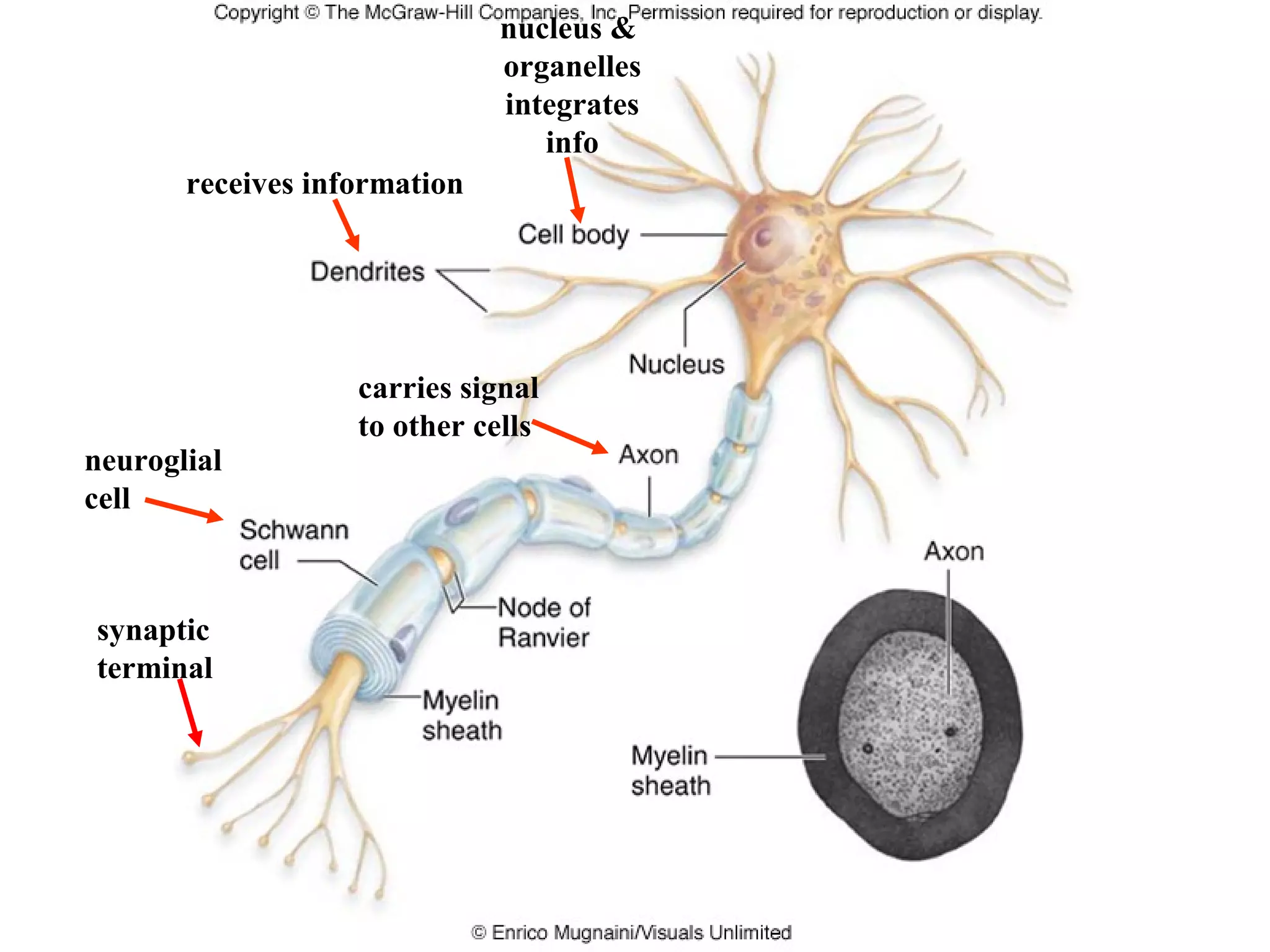
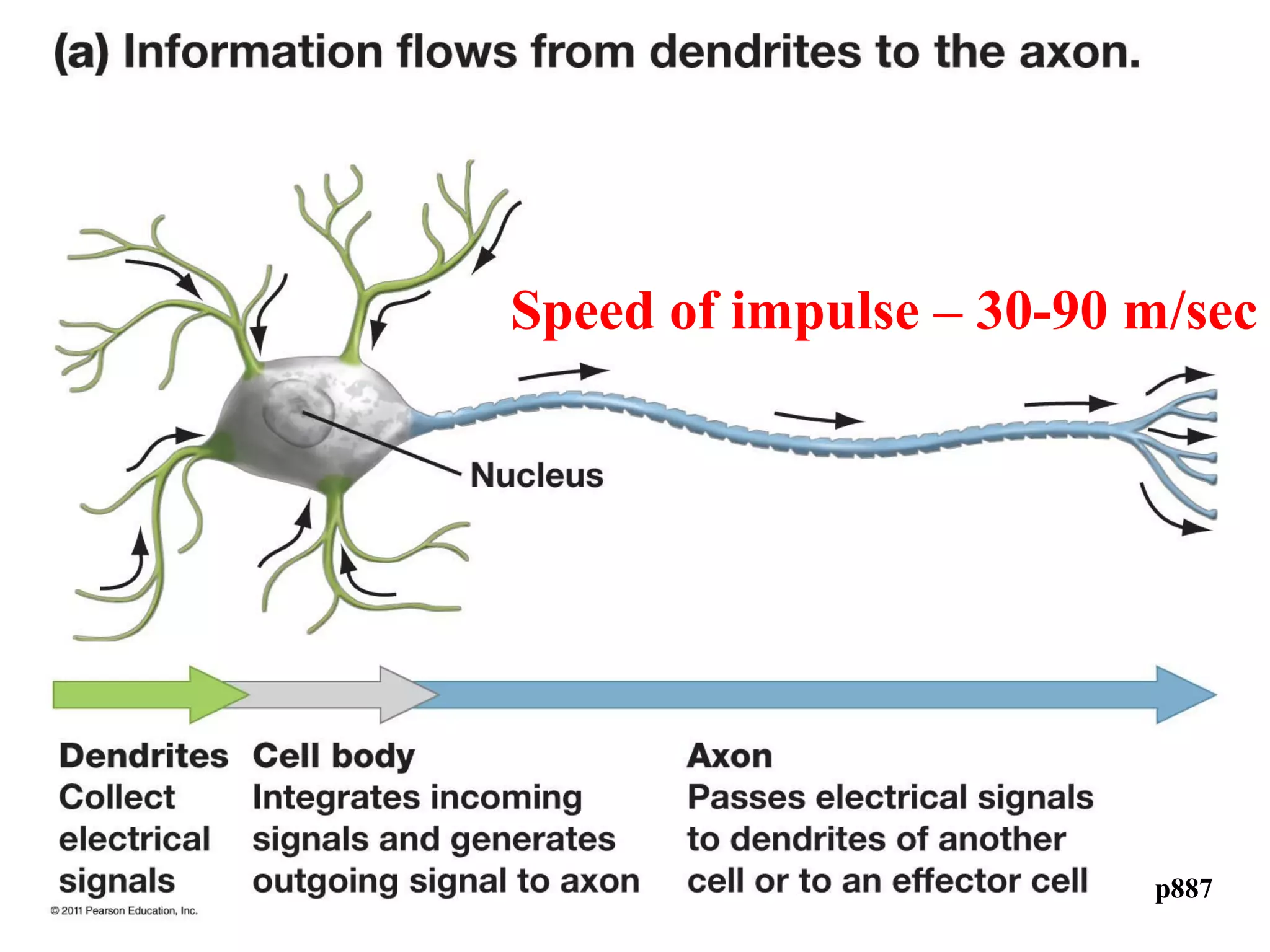
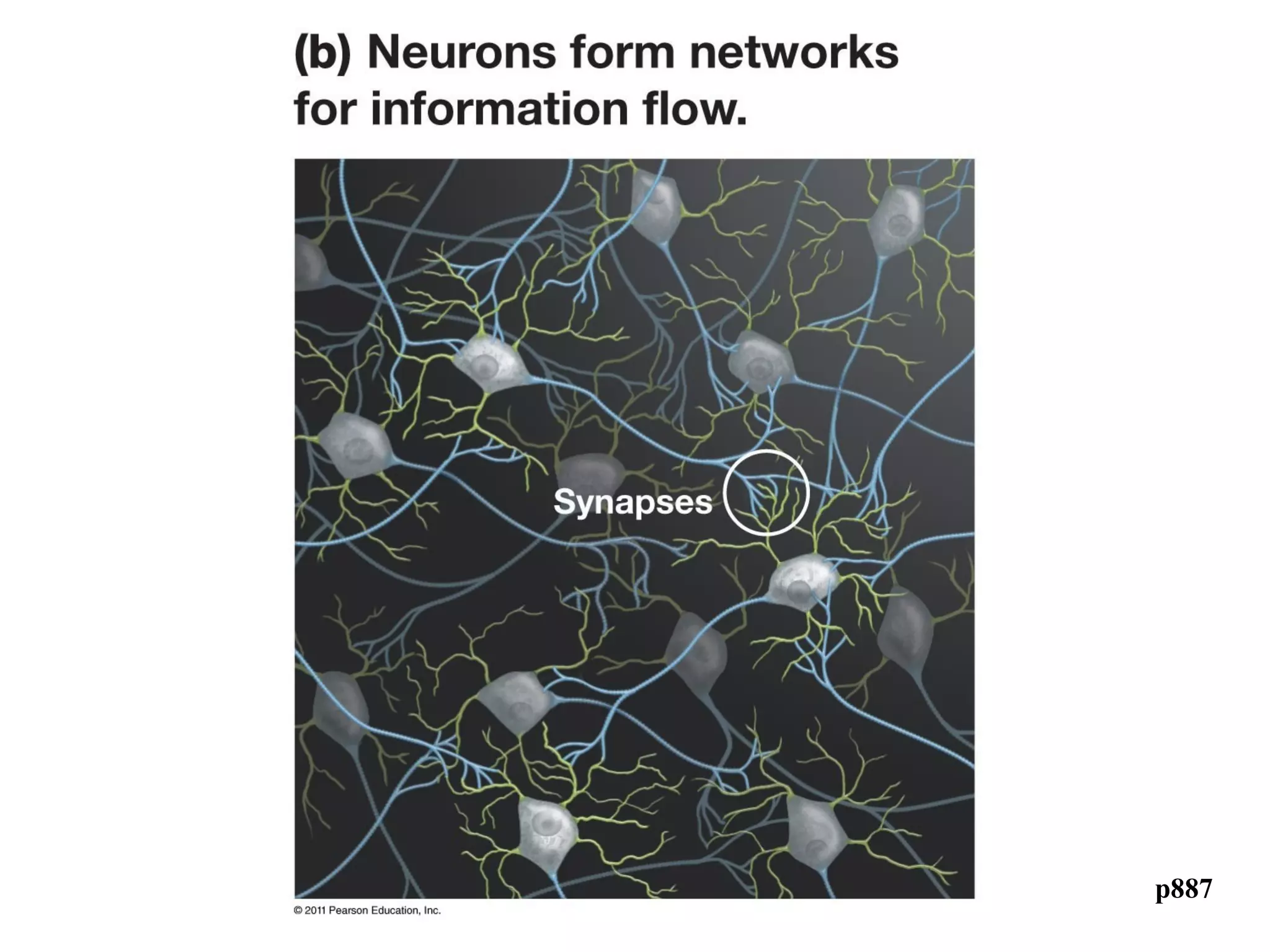
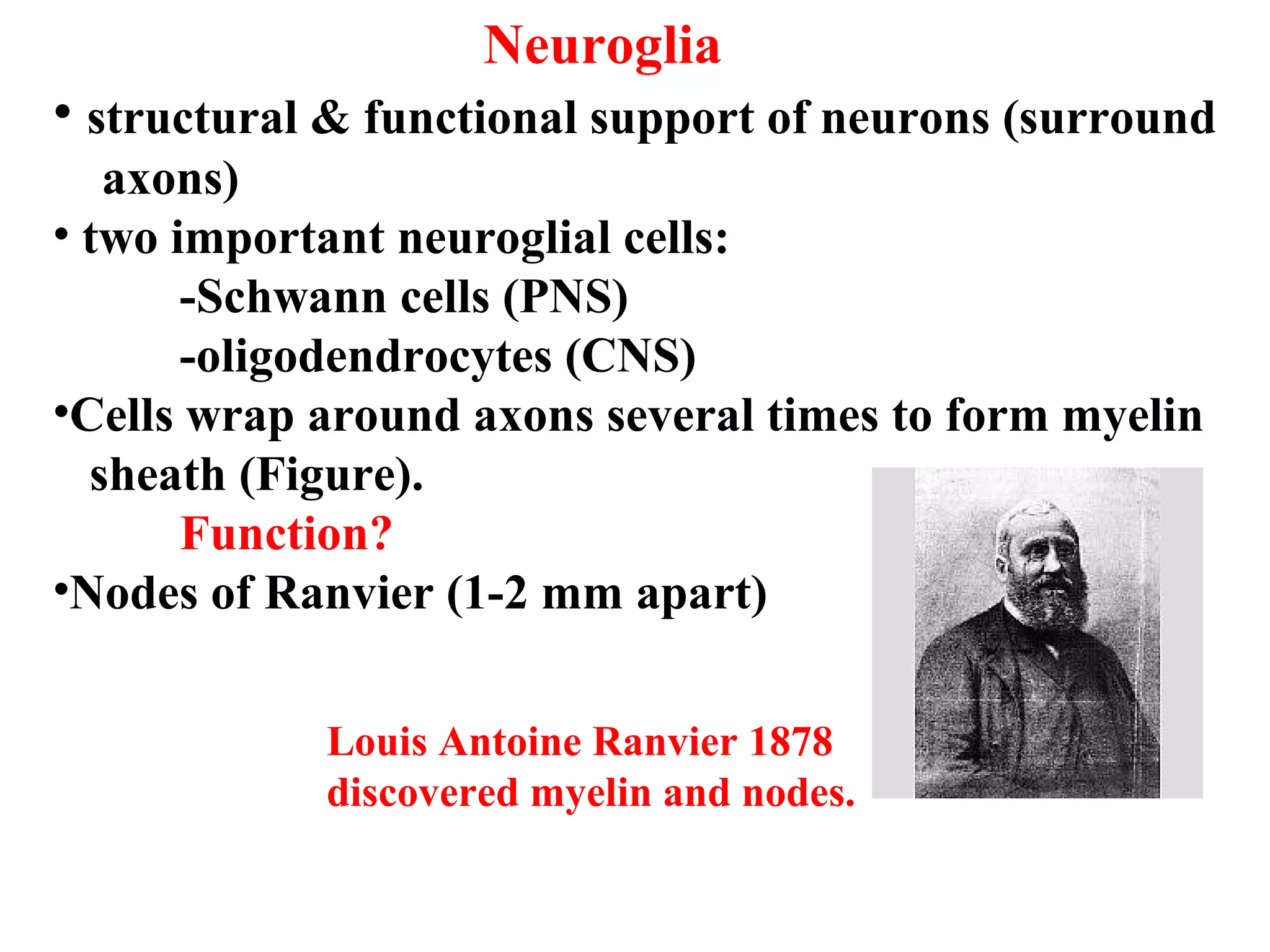
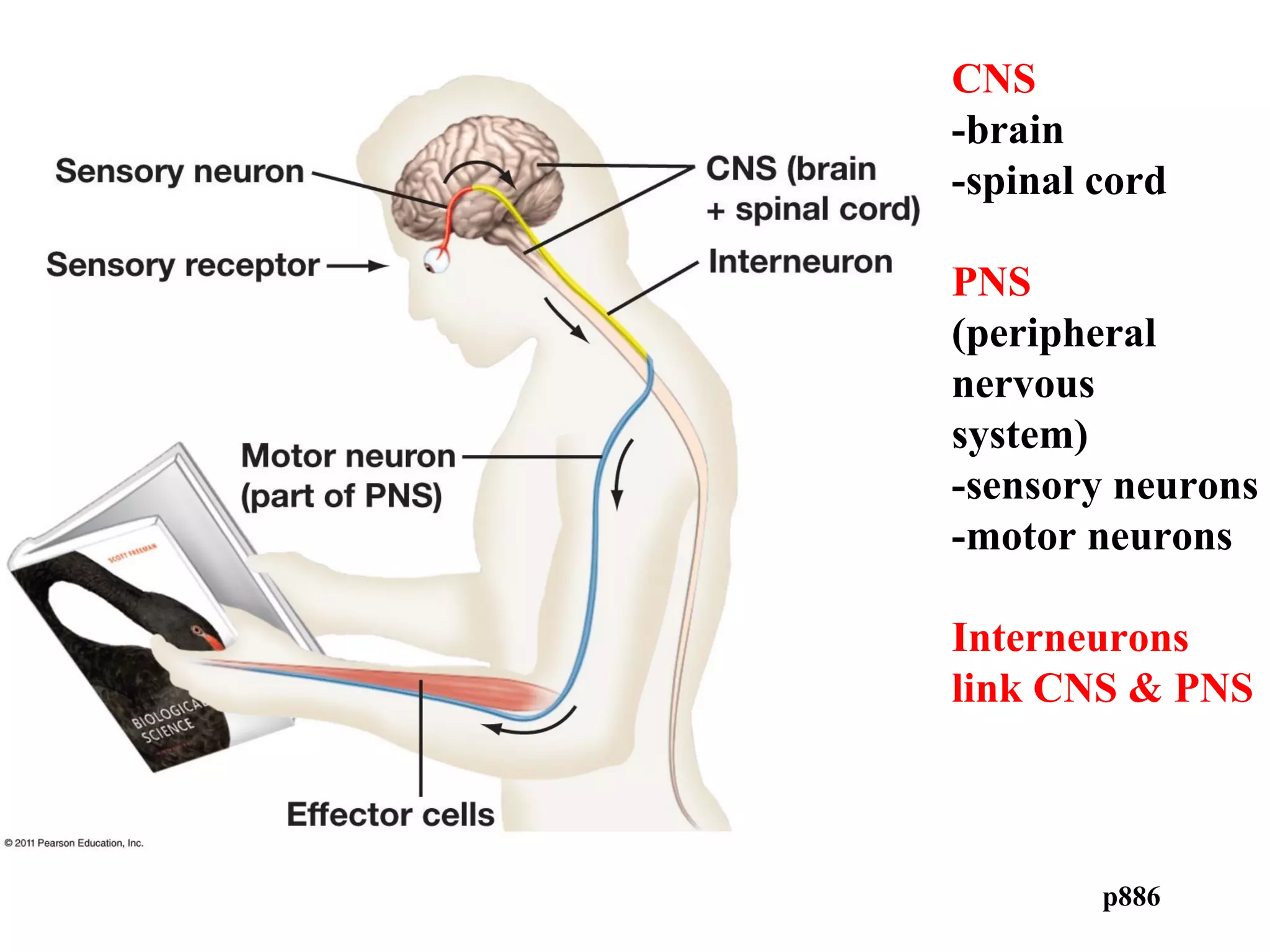
