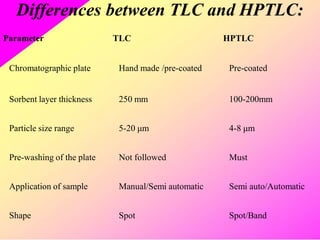
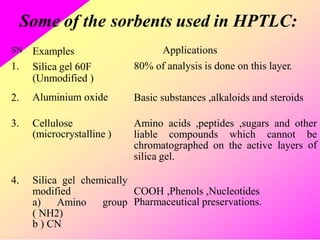
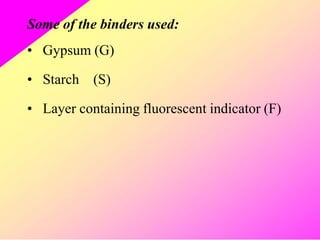
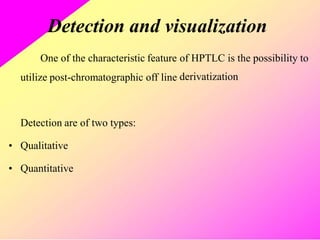
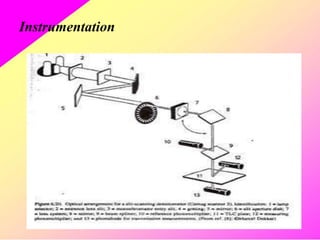
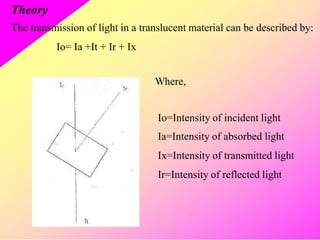
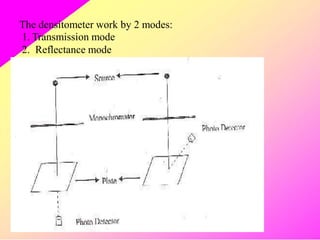
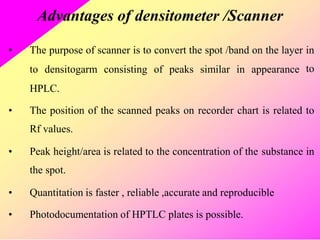
HPTLC is an improved form of TLC that utilizes a conventional TLC technique in a more optimized way. It allows for multiple sample application on pre-coated plates with thin adsorbent layers, providing simple, precise and reproducible chromatography. Key advantages of HPTLC over TLC include improved resolution, sensitivity and reproducibility due to thinner adsorbent layers and ability to apply many samples simultaneously. Detection methods for HPTLC include visualizing spots on the plate as well as instrumental analysis using a densitometer to directly measure components without elution. Proper sample preparation and selection of mobile phase and developing conditions are important for achieving good separation and resolution of components through HPTLC analysis.