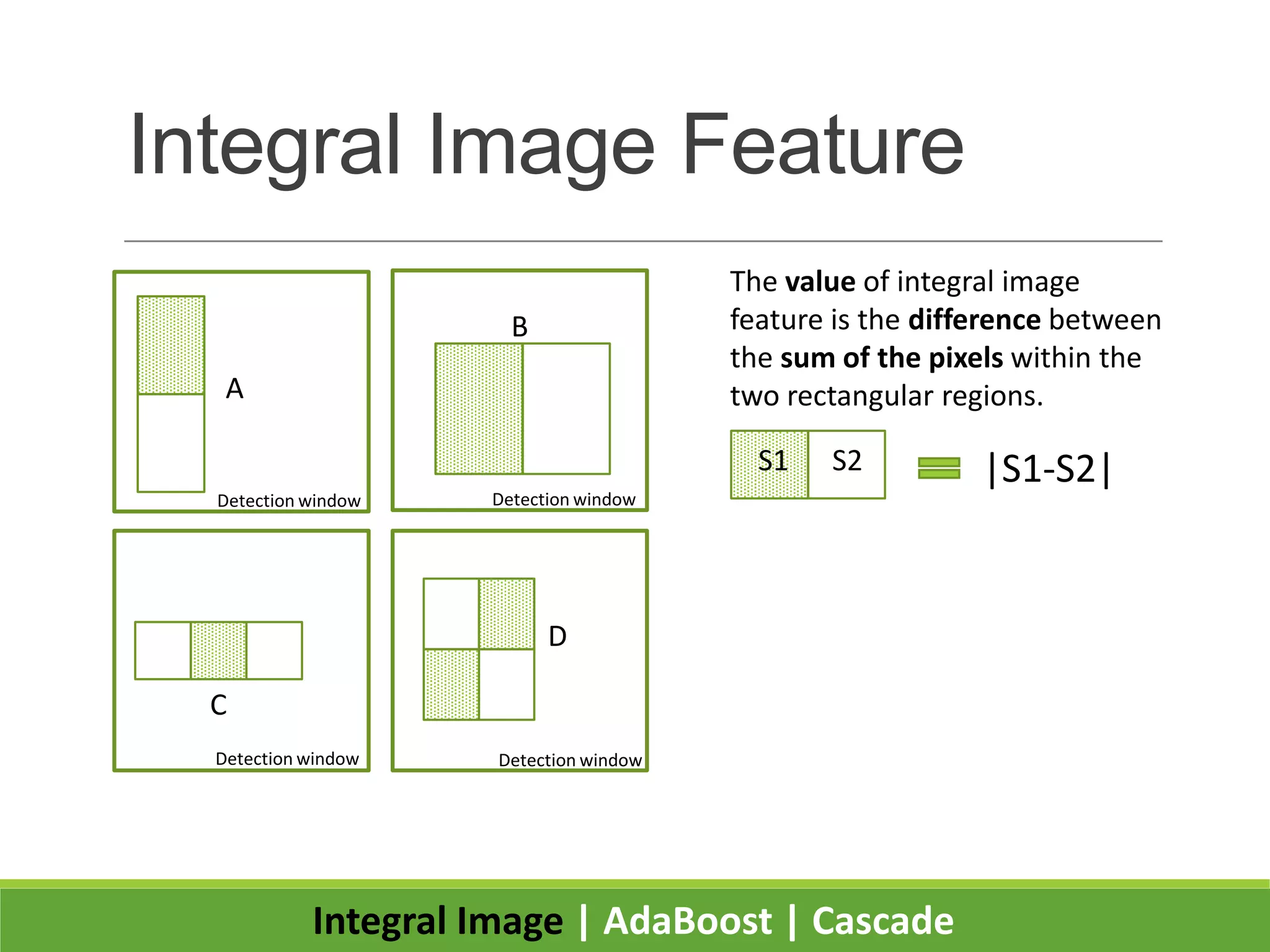
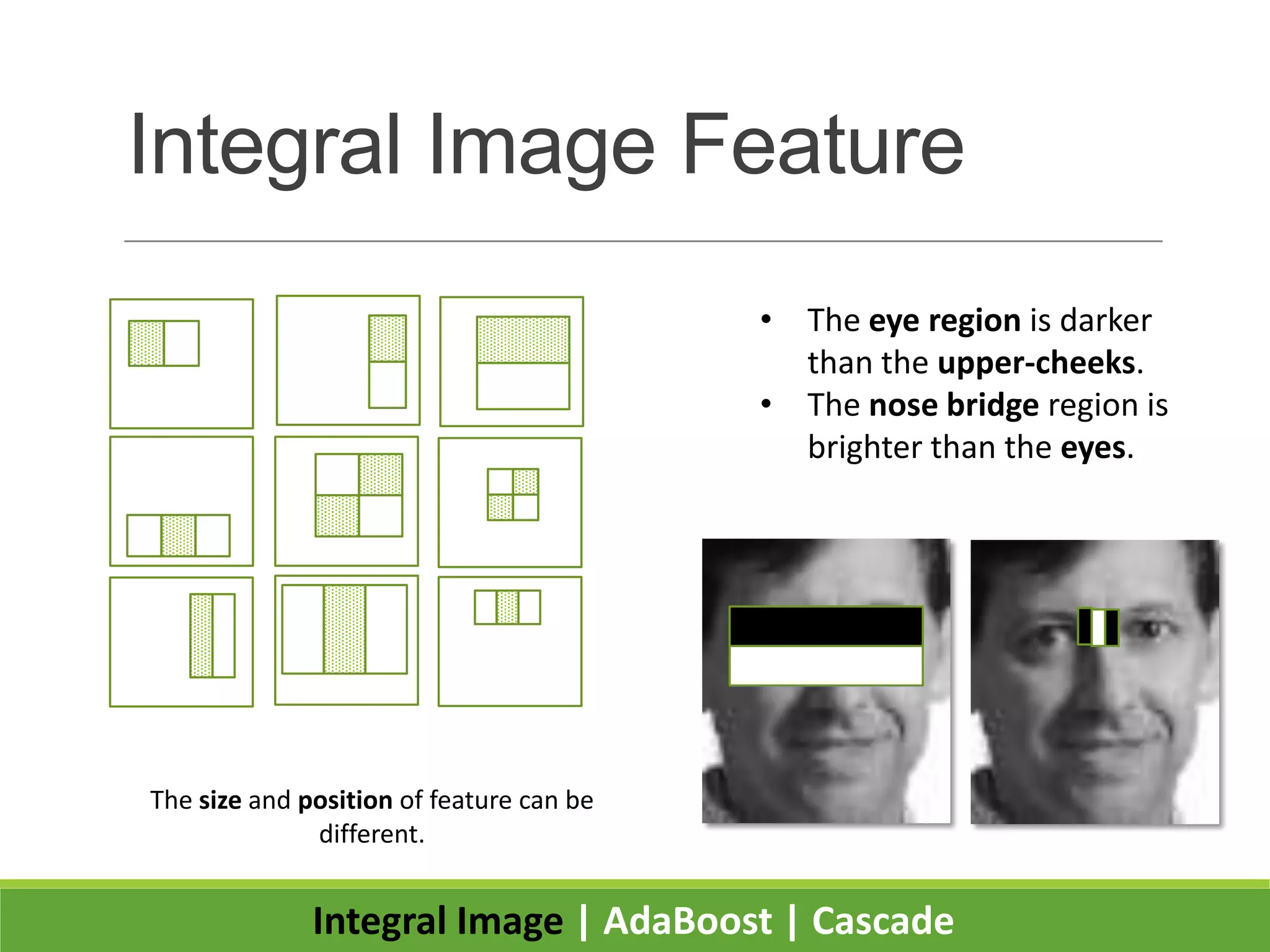
