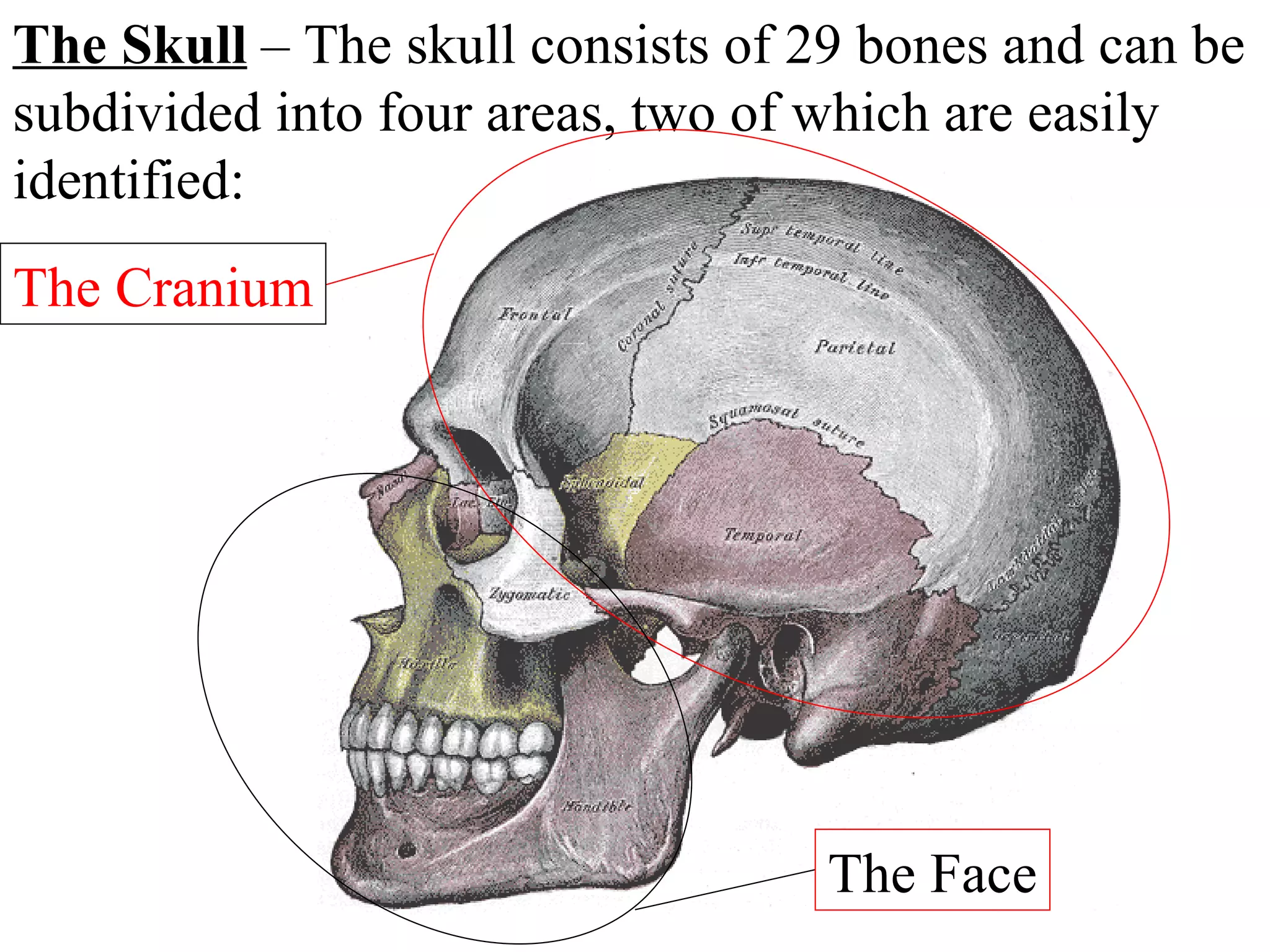
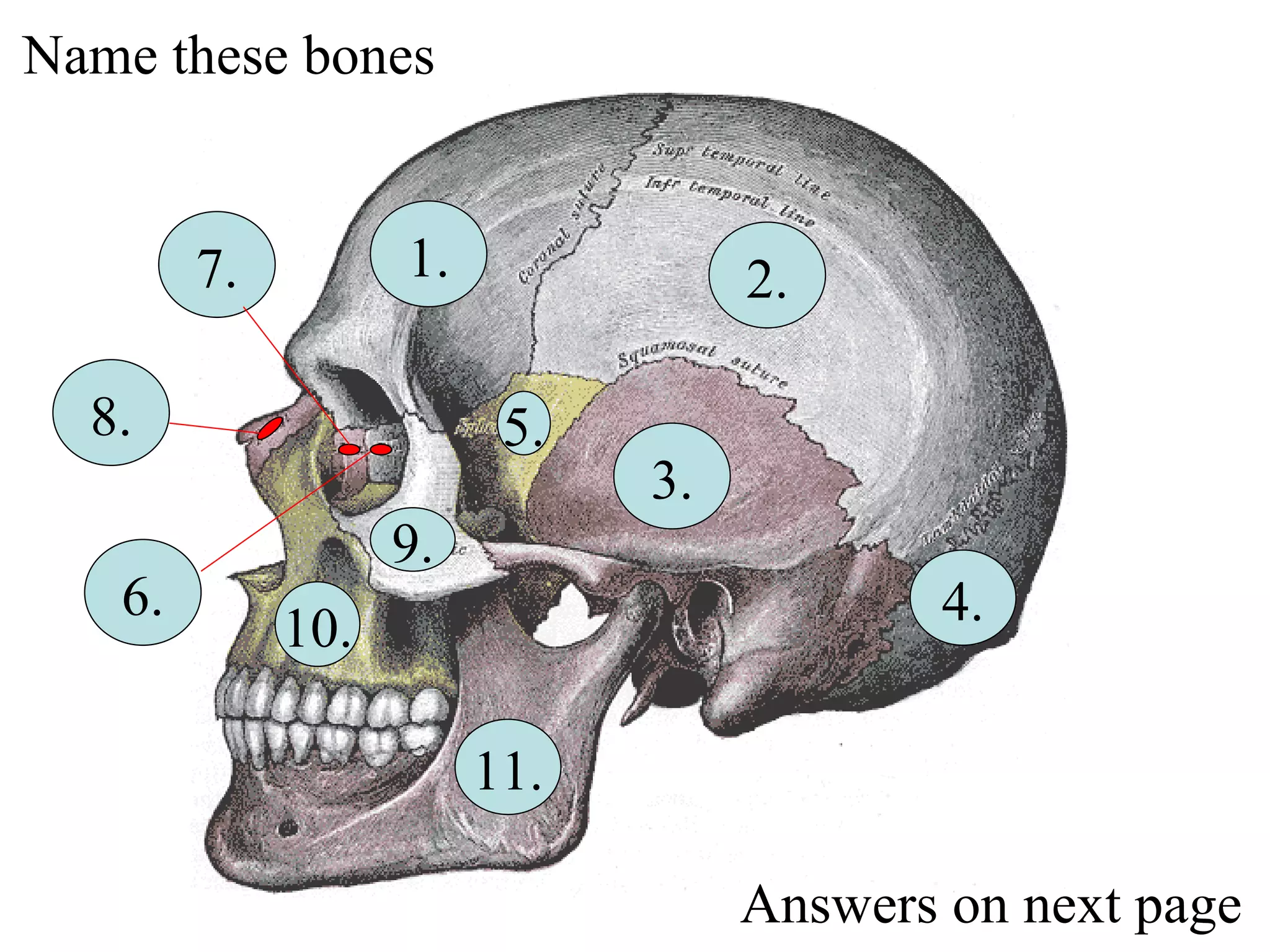
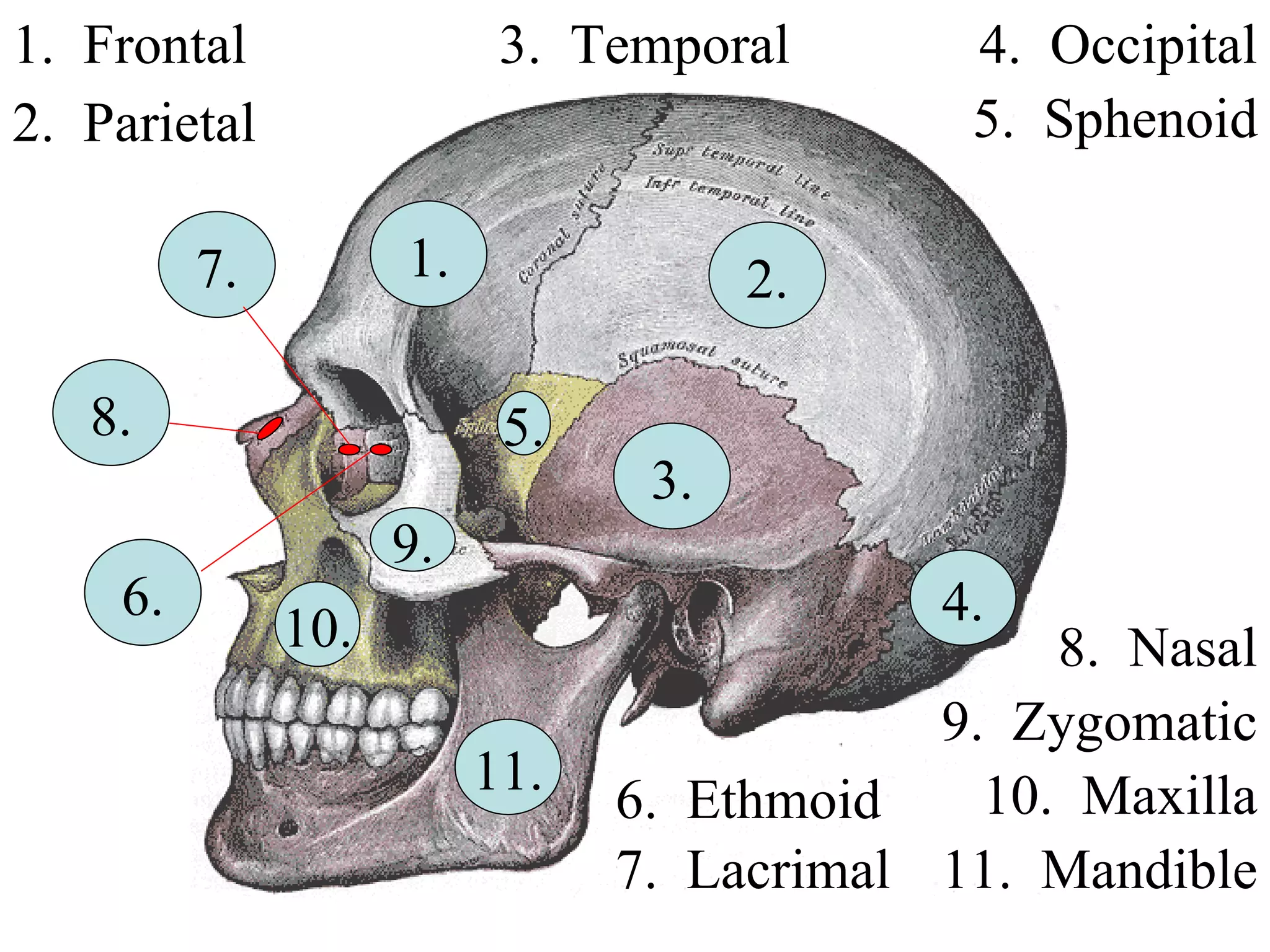
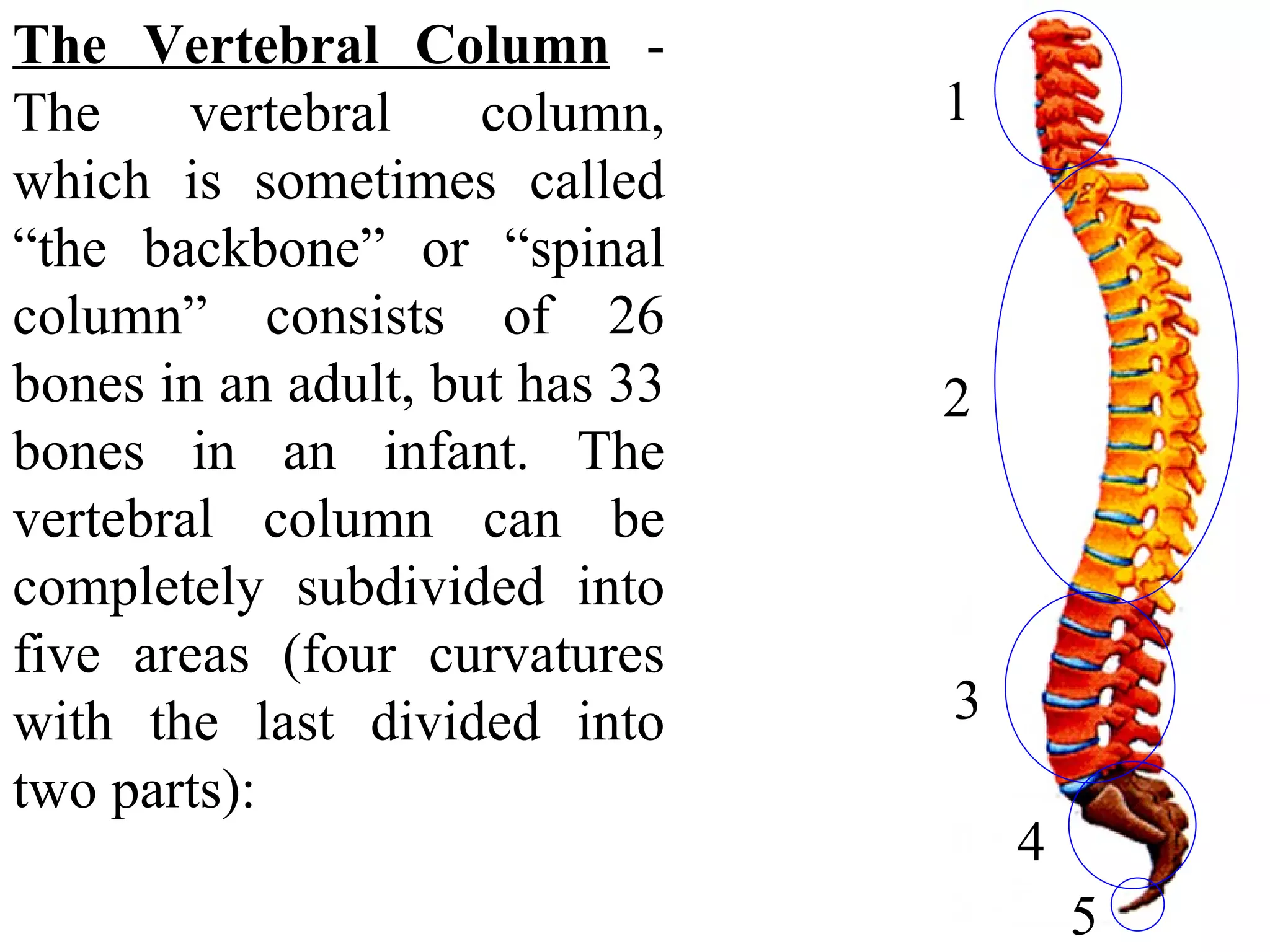
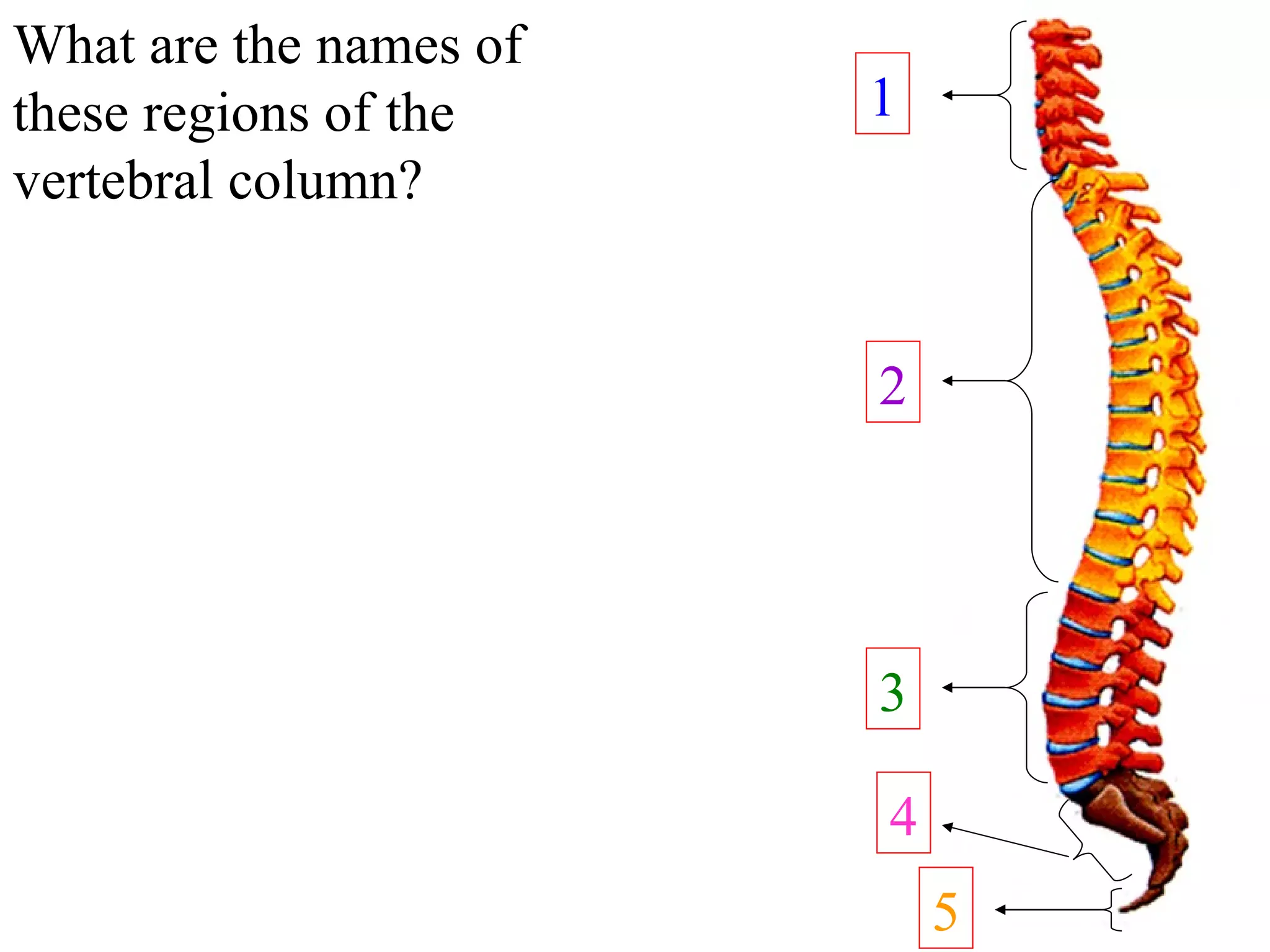
