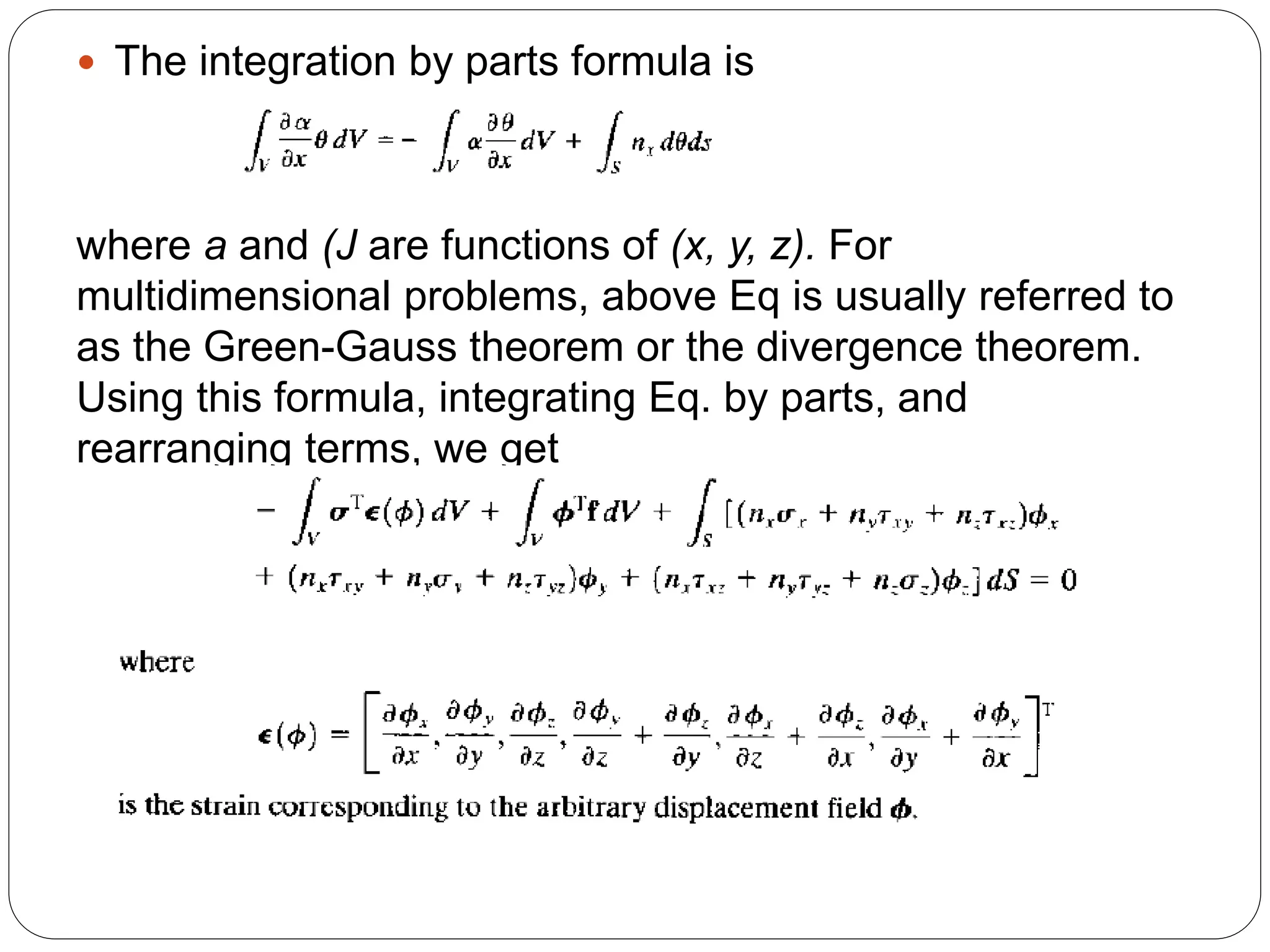
The document discusses the finite element method (FEM) for numerical analysis of structures. It provides the following key points:
1) FEM divides a structure into discrete elements connected at nodes, resulting in a finite number of degrees of freedom and a set of simultaneous algebraic equations to solve.
