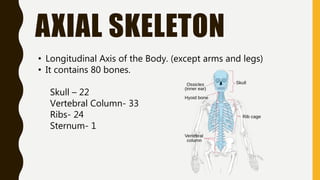
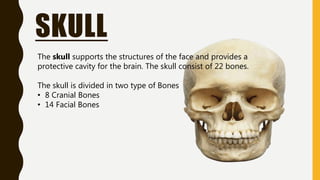
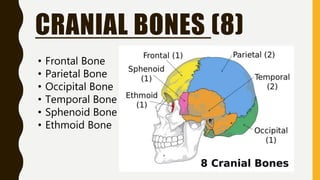
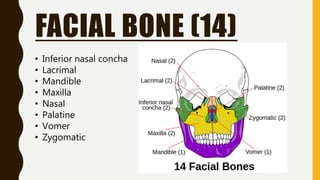
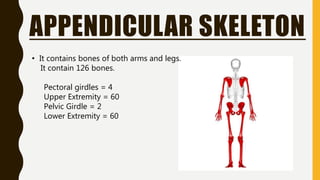
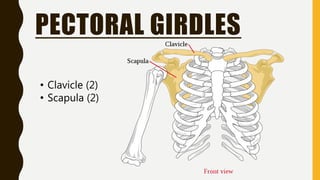
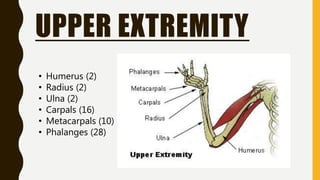
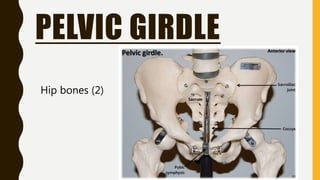
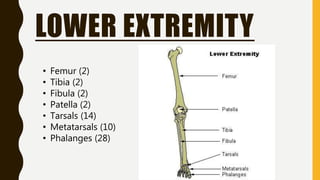
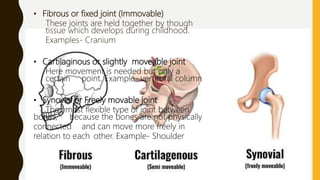
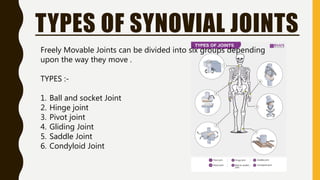
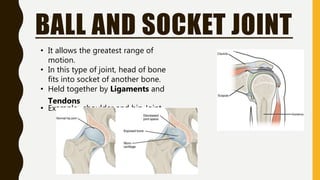
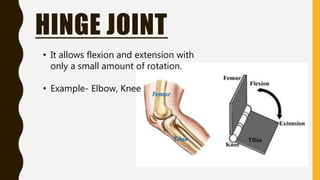
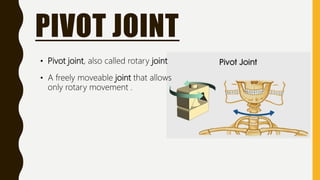
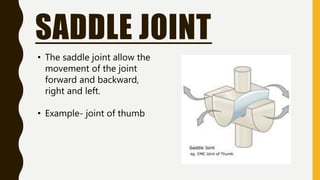
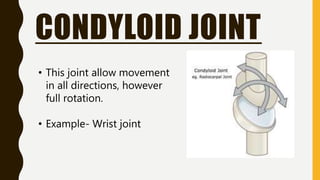
The document provides an overview of the human skeletal system, detailing its two main parts: the axial skeleton, comprising 80 bones including the skull, vertebral column, and ribs, and the appendicular skeleton, containing 126 bones including the limbs and girdles. It describes the types and functions of various bones and joints, highlighting the differences between fixed, slightly movable, and freely movable joints, along with their specific examples. Additionally, it categorizes six types of freely movable synovial joints based on their movement capabilities.