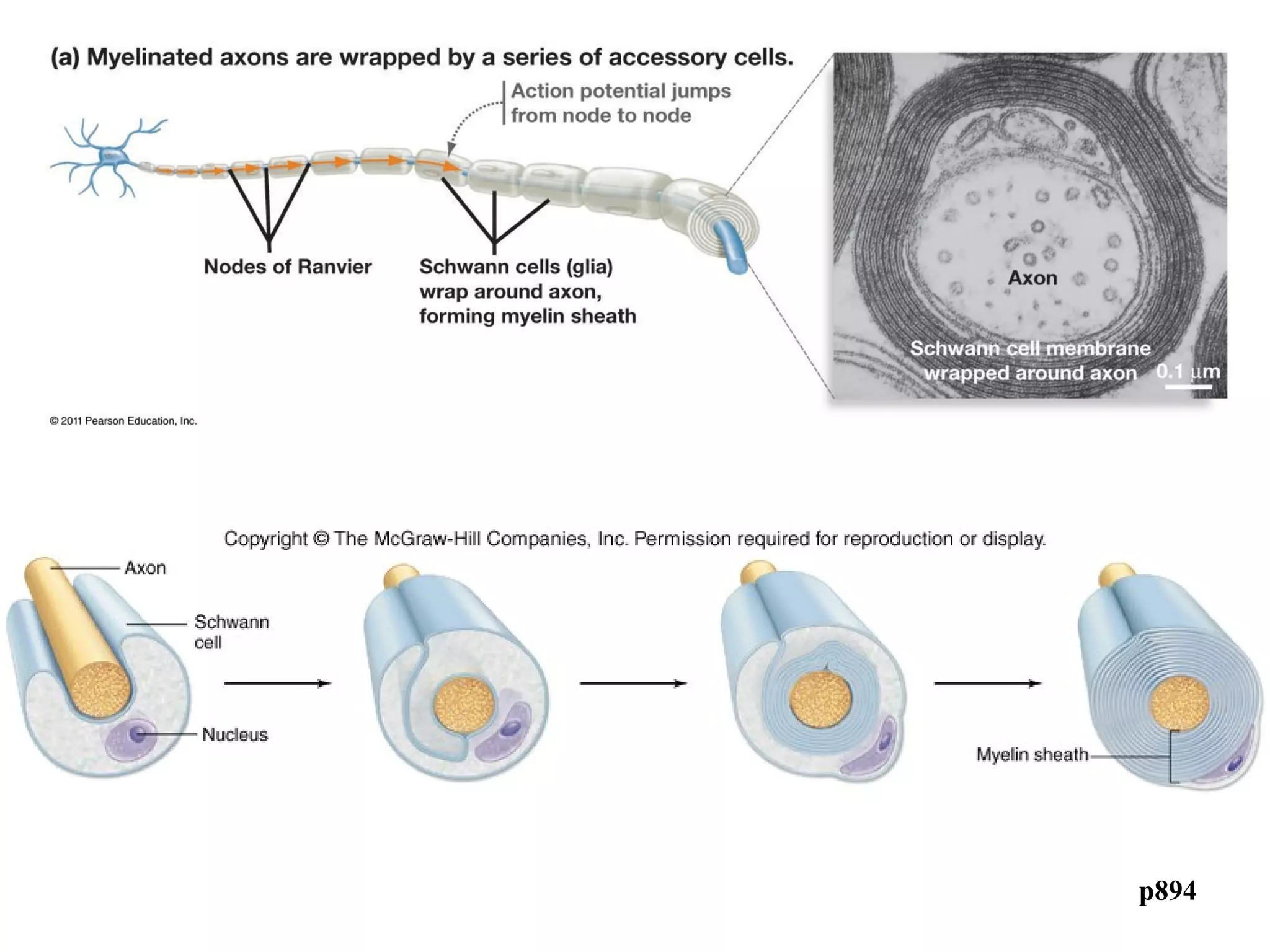
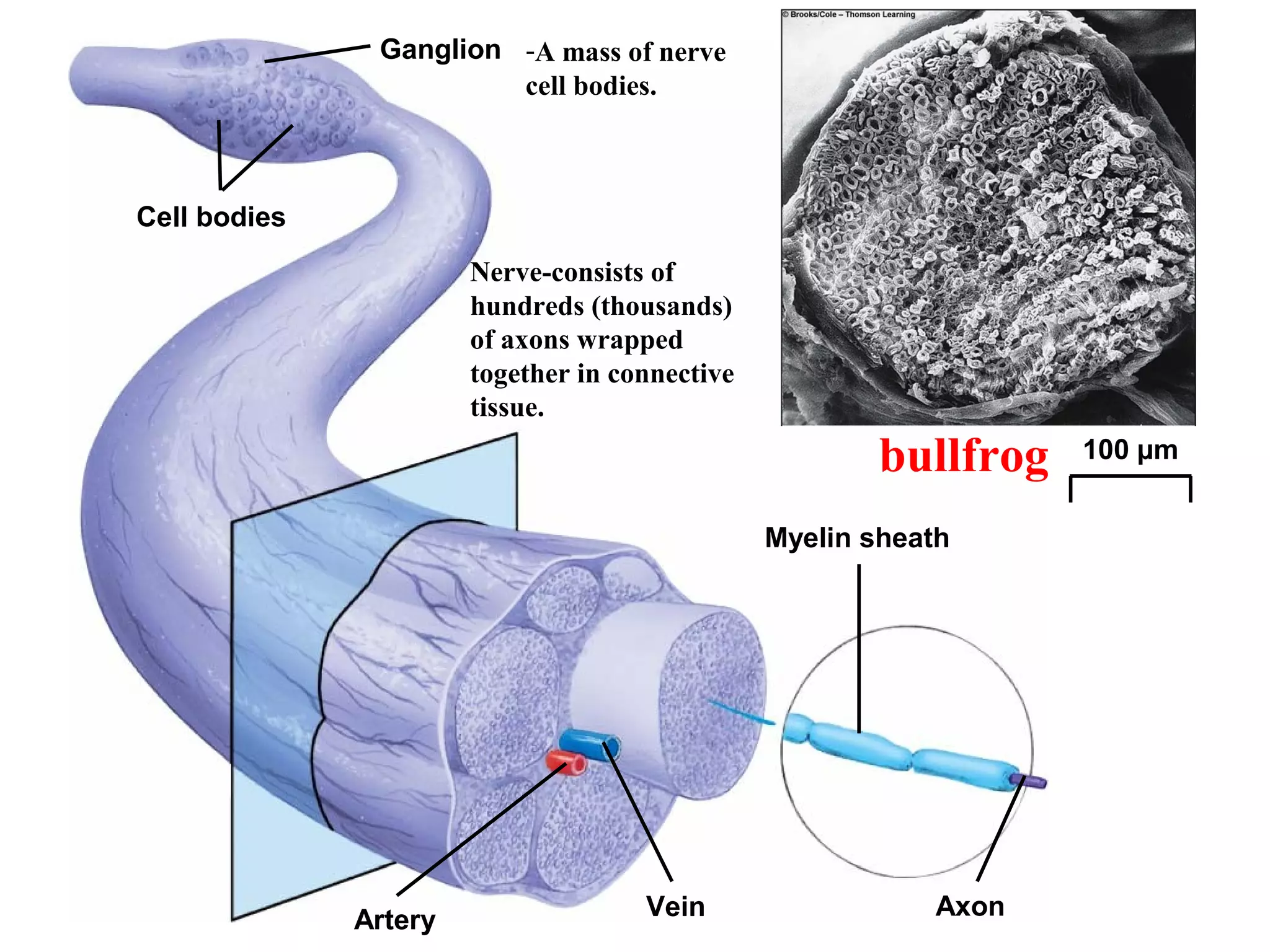
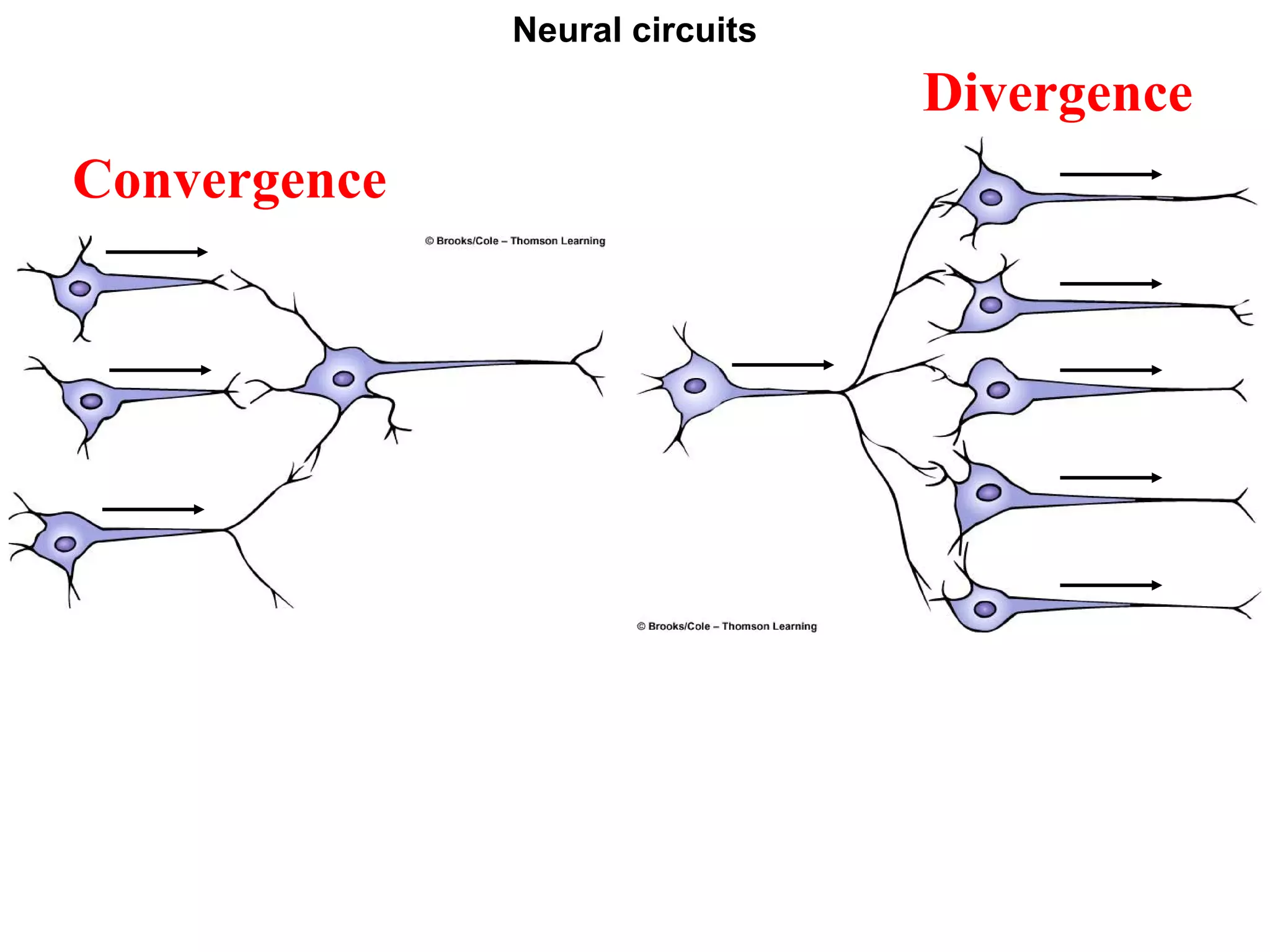
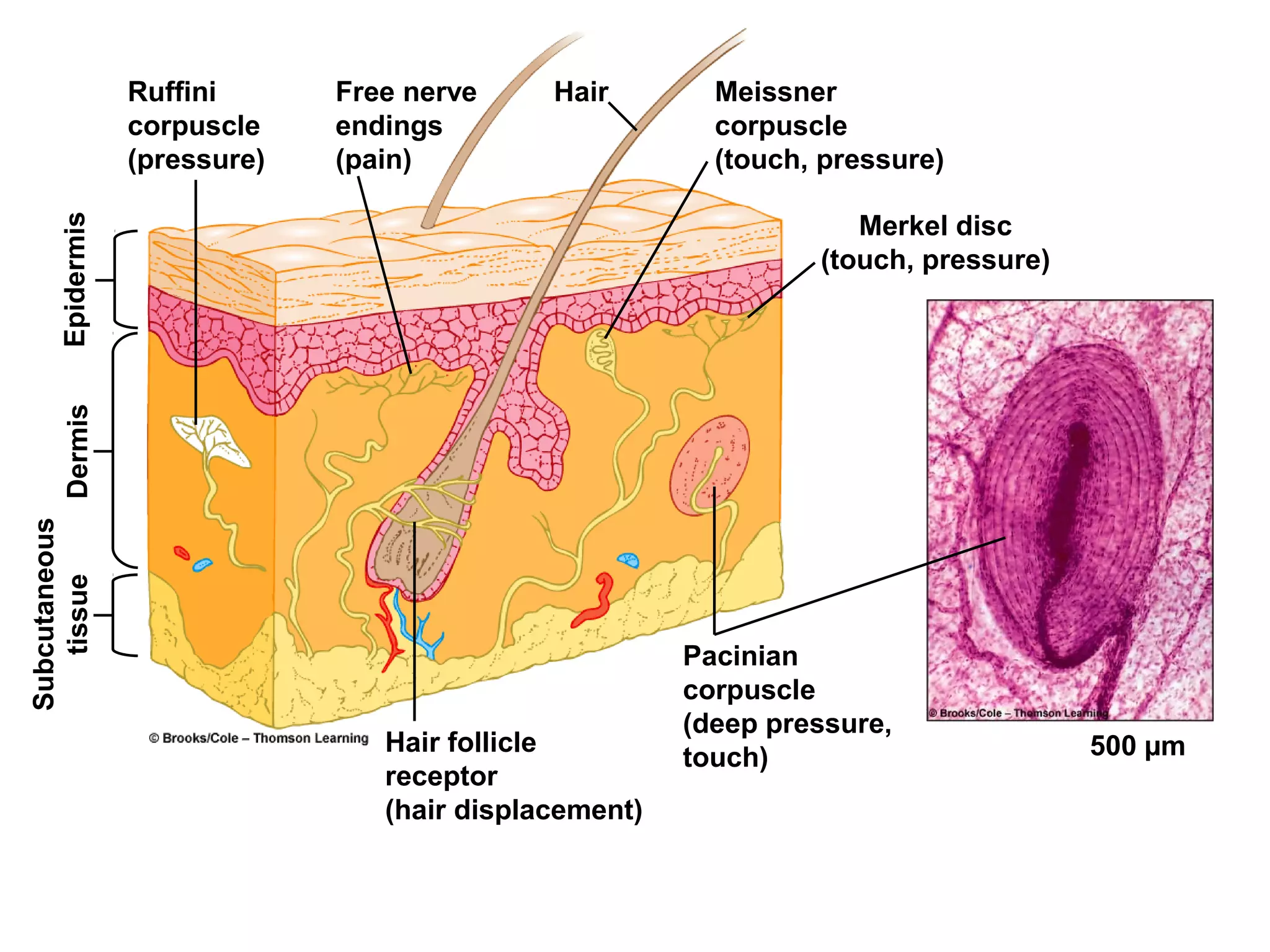