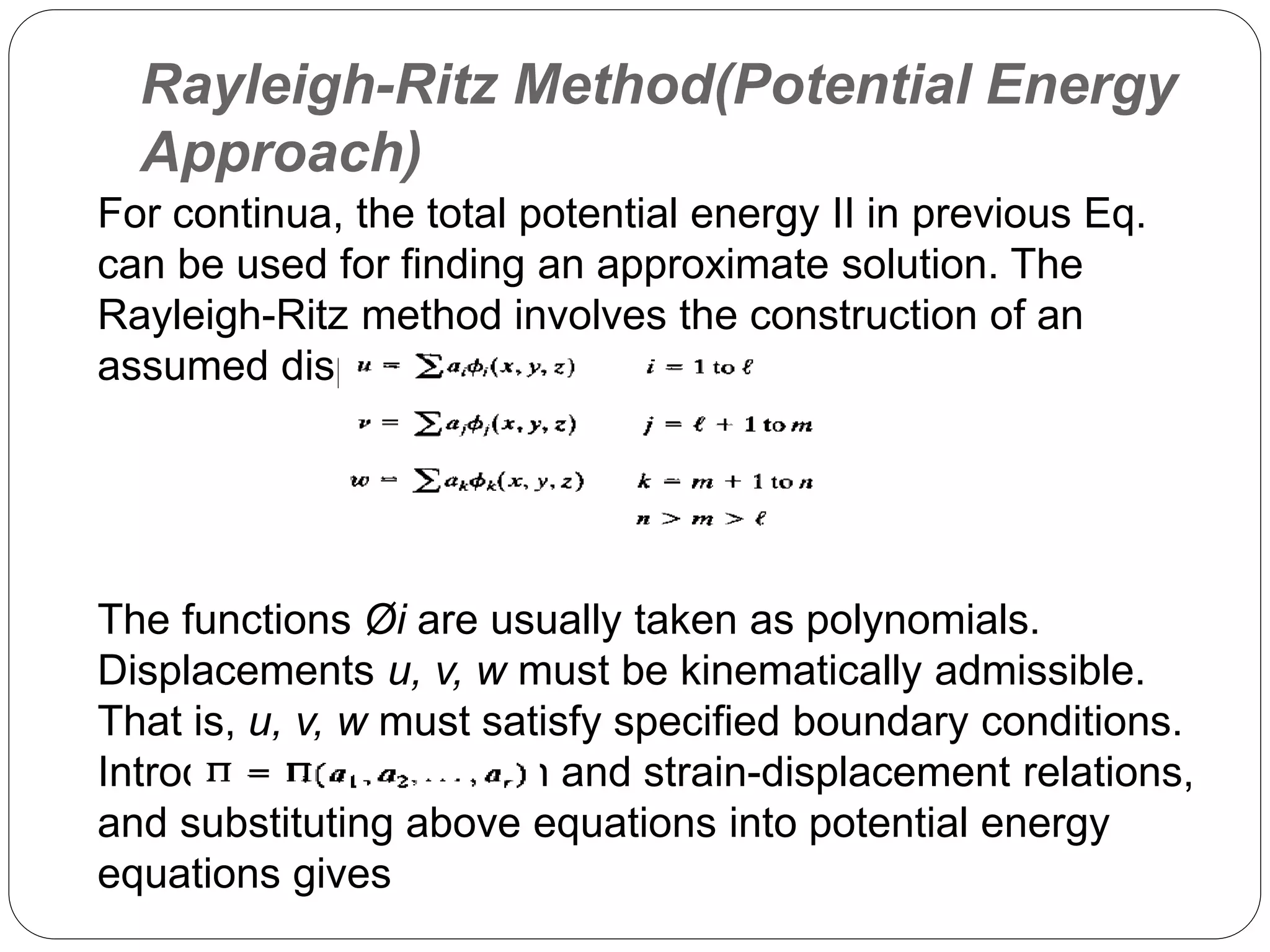
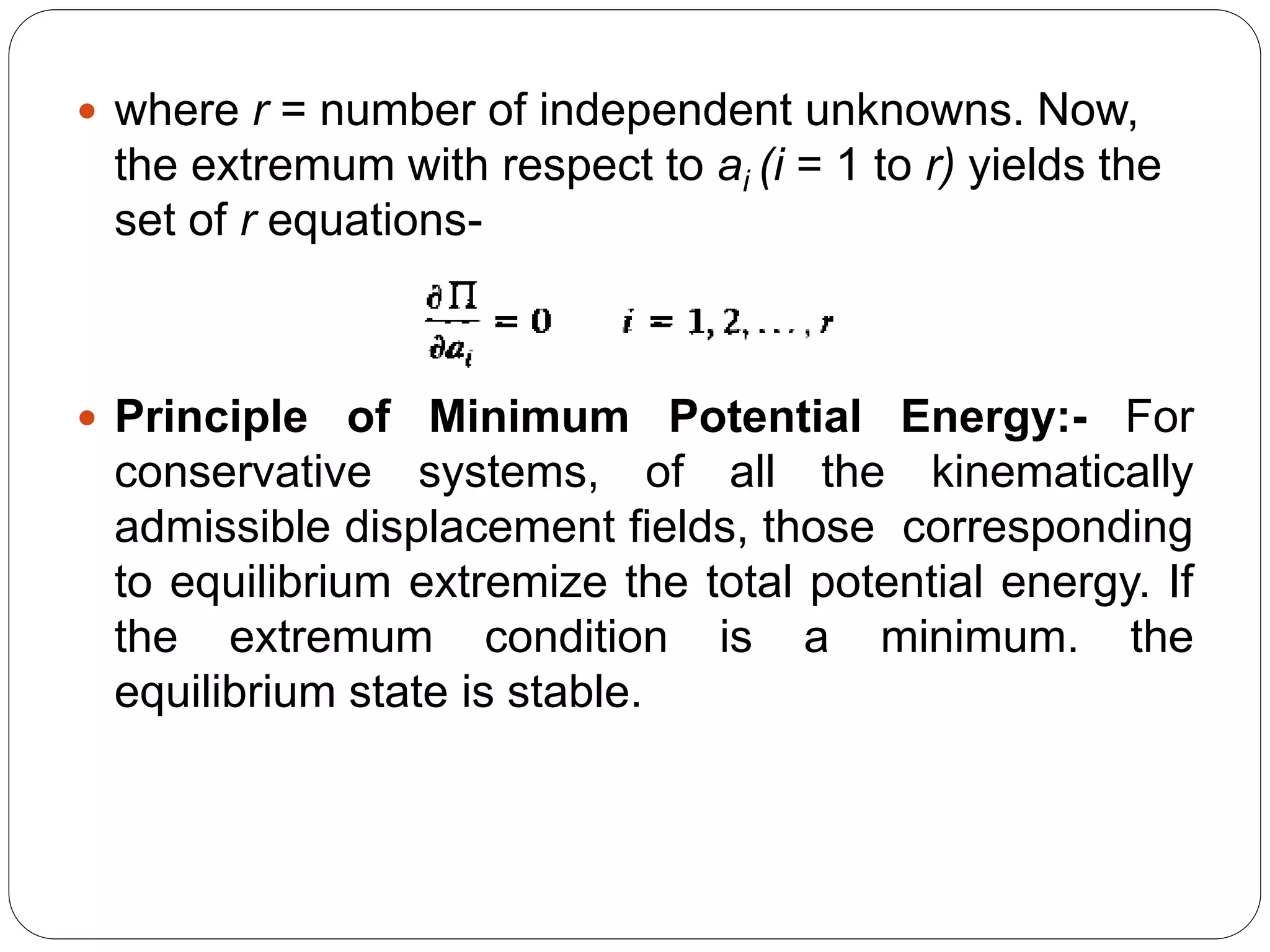
2) It uses approximate methods like the Rayleigh-Ritz method to obtain solutions for complex geometries and boundary conditions. This involves assuming displacement fields and minimizing the total potential energy.
