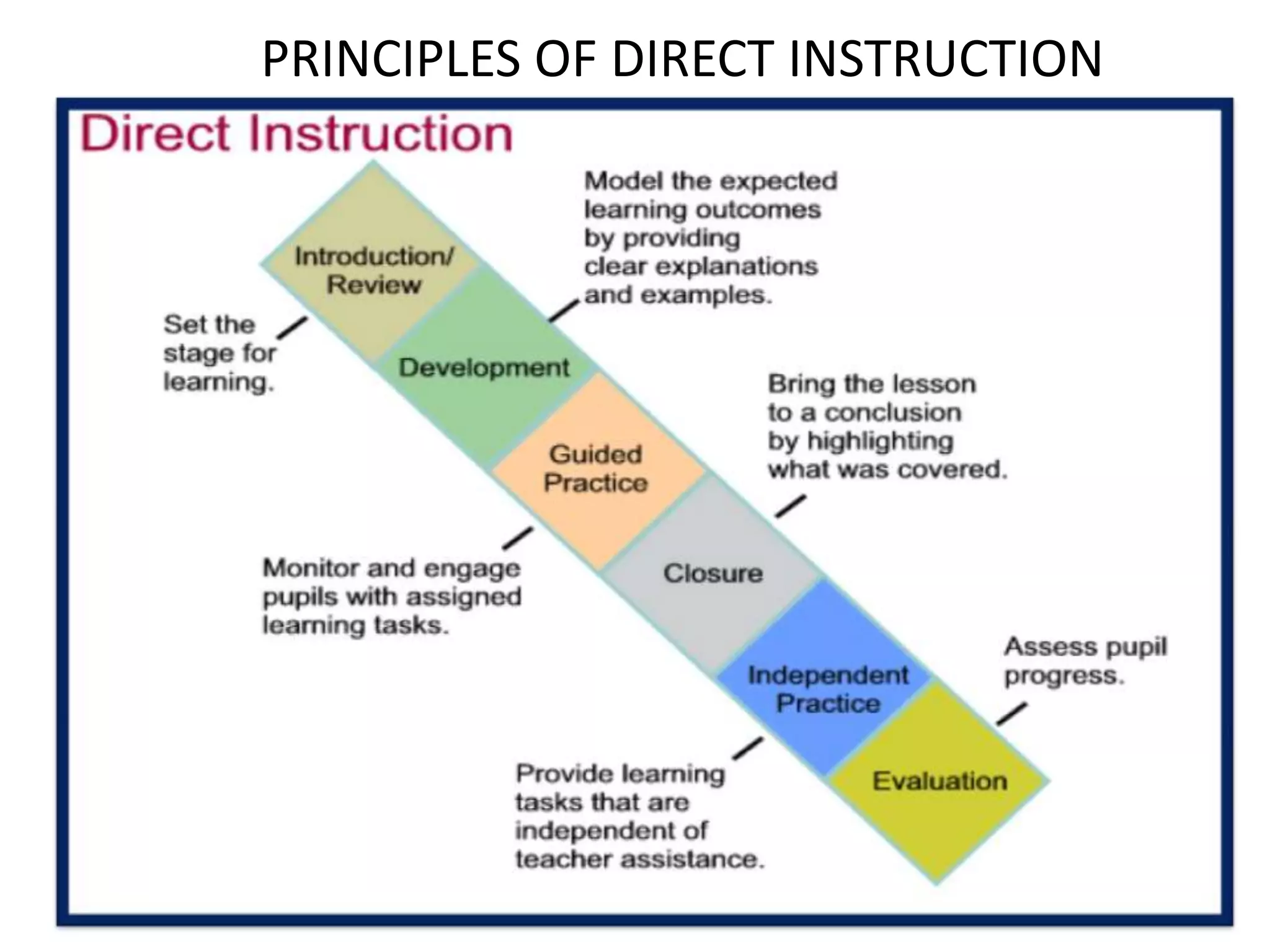
Direct instruction is a teaching strategy that relies on strict lesson plans and lectures from the teacher with little room for variation. It is teacher-directed with specific steps to guide students toward clearly defined learning outcomes. Some key characteristics include an academic focus on content, whole-class or small-group delivery, and constant monitoring to check for understanding from students. The principles of direct instruction include introducing new topics, providing clear explanations and examples while checking for understanding, guided practice with monitoring, and concluding lessons with independent practice and evaluation.