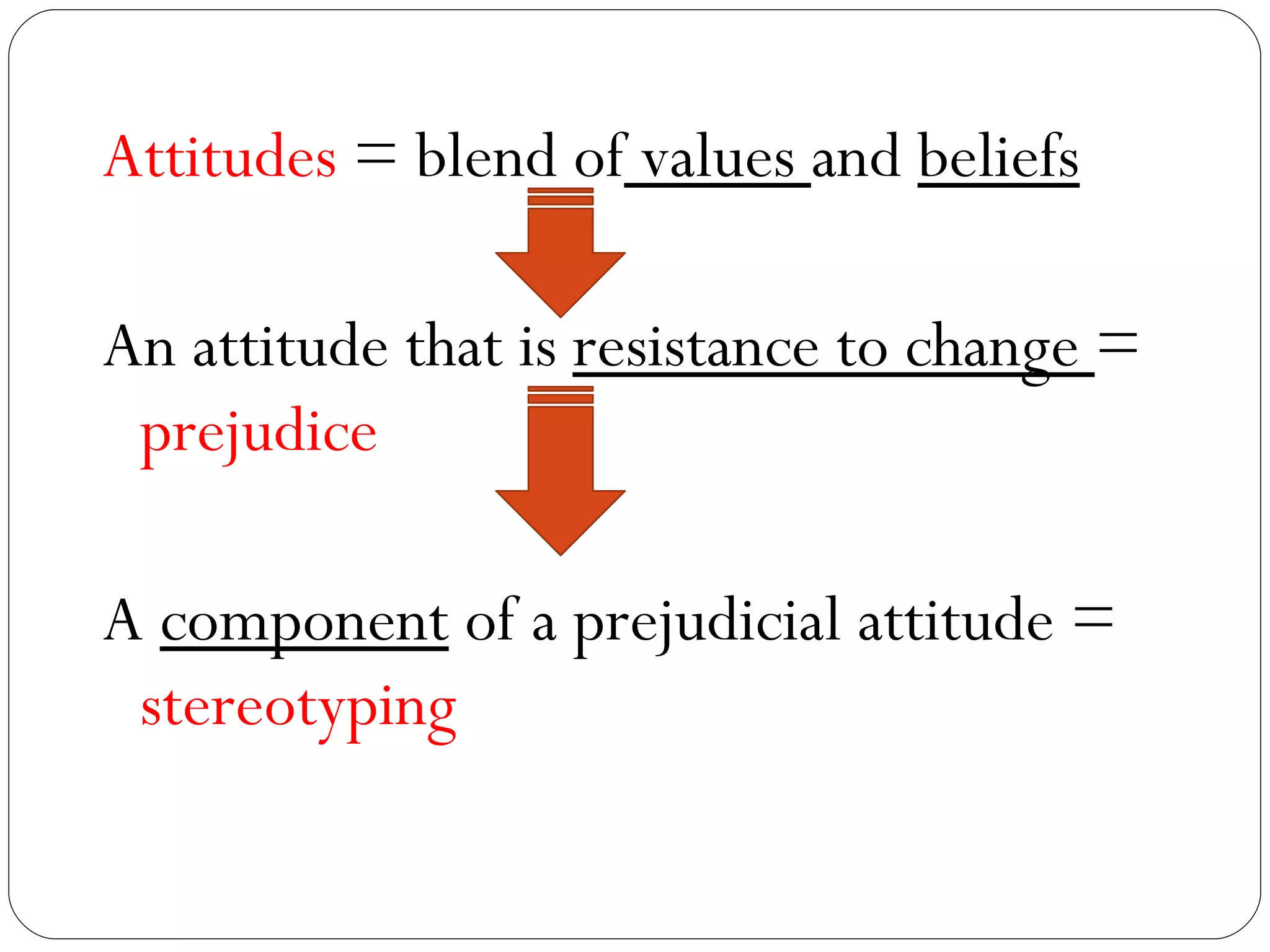
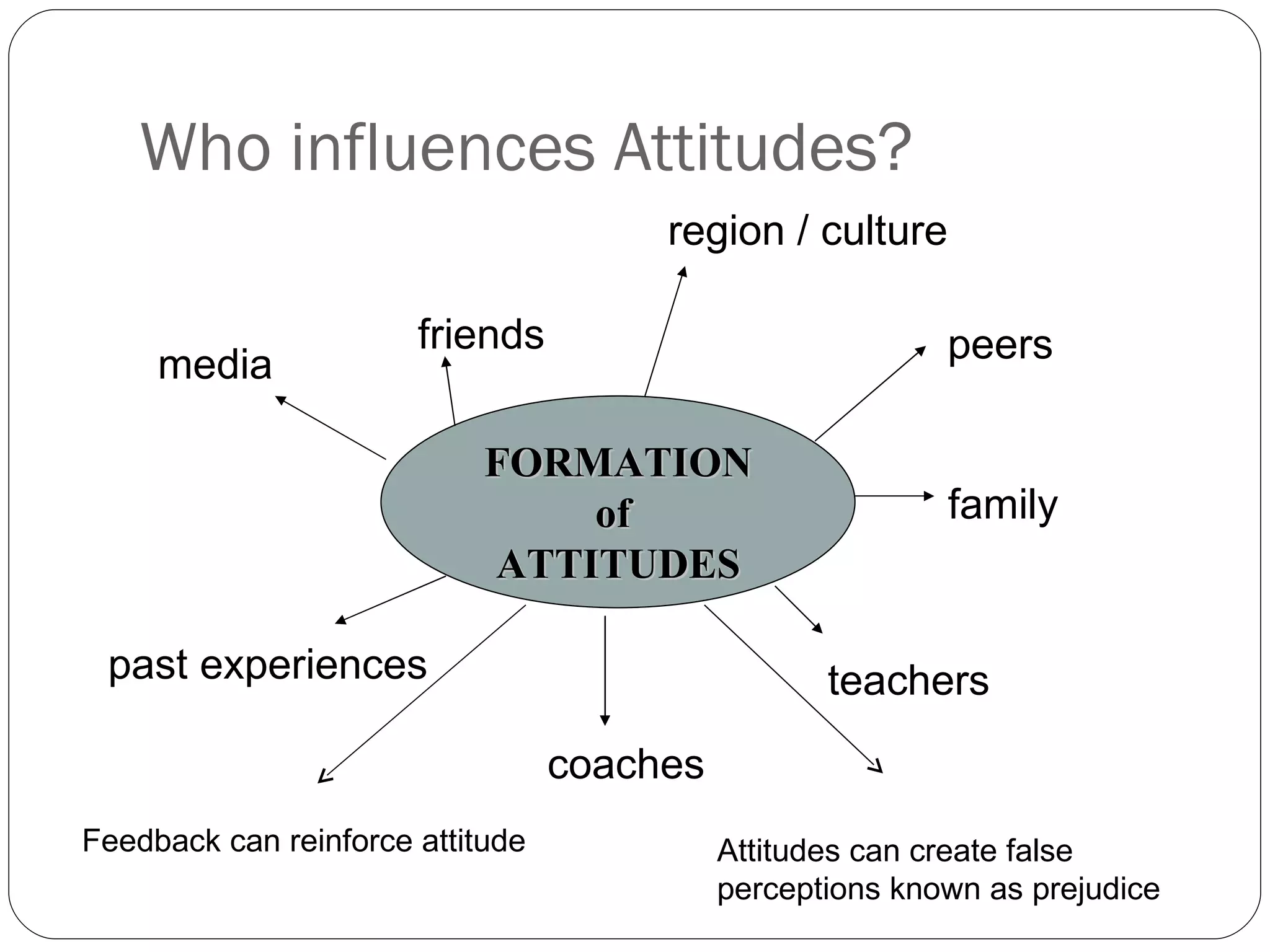
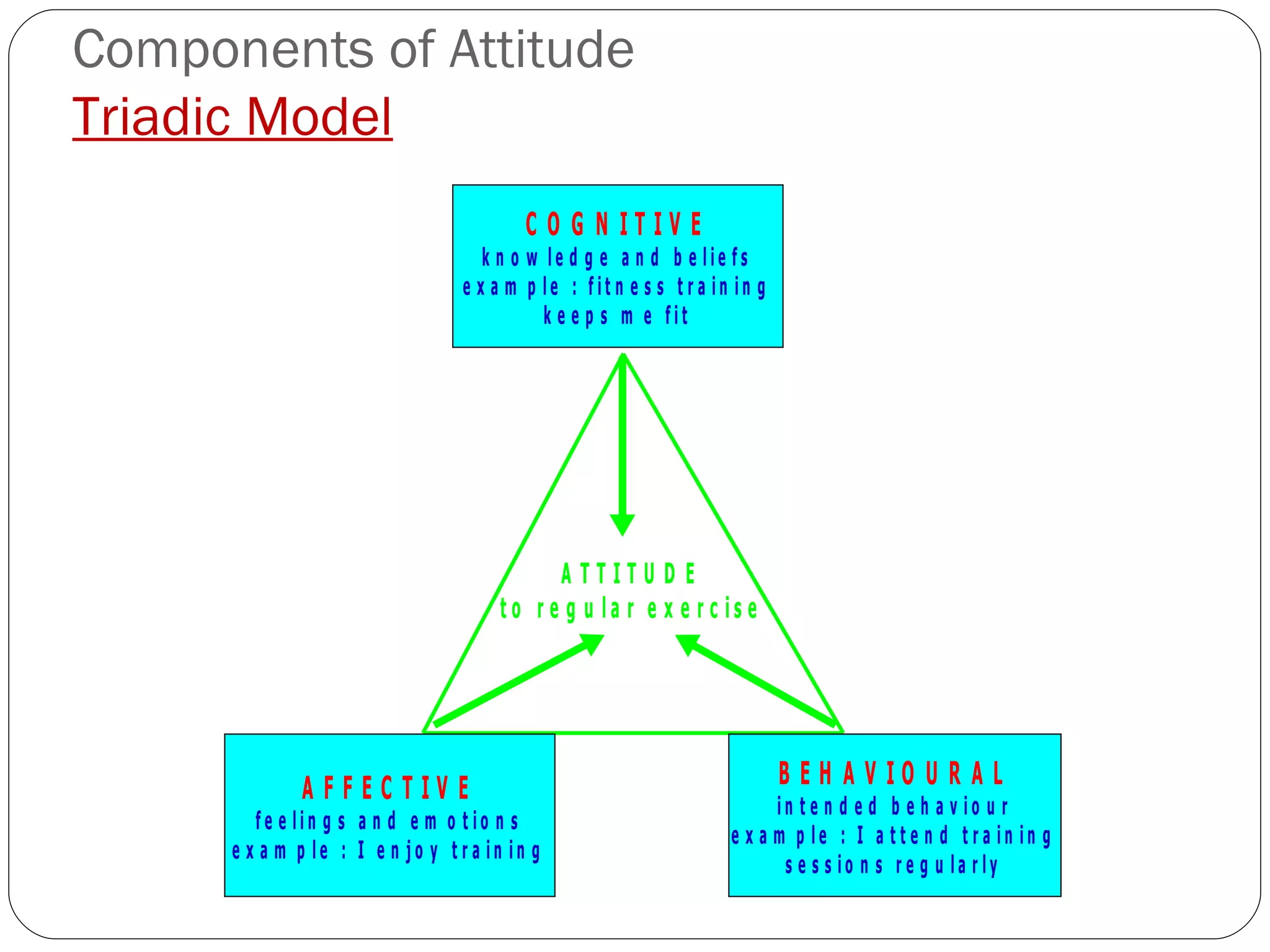