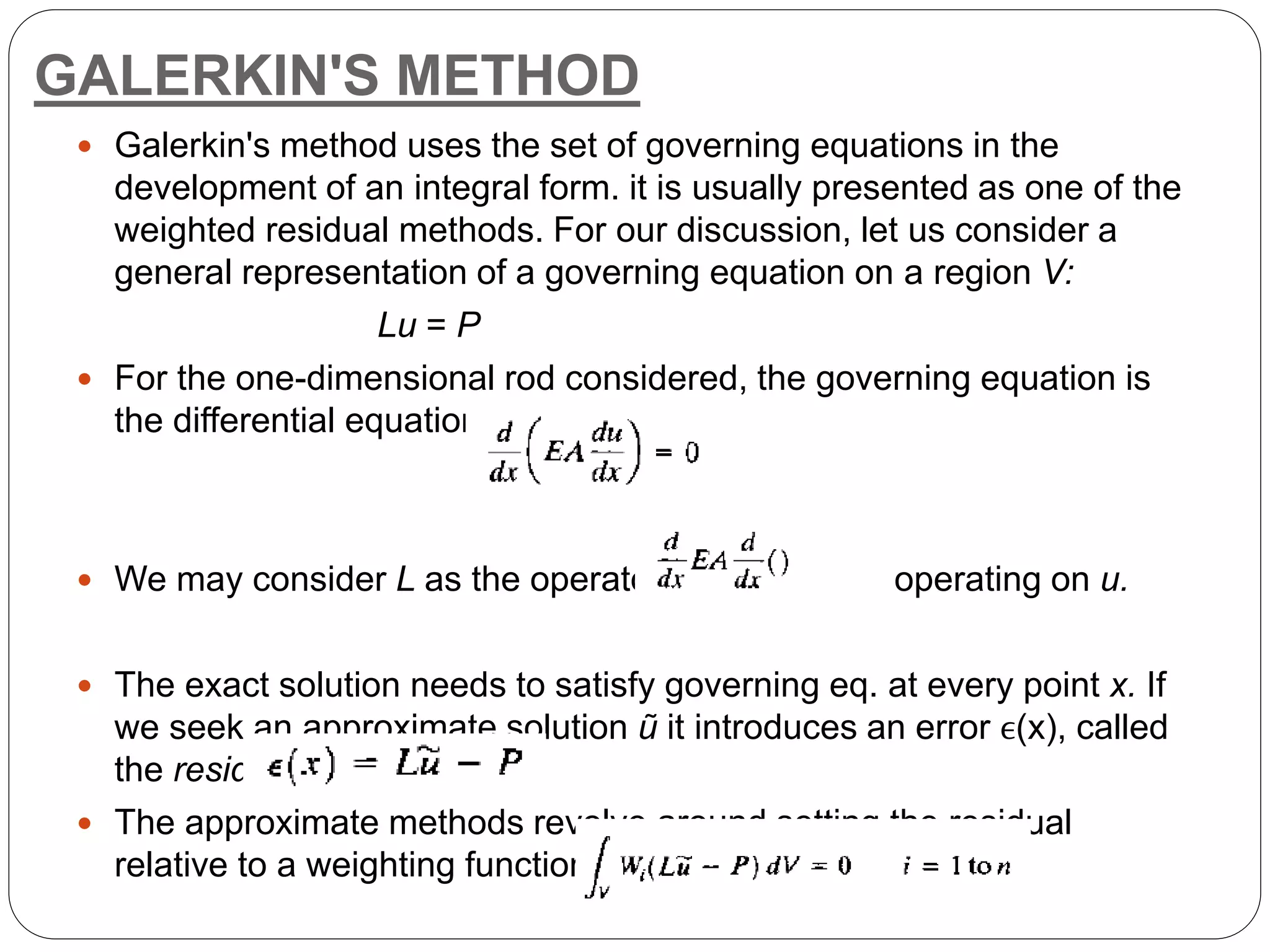
3) The Galerkin method is presented, which satisfies the governing differential equations in an integral sense by setting the residual equal to zero when multiplied by a weighting function.