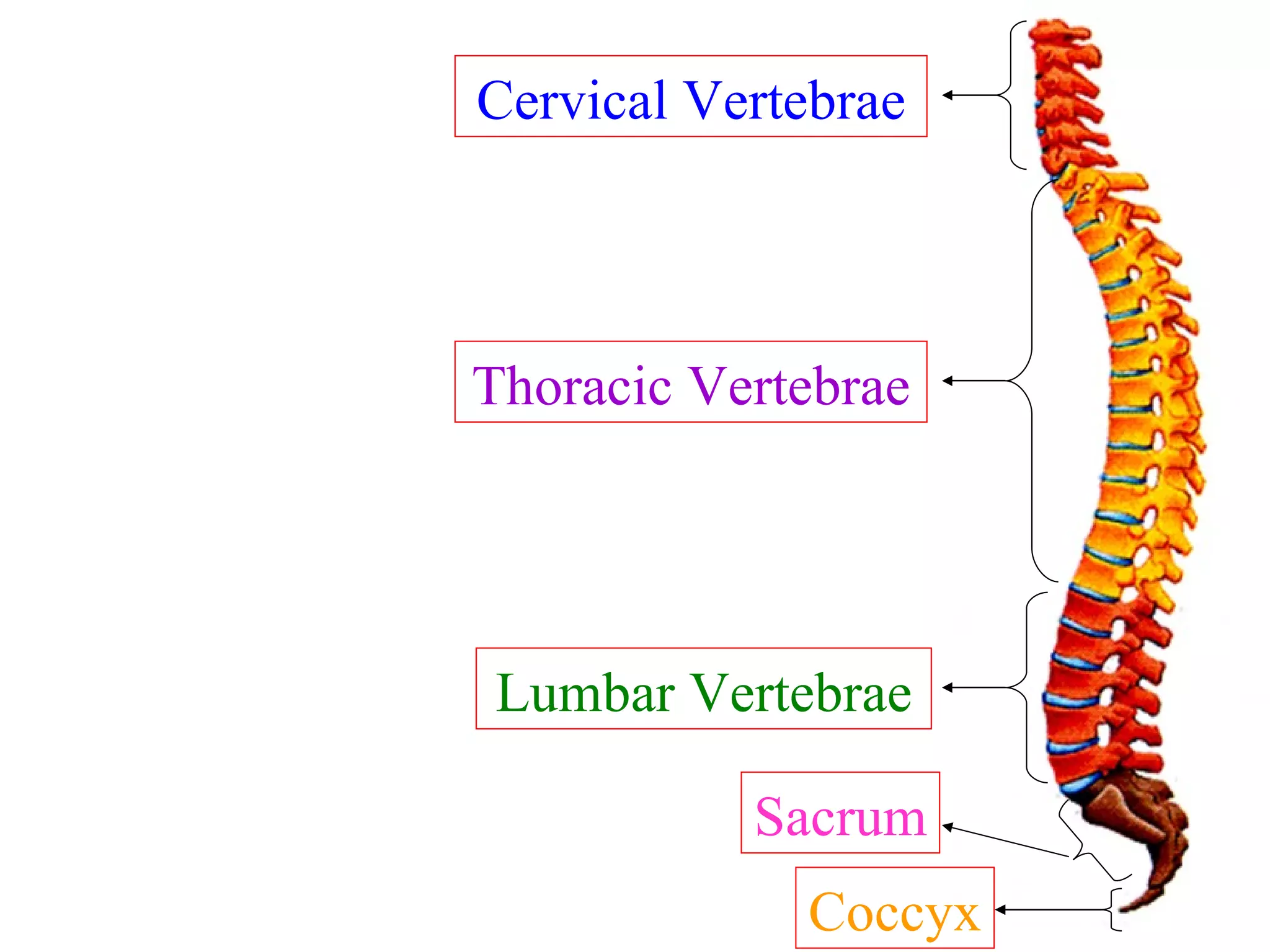
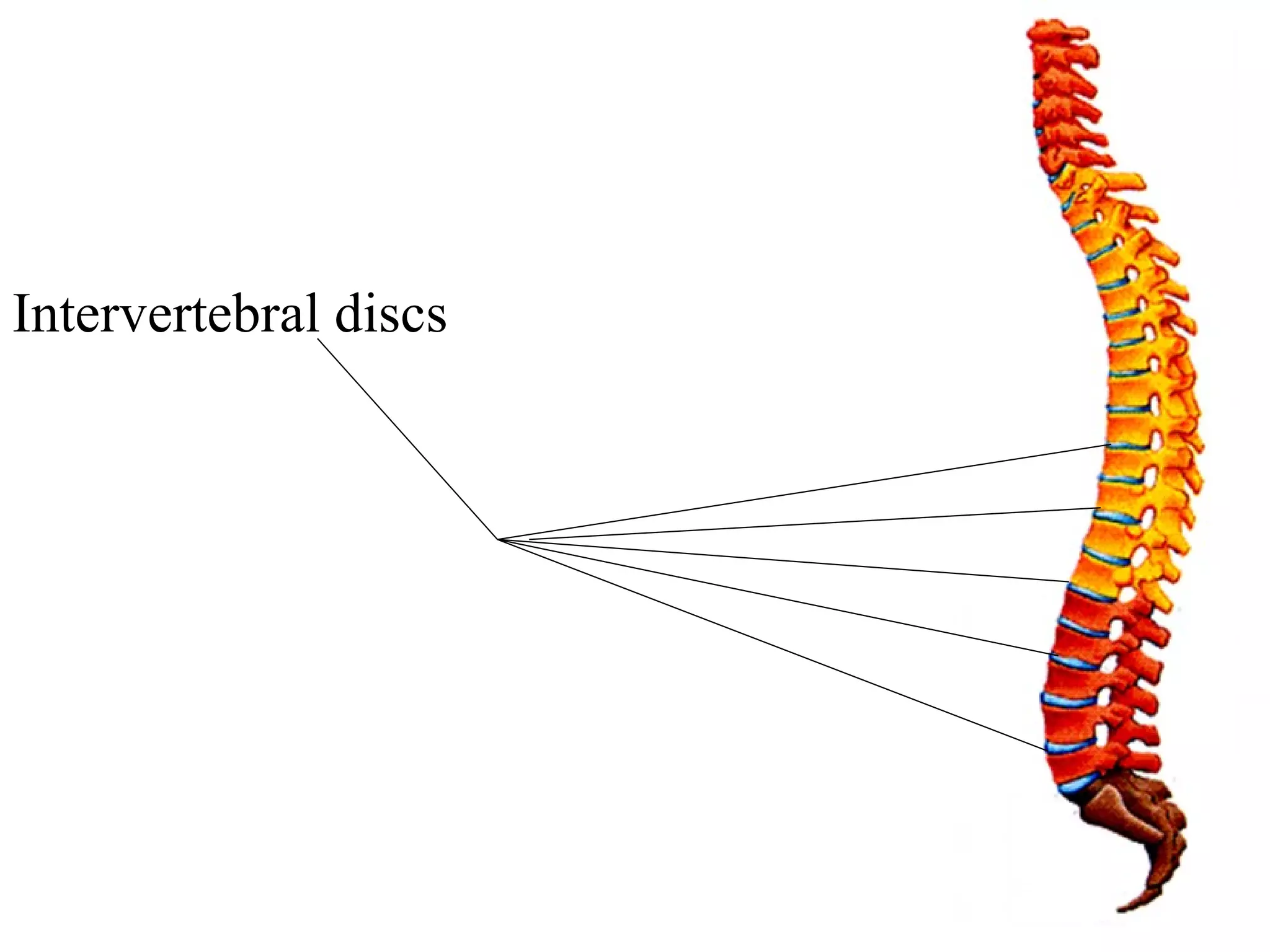
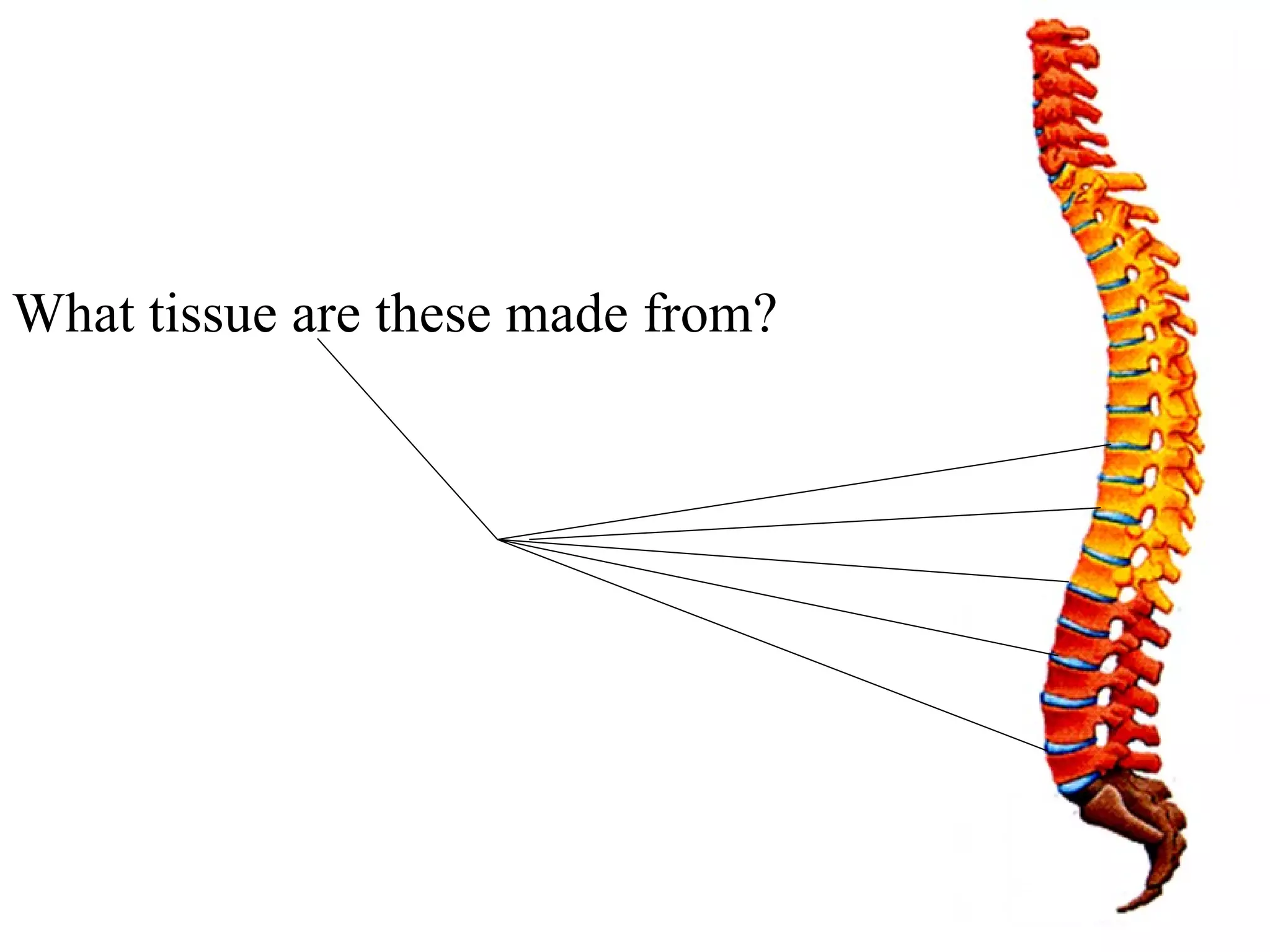
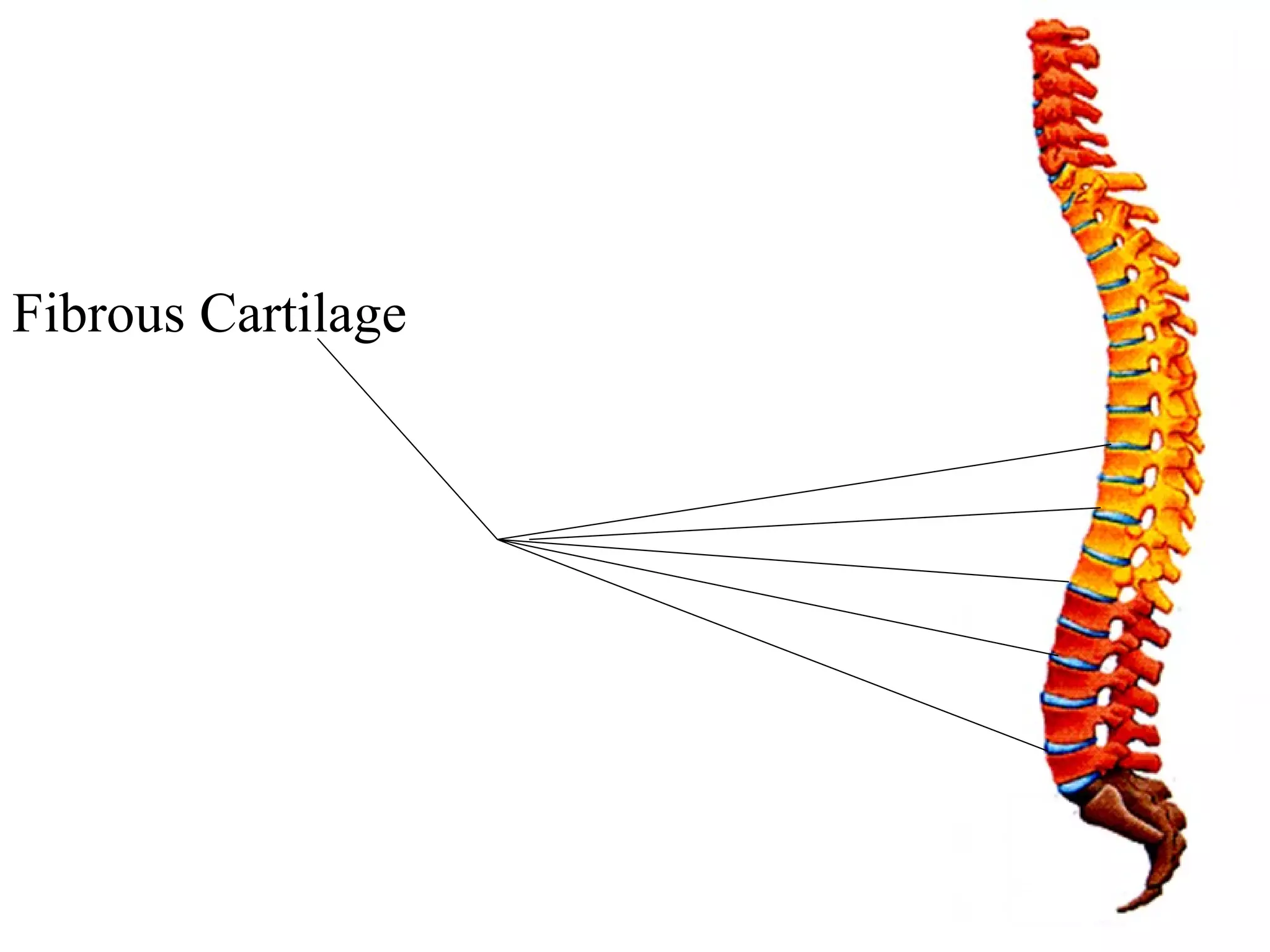
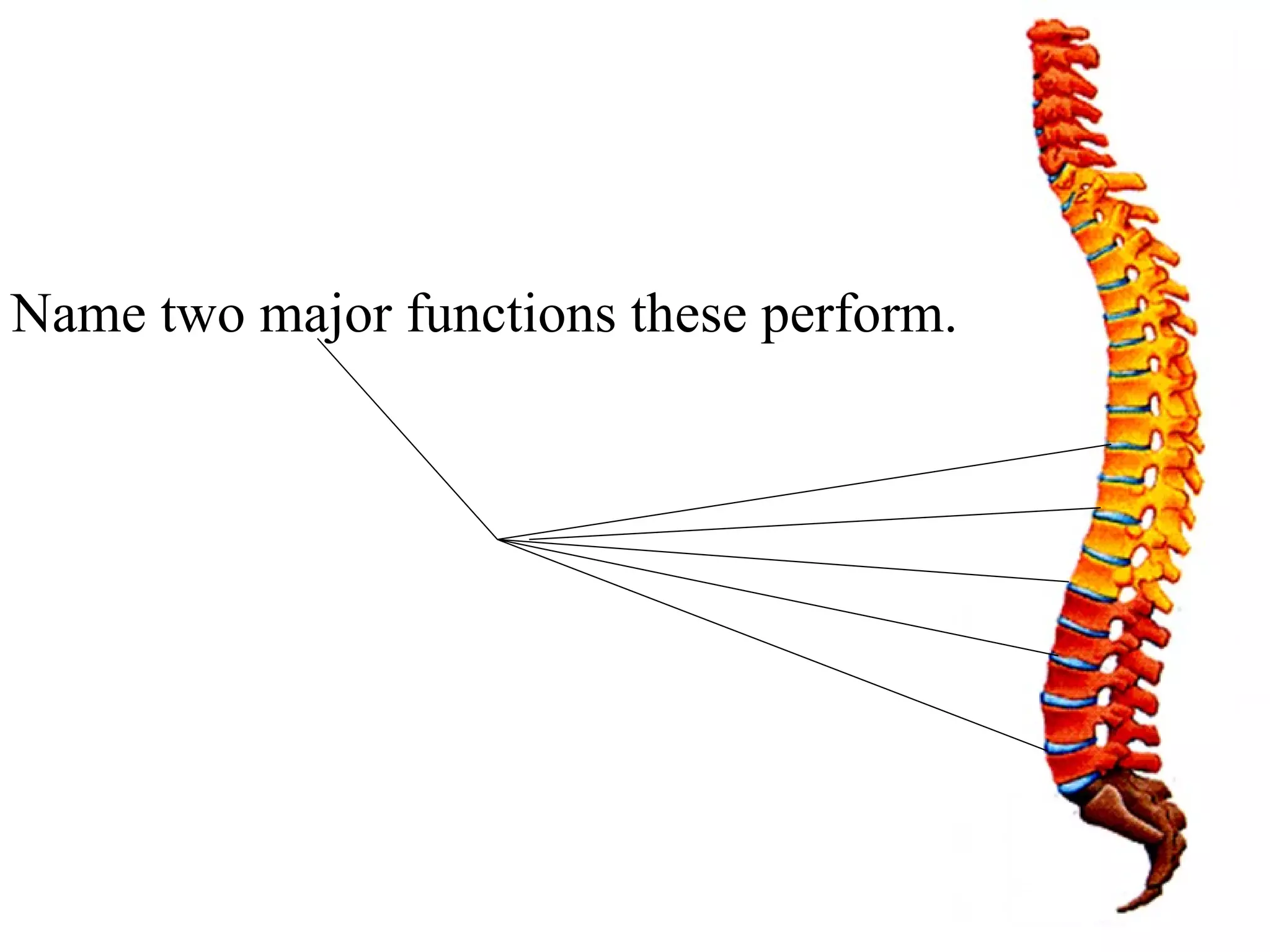
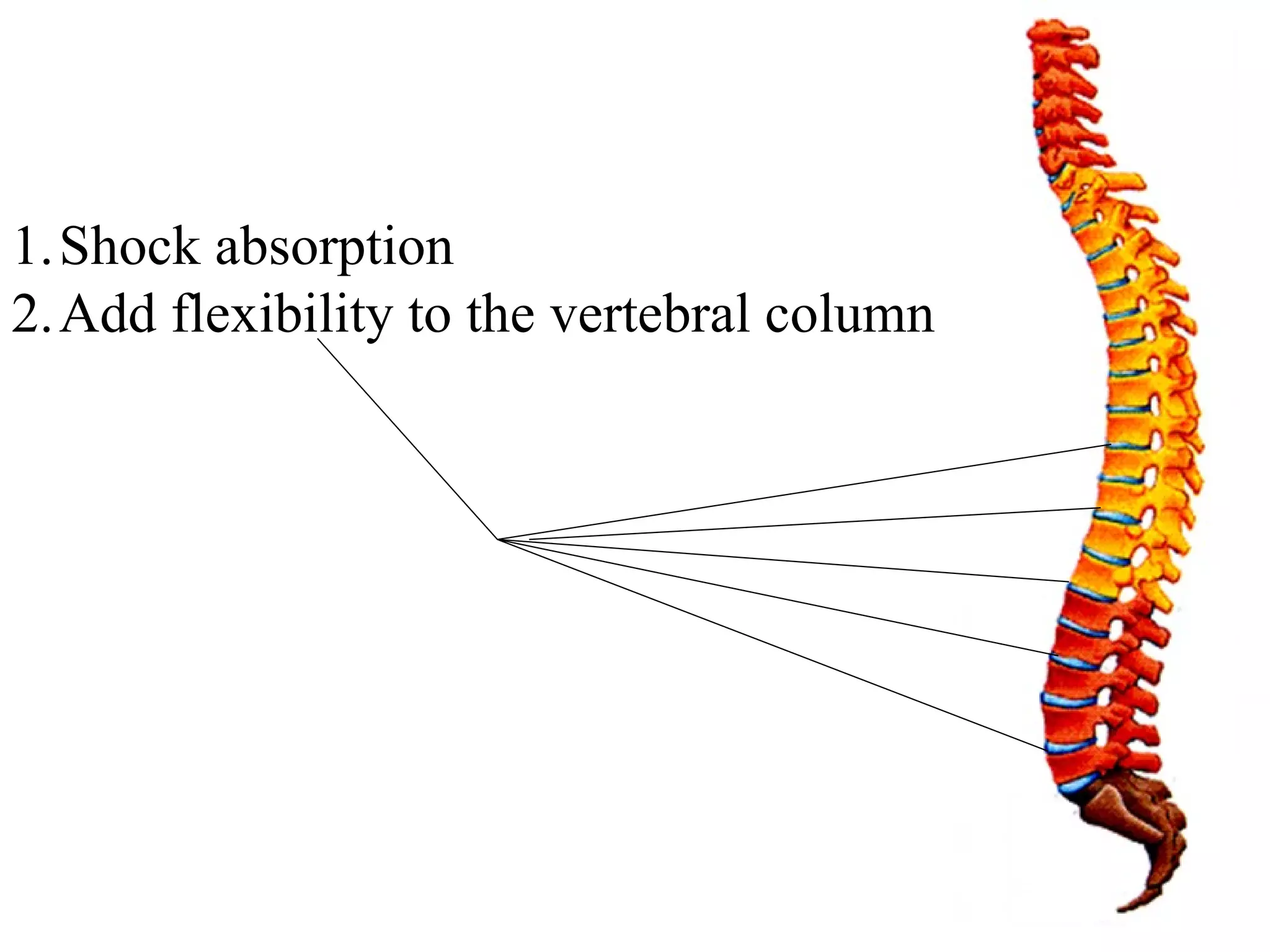
