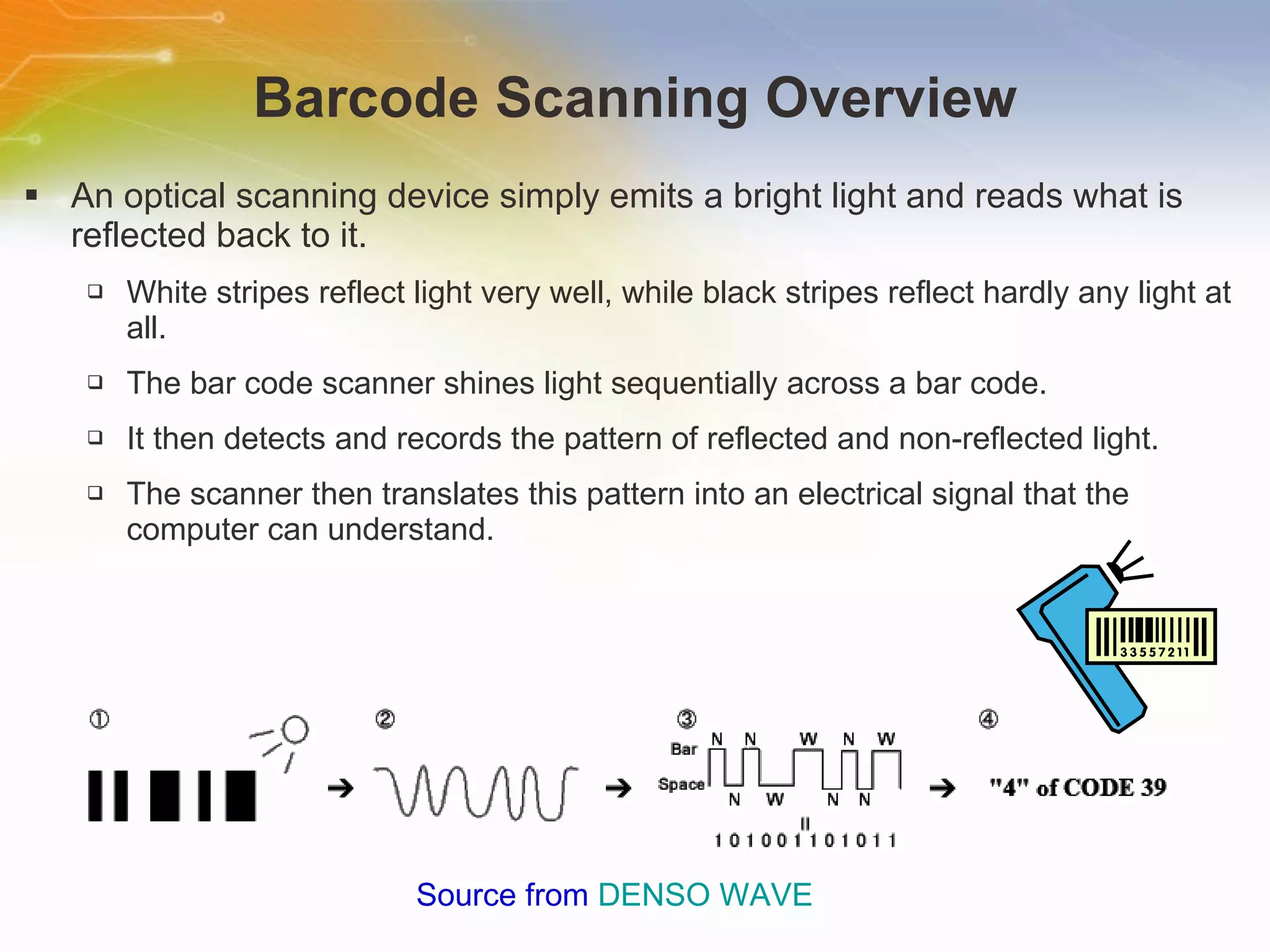
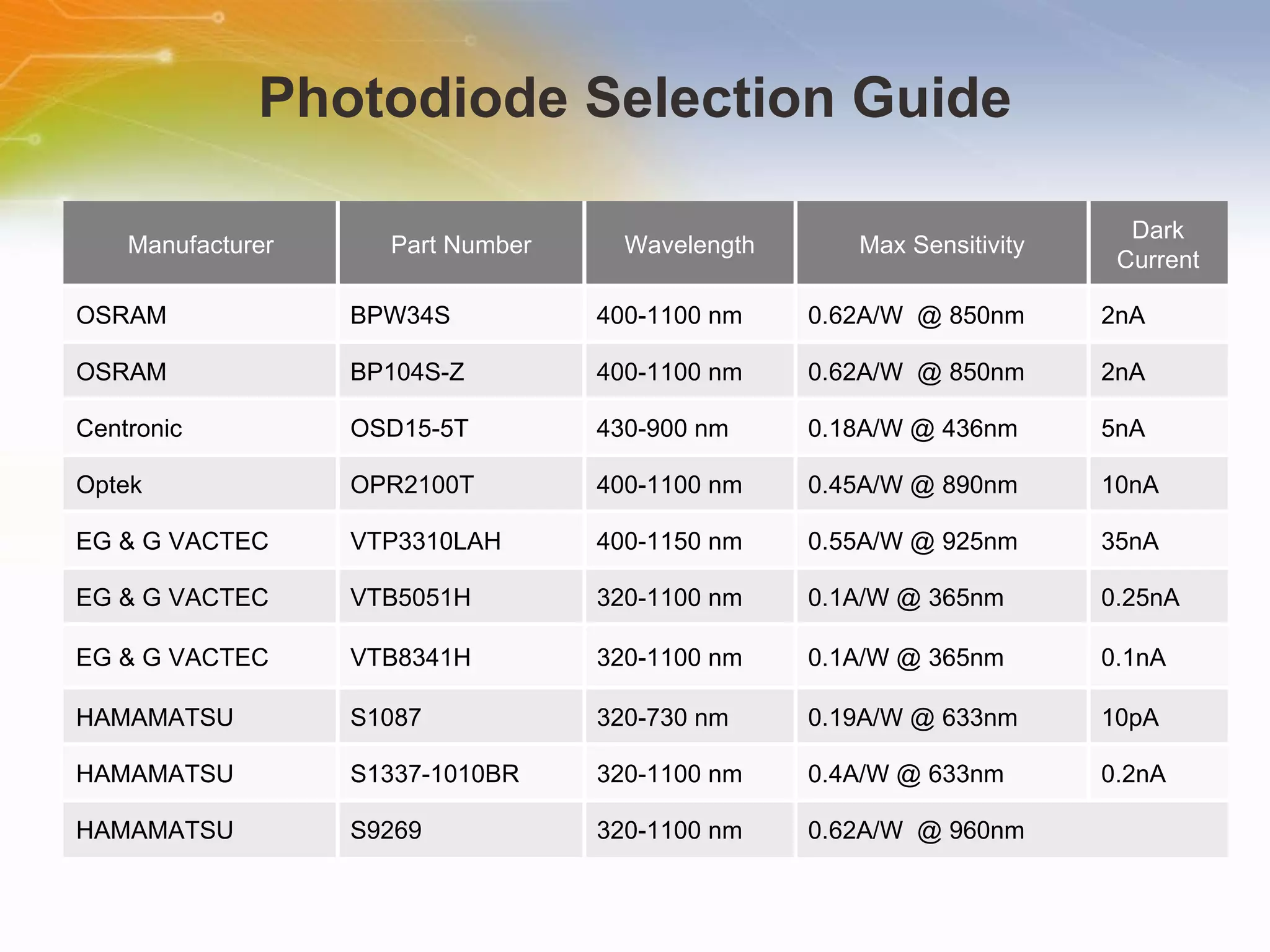
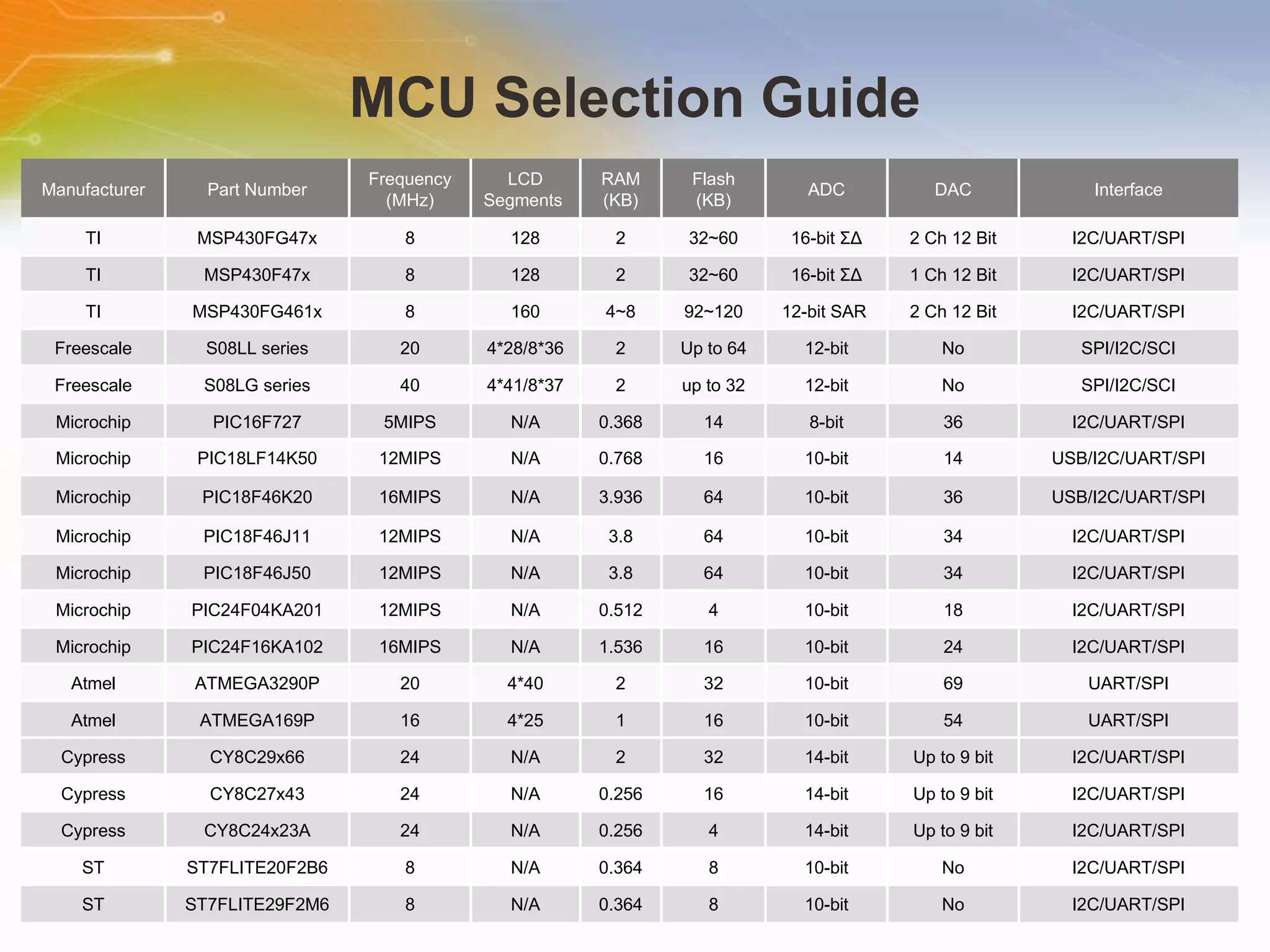
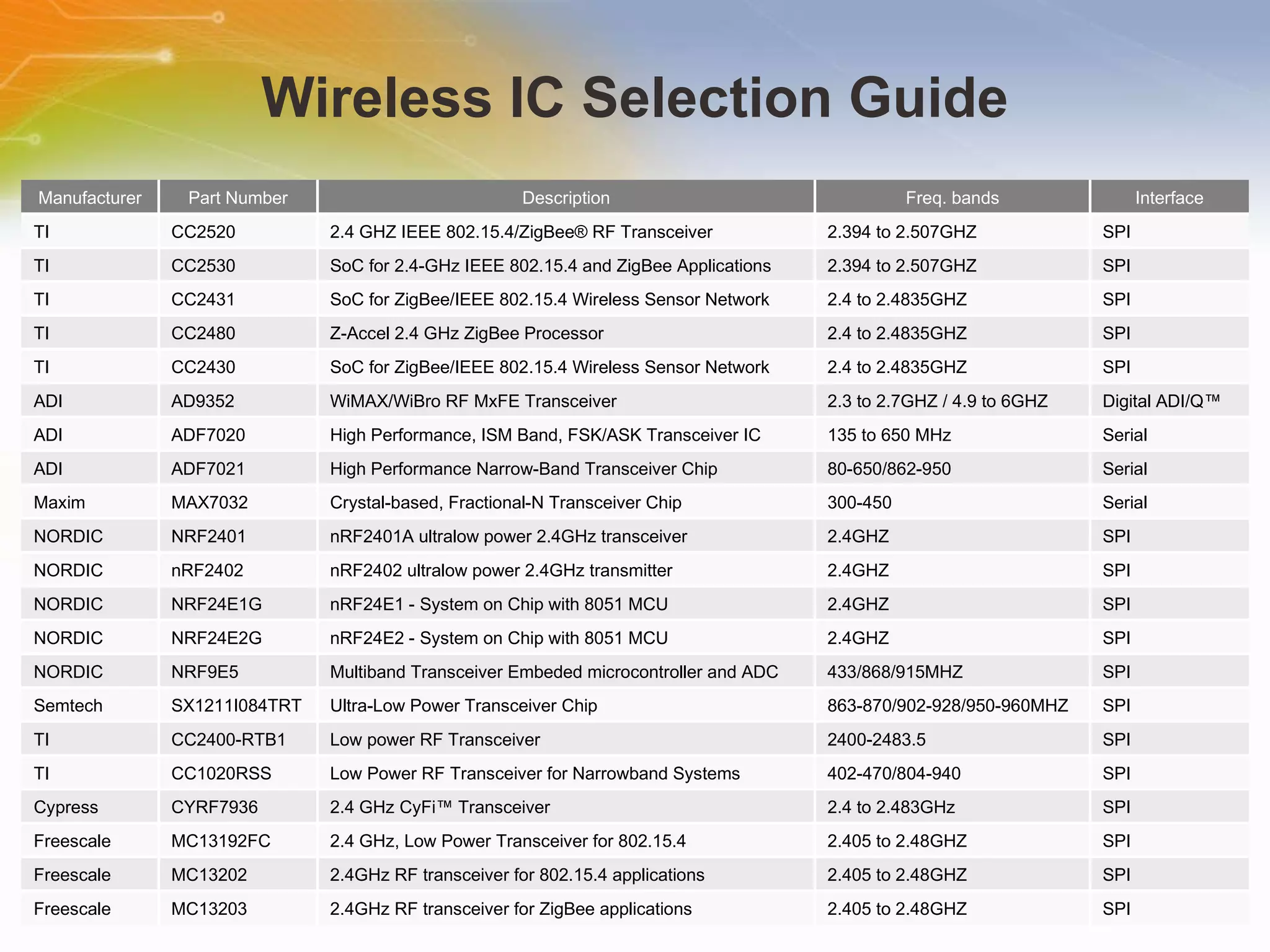
This document introduces solutions for handheld laser barcode scanners. It provides recommendations for core chips, laser diodes, drivers, motors, wireless modules, and other peripherals suitable for barcode scanning applications. Tables list part numbers and specifications for various components from manufacturers like TI, Microchip, Cypress, and Nordic. Additional resources are provided for technical support and purchasing components.