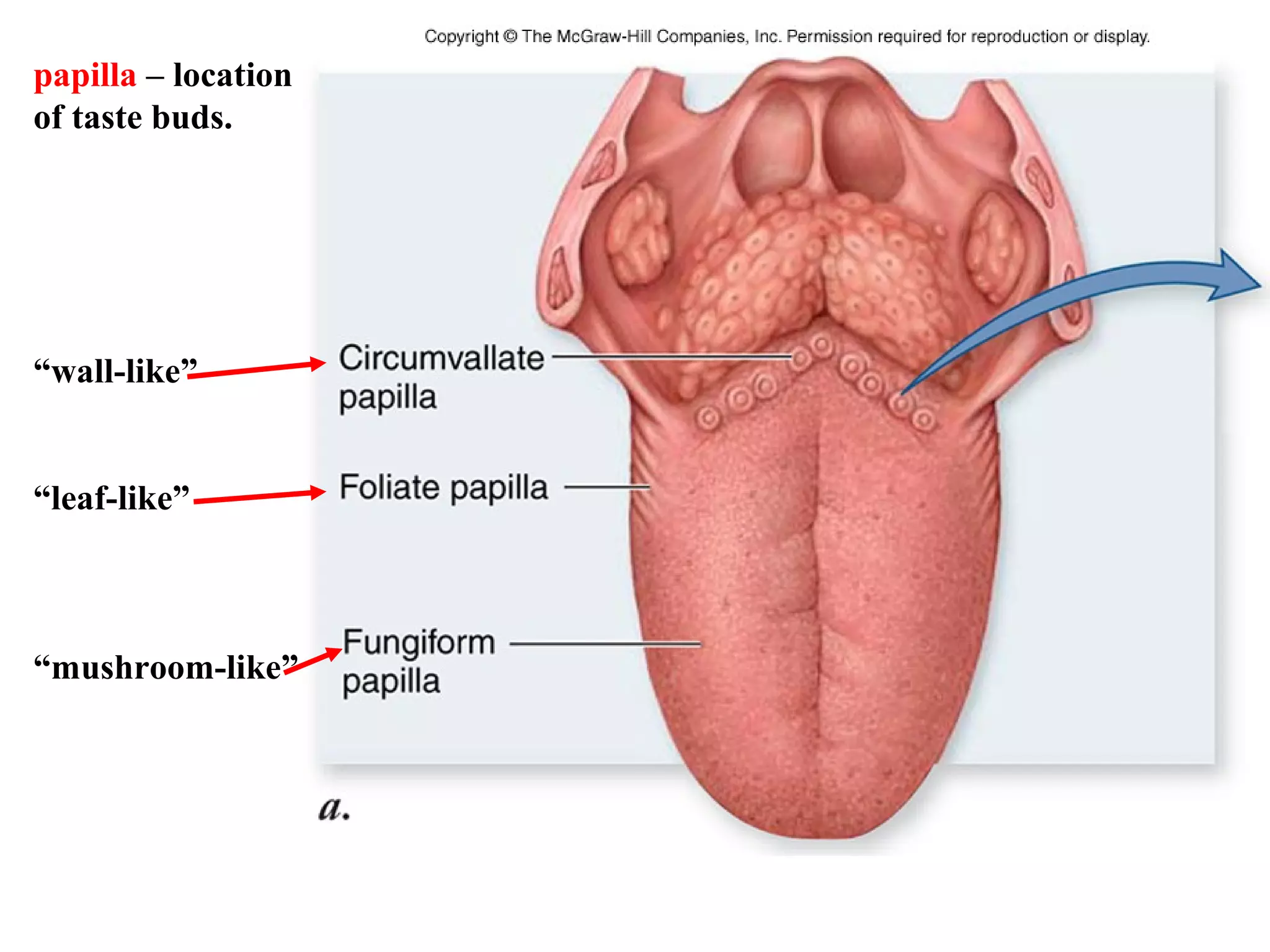
1) Neurons detect stimuli and transmit signals along their axons via electrical impulses. Neuroglial cells structurally and functionally support neurons.