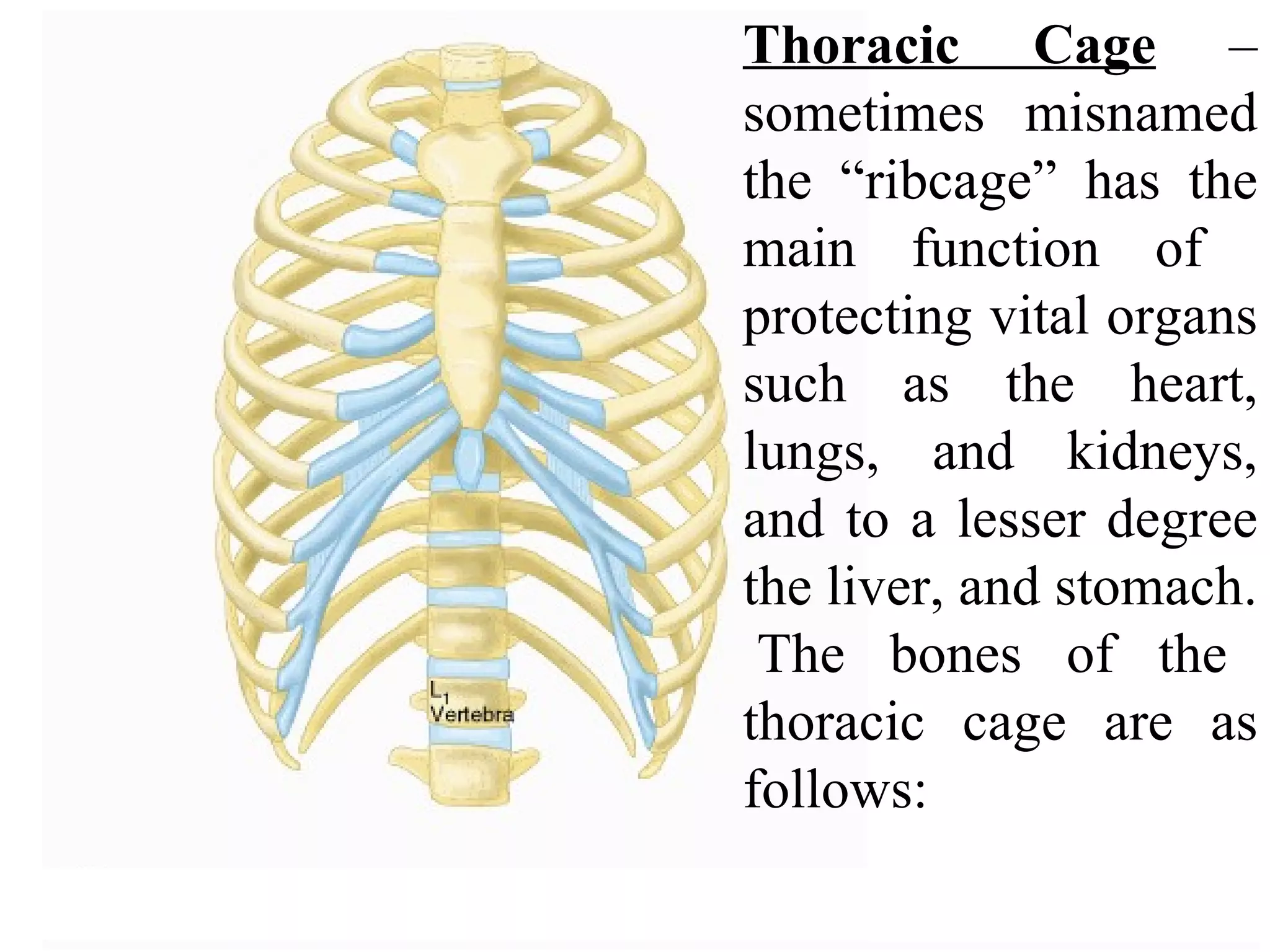
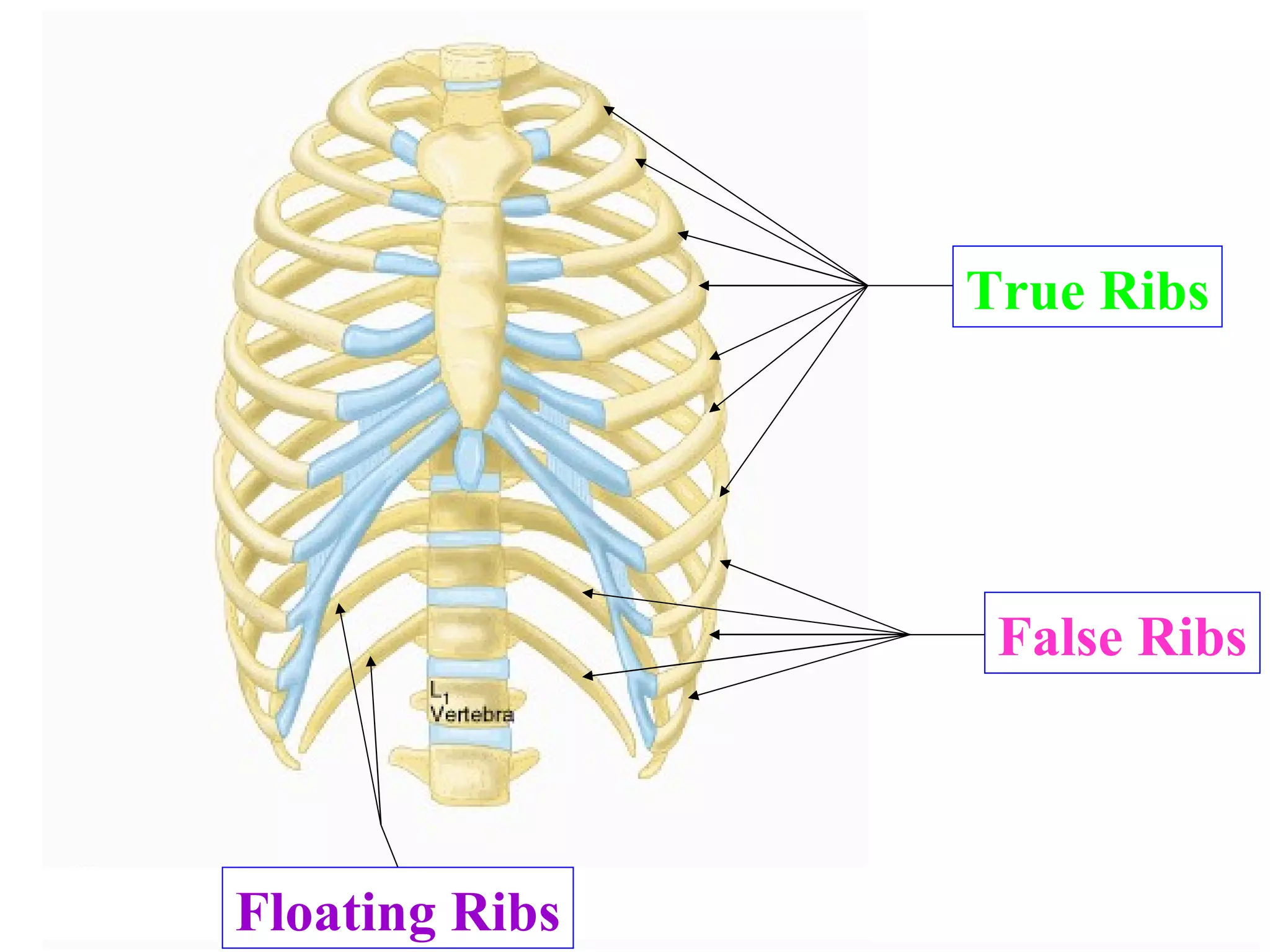
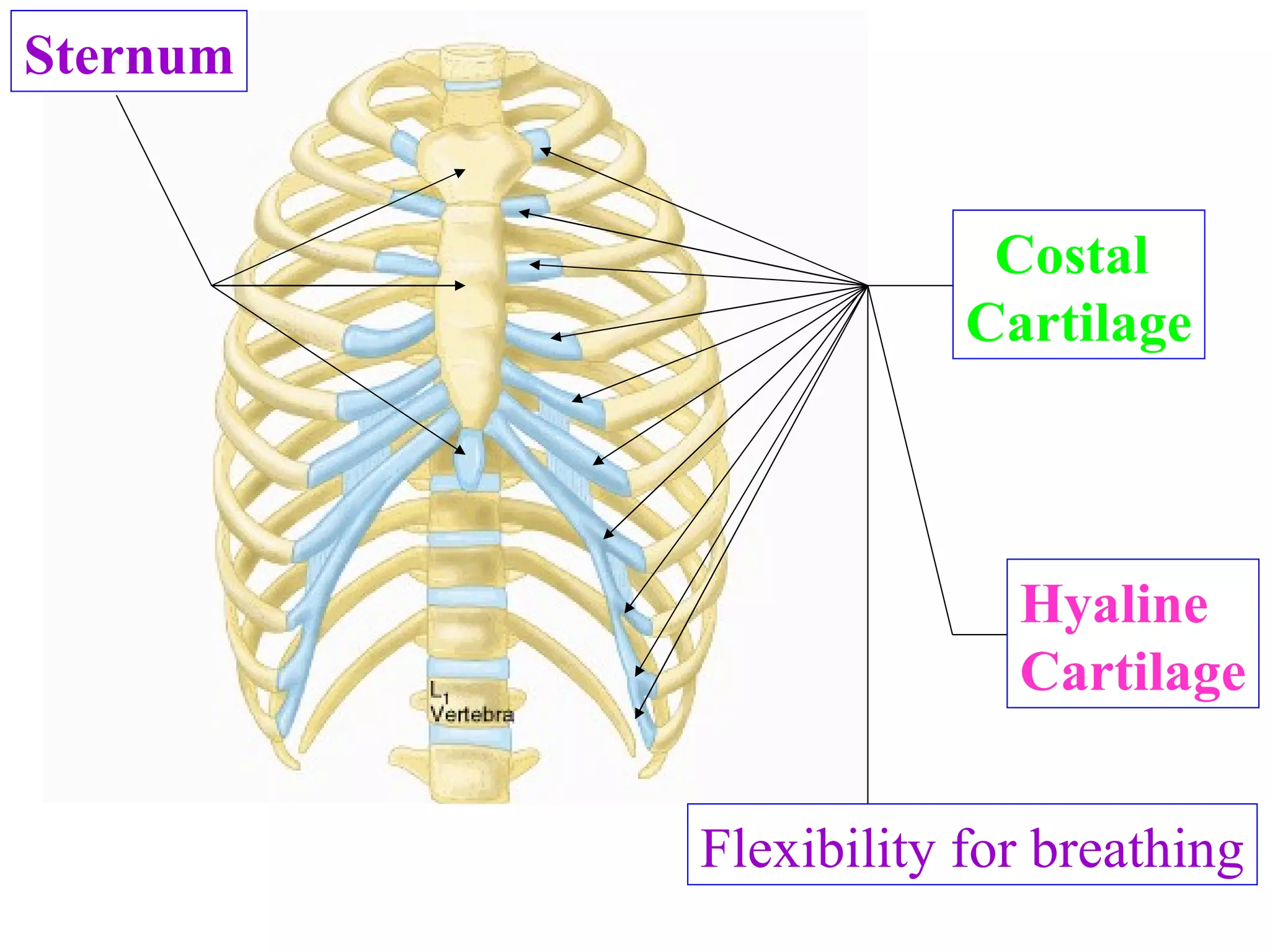
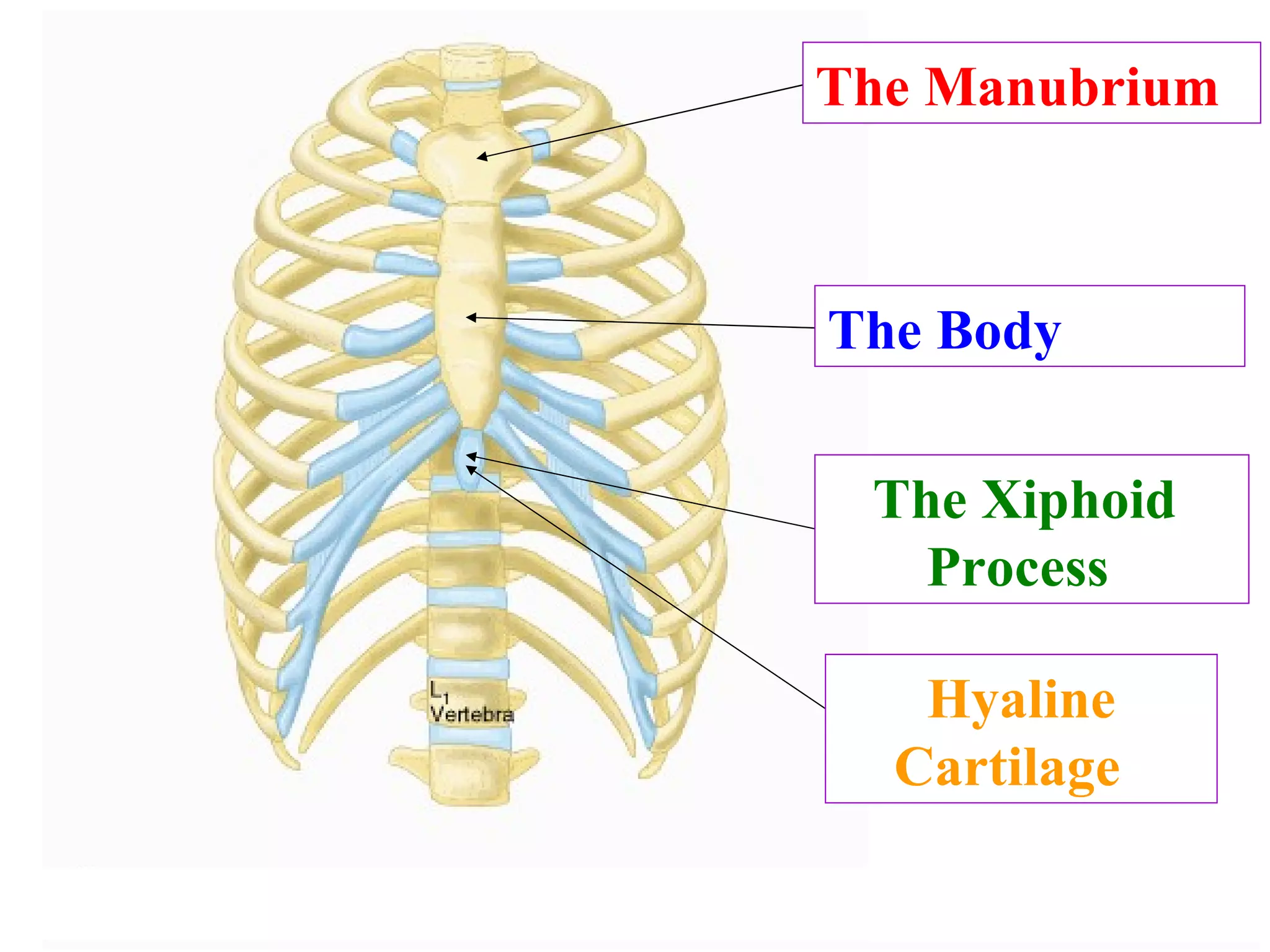
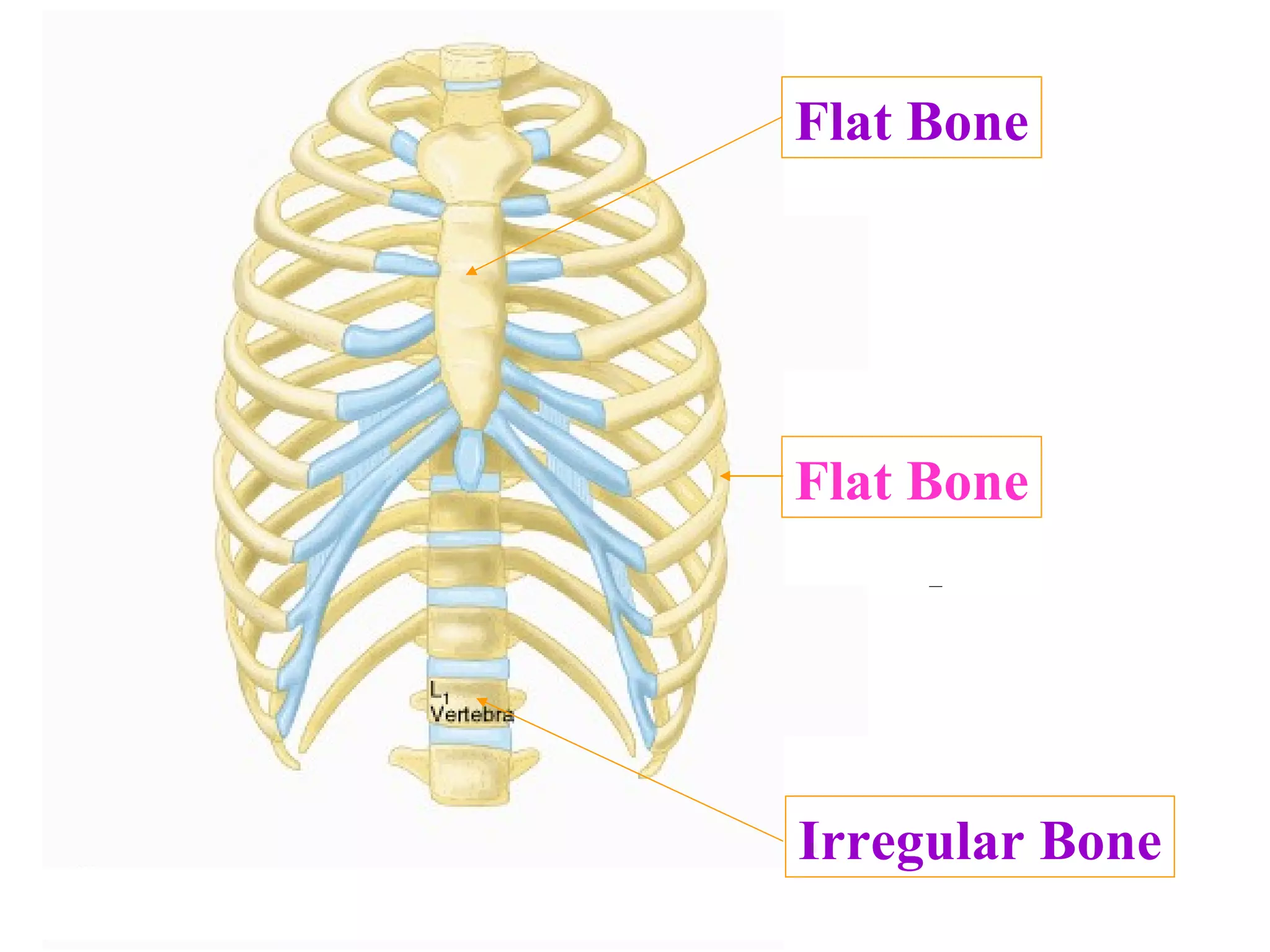