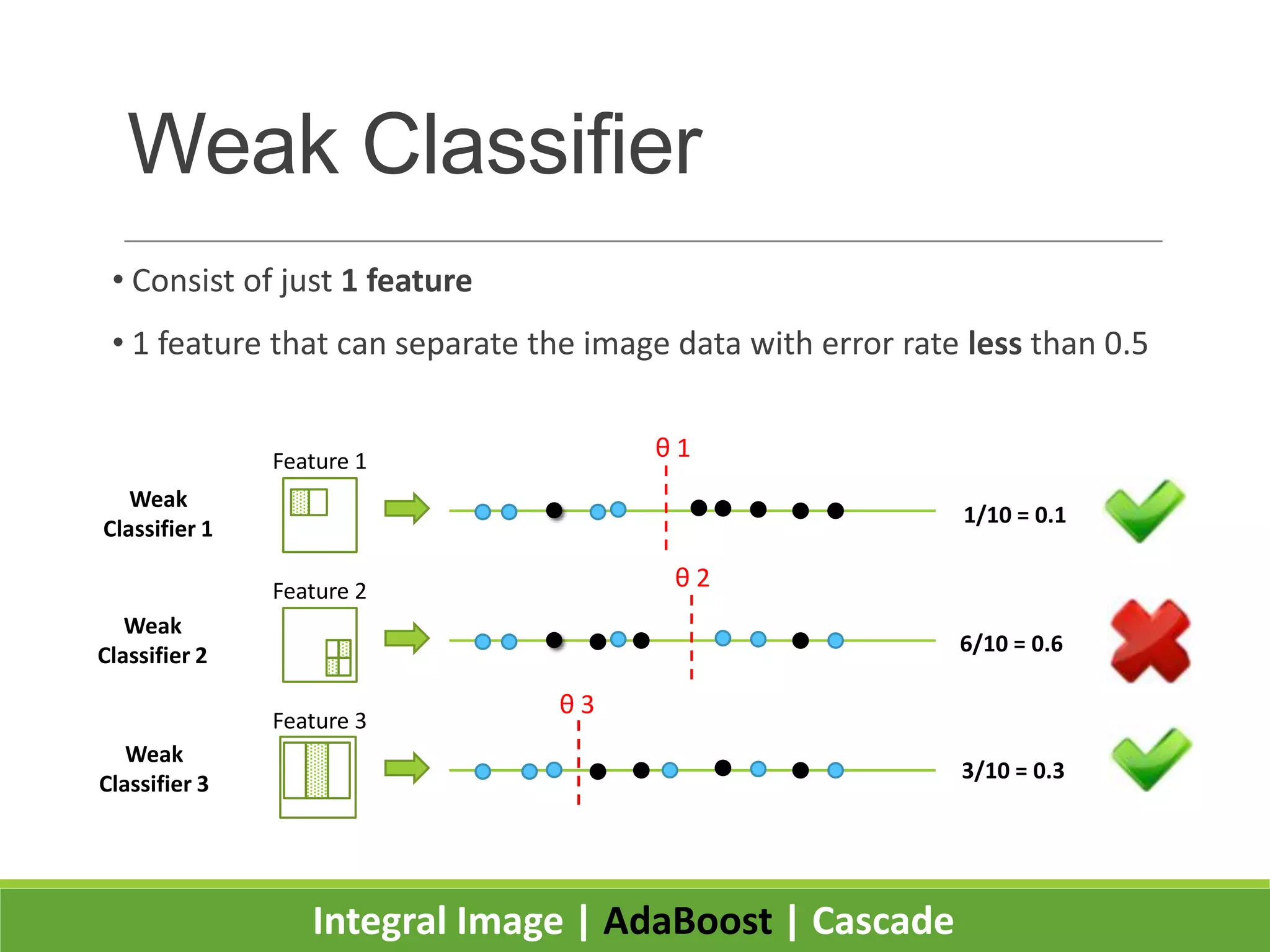
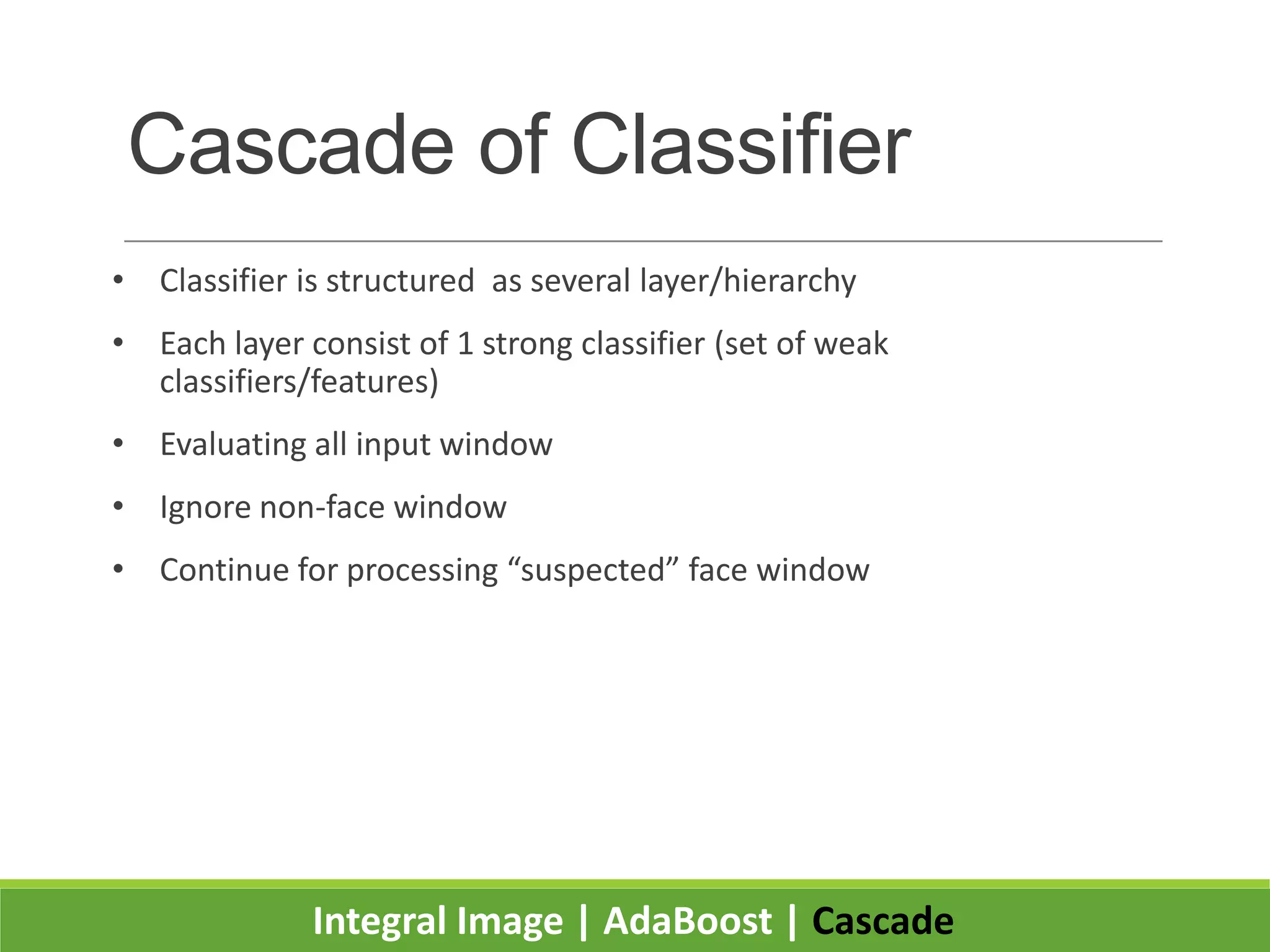
