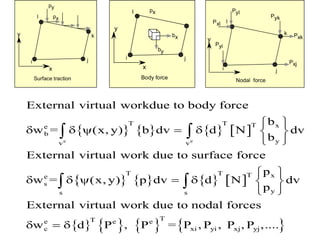
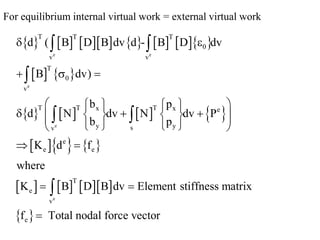
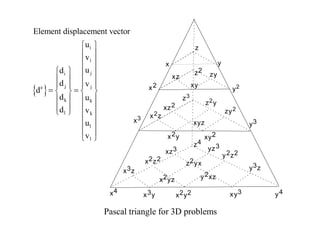
1. The general procedure for the finite element method involves discretizing the domain into elements, selecting displacement functions to approximate displacements within each element, and establishing relationships between displacements, strains, and stresses to set up the governing equations.
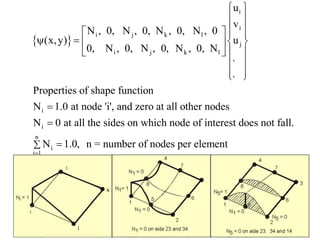
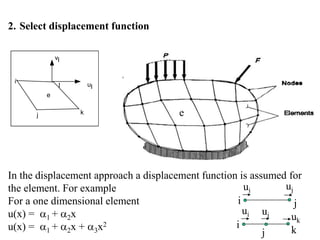
2. A displacement-based approach is used where shape functions are chosen to describe the displacement field within an element and ensure continuity of displacements between elements.
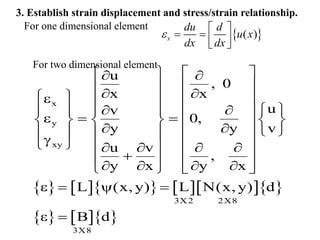
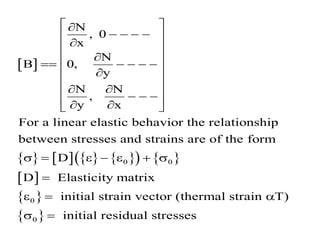
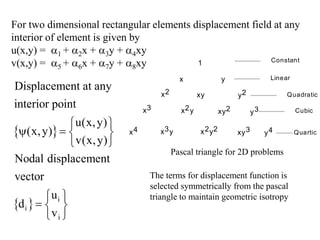