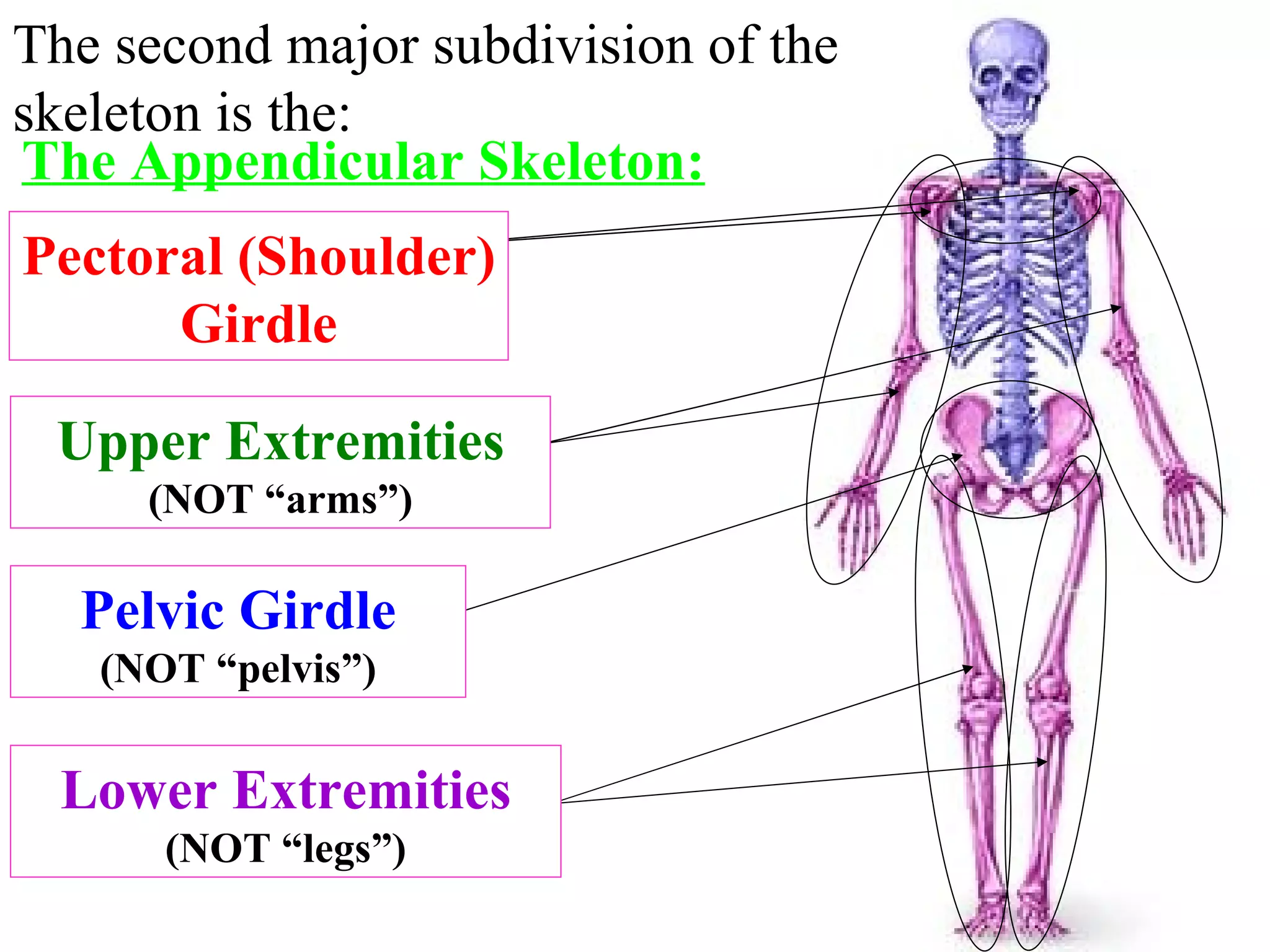
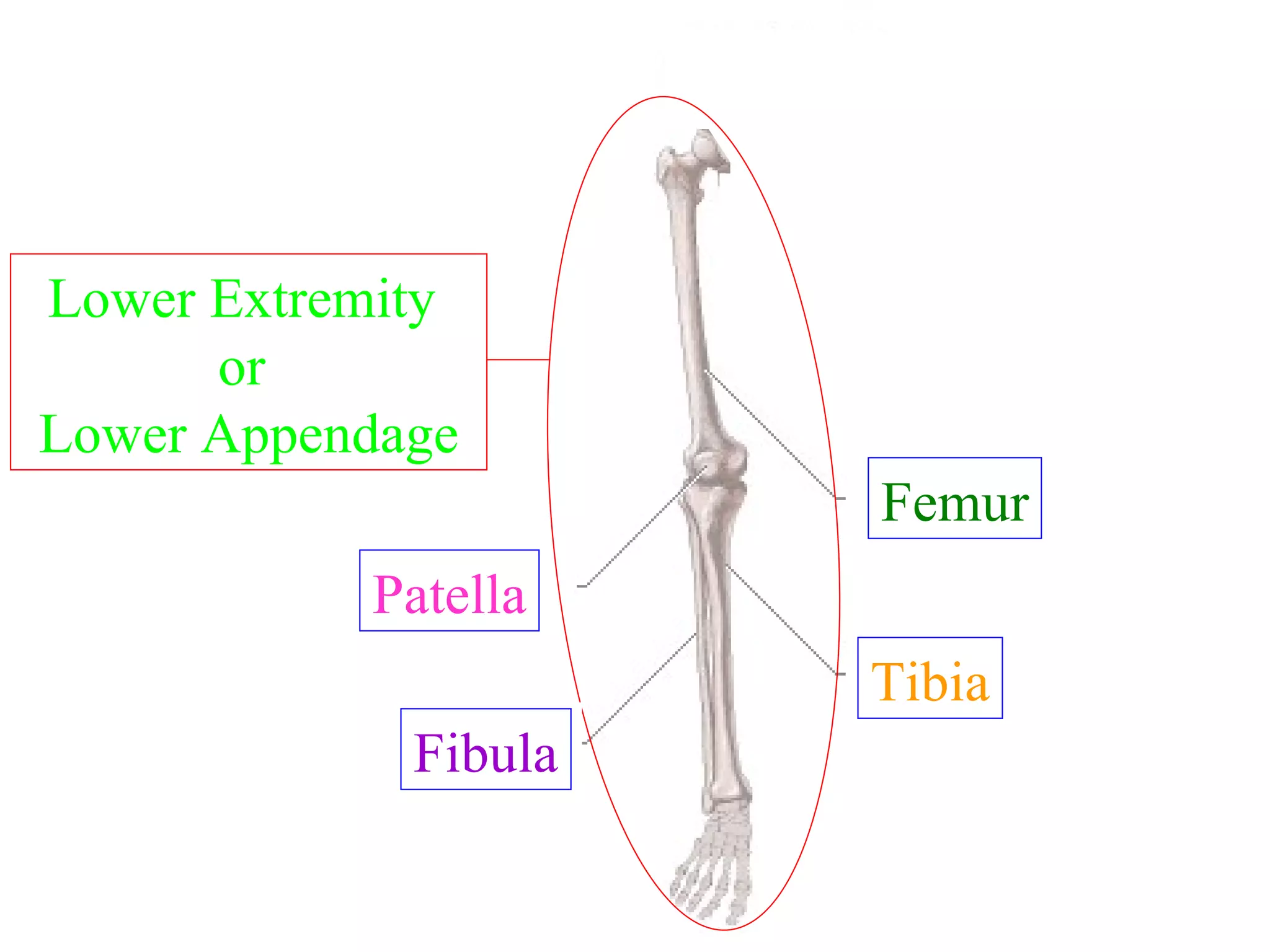
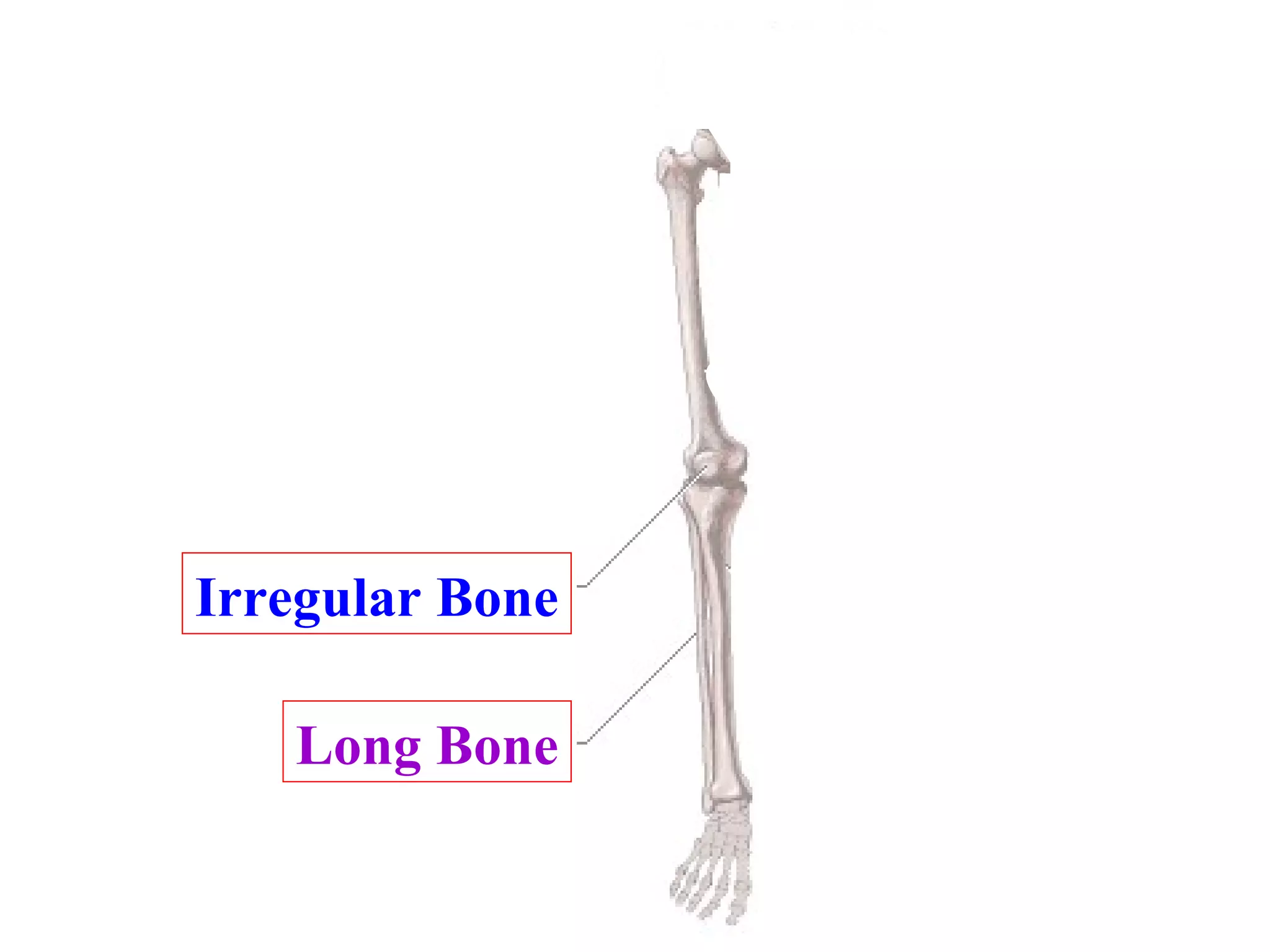
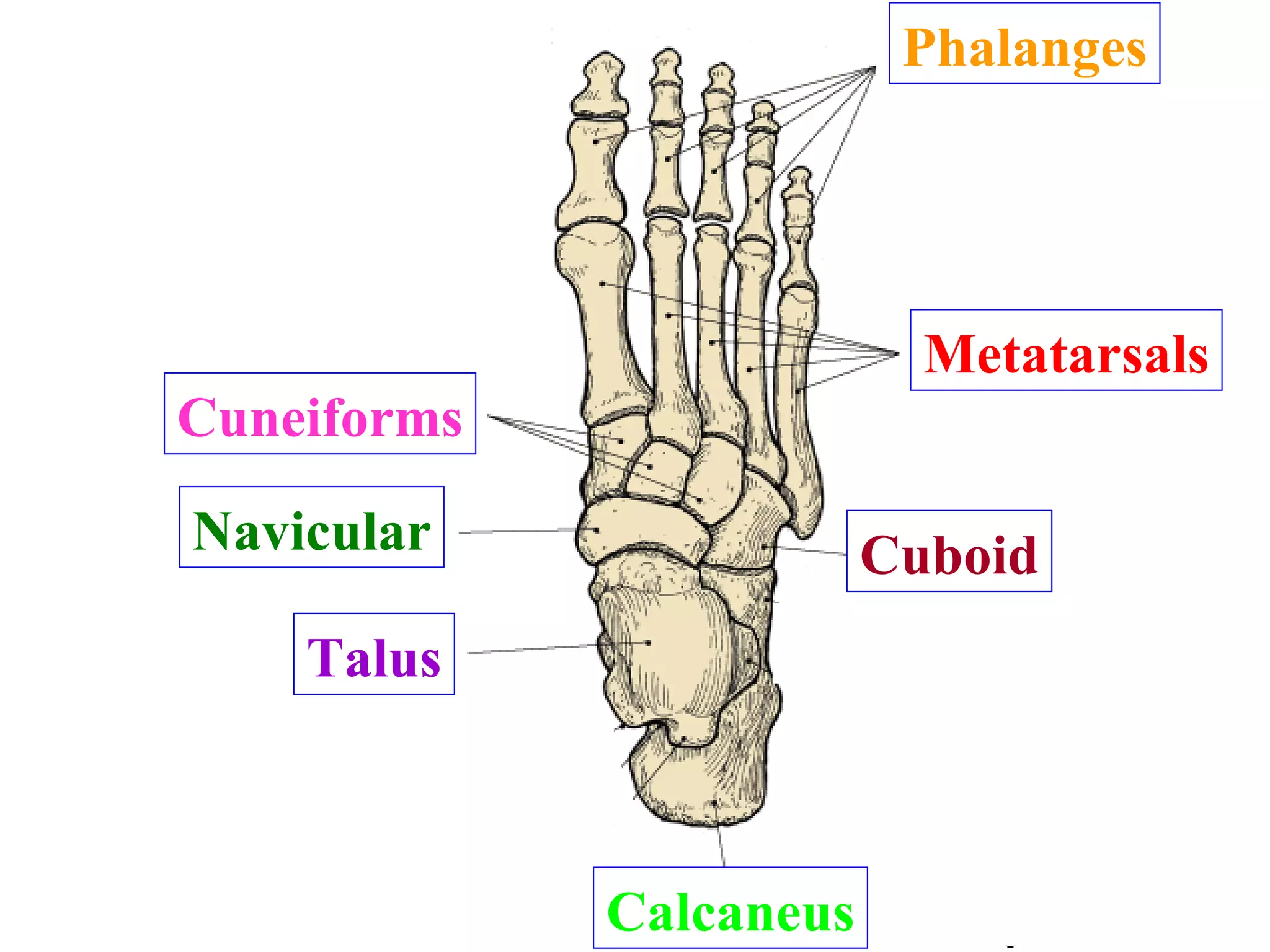
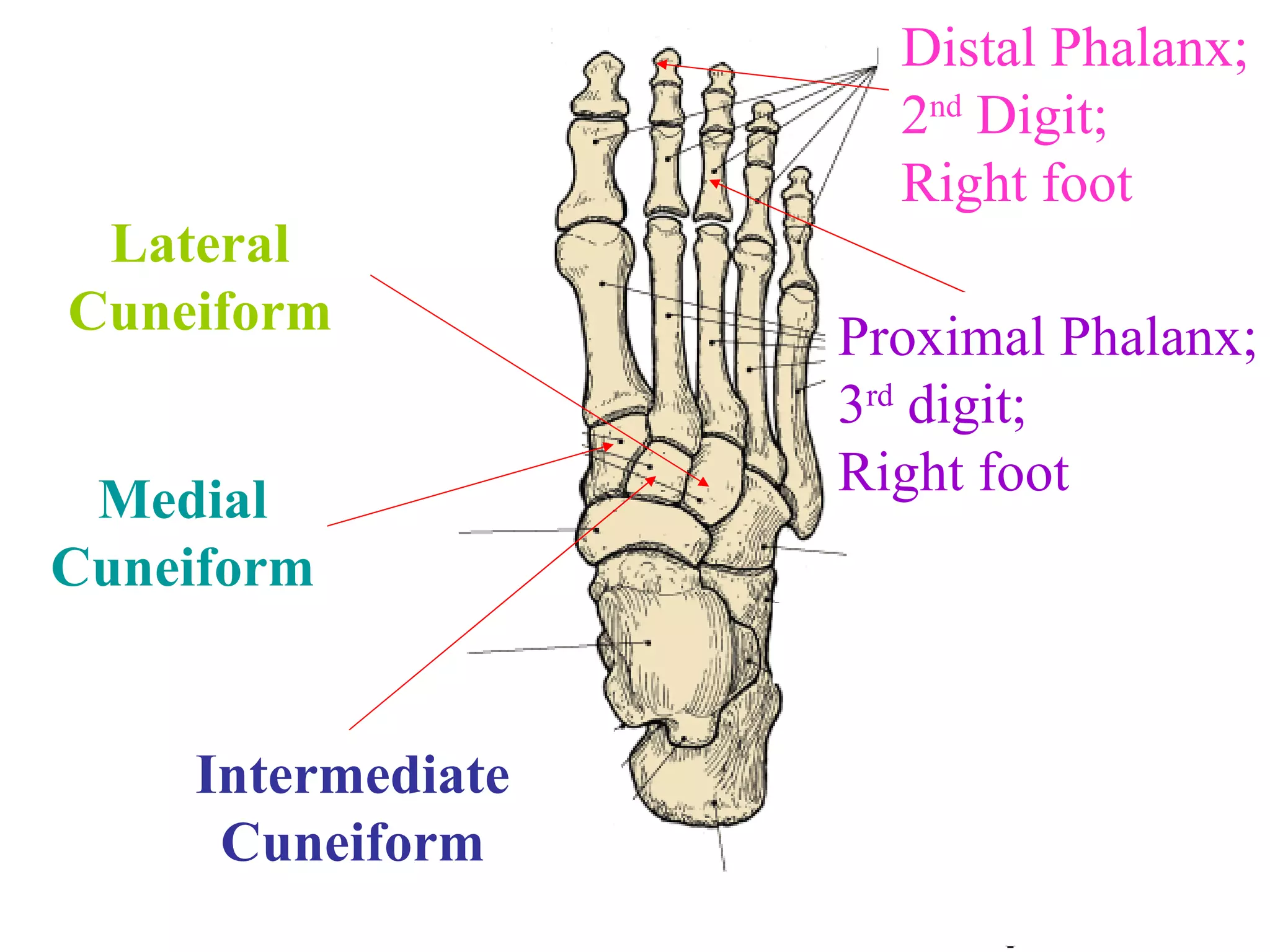
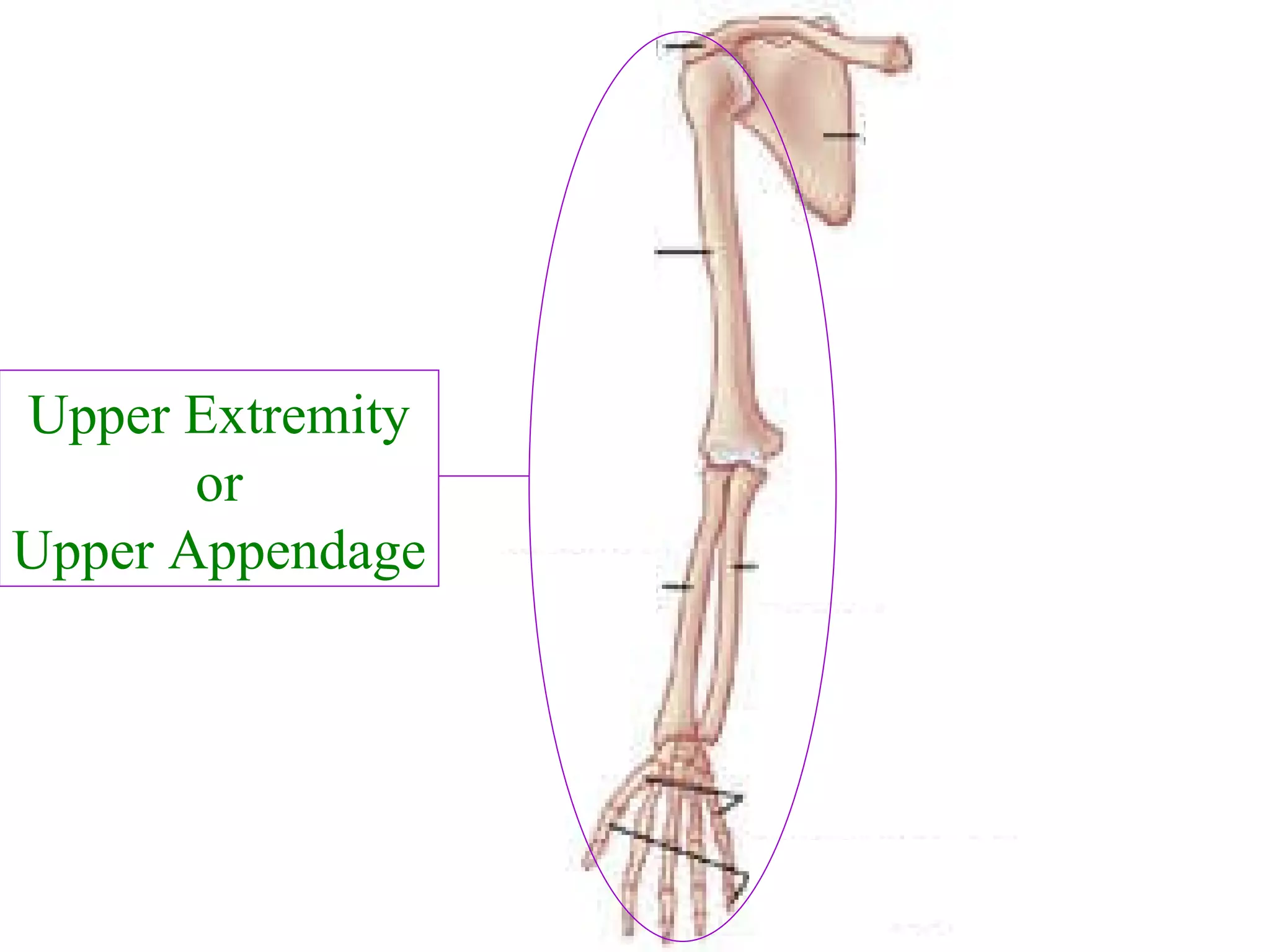
