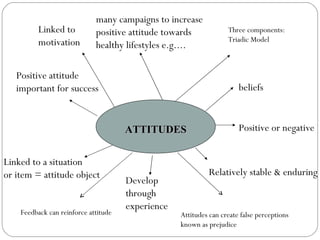
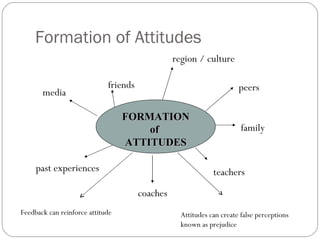
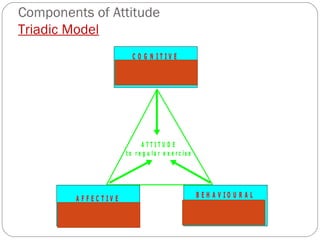
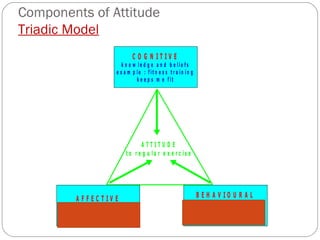
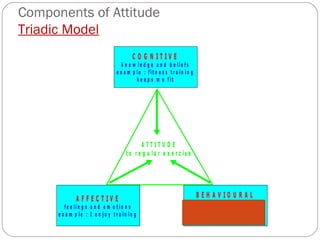
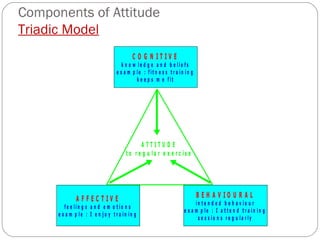
The document discusses attitudes, their formation, components, and relationship to behavior. It defines an attitude as having three components - cognitive, affective, and behavioral. Attitudes are formed through learning and experiences from friends, family, media and other social influences. The document also discusses prejudice and stereotyping, how attitudes can be changed, and strategies to improve attitude like goal setting and rewards. It notes that while attitude predicts behavior, the relationship is not always 100% and other factors can influence whether intentions and plans are carried out.