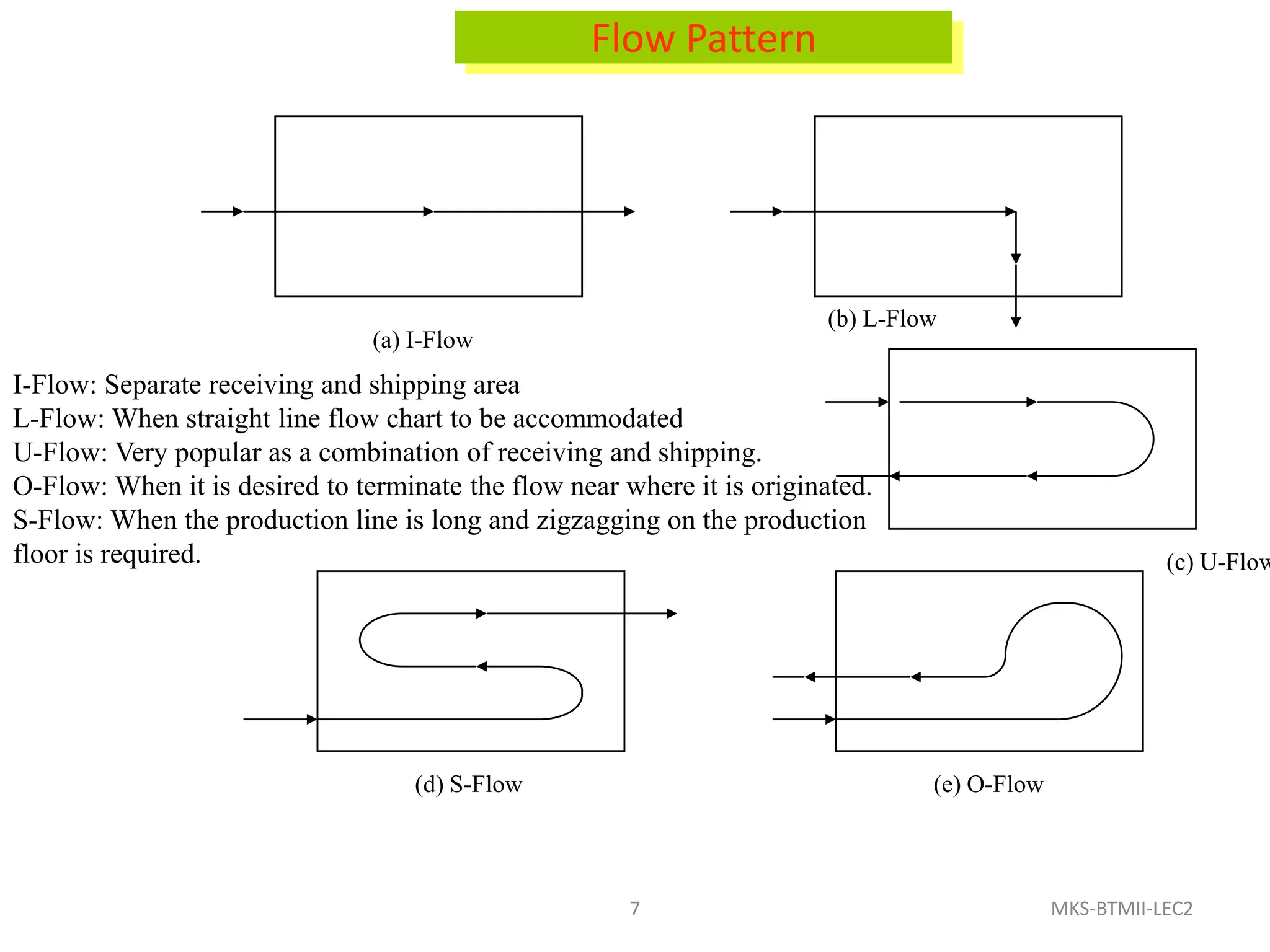
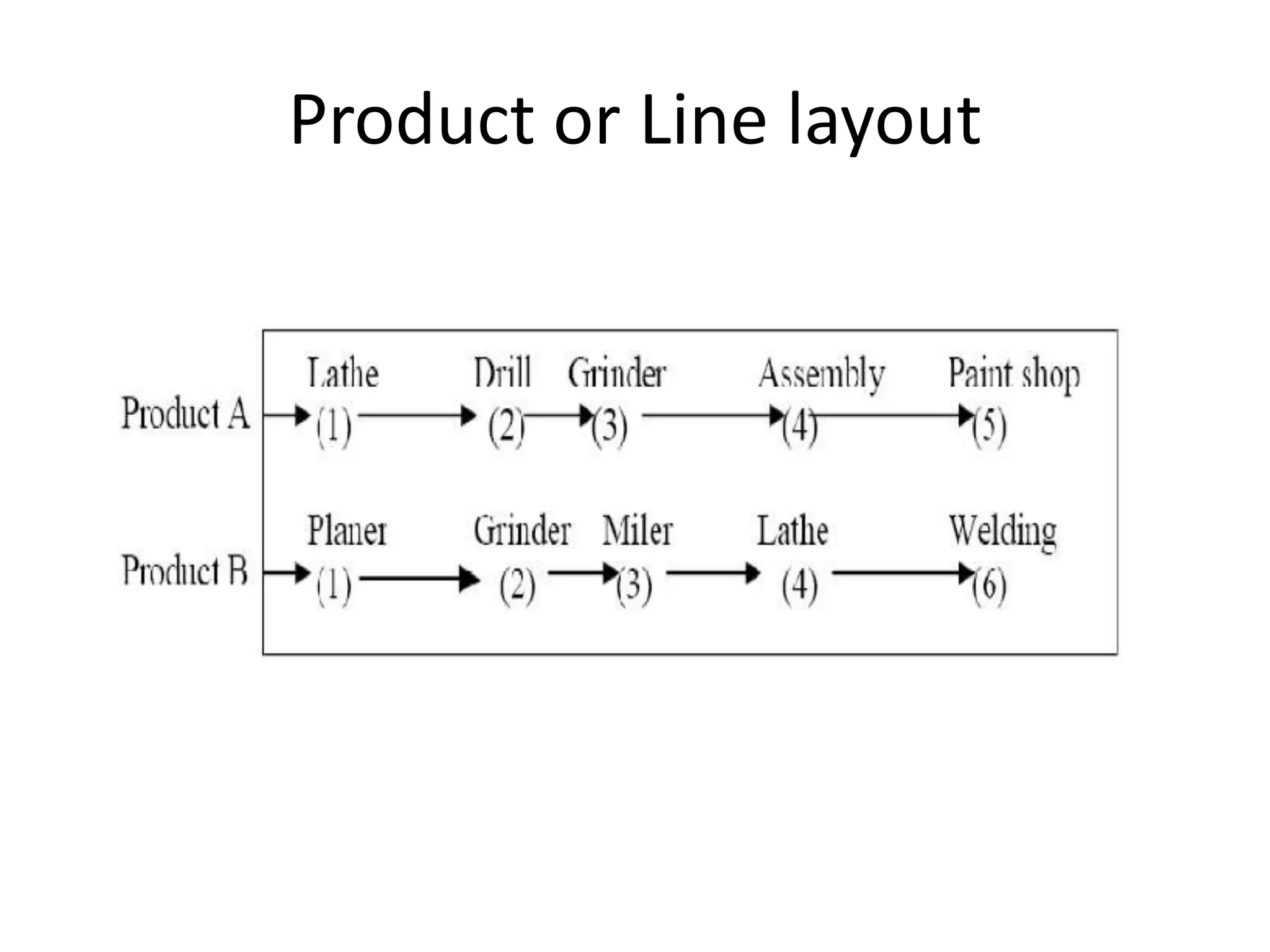
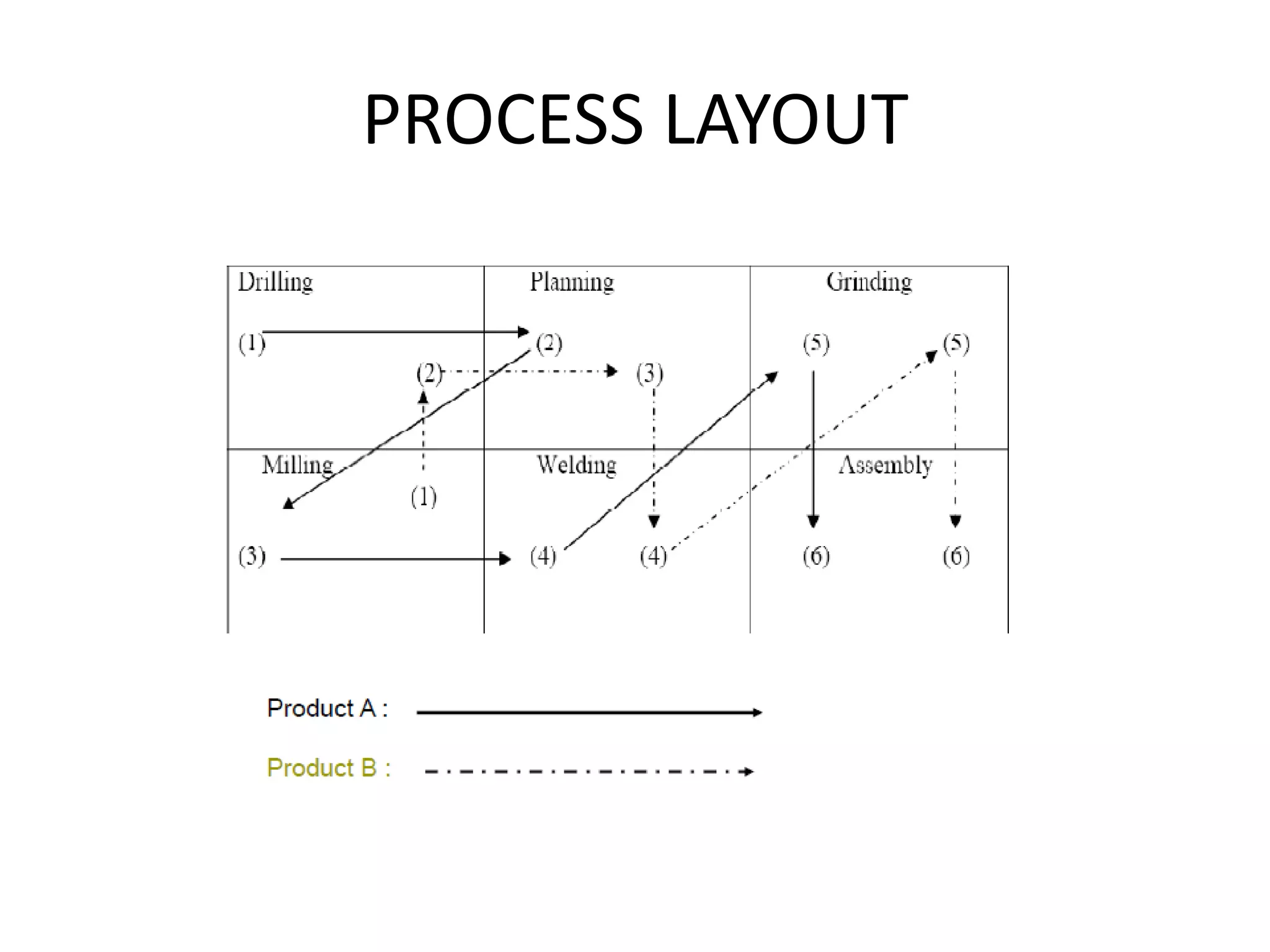
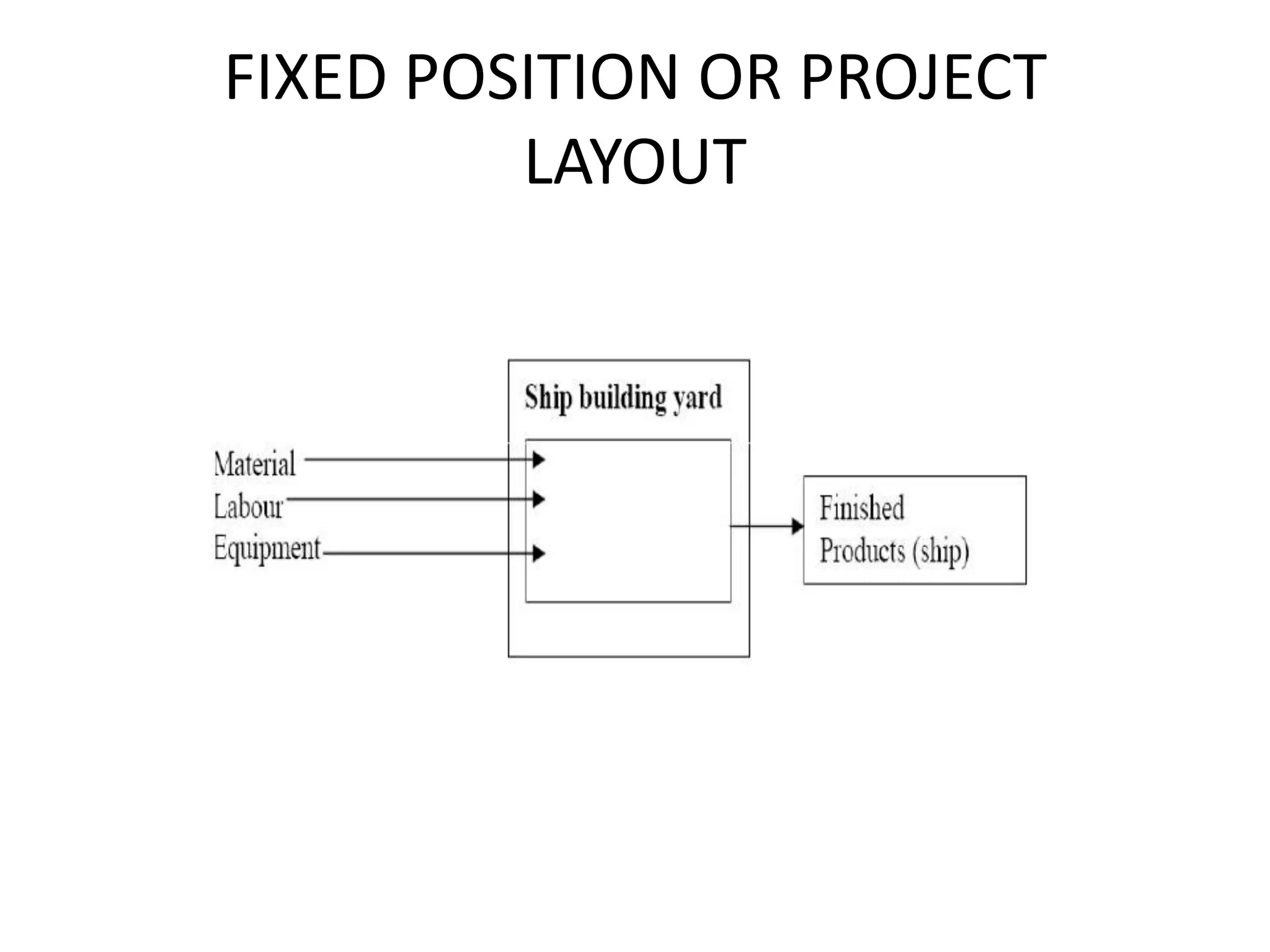