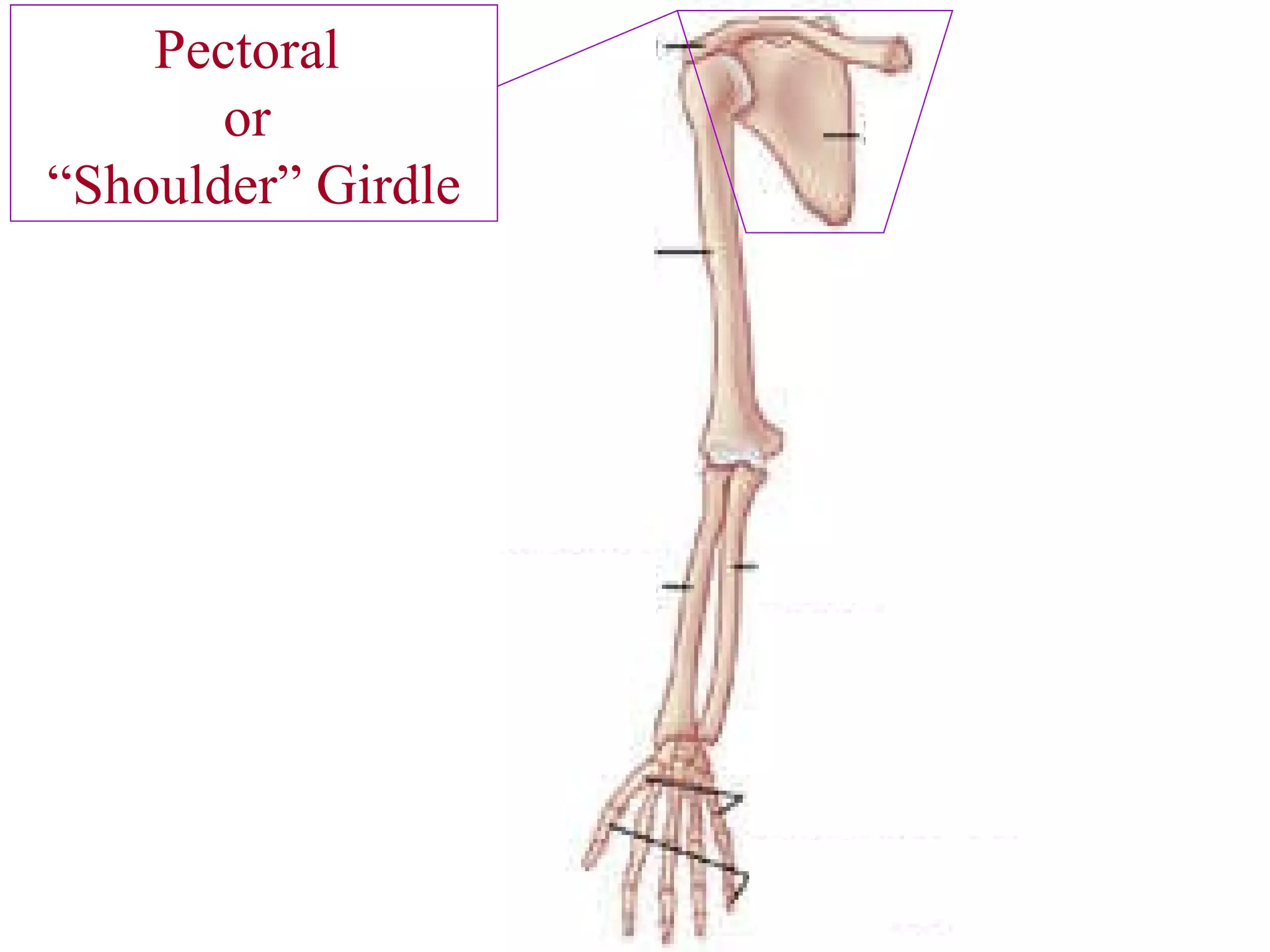
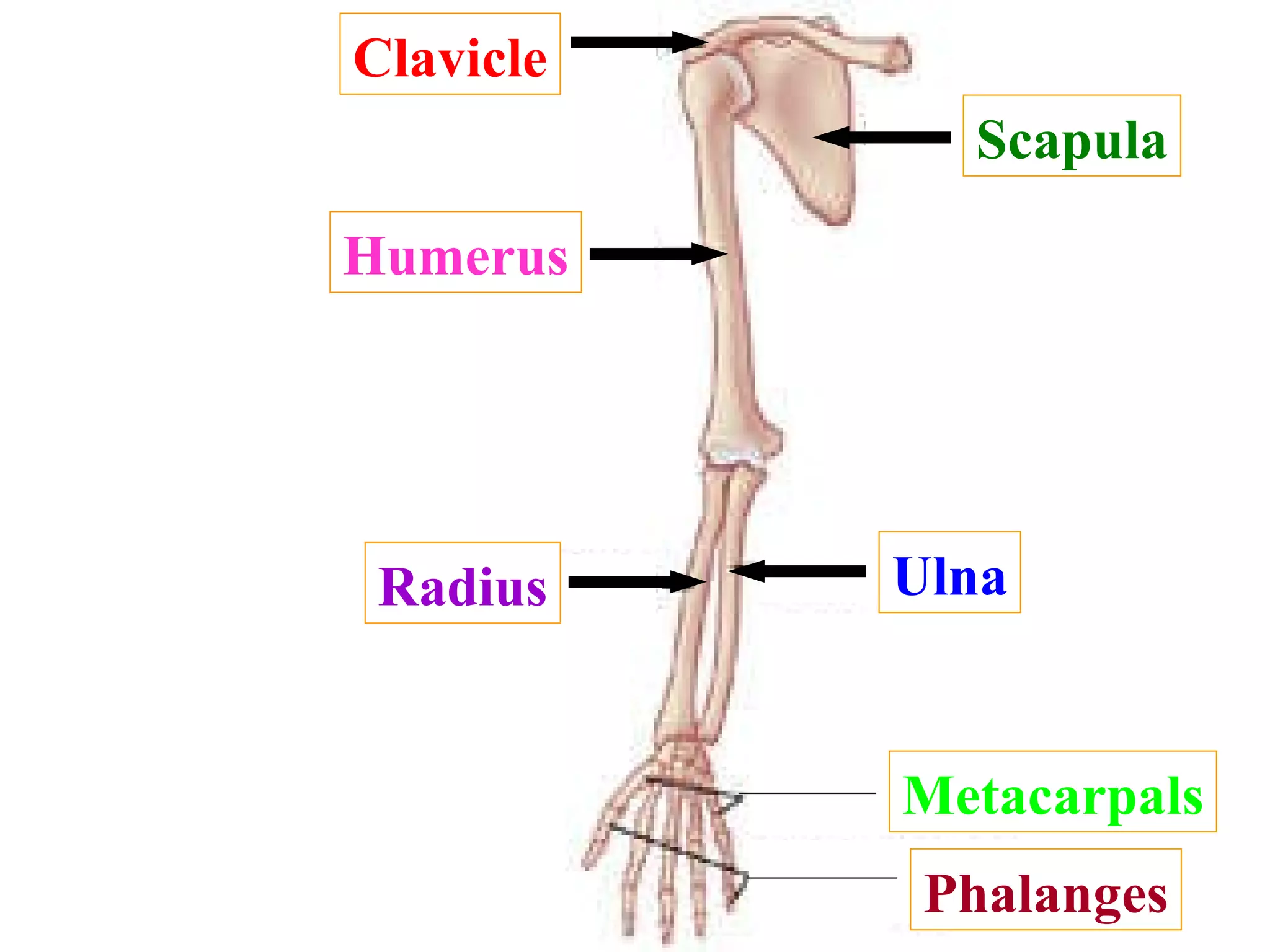
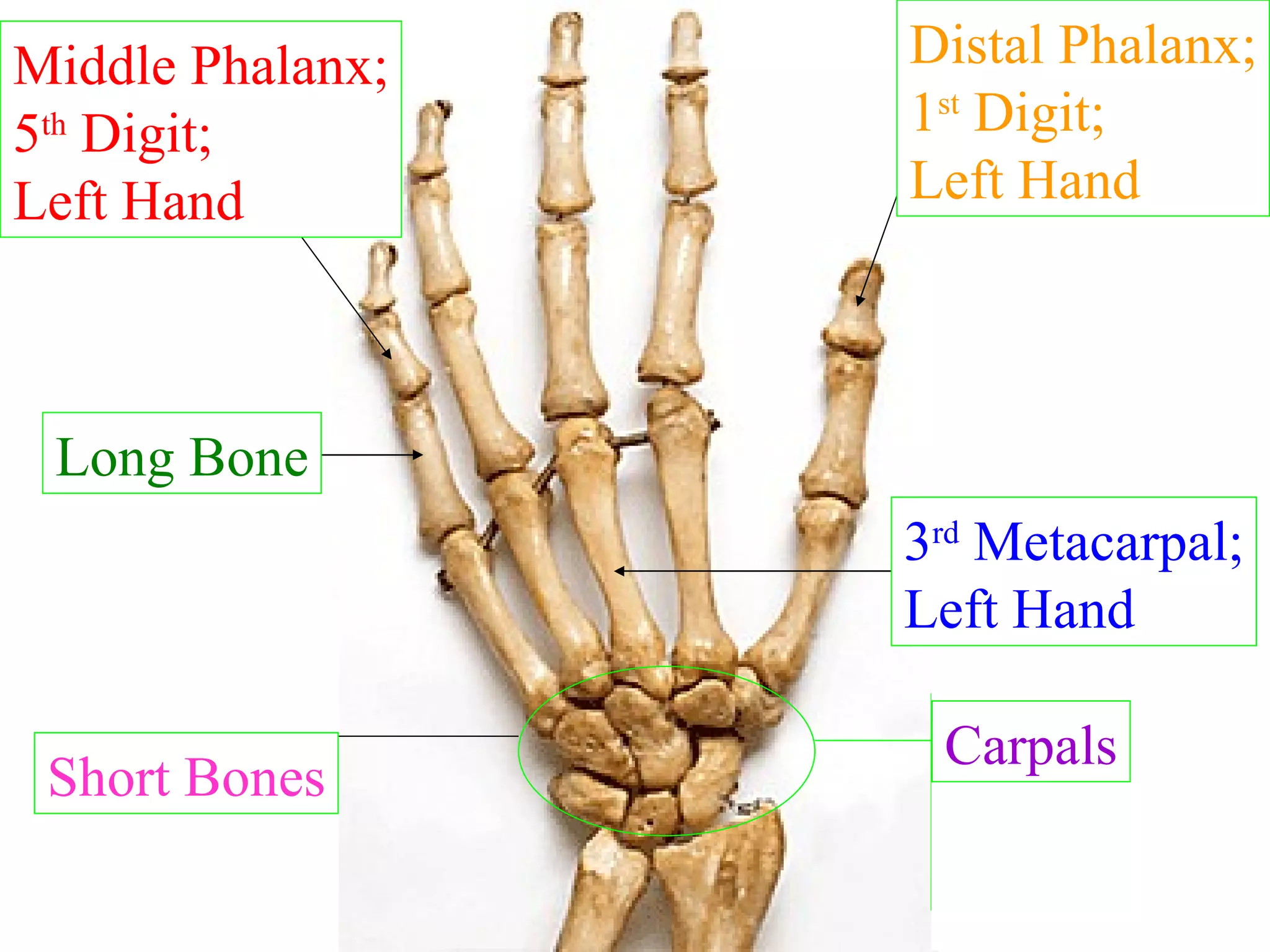
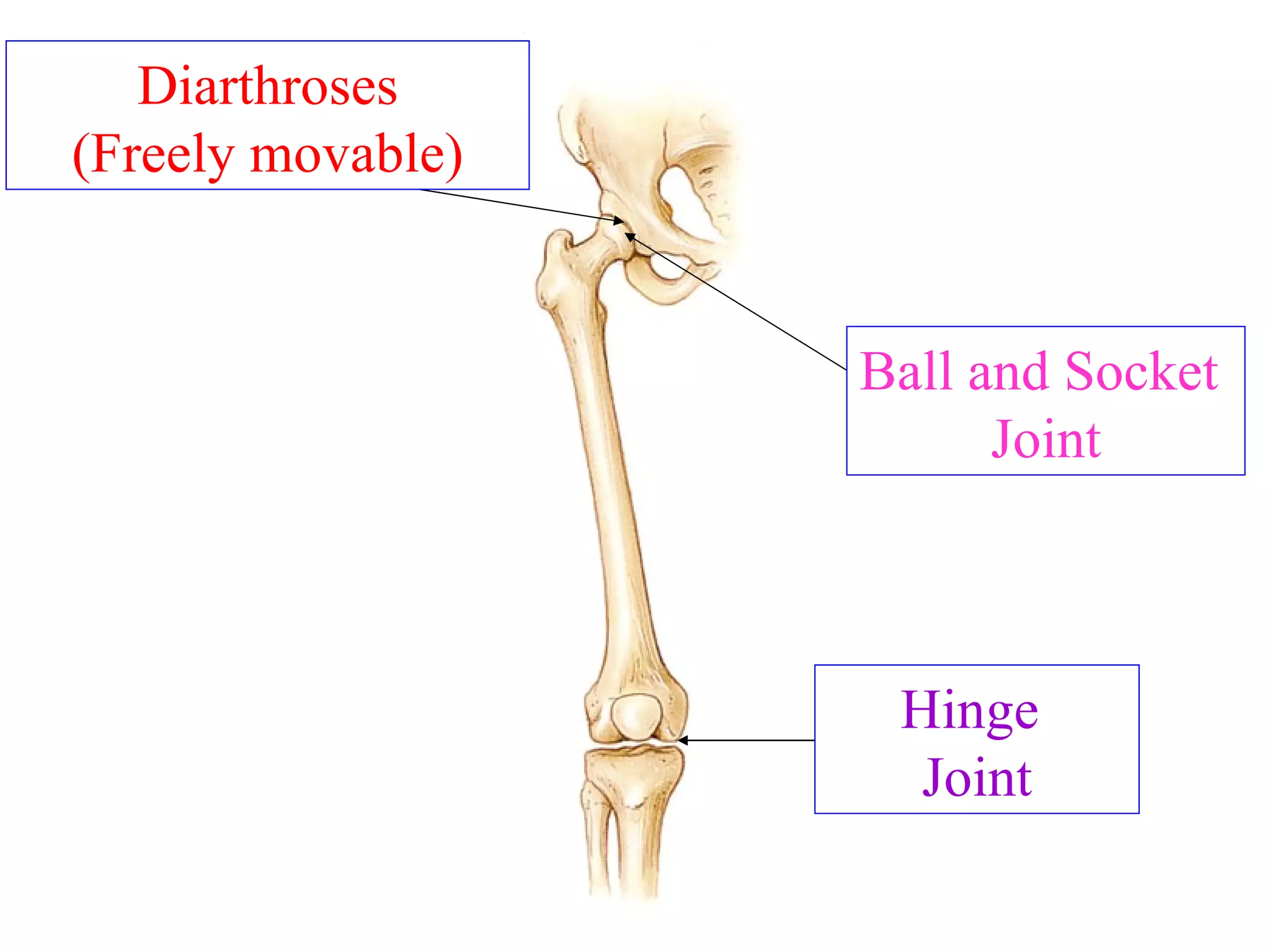
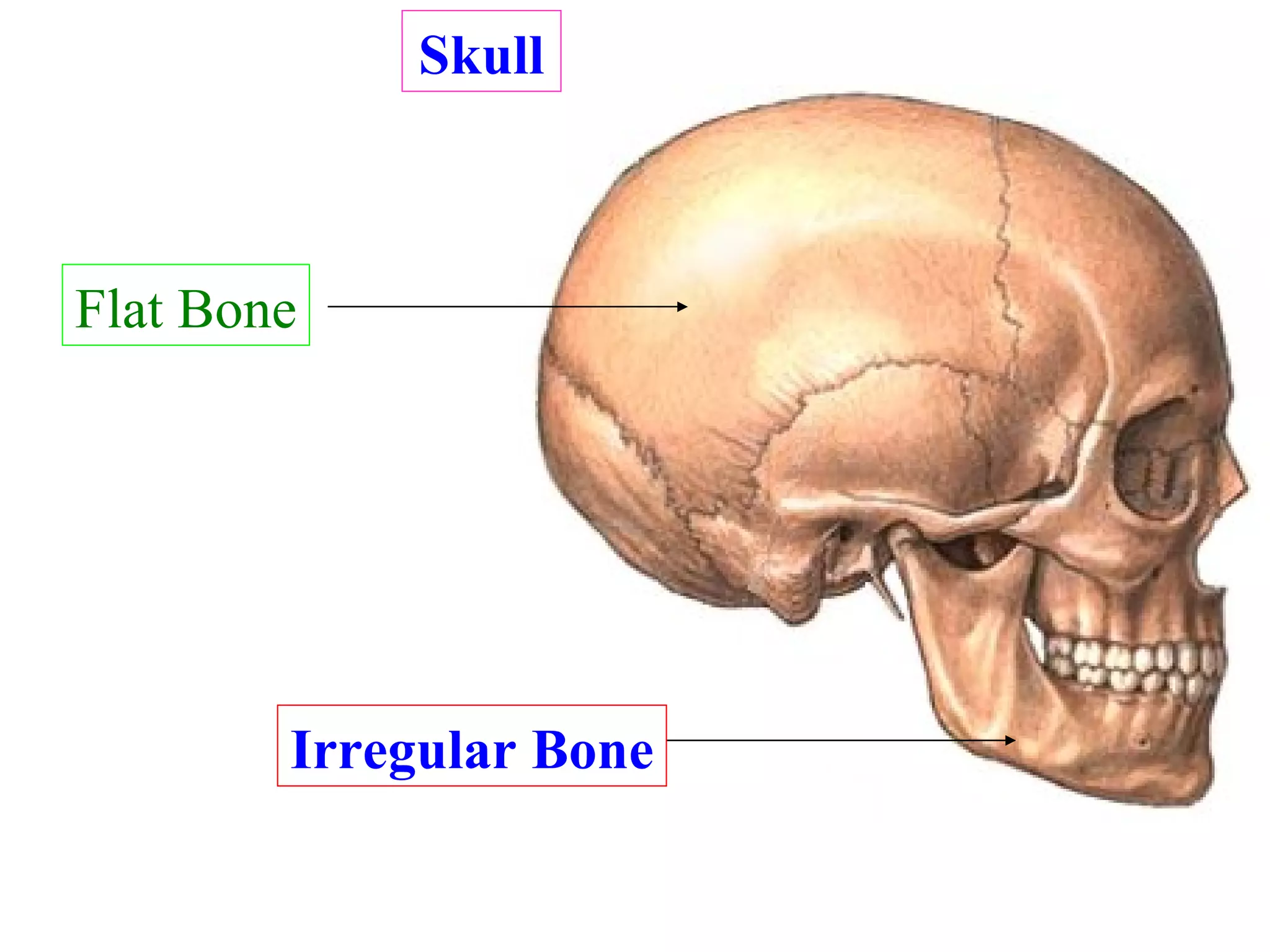