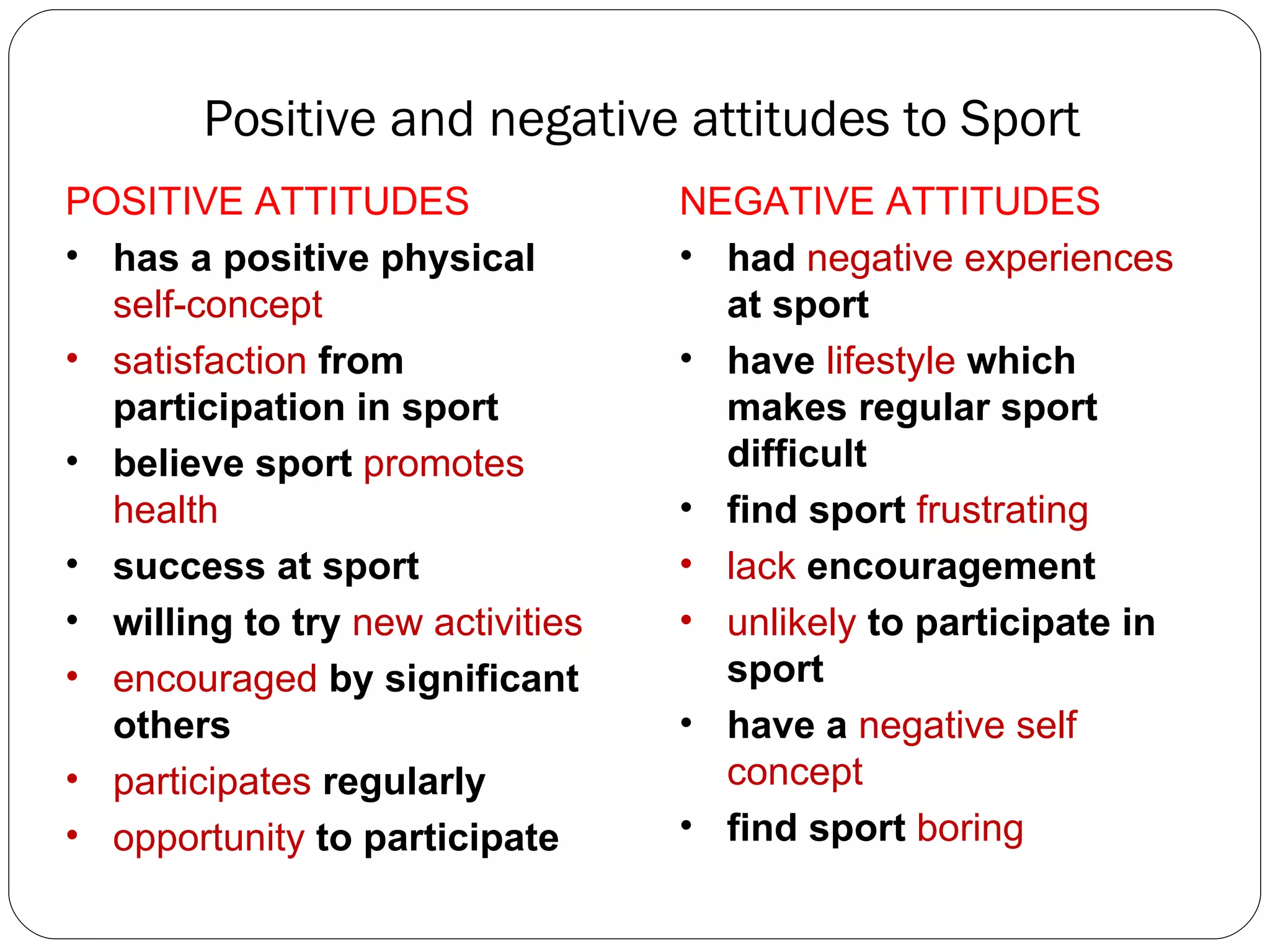
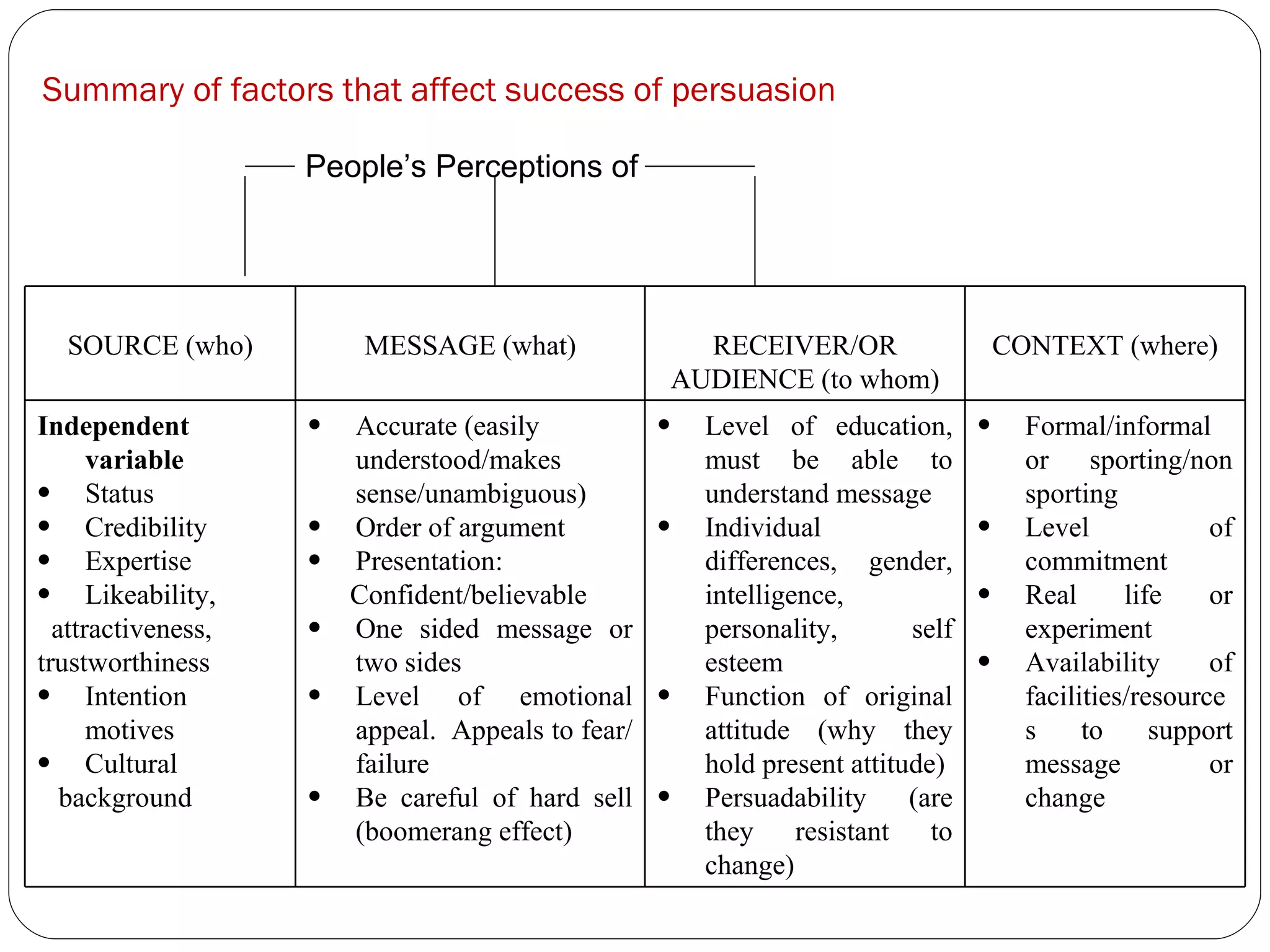
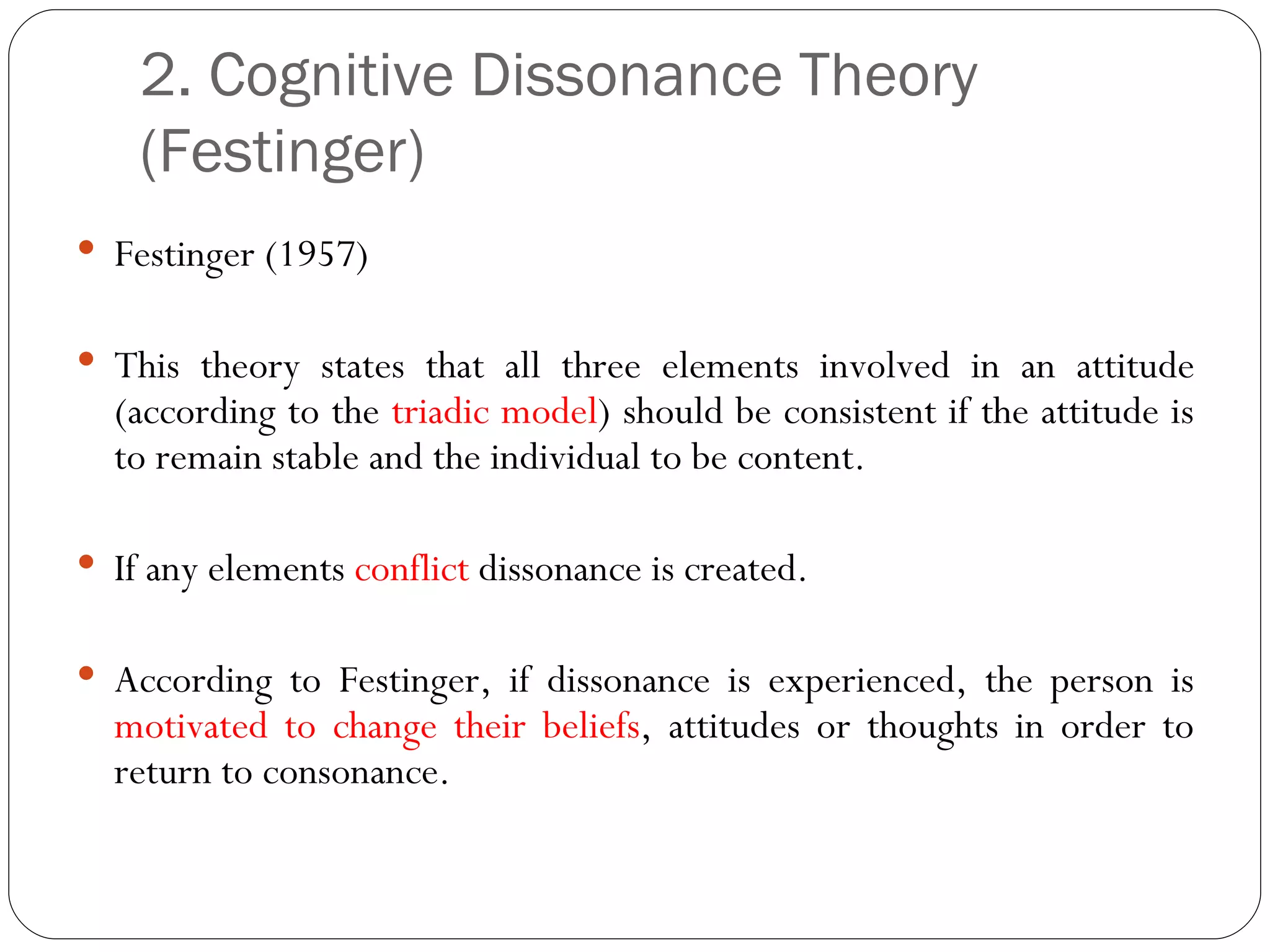