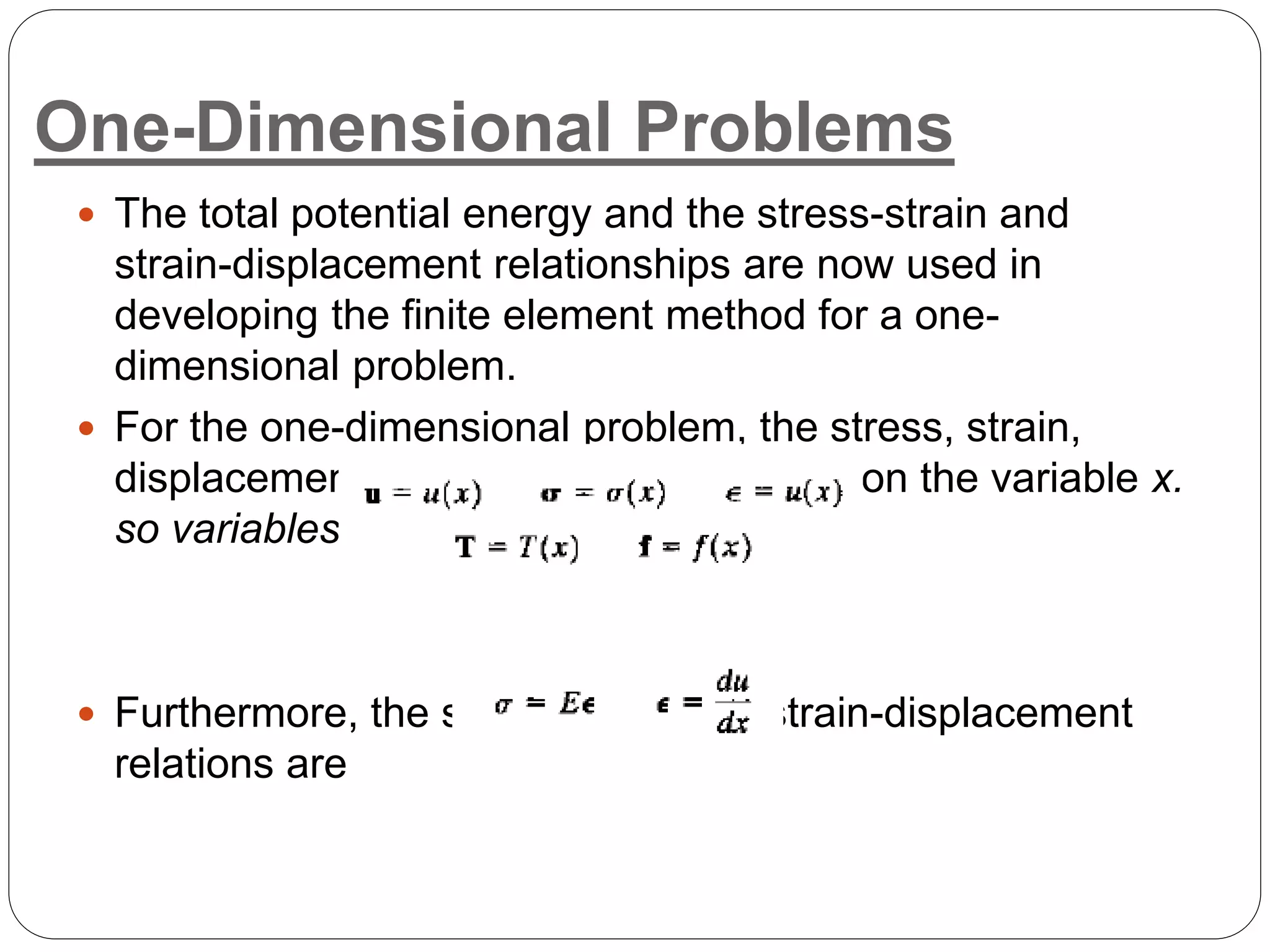
4) Applications to 1D problems are discussed,



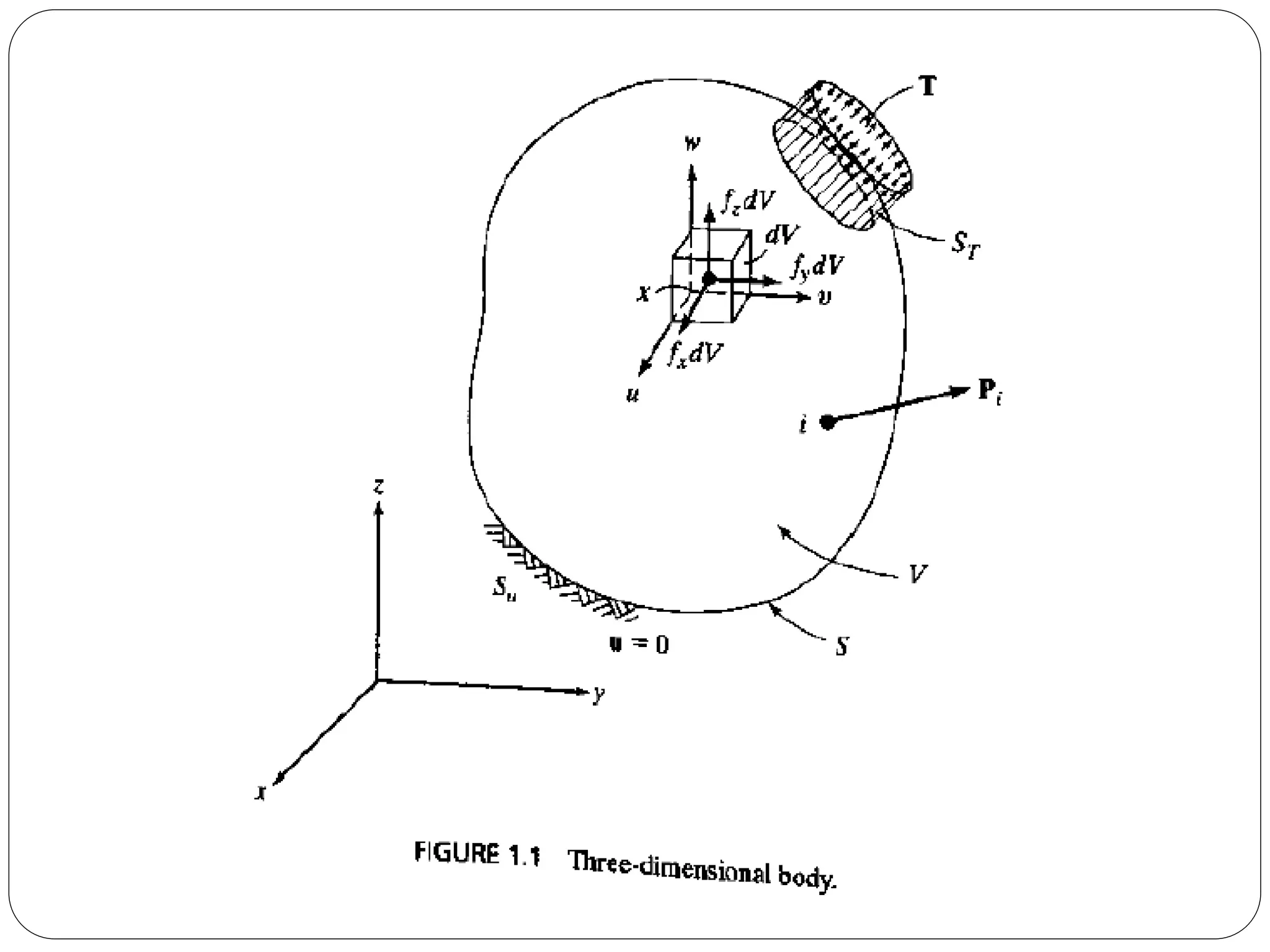
![BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
Referring to Fig., we find that there are displacement boundary
conditions and surface-loading conditions. If u is specified on part of
the boundary denoted by Su, we have
U= 0 OR Sx
We can also consider boundary conditions such as u = a, where a