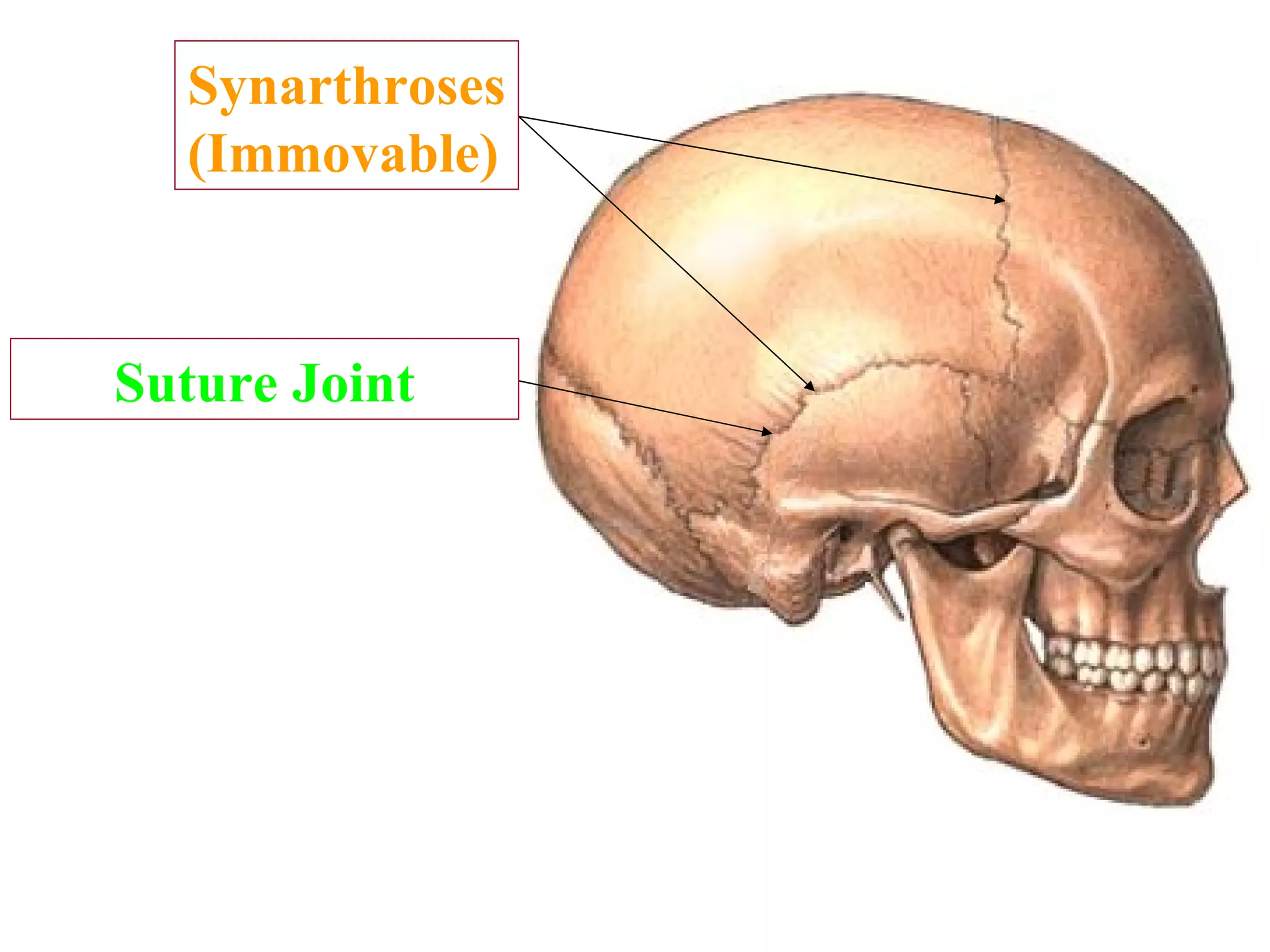
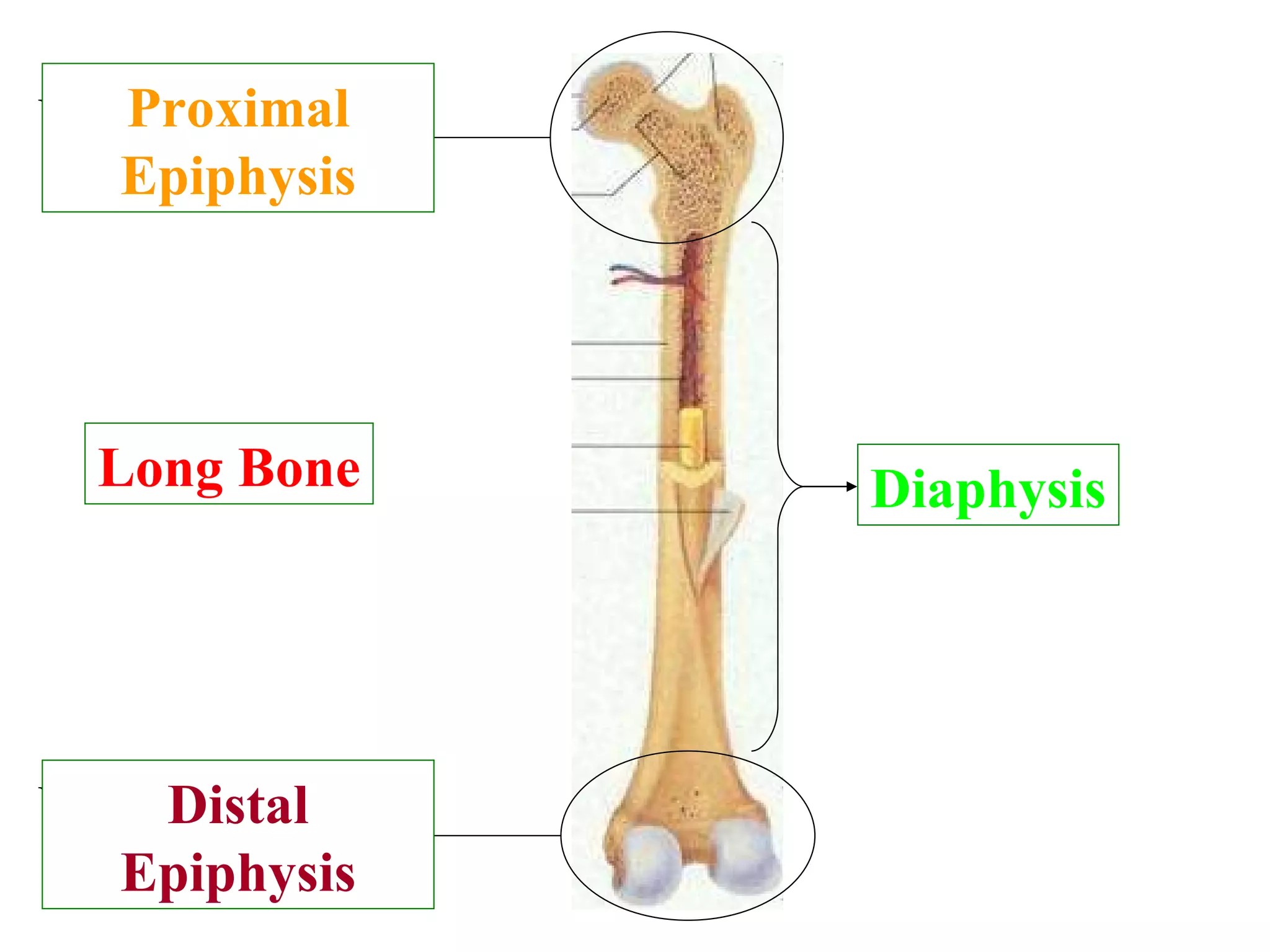
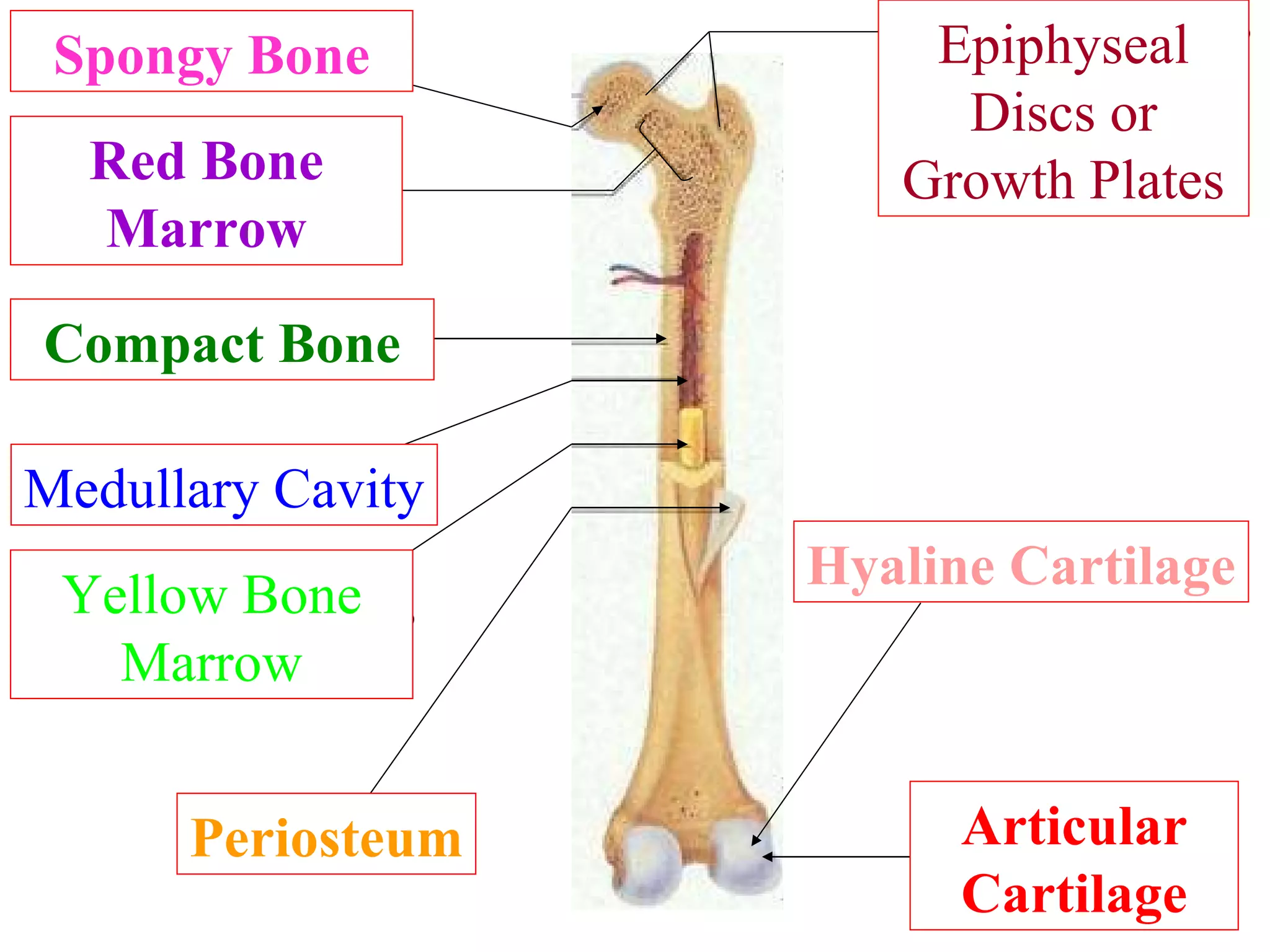
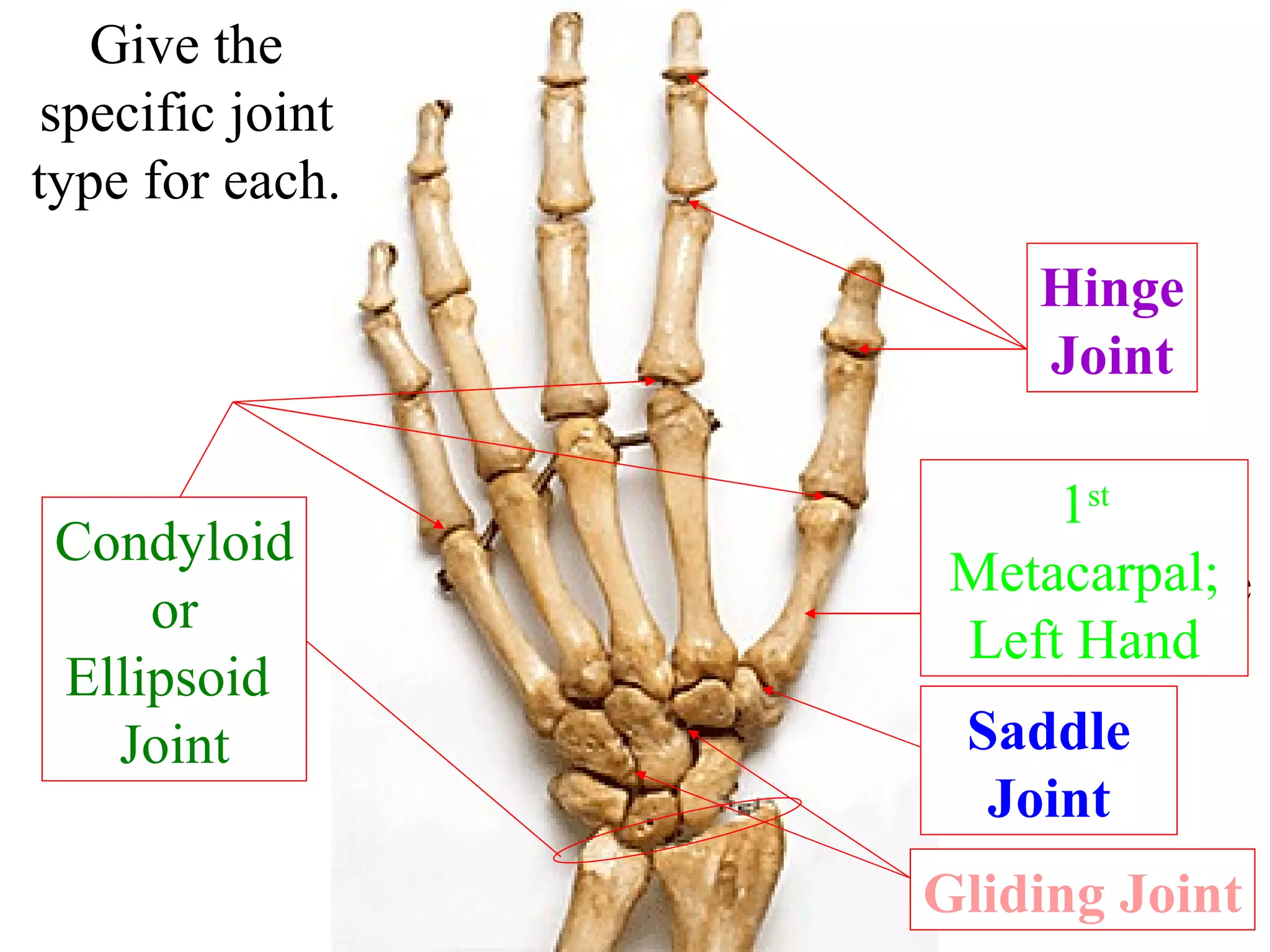
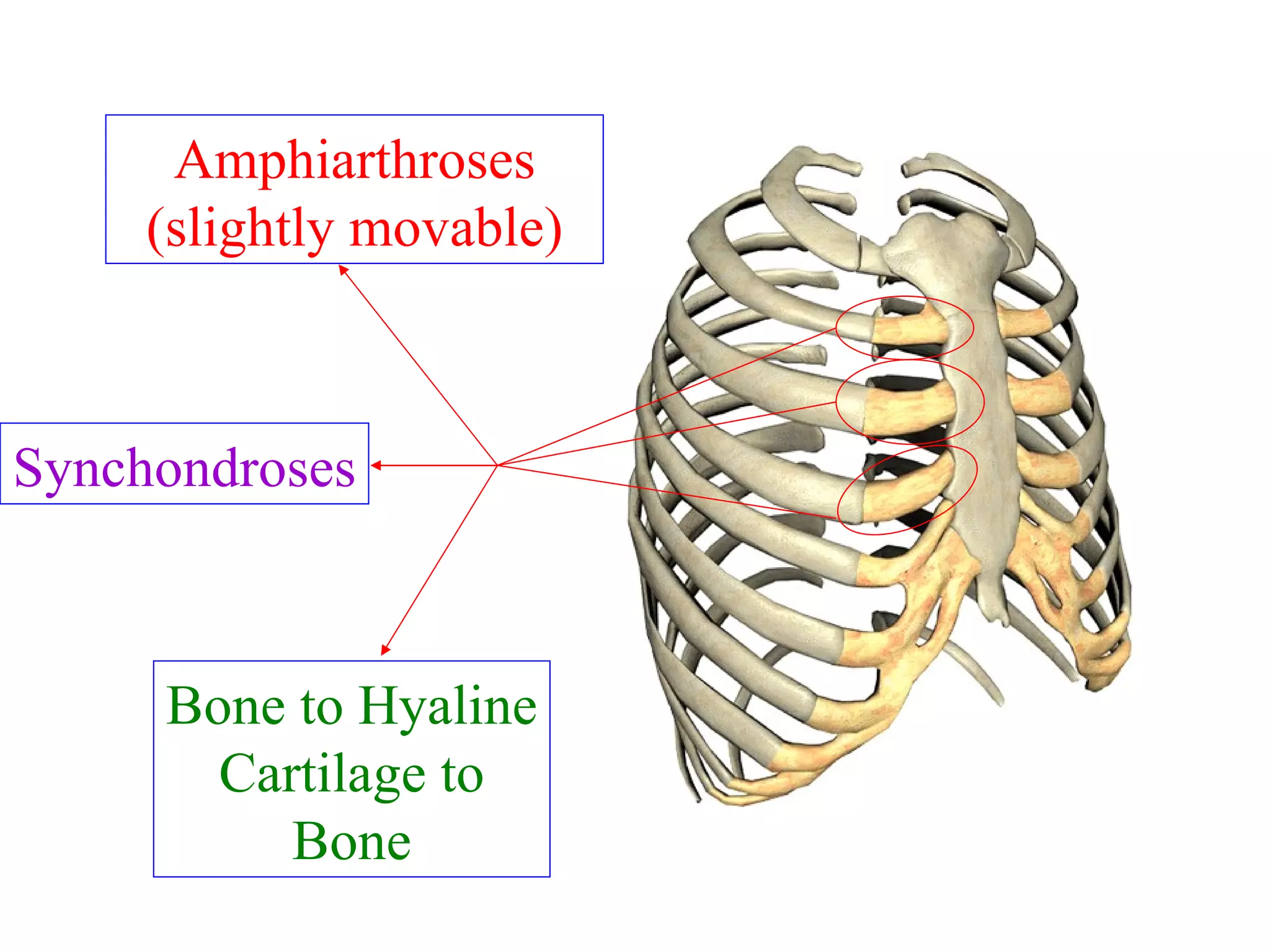
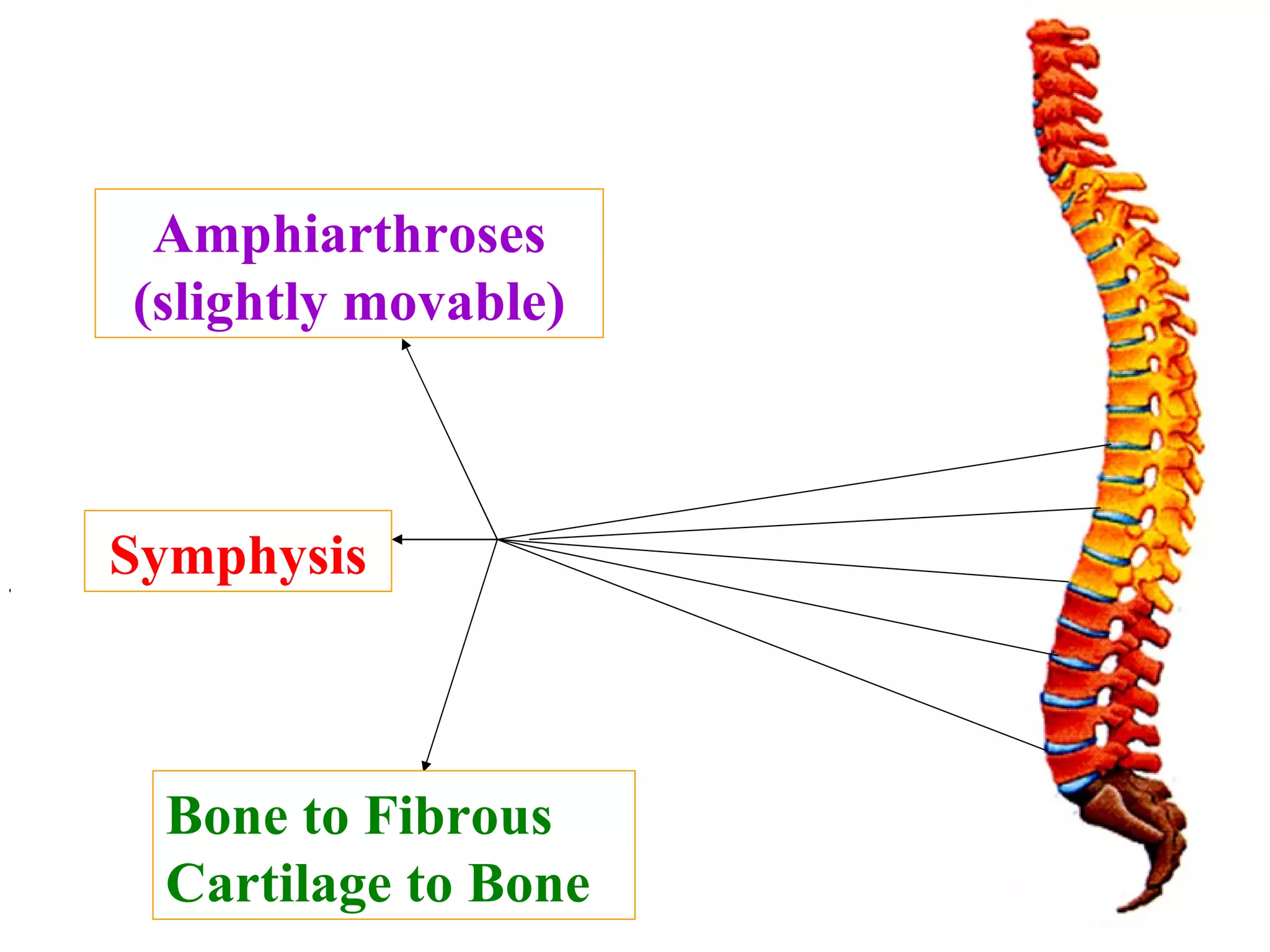
The axial skeleton consists of the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. It protects vital organs like the brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs and kidneys. Each forms a protective box structure. The skull has 29 bones including the cranium and face bones. The vertebral column has 26 bones and connects the skull to the pelvis. The thoracic cage includes ribs and sternum and provides flexibility for breathing.