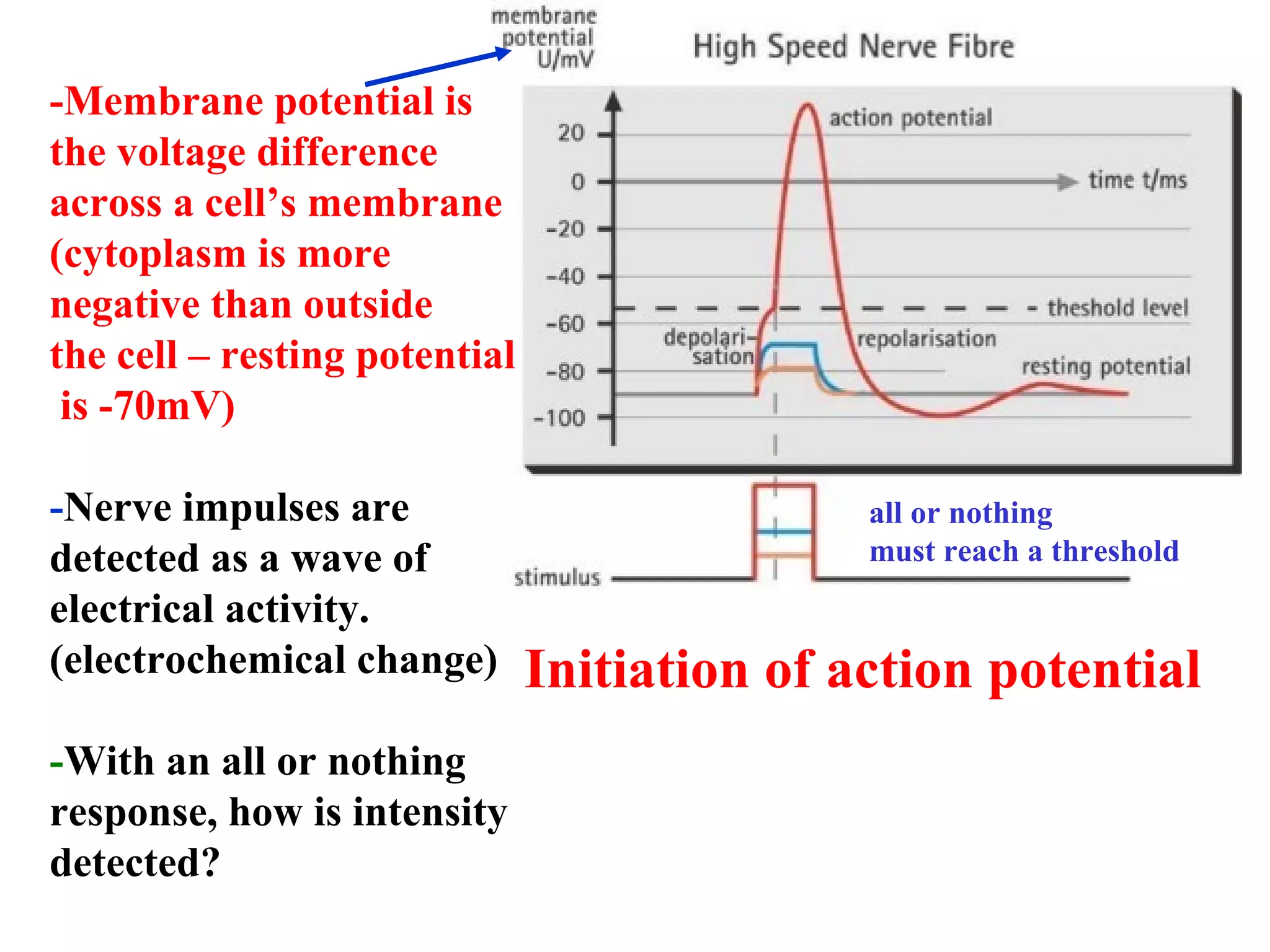
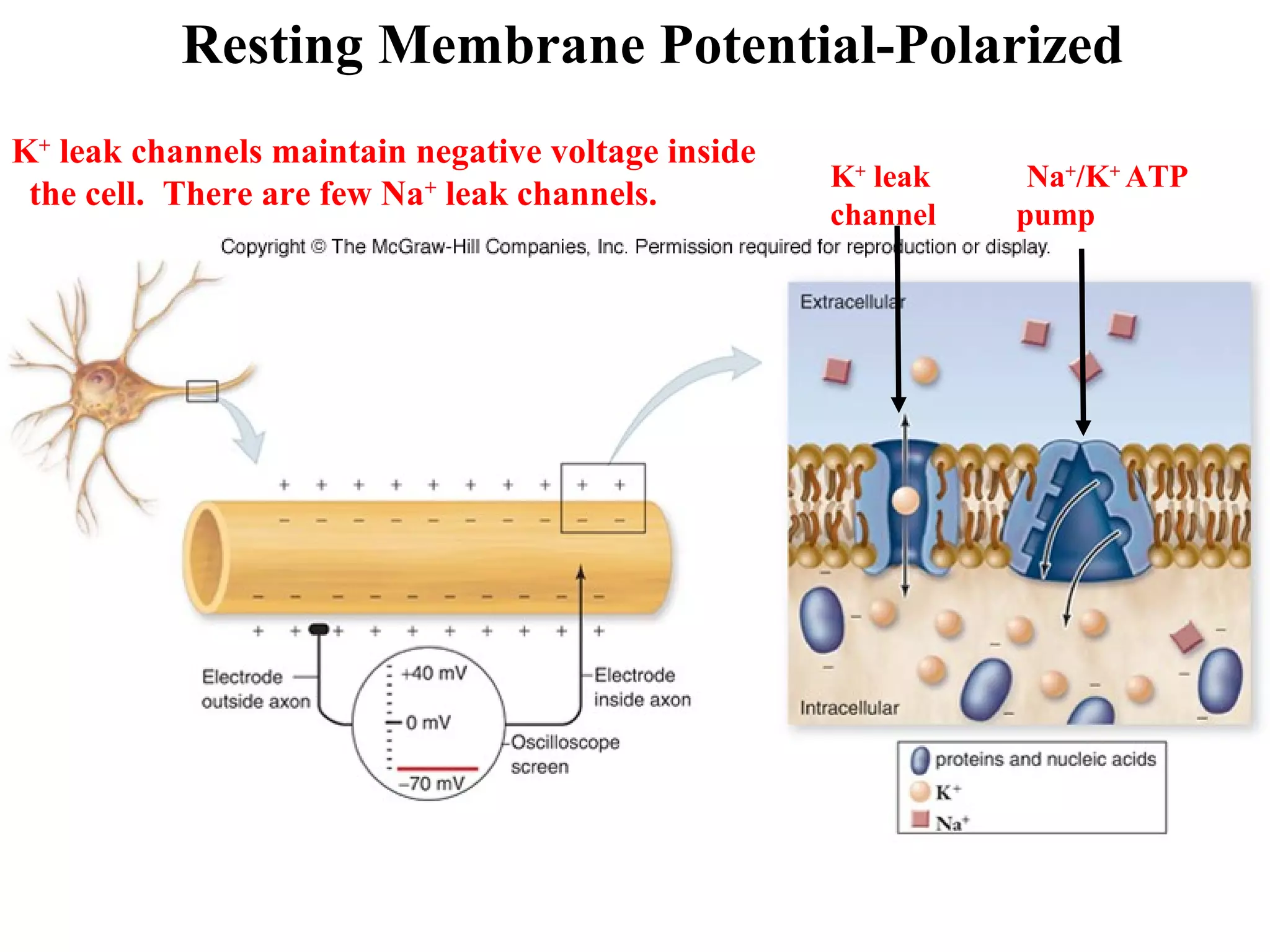
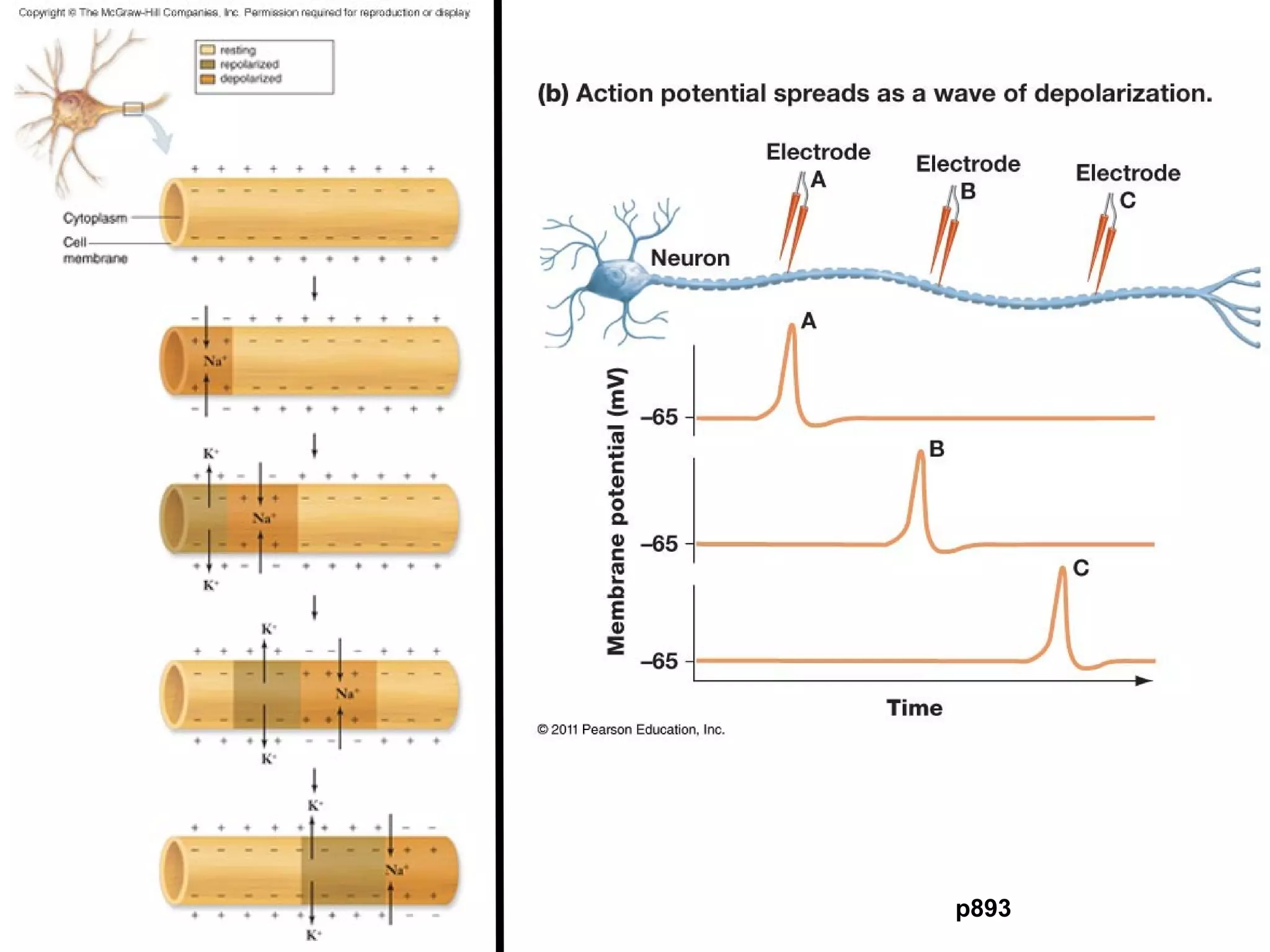
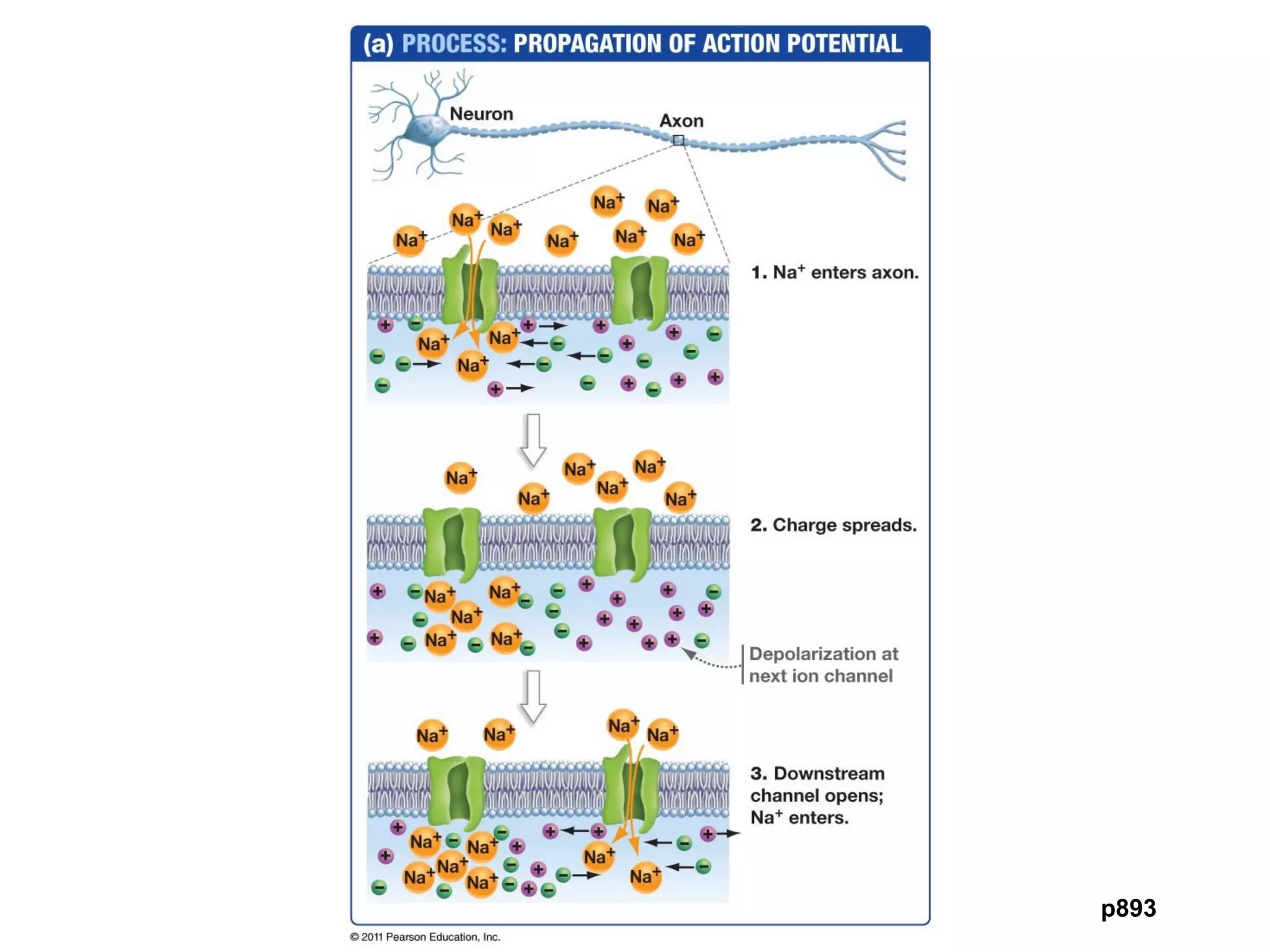
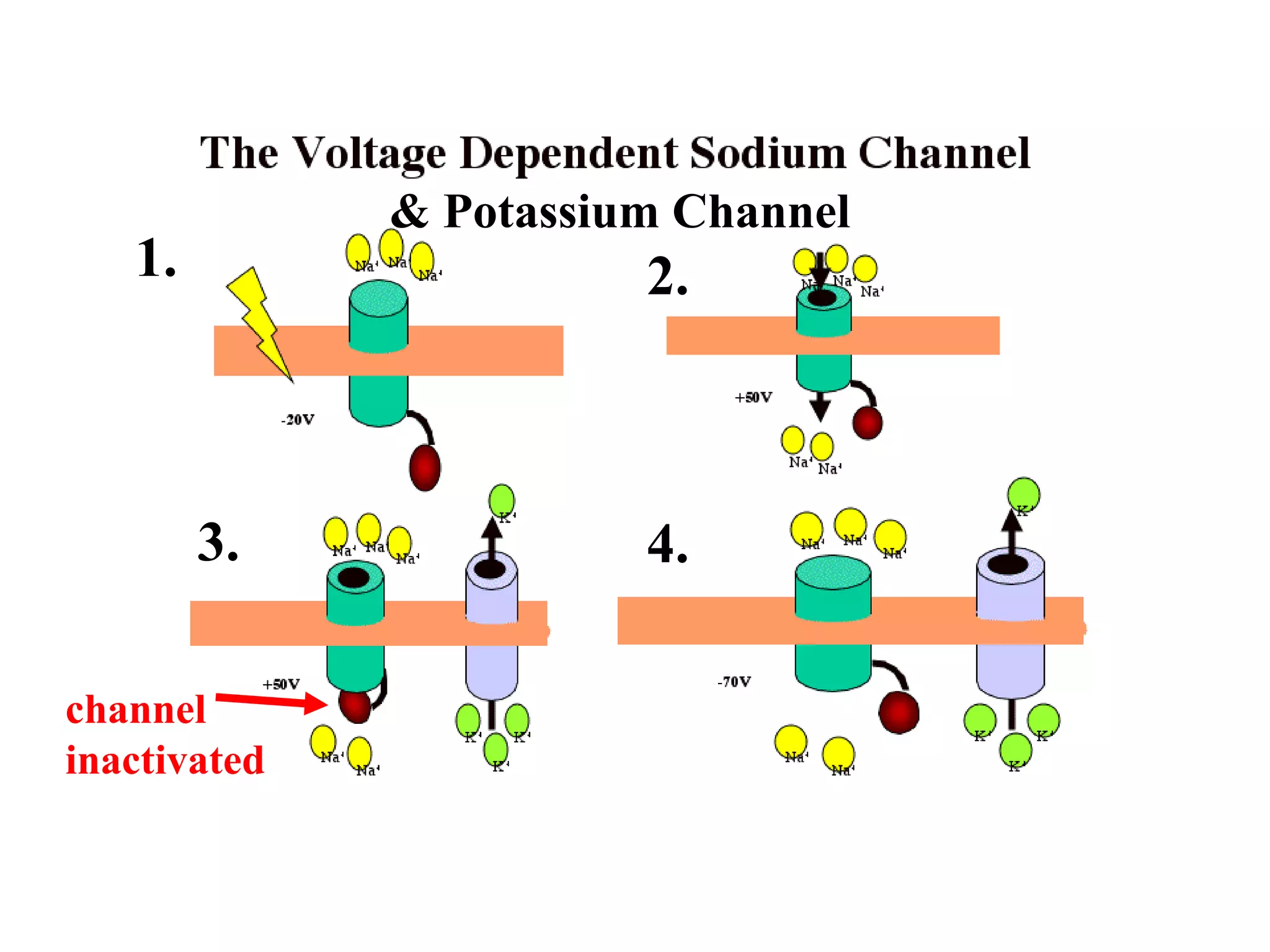
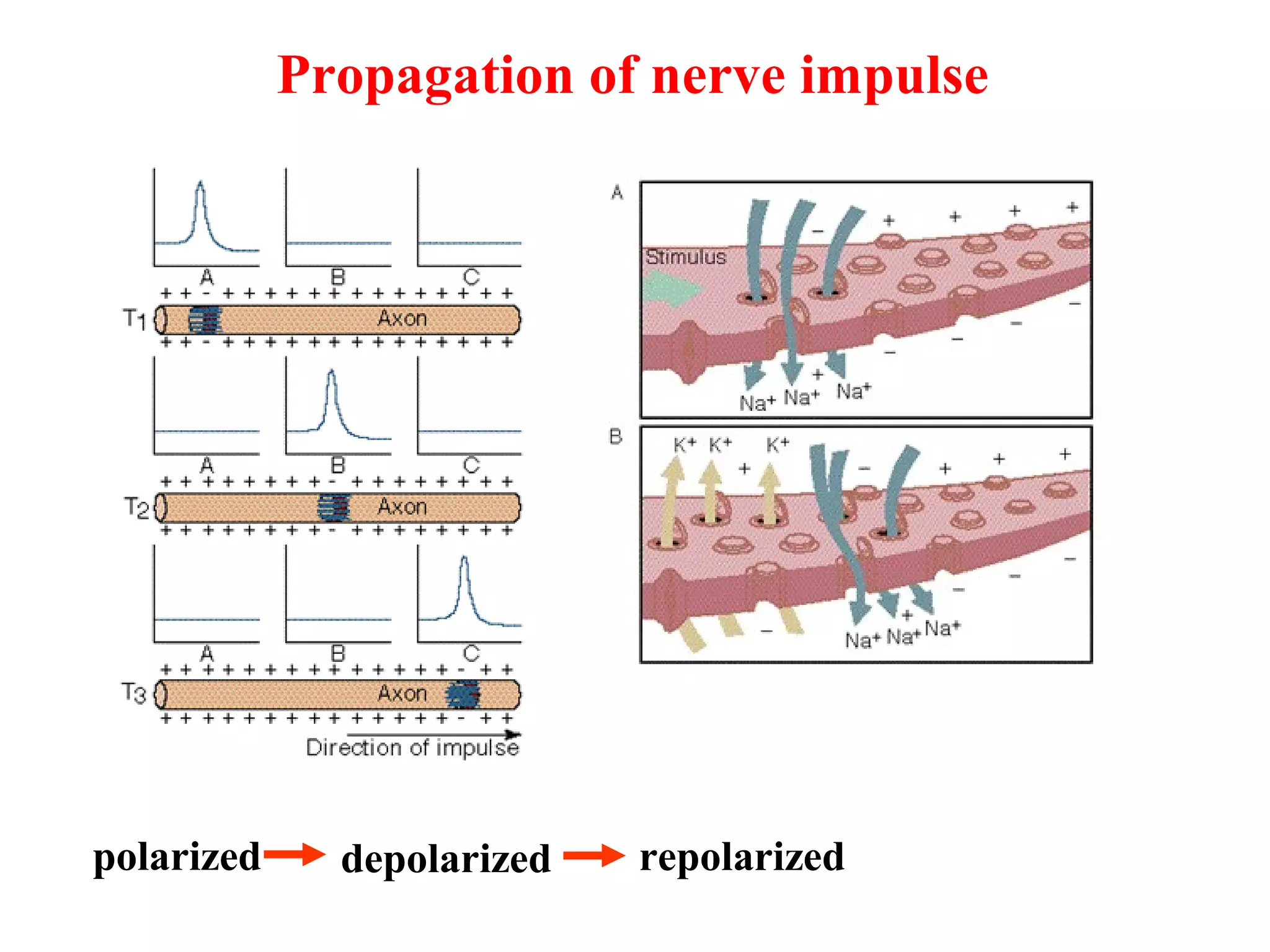