is a given displacement.
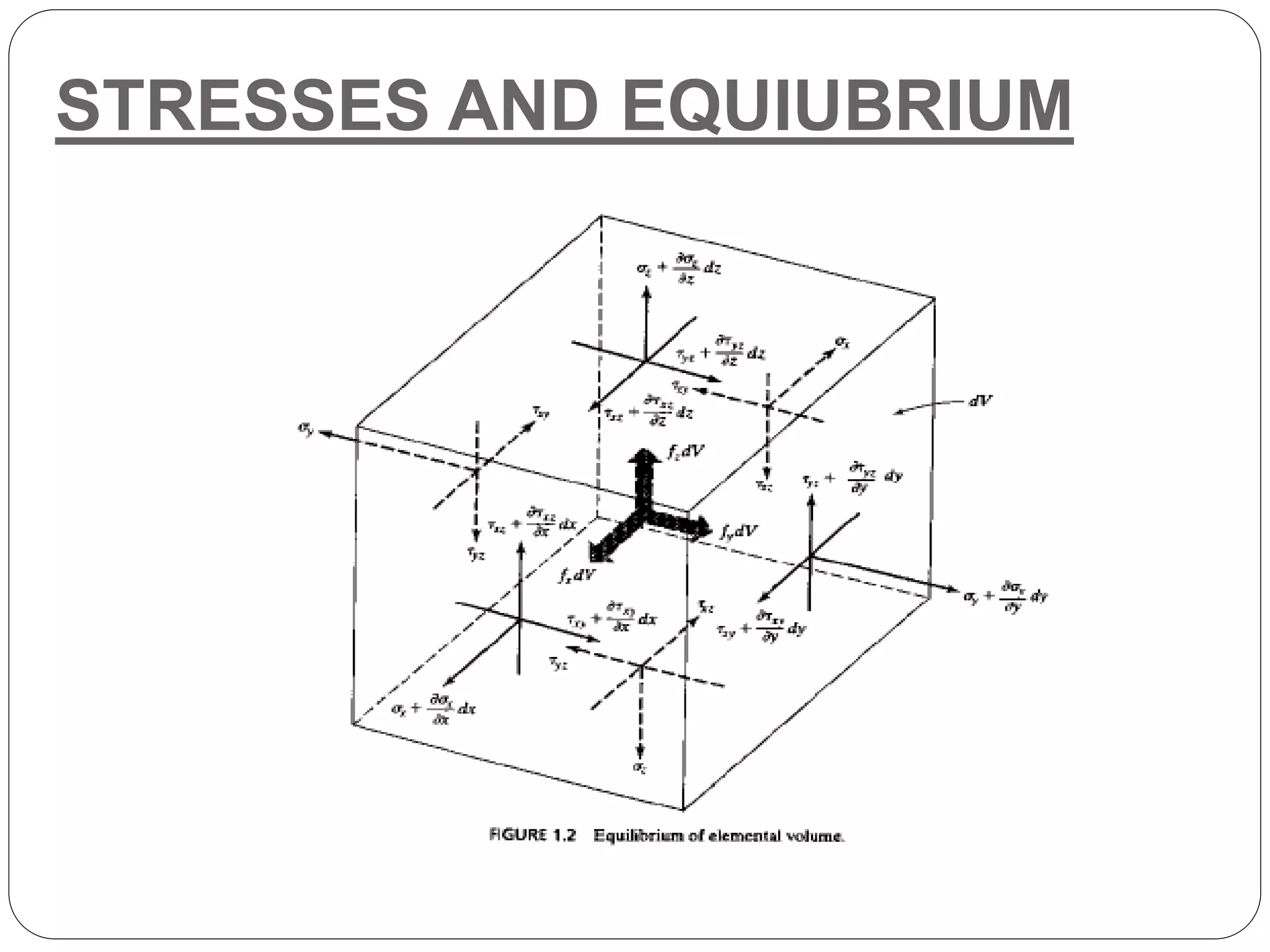
We now consider the equilibrium of an elemental tetrahedron ABCD,
shown in Fig., where DA, DB, and DC are parallel to the X-, y-, and
z-axes, respectively, and area ABC, denoted by dA, lies on the
surface. If n = [nx, ny, nz]T is the unit normal to dA, Consideration of
equilibrium along the three axes directions gives
These conditions must be satisfied on the boundary, St, where the
