Embed presentation
Downloaded 79 times

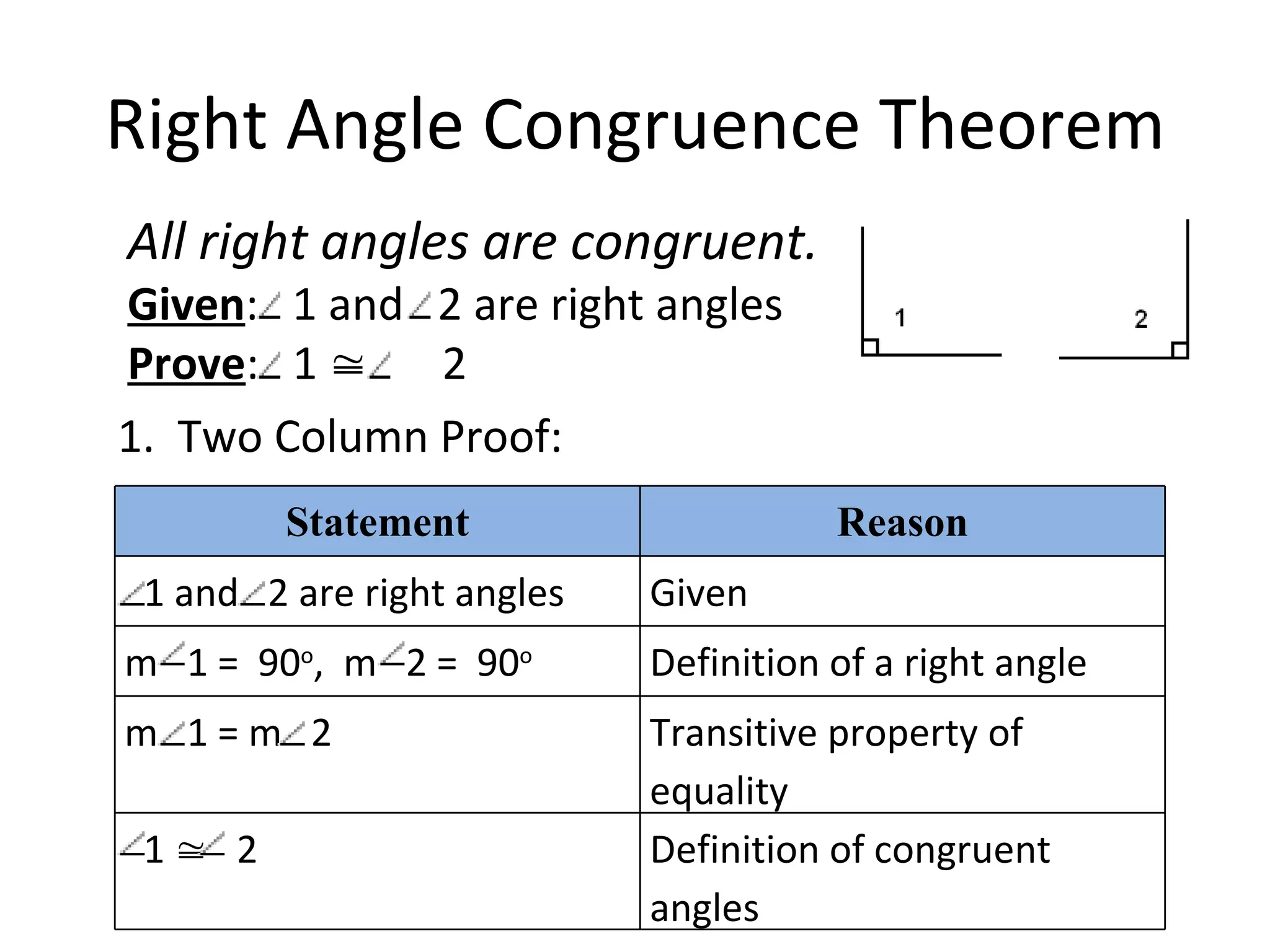

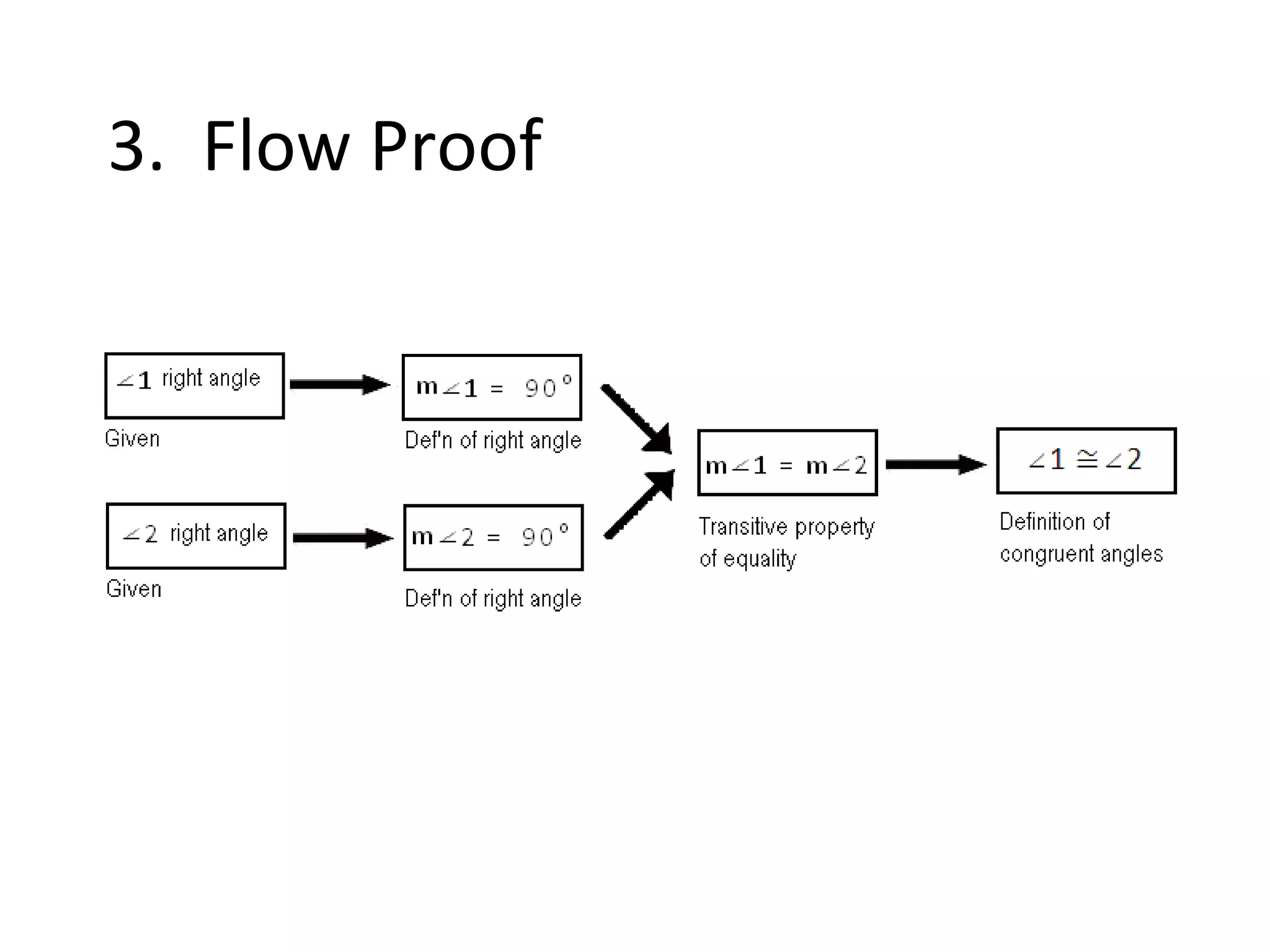