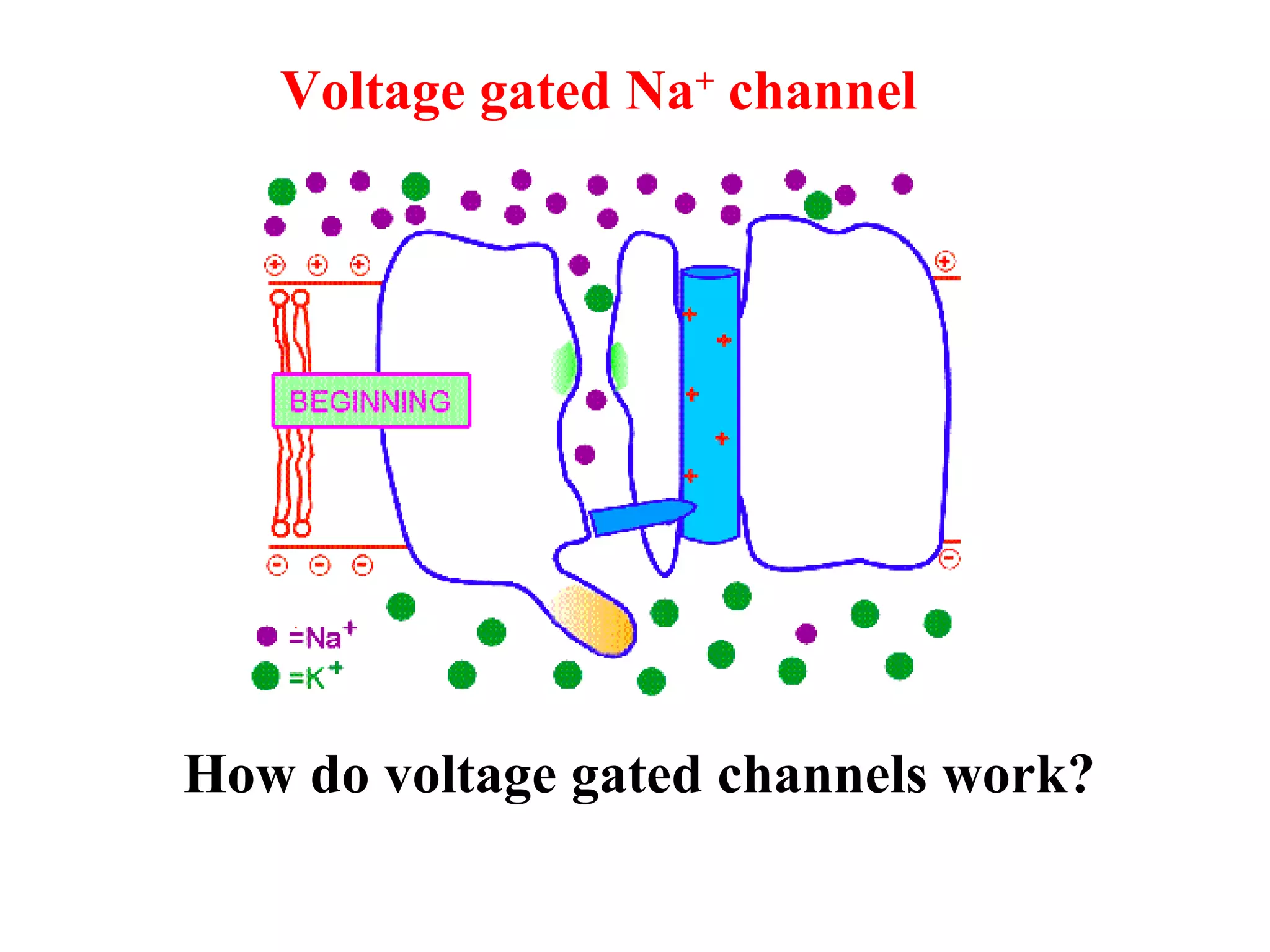
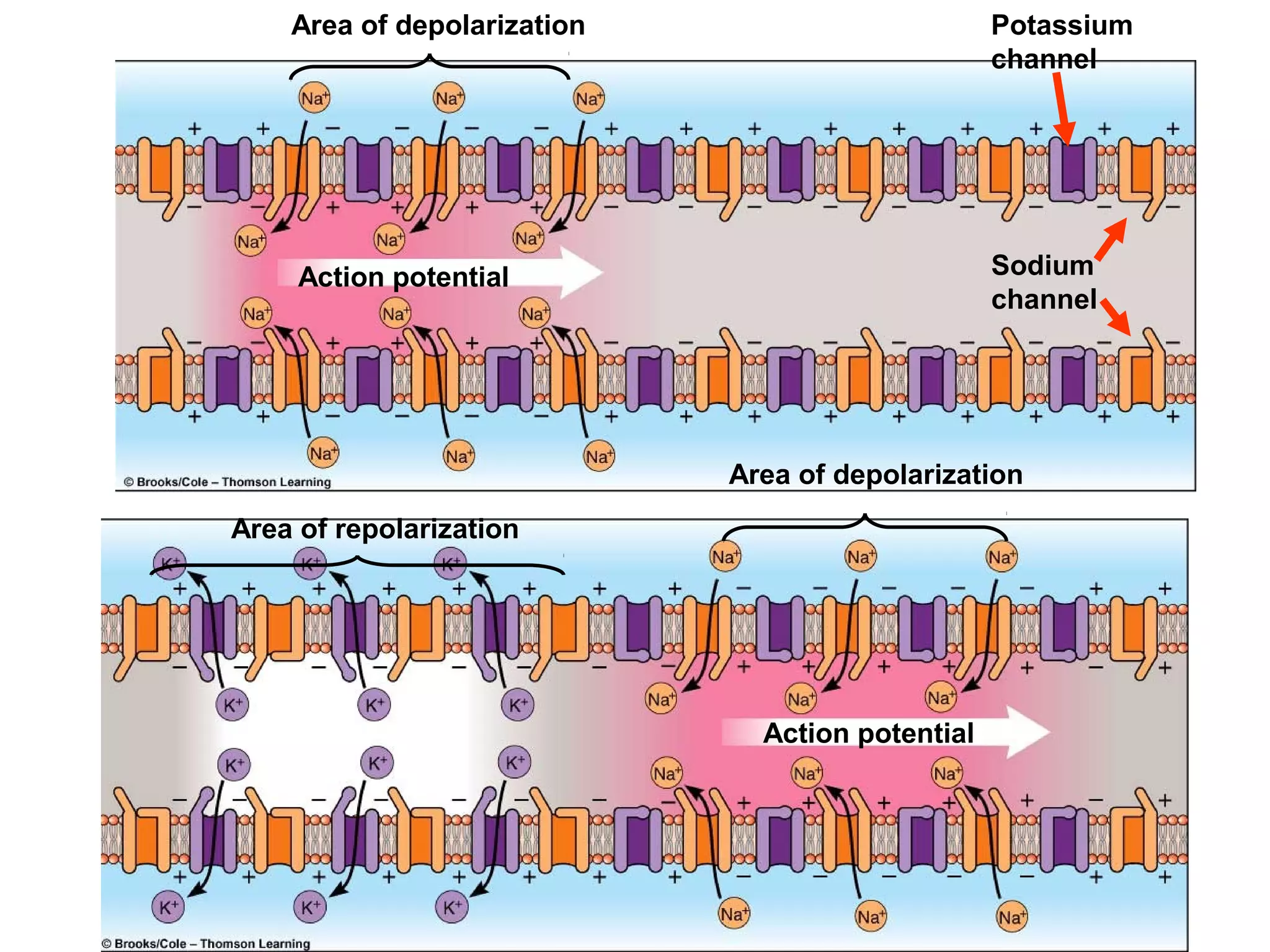
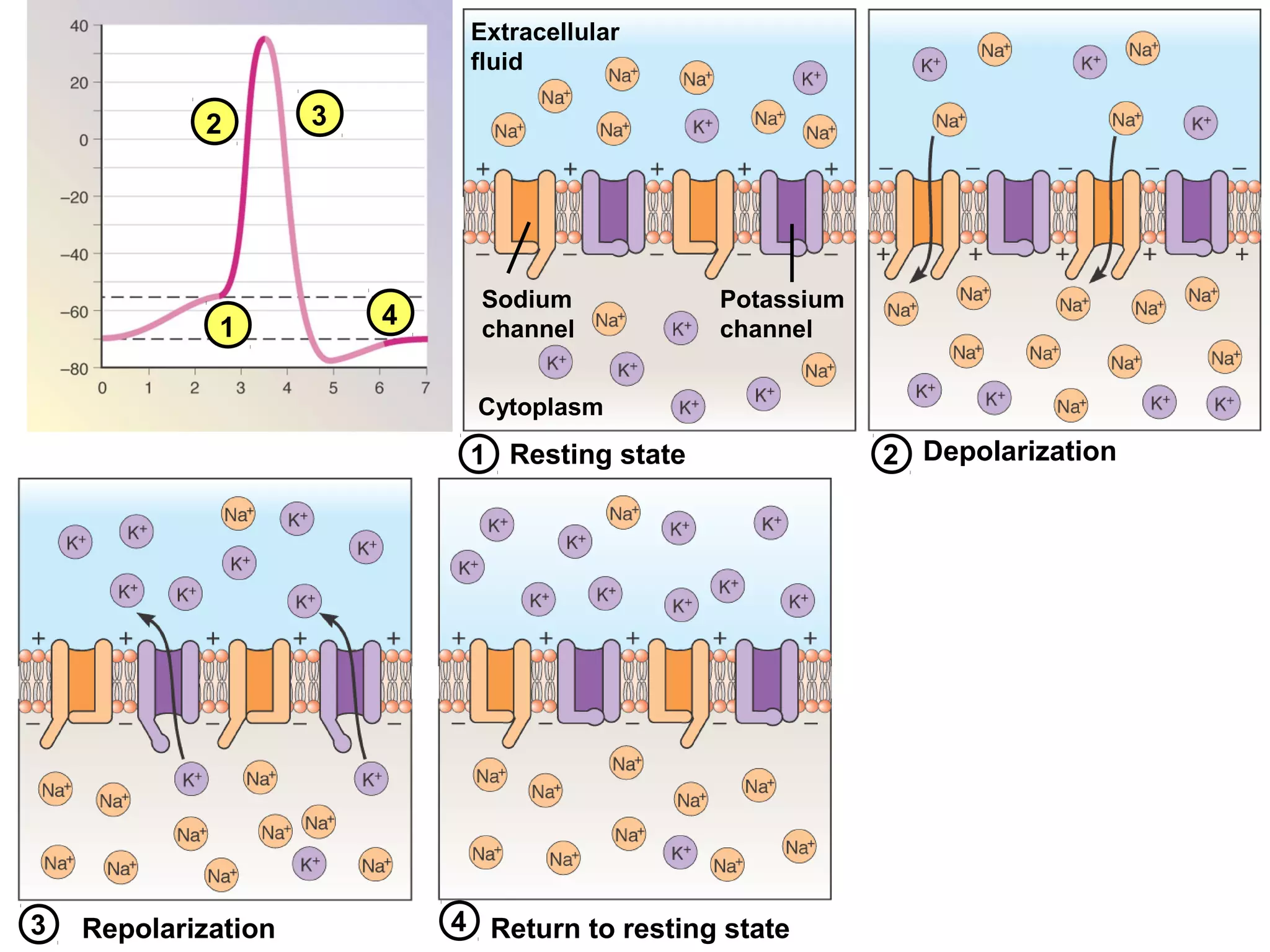
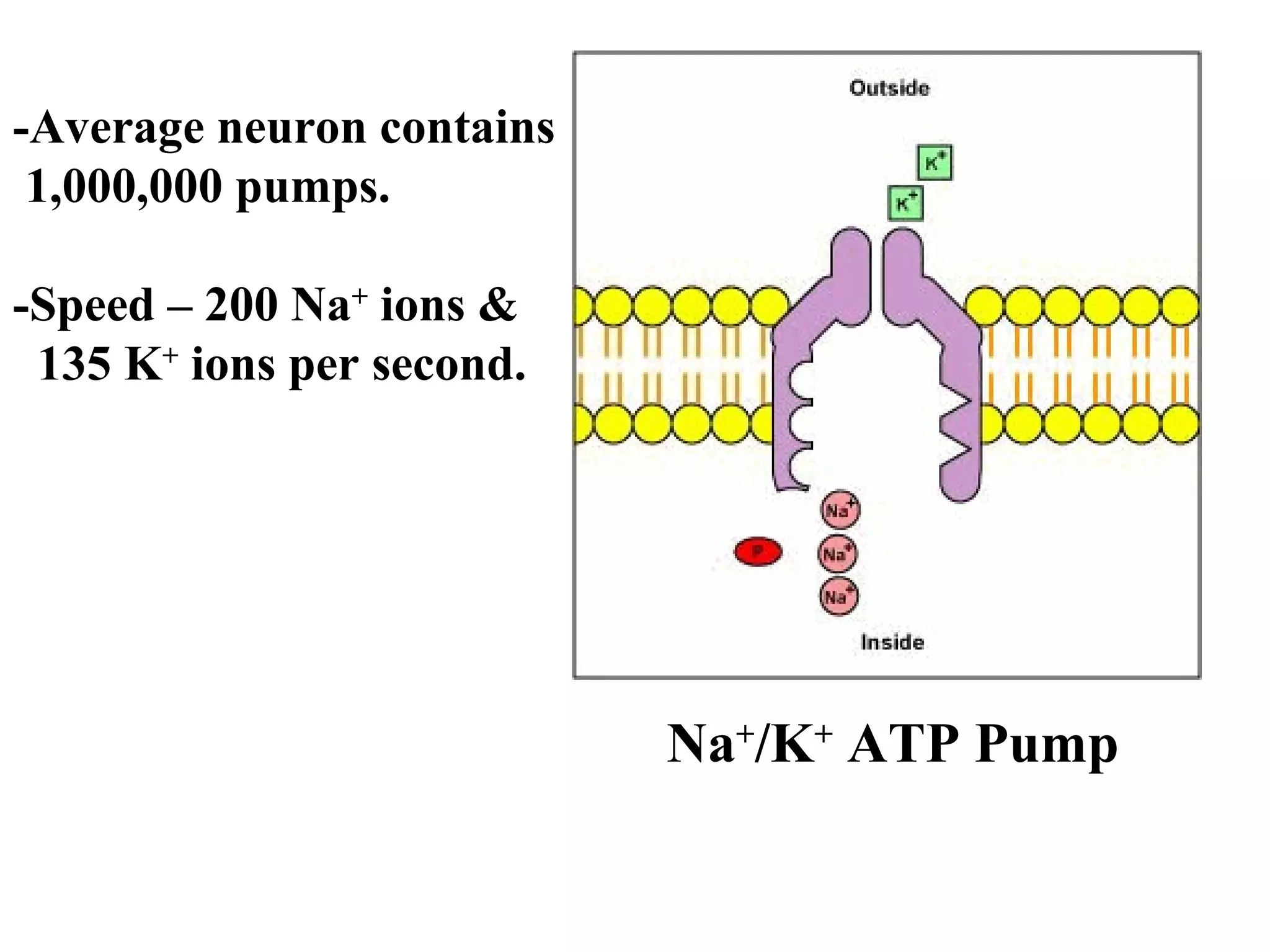
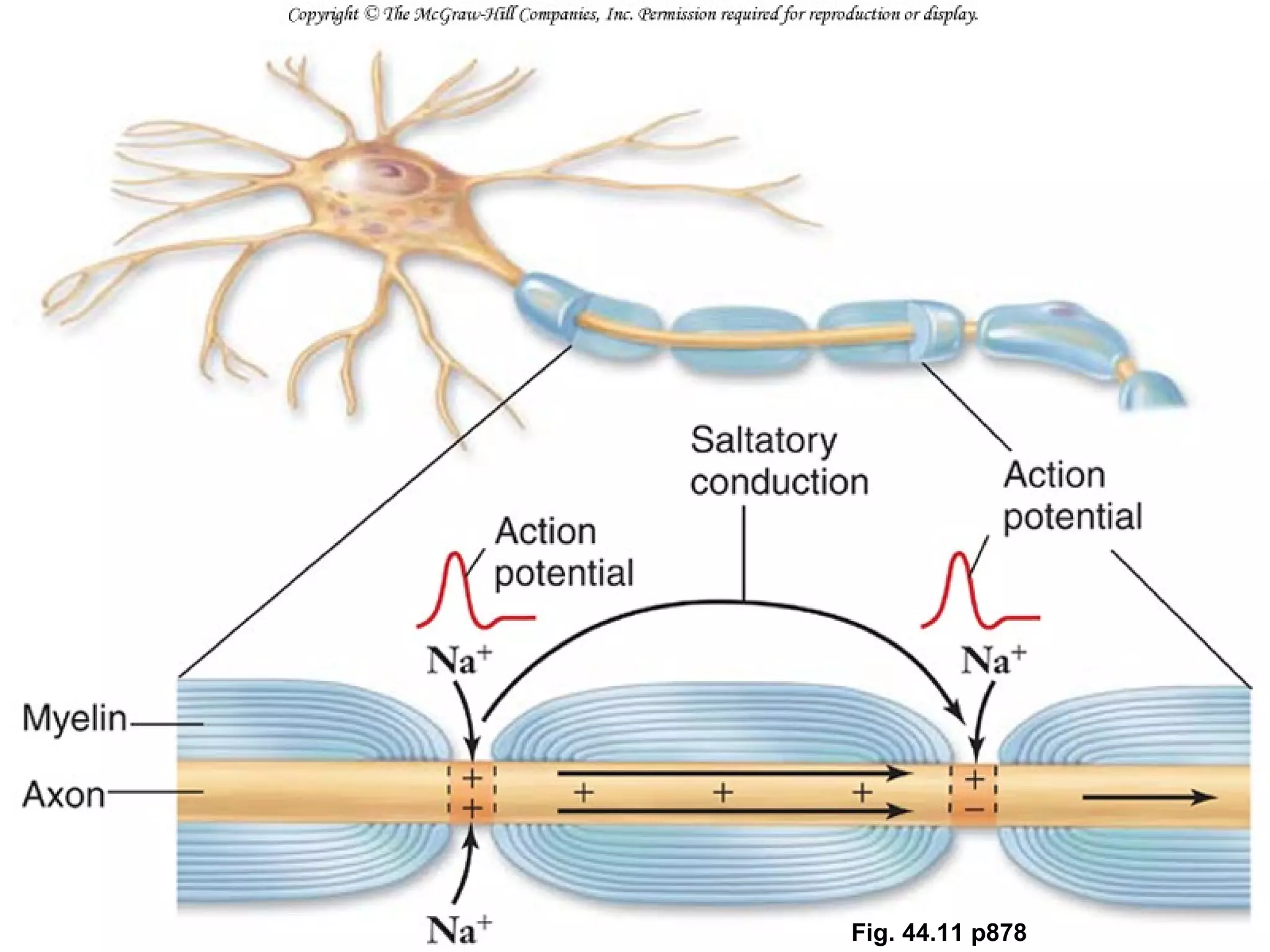