tractions are applied. In this description, the point loads must be
treated as loads distributed over small, but finite areas.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finiteelementmethod-170409063521/75/Finite-element-method-7-2048.jpg)





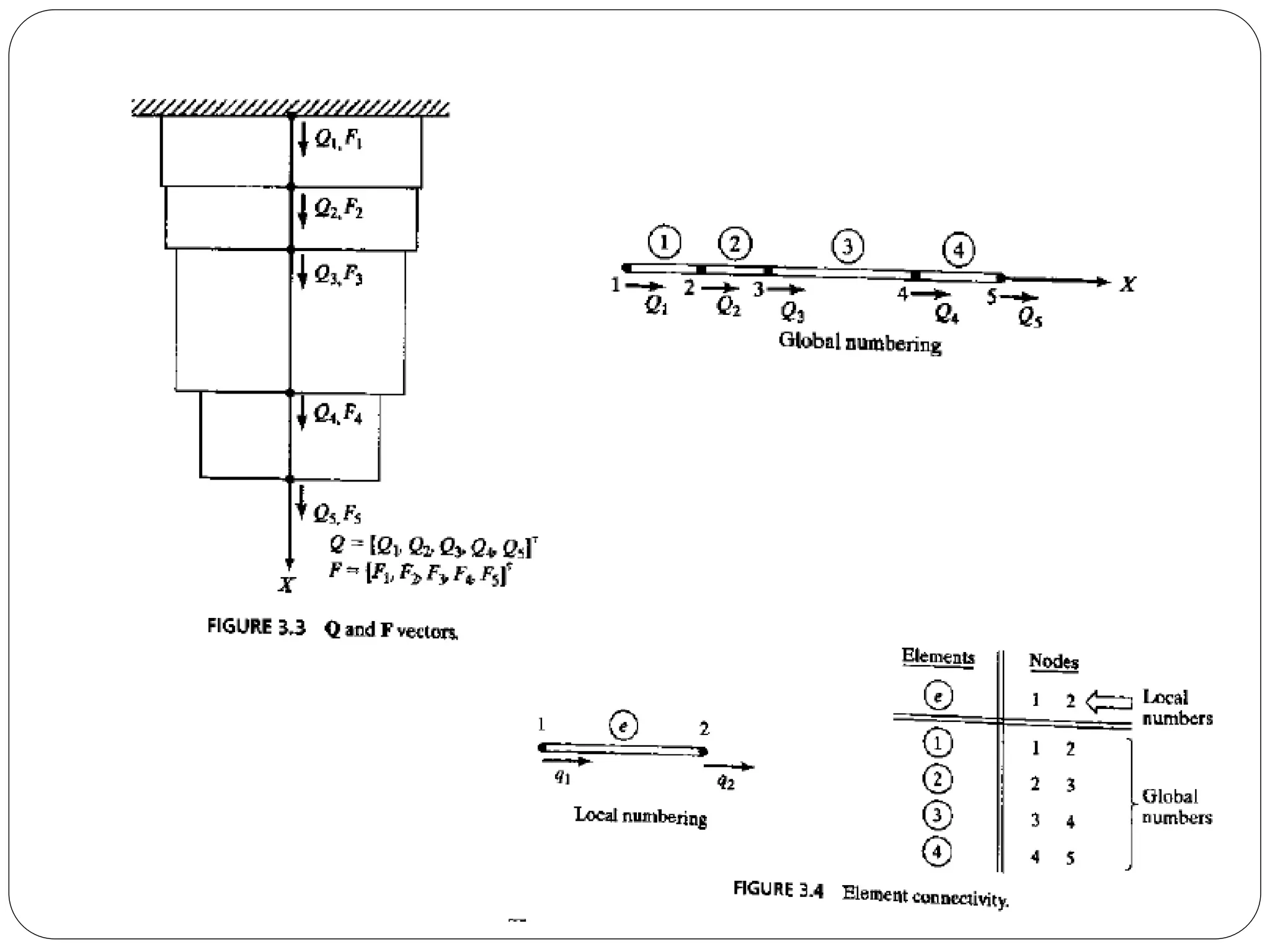
![ The first step is to model the bar as a stepped shaft, consisting of a
discrete number of elements, each having a uniform cross section.