3. The strain-displacement and stress-strain relationships are developed using the shape functions and material properties to create the elemental stiffness matrix which are then assembled in the global finite element model.
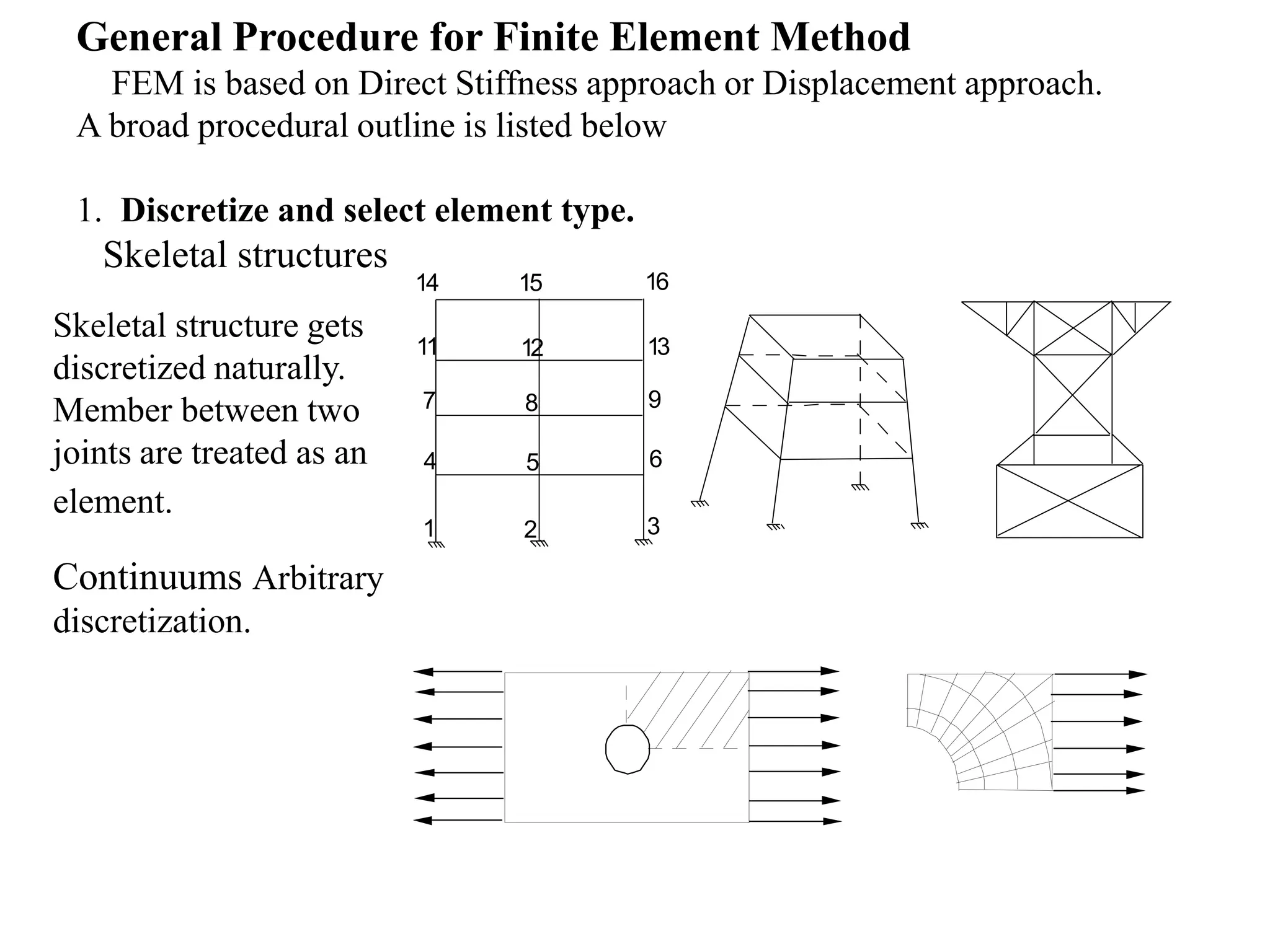
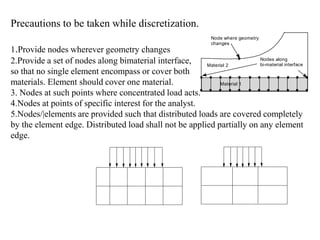
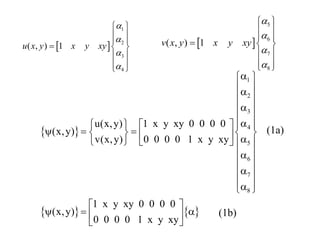
![1 1
1 1 1 1
1 2
1 1 1 1
2 3
2 2 2 2
2 4
2 2 2 2
3 5
3 3 3 3
6
3 3 3 3 3
7
4 4 4 4
4
8
4 4 4 4
4
1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1
u x y x y
v x y x y
u x y x y
v x y x y
u x y x y
v x y x y
x y x y
u
x y x y
v
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
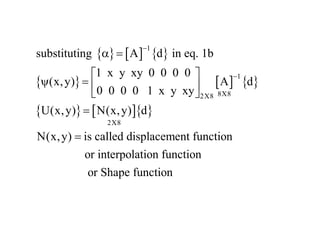
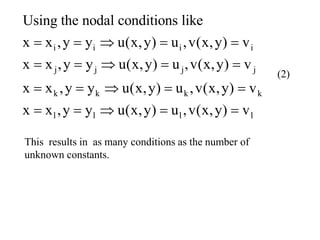
Using nodal boundary condition listed in eq. (2) in eq. 1a, following matrix
eqn. Can be obtained
1
(3)
d A
A d
a
a
For quadrilateral element [A] is of size 8 X 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/generalformulation-240209114047-cfc2982c/85/generalformulation-ppt-10-320.jpg)