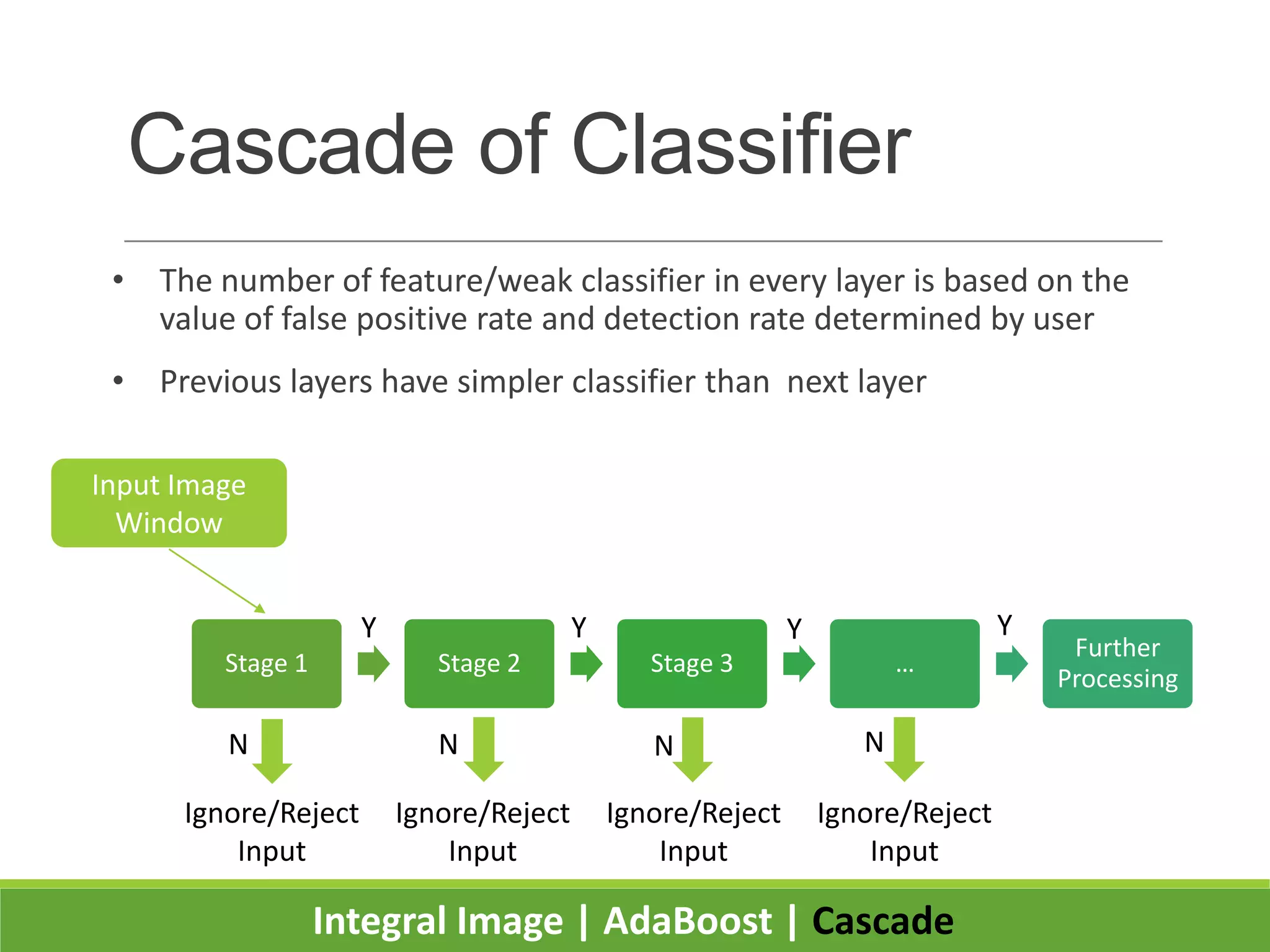
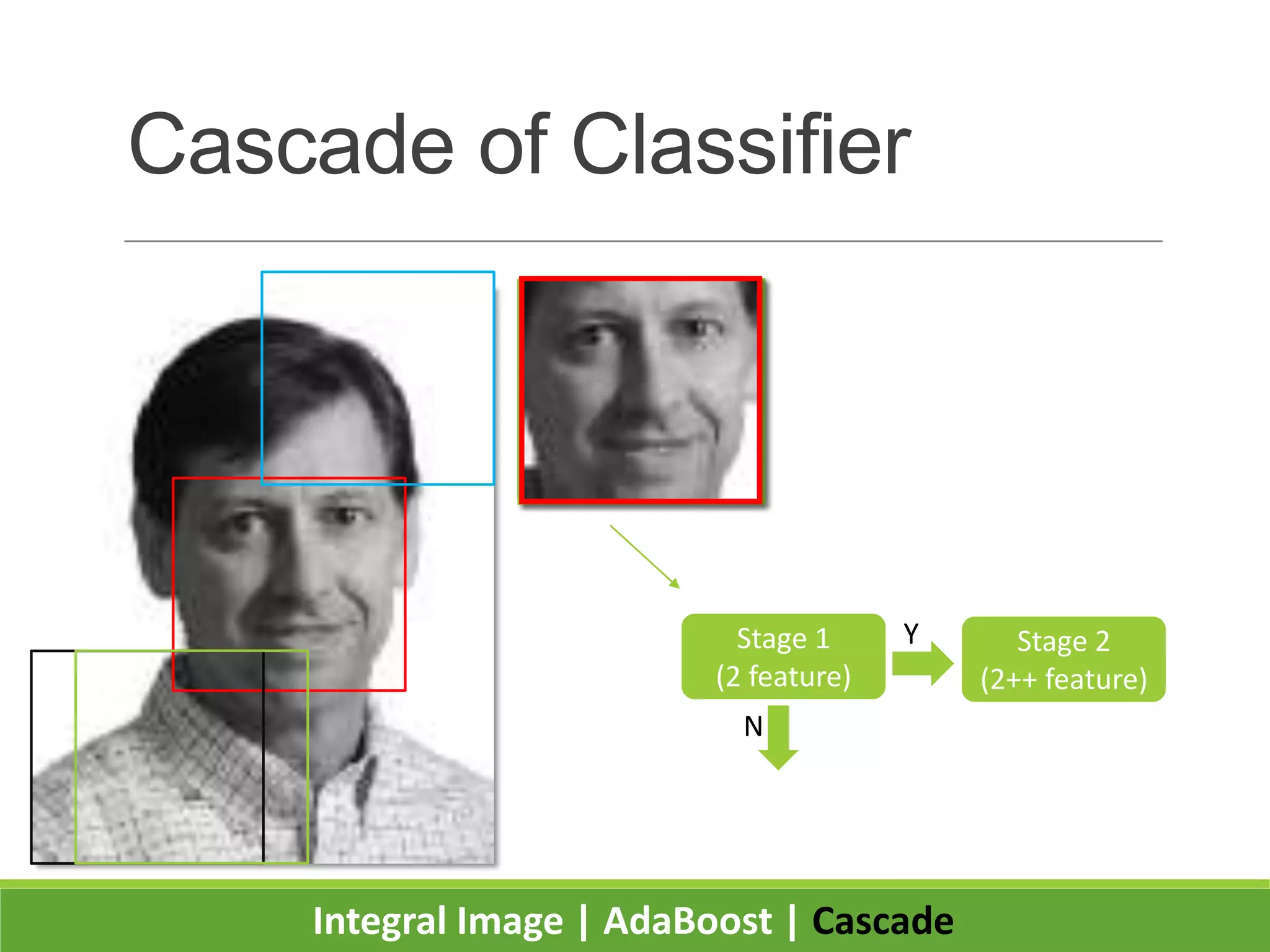