Specifically, let us model the bar using four finite elements. A simple
scheme for doing this is to divide the bar into four regions, as shown in
Fig.
In the finite element model, every element connects to two nodes.
However, cross-sectional area, traction, and body forces can differ in
magnitude from element to element.
Better approximations are obtained by increasing the number of
elements.
It is convenient to define a node at each location where a point load is
applied.
In a one-dimensional problem, every node is permitted to displace only
in the ±x direction. This, each node has only one degree of freedom
(dof).
The five-node finite element model in Fig. has five dofs.
The displacements along each dof are denoted by Q1, Q2, Q3... Q5. In
fact, the column vector Q = [Q1. Q2 .. 'Q5]T is called the global](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finiteelementmethod-170409063521/75/Finite-element-method-22-2048.jpg)
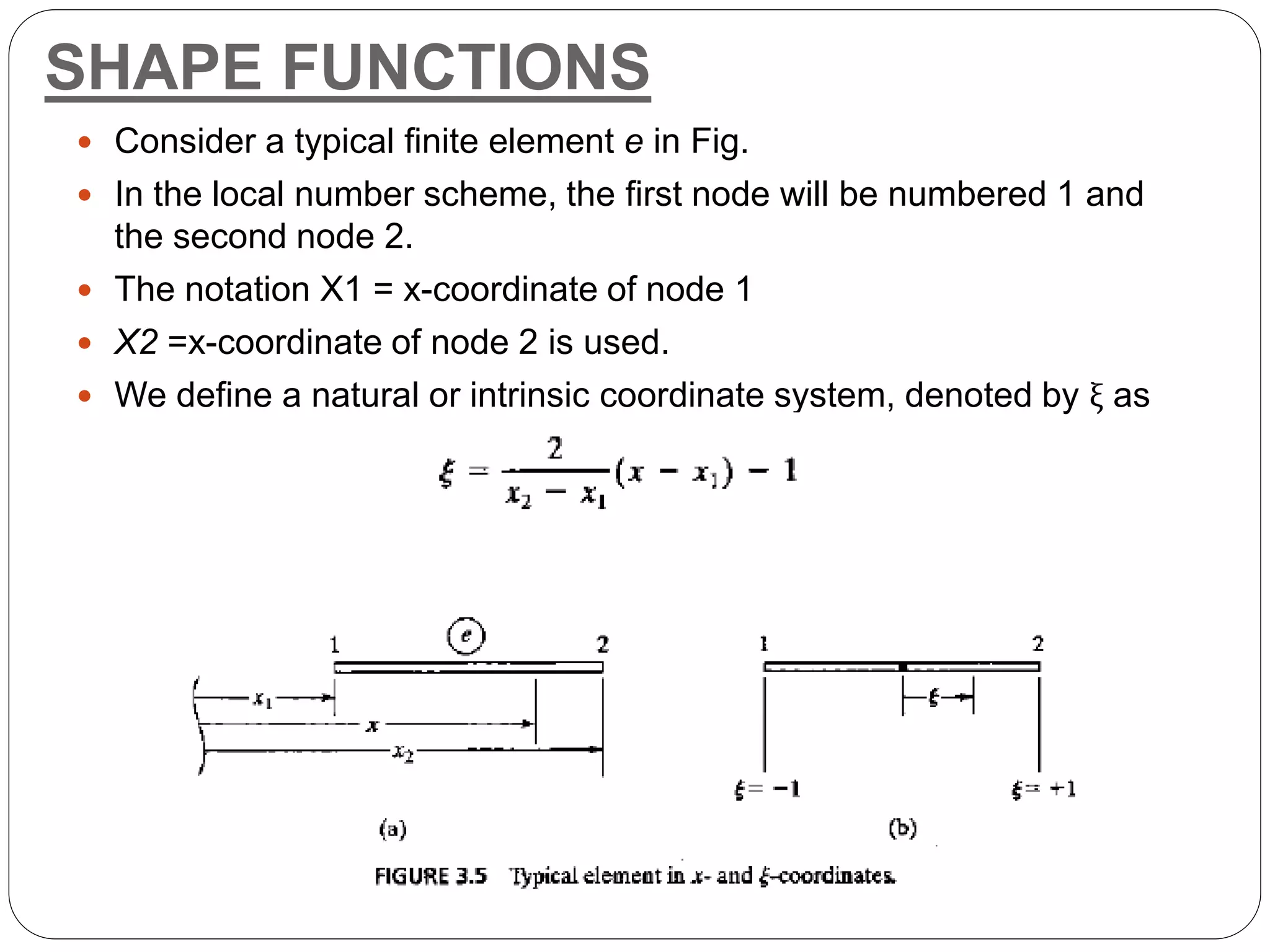