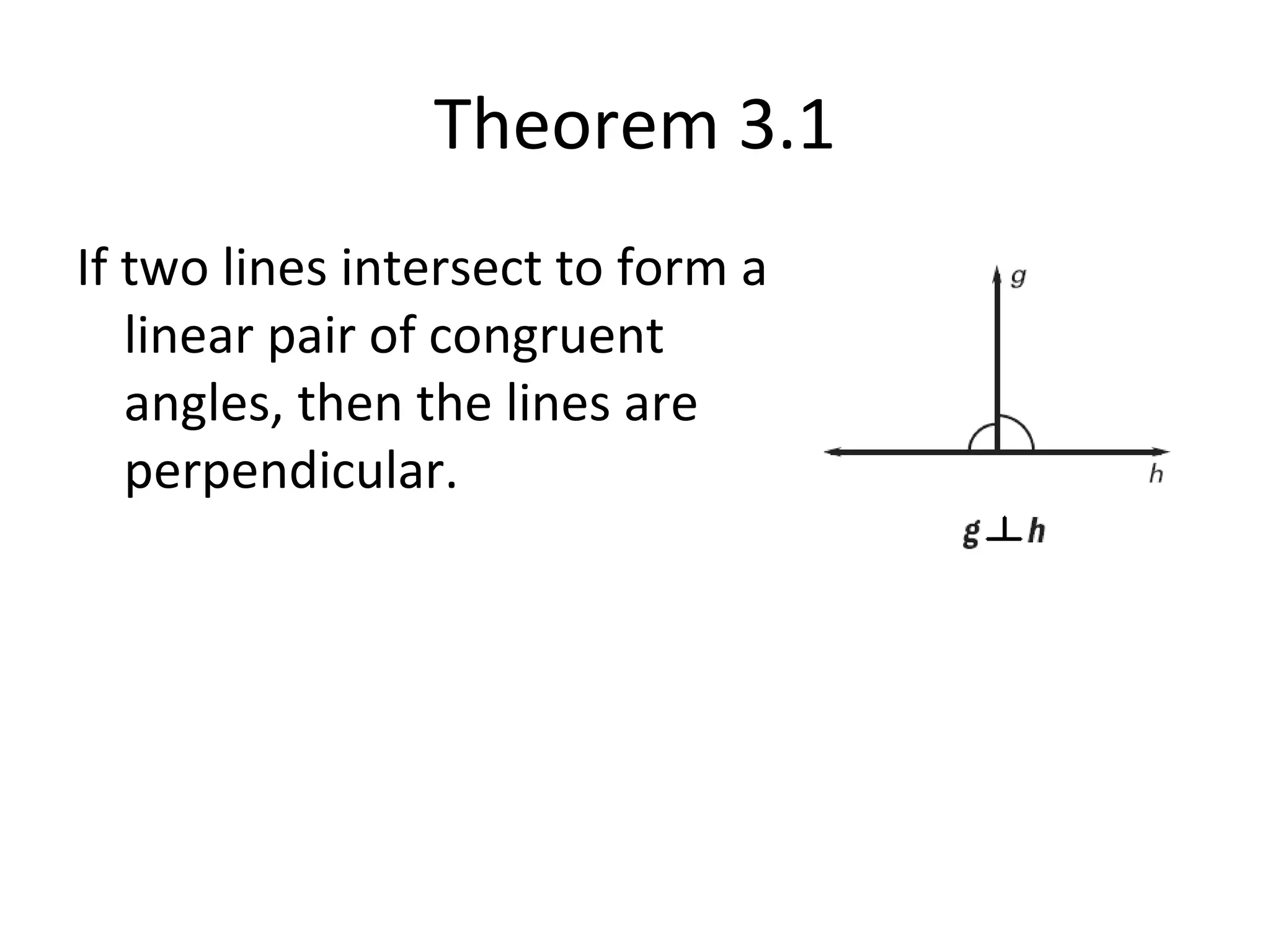
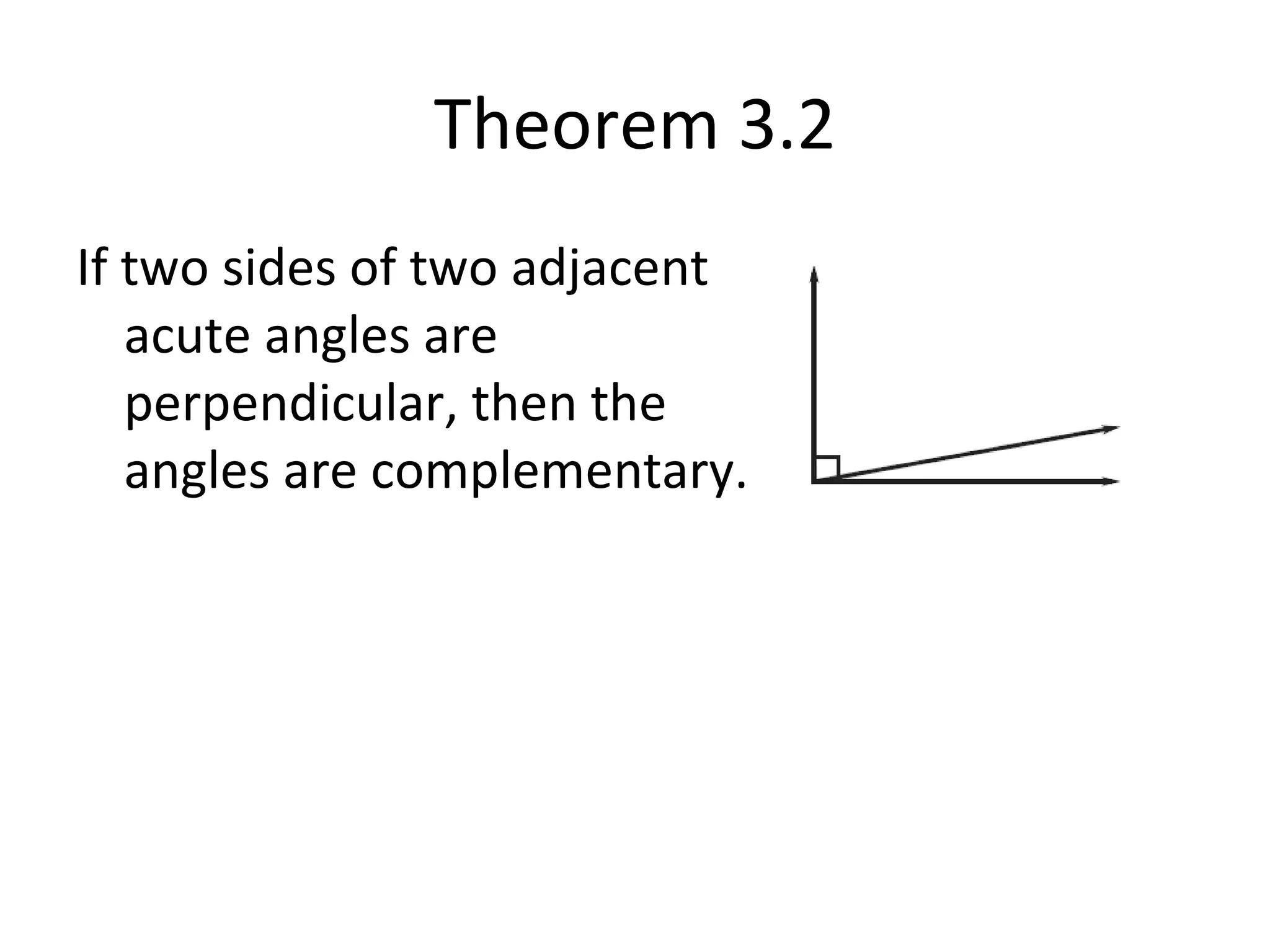
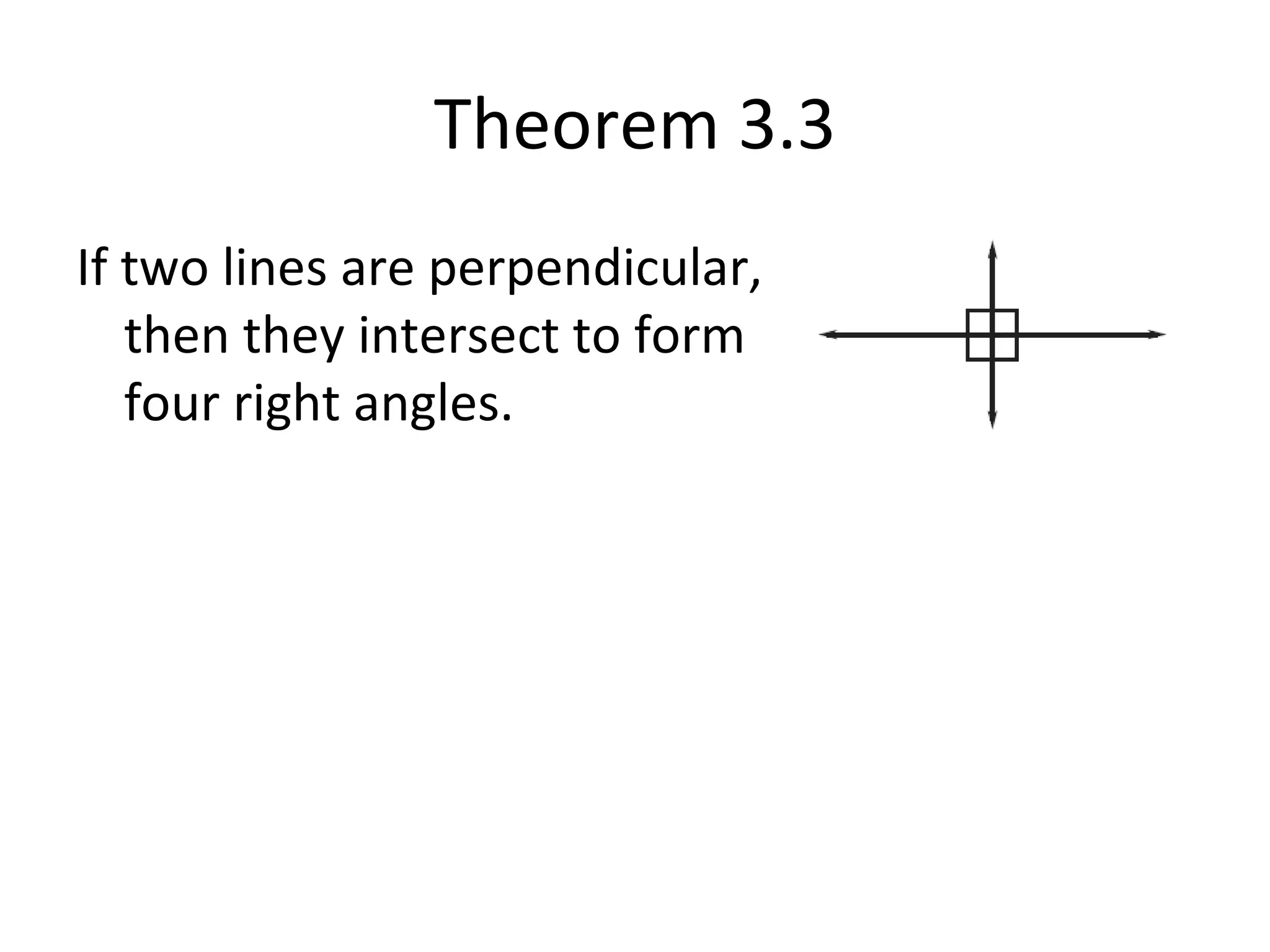