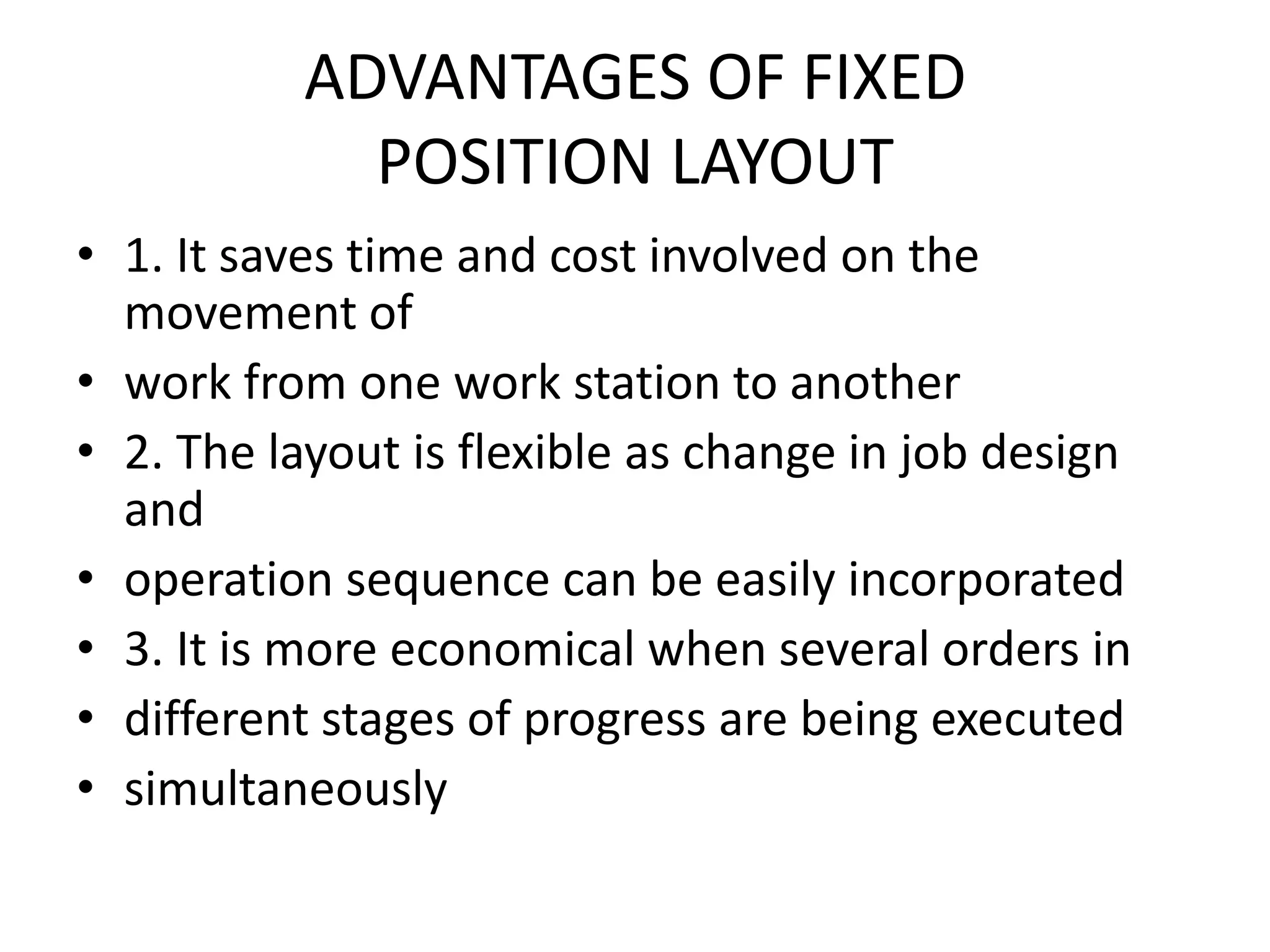
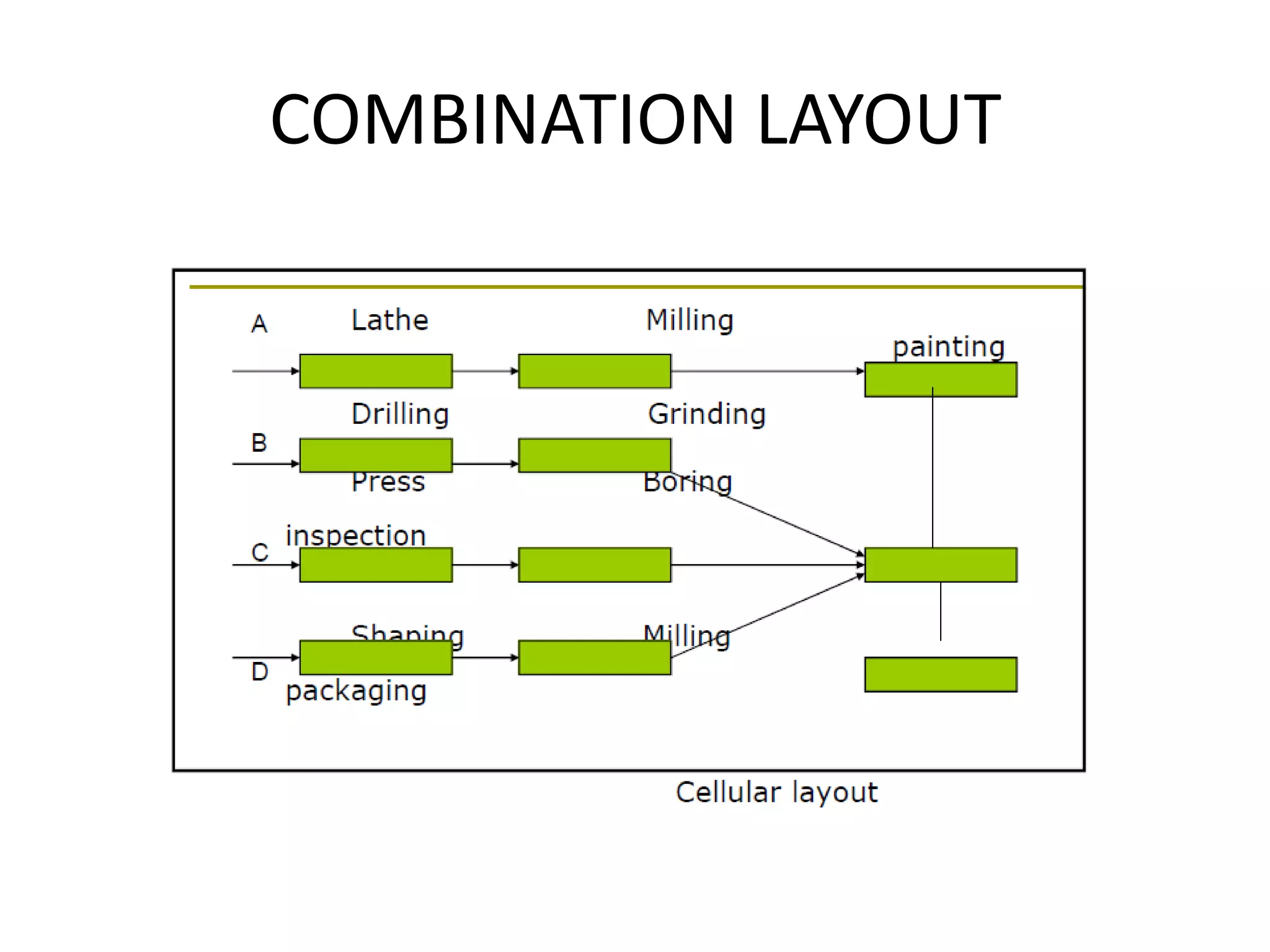
The document discusses different types of facility and plant layouts. It describes layout as planning the location of machines, workstations, storage areas, and infrastructure to optimize material and personnel flow. The objectives are to develop an economical layout that meets production needs while considering building constraints. Key factors for the layout decision include production type and scale, equipment, and expansion potential. The main types discussed are product/line layout, which facilitates continuous flow but requires more capital; process/functional layout, which has lower initial costs but higher material handling; and combination layouts.