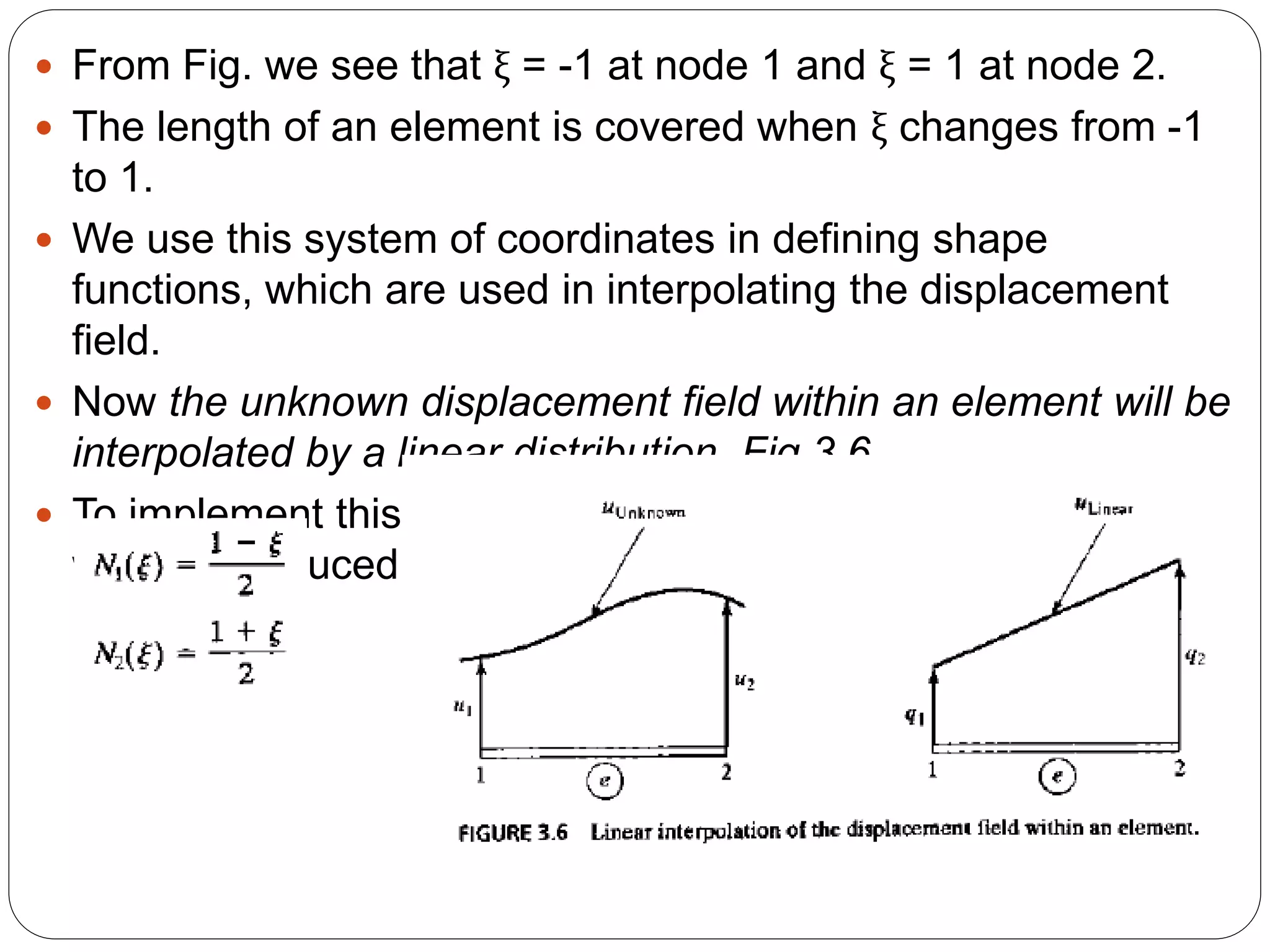

![ The shape functions N1 and N2 are shown in Figs. Respectively.
The graph of the shape function N1 in Fig.(a) is obtained from equation
N1(ξ) by noting that N1 = 1 at ξ = -1, N1 = 0 at ξ = 1.
and N1 is a straight line between the two points.
Similarly, the graph of N2 in Fig. 3.7(b) is obtained from Eq. N2(ξ).
Once the shape functions are defined, the linear displacement field within
the element can be written in terms of the nodal displacements q1 and q2
as
u= N1q1 + N2q2
or, in matrix notation, as u=Nq
Where N = [N1 N2] and q=[q1 q2]T
In these equations, q is referred to as the element displacement
vector.
It is readily verified from equation of u that u=q1 at node 1 and u=q2 at
node 2, and that u varies linearly.
It may be noted that the transformation from x to ξ in eq of u can be
written in terms of N1 and N2 as
x= N1x1 + N2x2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finiteelementmethod-170409063521/75/Finite-element-method-27-2048.jpg)