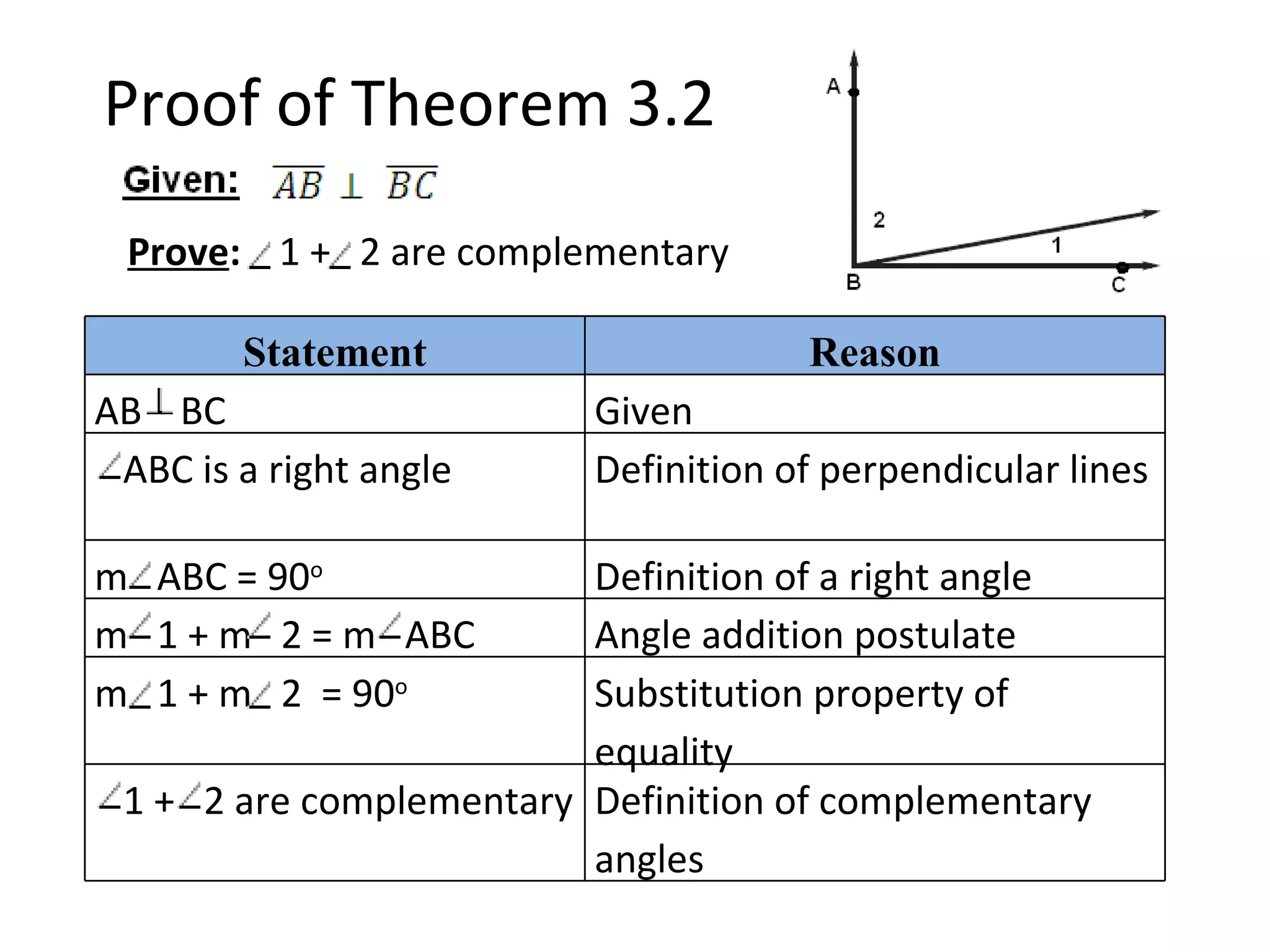

The document discusses different types of proofs used to prove theorems about perpendicular lines. It presents three theorems: 1) if two lines intersect to form congruent angles, they are perpendicular, 2) if two adjacent acute angles have perpendicular sides, they are complementary, and 3) if two lines are perpendicular, they intersect to form four right angles. It also provides an example proof of theorem 3.2 using a two-column format.









