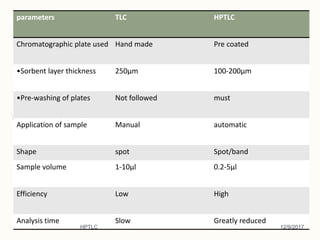
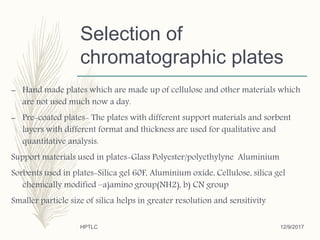
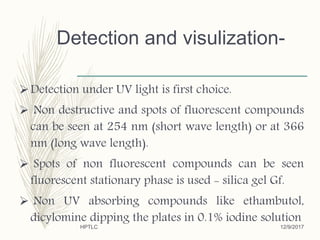
Mr. Amit H. Kanse from Rajgad Dnyanpeeth College of Pharmacy presented on quality assurance techniques using High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC). HPTLC is an automated, sophisticated form of TLC that allows for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of multiple samples simultaneously. It has higher efficiency and resolution than TLC due to factors such as smaller particle size, shorter migration distances, and automated functionality. The presentation covered the principles, instrumentation, steps like sample preparation and detection, and applications of HPTLC in fields like pharmaceuticals, forensics, and environment analysis.