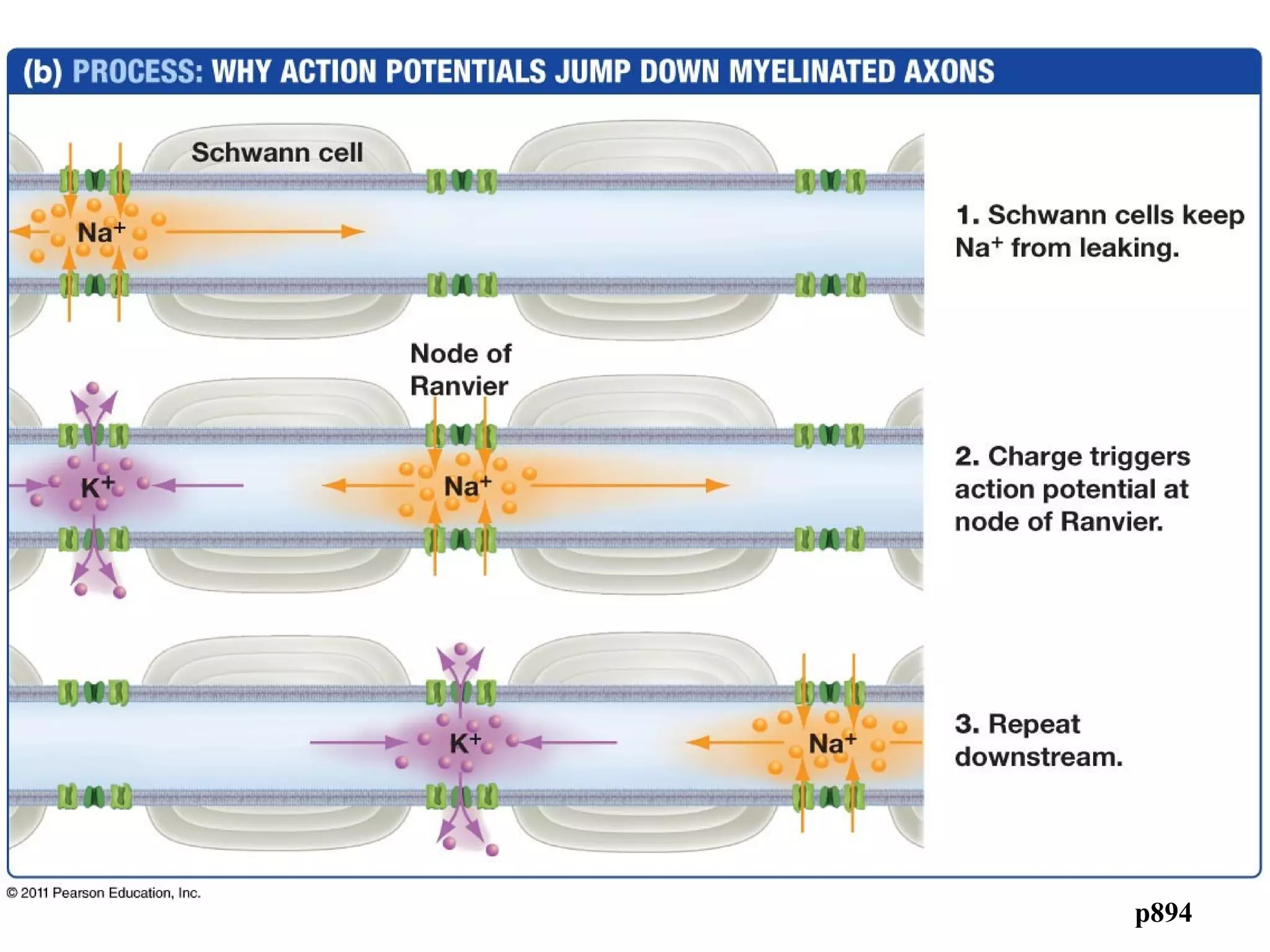
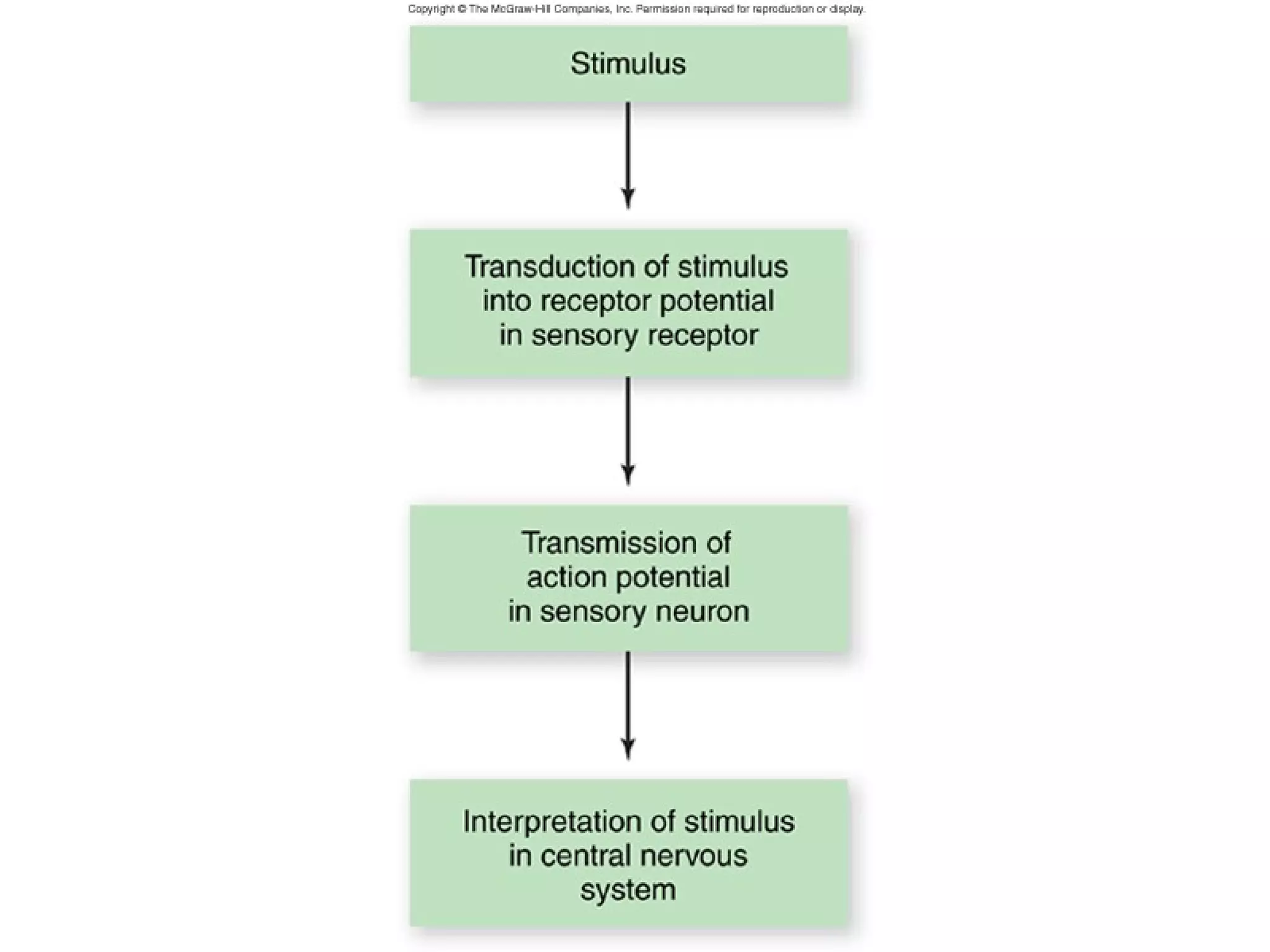
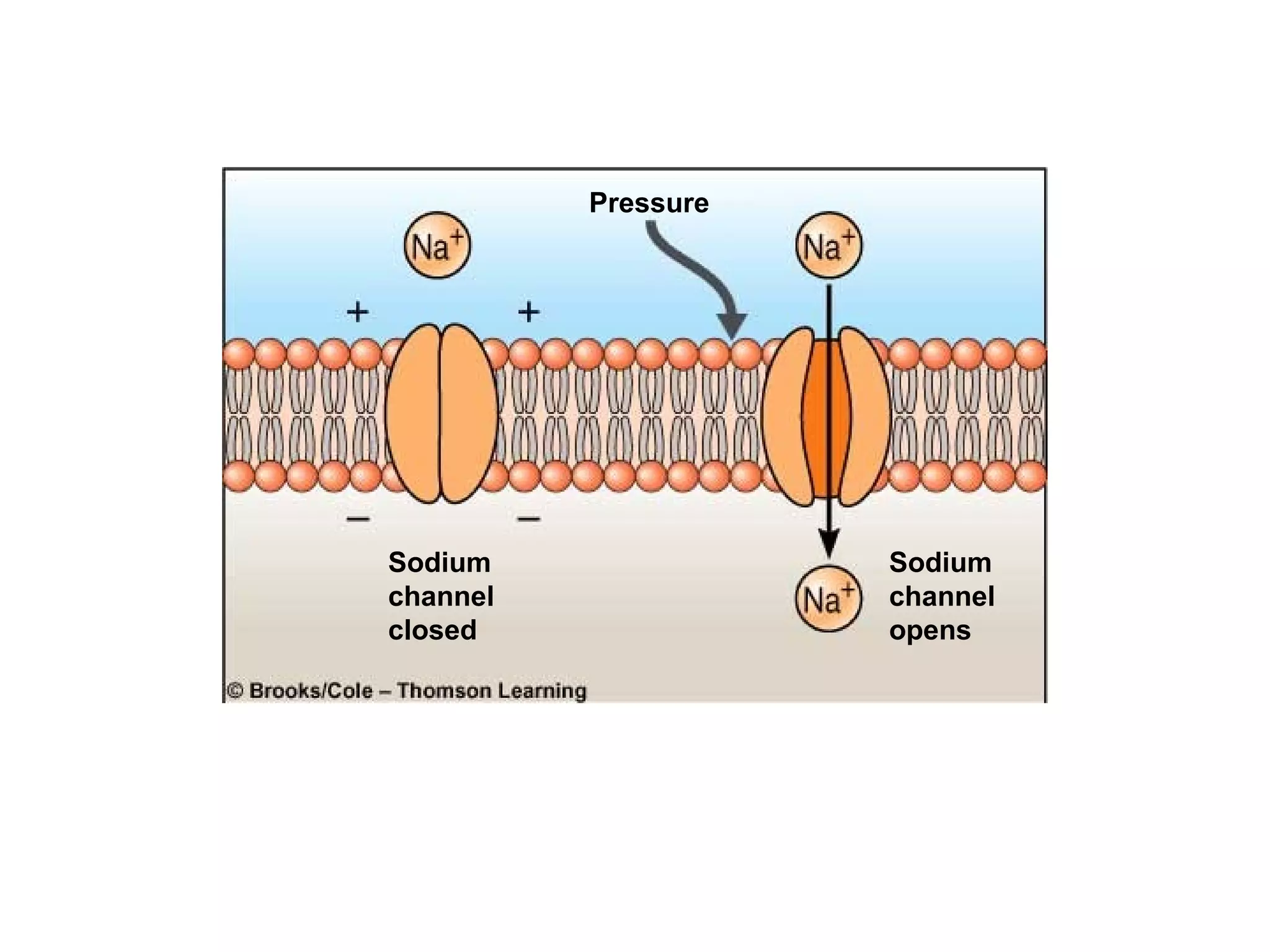
2) An action potential is generated when a threshold stimulus causes voltage-gated sodium channels to open, depolarizing