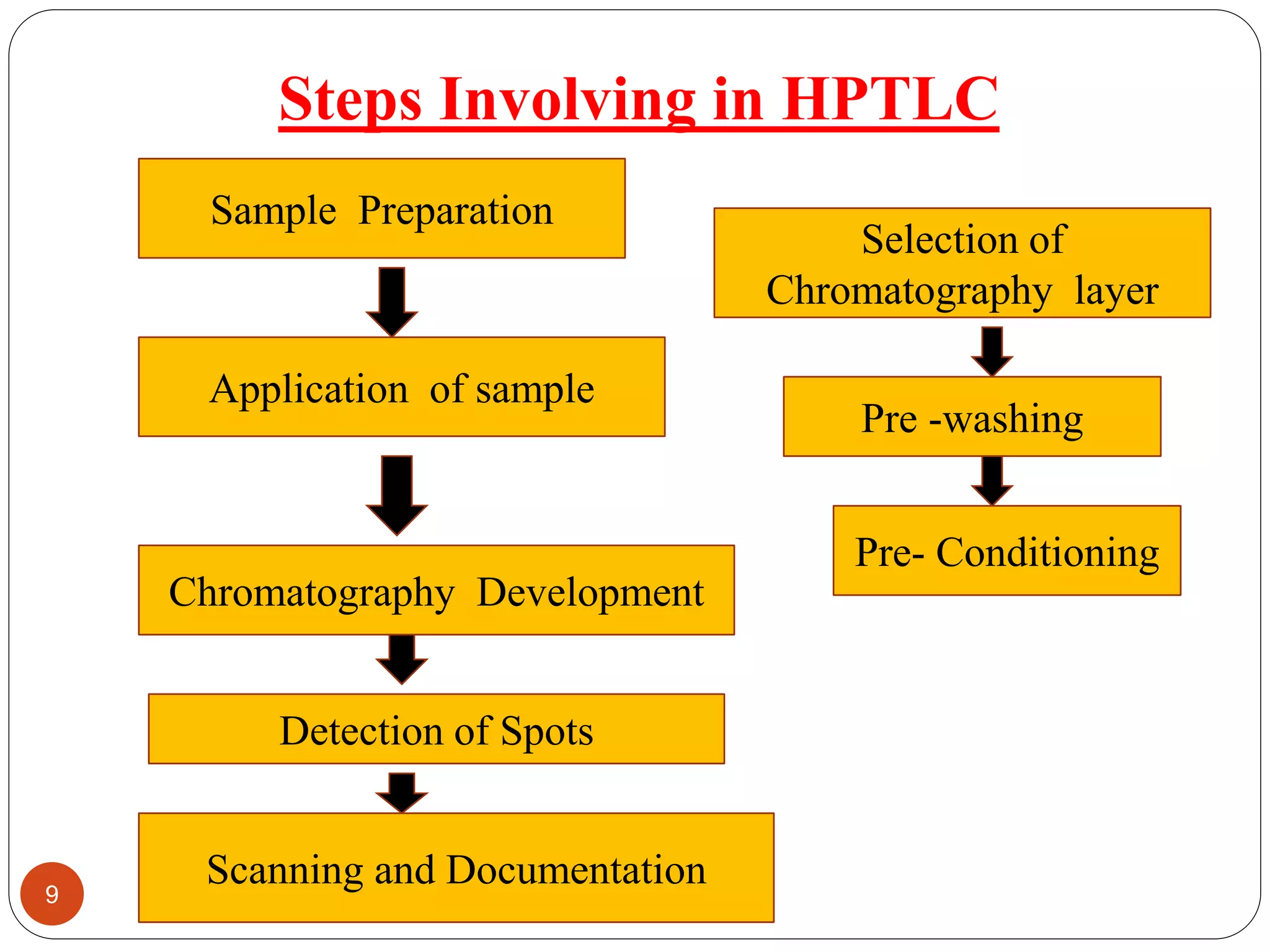
This document provides a comprehensive overview of High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC), highlighting its principles, differences from traditional TLC, and various steps involved in the HPTLC process. Key features include simultaneous sample processing and low analysis costs, with applications across pharmaceutical, food analysis, clinical, industrial, and forensic fields. The document details materials used, mobile phases, sample preparation, chromatographic development, and detection methods for effective analysis.