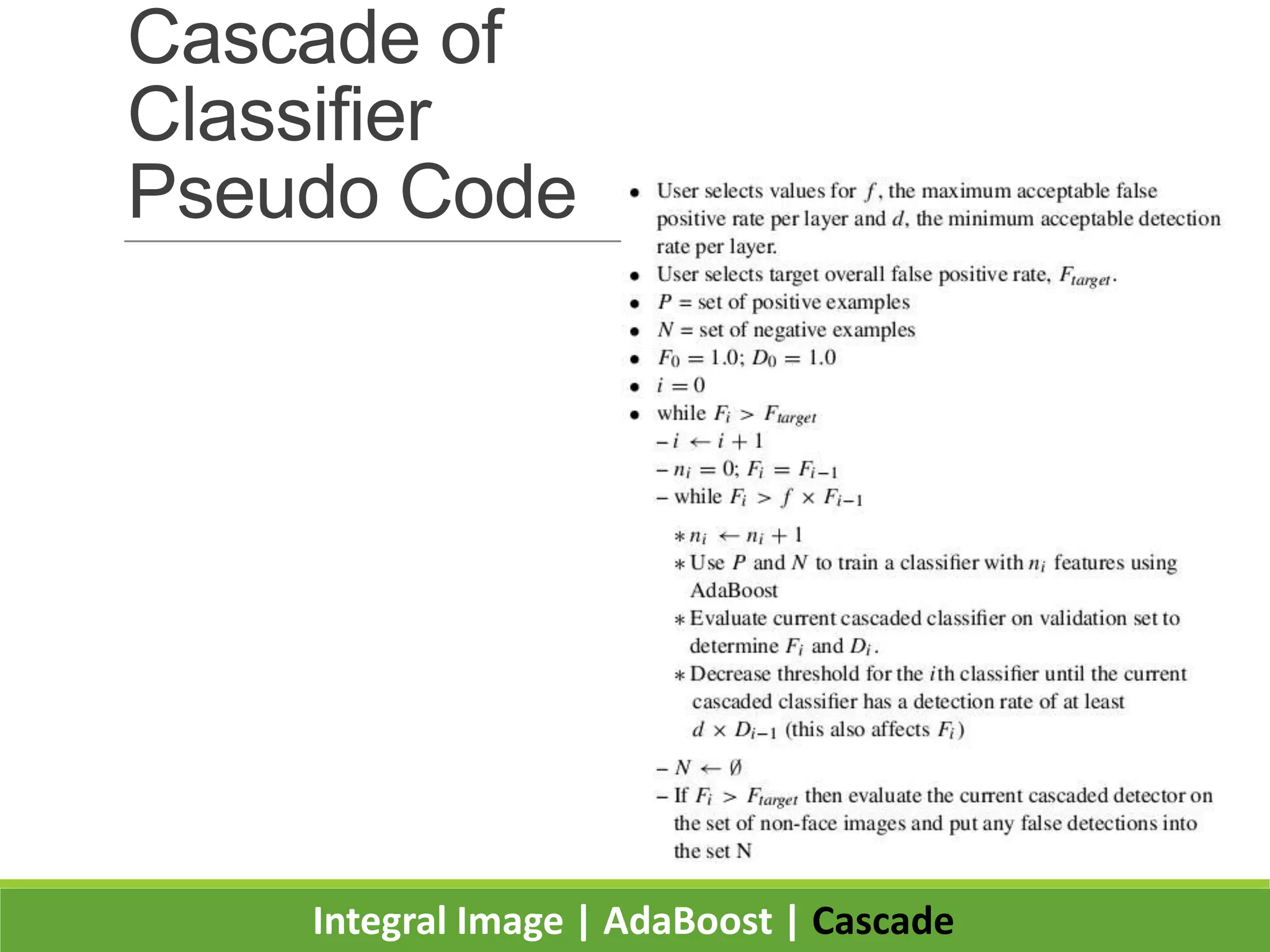
2. It introduces integral images as an image representation for fast feature extraction, AdaBoost for selecting important features, and a cascade structure for increased detection speed while maintaining accuracy.