the neuron. Potassium channels then repolarize the membrane.
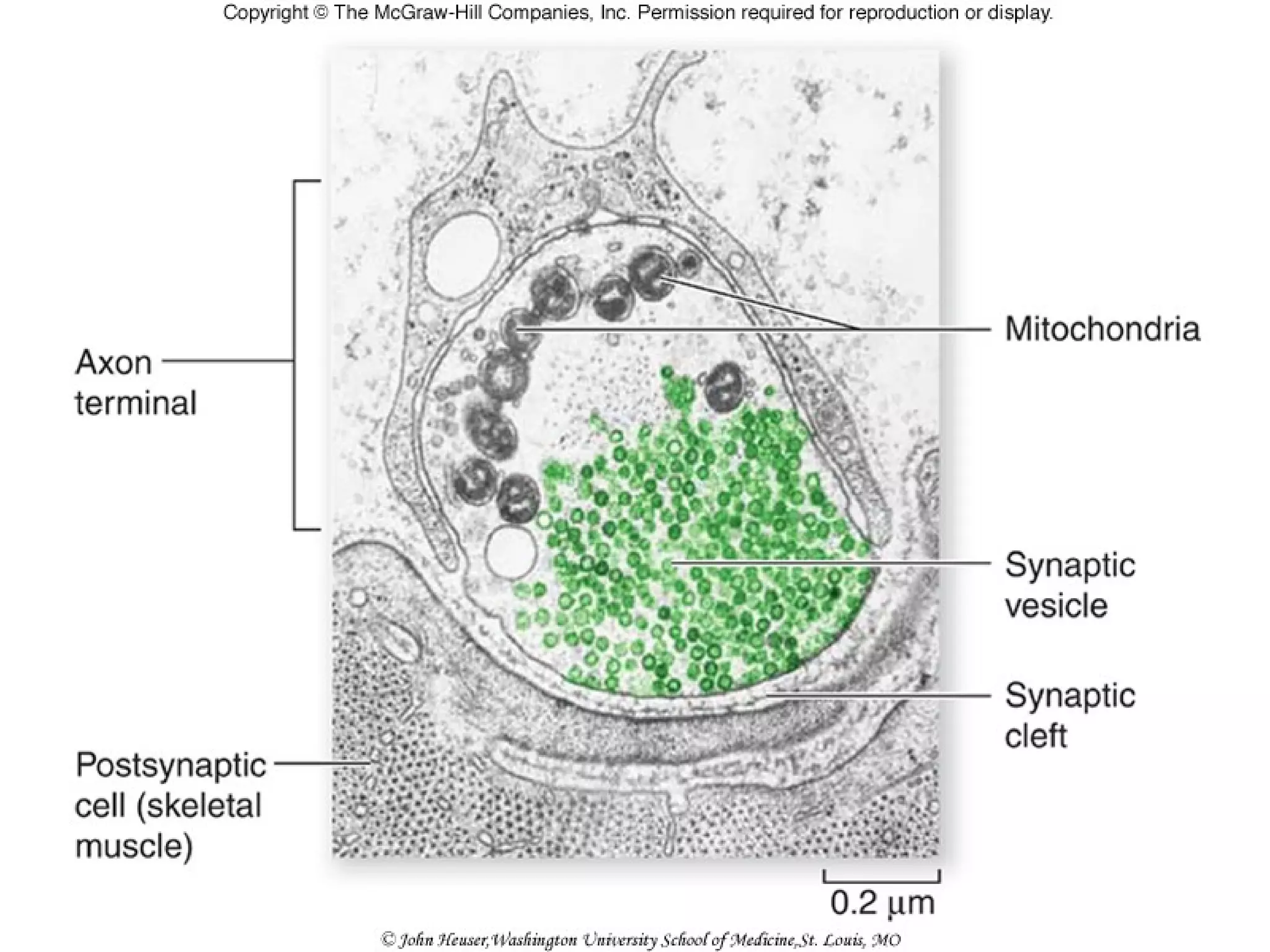
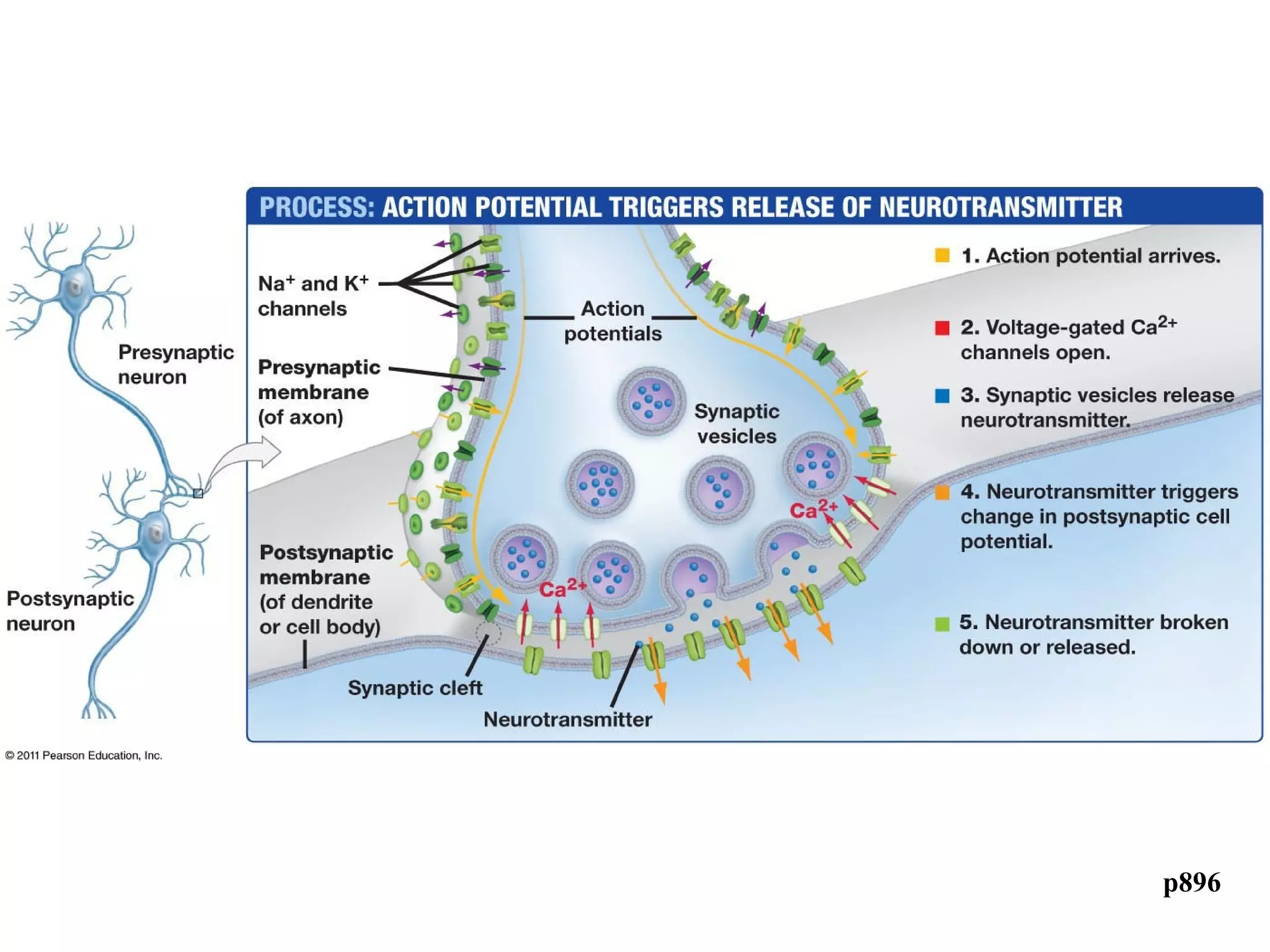
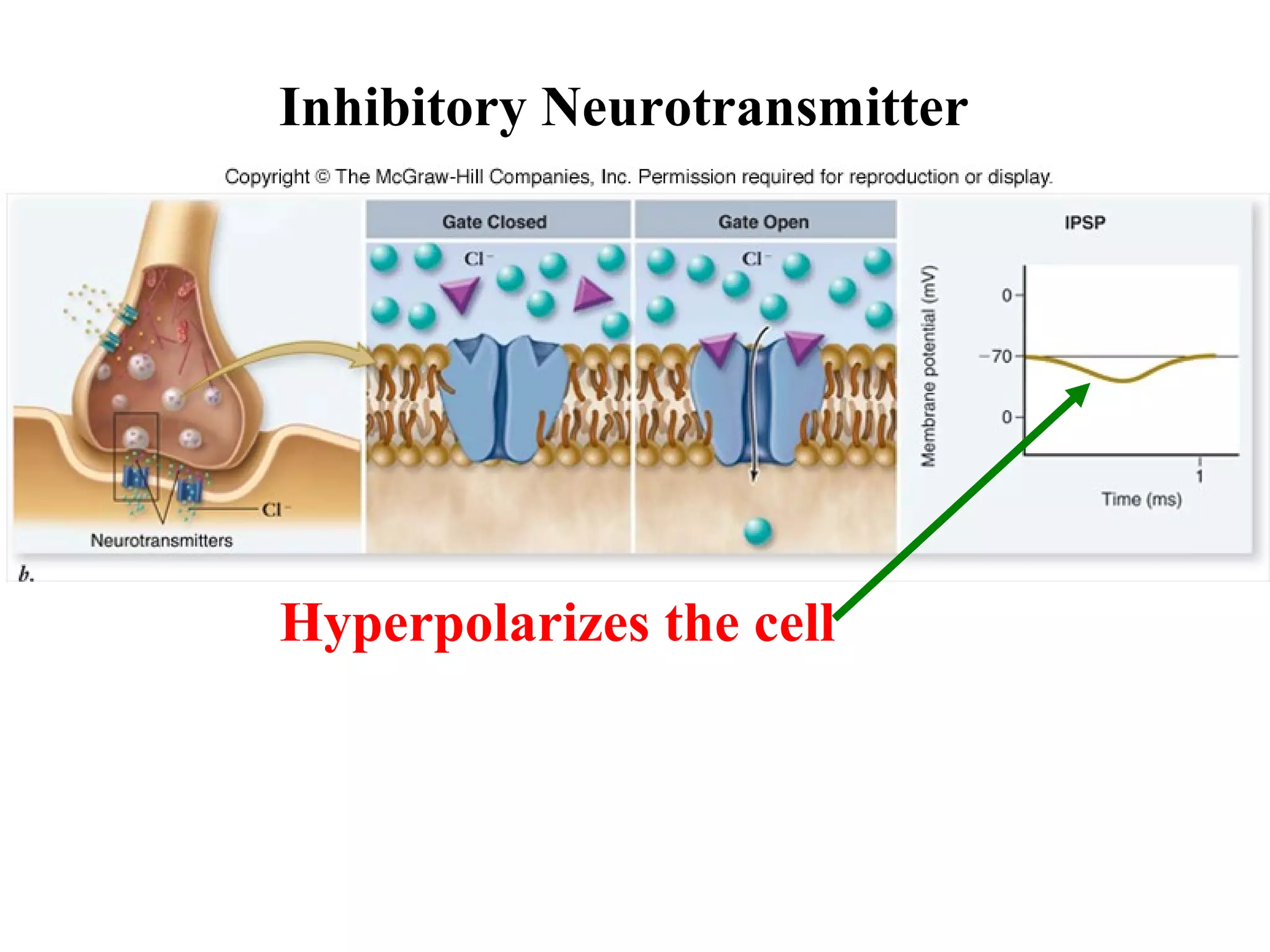
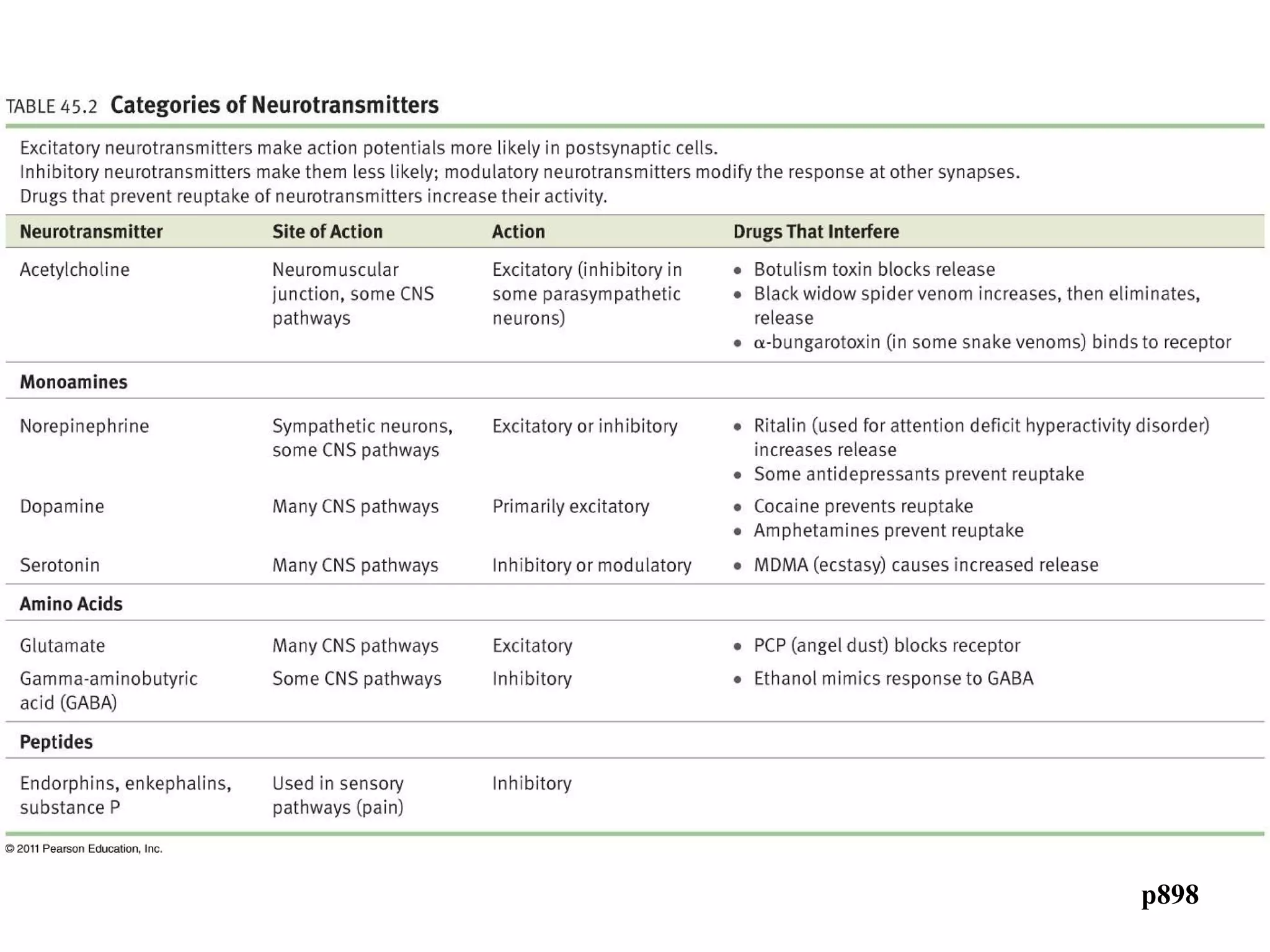