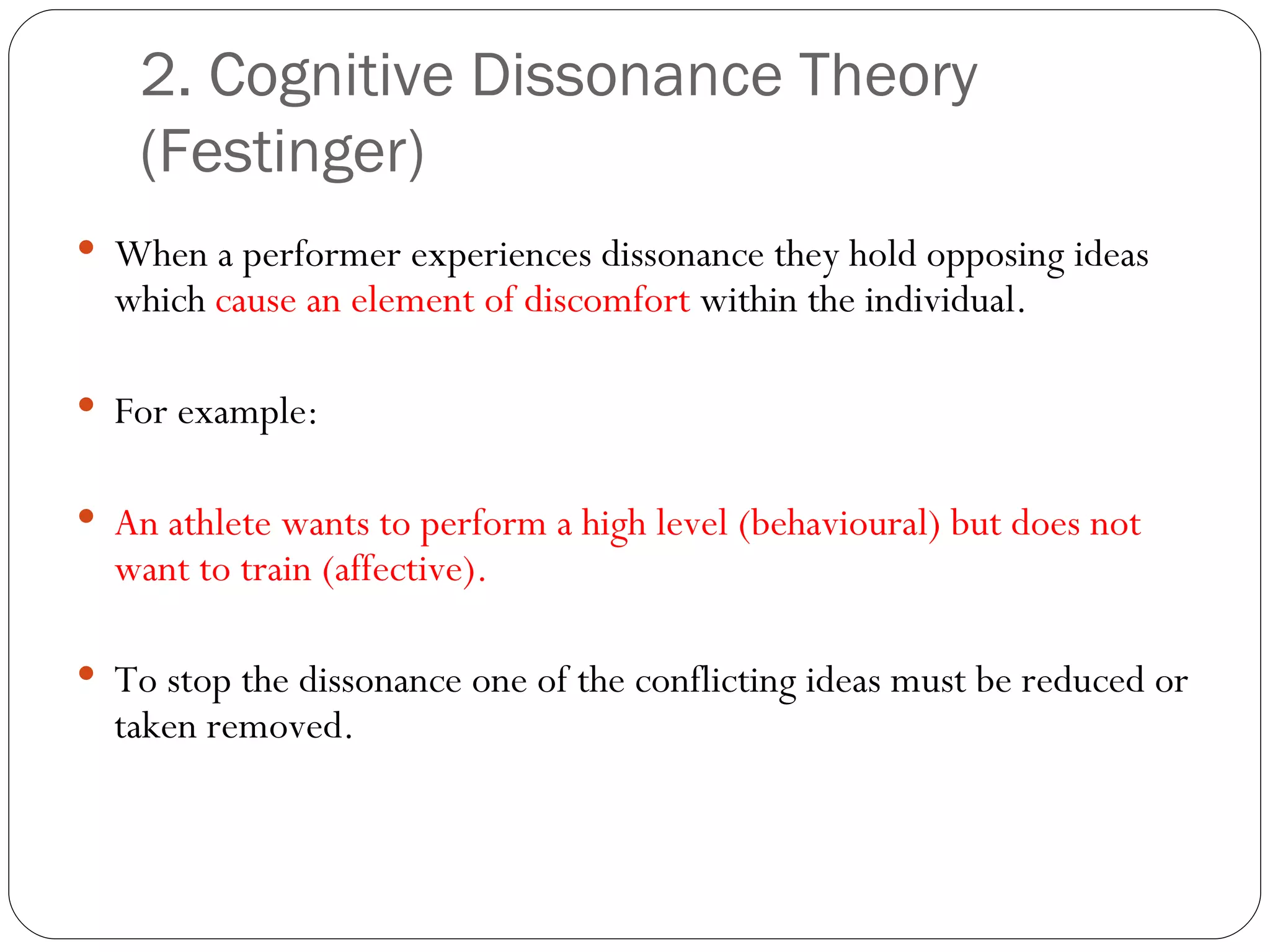
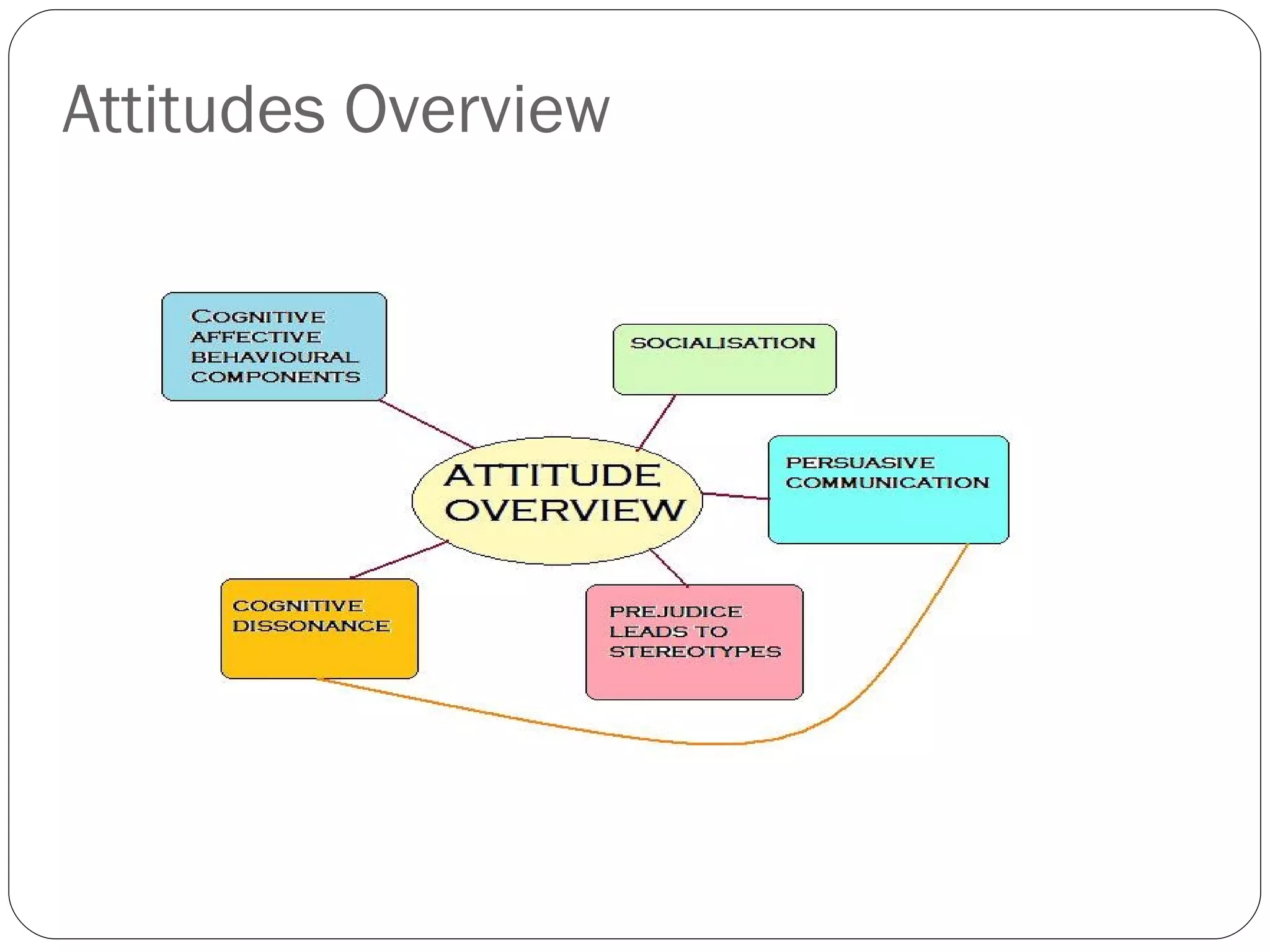
The document discusses attitudes, how they are formed, and how they can influence behavior and performance. It defines attitudes and explains that they have cognitive, affective, and behavioral components. Attitudes are influenced by peers, family, media, and past experiences. They can be changed through persuasive communication that targets the different components of attitudes, or through cognitive dissonance when a person experiences conflicting beliefs and is motivated to resolve the discomfort. Stereotyping and prejudice occur when attitudes are based on false information and are resistant to change.