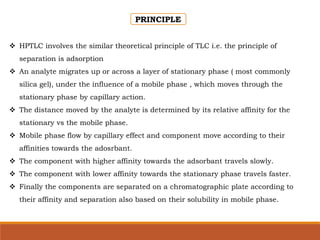
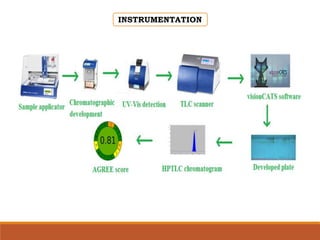
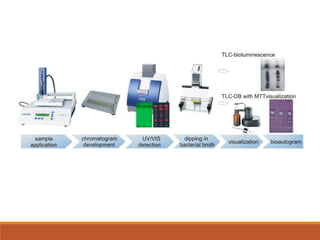
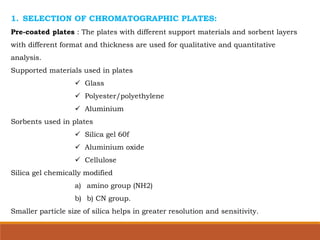
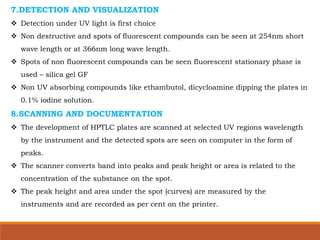
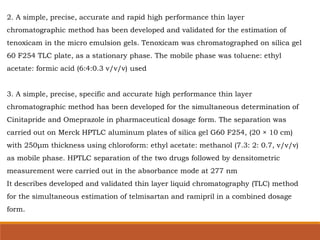
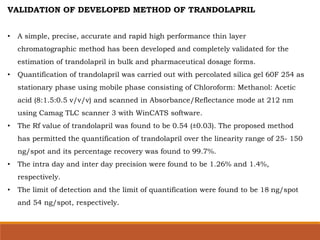
The document discusses the development, validation, and application of High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) as an advanced form of thin-layer chromatography, emphasizing its superior resolution and analytical capabilities for various substances, particularly botanicals and pharmaceuticals. It provides detailed methodology, including sample preparation, chromatographic development, and detection techniques, along with examples of validated methods for estimating various drugs in different formulations. Additionally, the document highlights the advantages and applications of HPTLC, such as low costs, multiple detection methods, and efficient data processing.














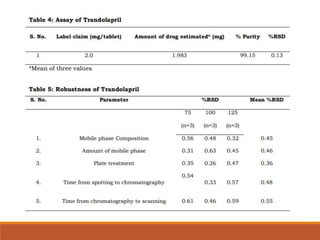
![• The proposed method can be successfully applied for the estimation of drug
content of different marketed formulations simultaneously on a single plate and
provides a faster and cost effective quality control tool for routine analysis of
trandolapril as bulk drug and in tablet dosage forms.
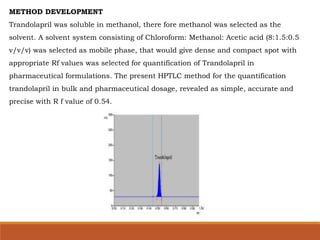
TRANDOLAPRIL
• Trandolapril, chemically, it is (2S, 3aR, 7aS)-1-[(S)-N-[(S)-1-carboxy-3-
phenylpropyl] alanyl] hexahydro-2- indolinecarboxylic acid, 1-ethyl ester [1] and is
not official in any pharmacopoeia.
• Trandolapril is an orally administered angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor
that has been used in the treatment of patients with hypertension and congestive
heart failure, and myocardial infarction. Literature survey revealed that few HPLC
methods were reported for the estimation of trandolapril in the biological fluids.
The present study illustrates development and validation of a simple, accurate,
precise and specific HPTLC method for the estimation of trandolapril tablet dosage
forms.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hptlc-221013140841-596c0a6c/85/HPTLC-pptx-24-320.jpg)







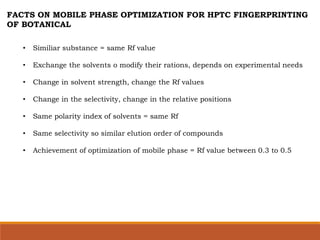

![MOBILE PHASE OPTIMIZATION
STEP 1
• 7 to 12 net solvents for 1-8 selectivity groups
Results
• Suitable RF value
• Too much RF value ( above 0.7 to 0.8) = then exchange solvent
• Too low RF value ( below 0.2 ) = exchange with high polarity solvents
STEP 2
• Dilution with hexane for down the high Rf
• Polar modification with acids or ammonia for increase the lower Rf
STEP 3
• Two solvents combination of different selectivity groups ratio of 1 : 1
• Short cut shunt - solvent of high Rf and solvent of low Rf can be directly
combine with each other.
• [ ratio = 1 : 1 or 10% high Rf solvent in to low Rf solvent, if results are good then
go direct combination of two solvents]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hptlc-221013140841-596c0a6c/85/HPTLC-pptx-42-320.jpg)