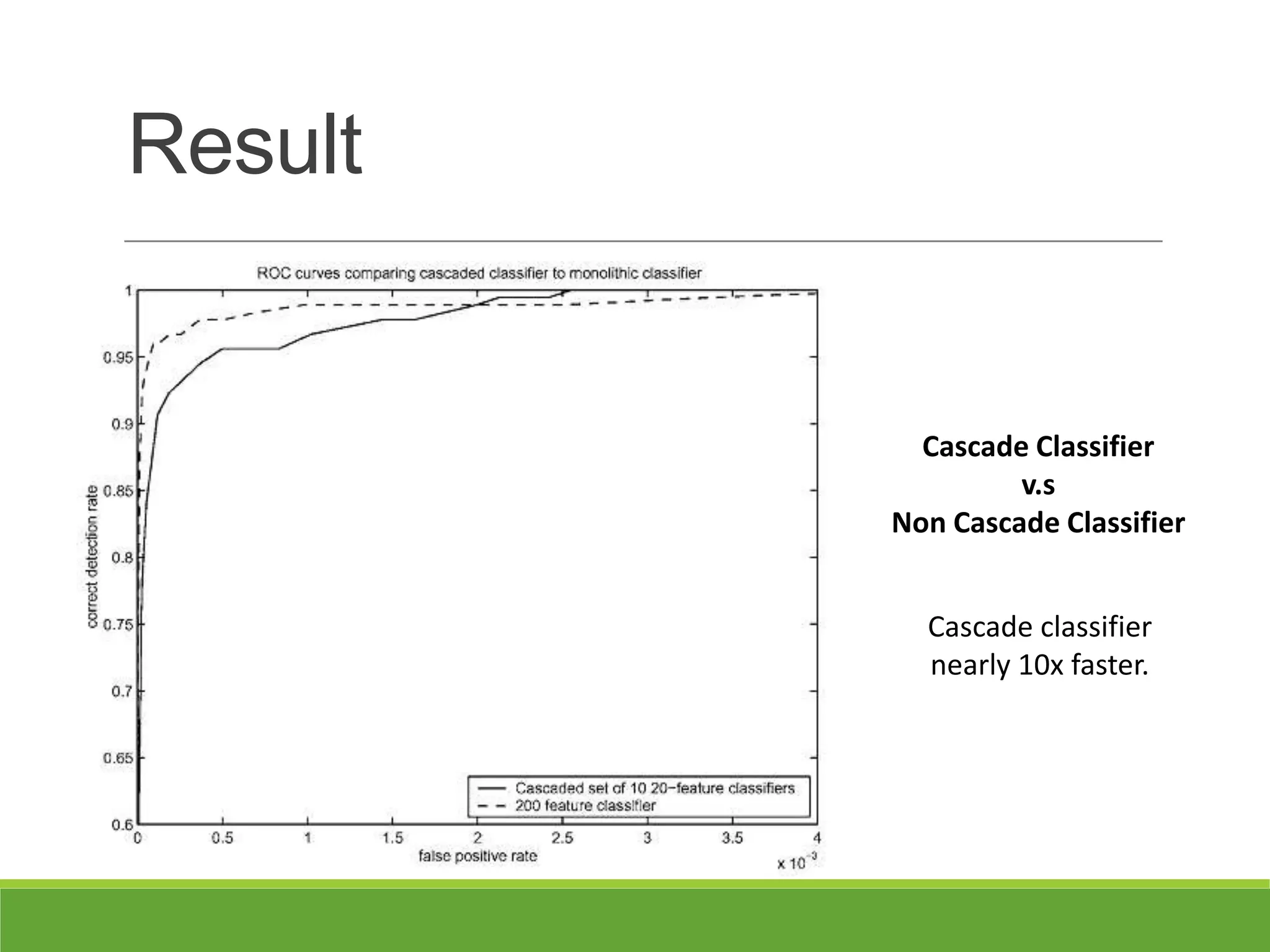
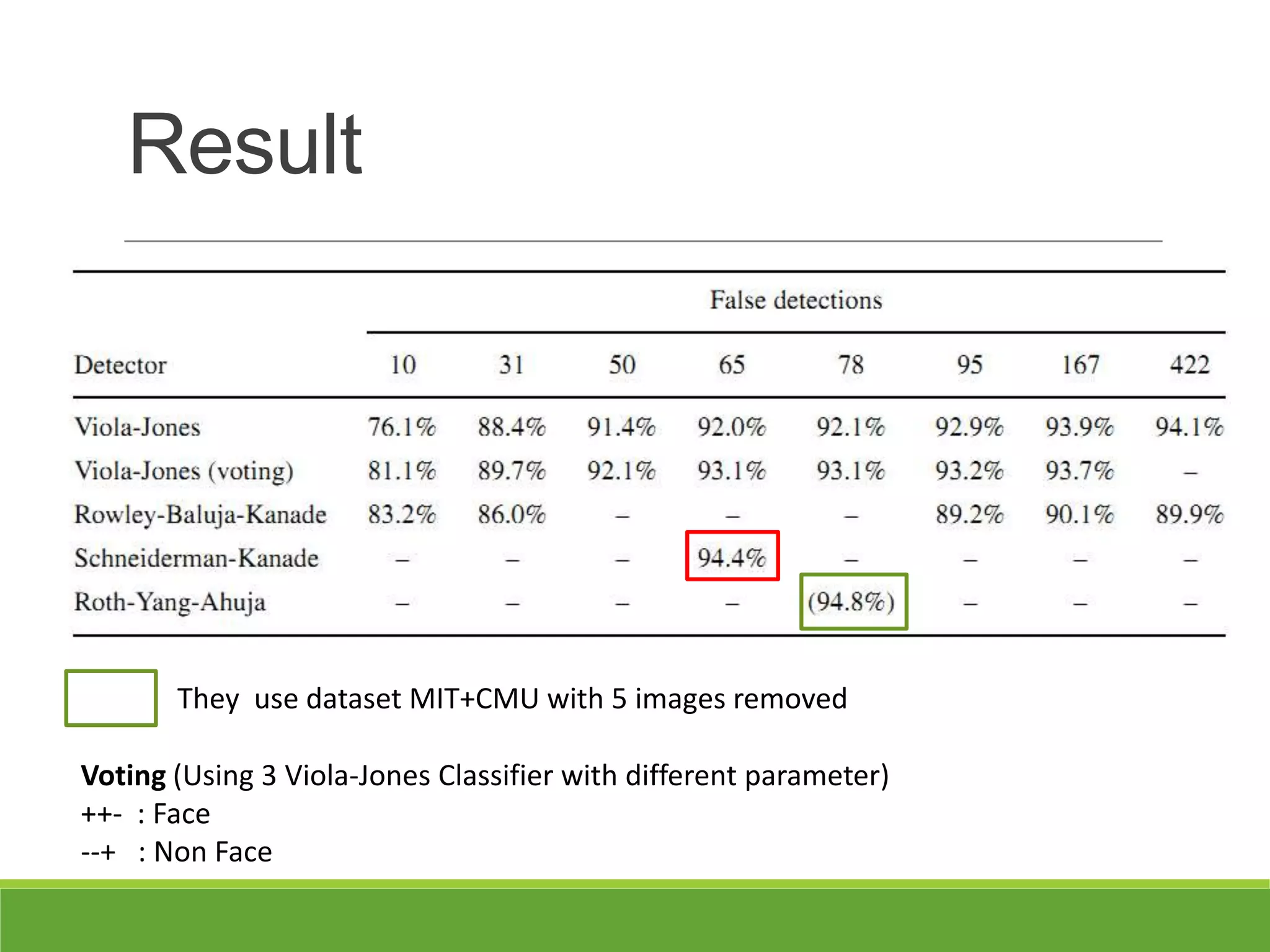
3. Experiments showed the cascade classifier approach was nearly 10 times faster than a single classifier while maintaining high detection rates, enabling real-time face detection.