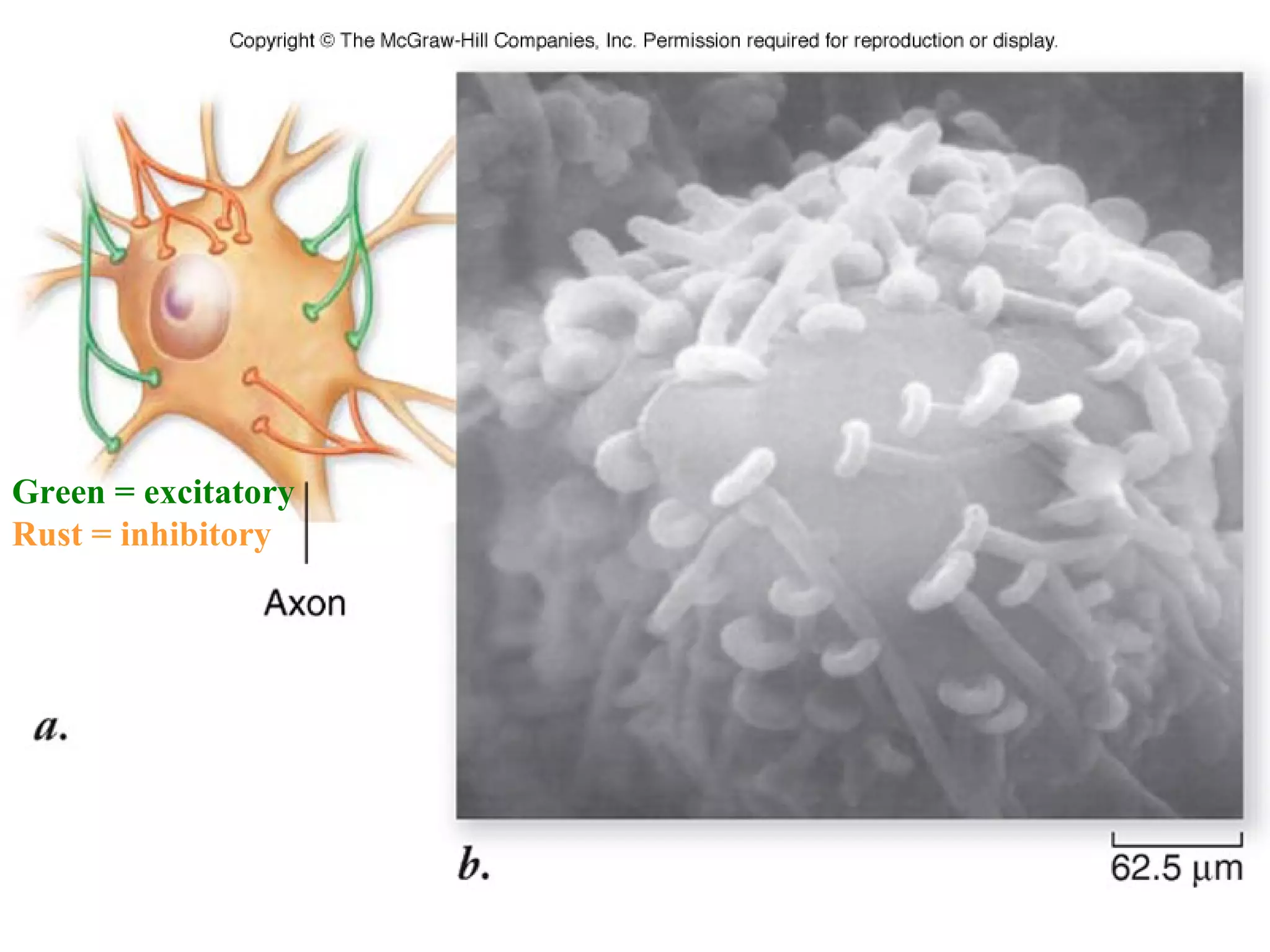
3) At a synapse, an action potential causes neurotransmitter release from the presynaptic neuron. This may excite or inhibit the postsynaptic neuron depending on the neurotransmitter.