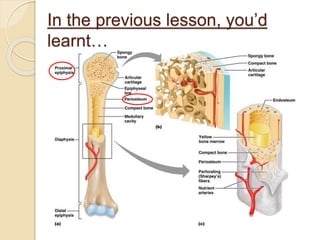
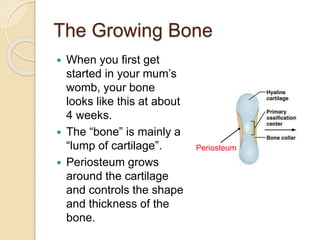
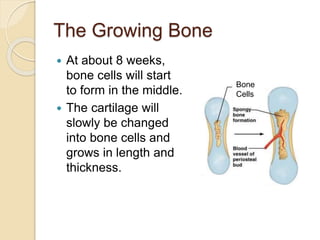
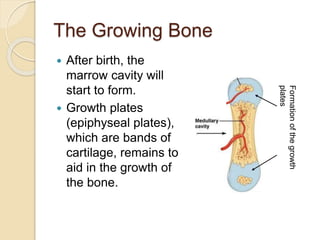
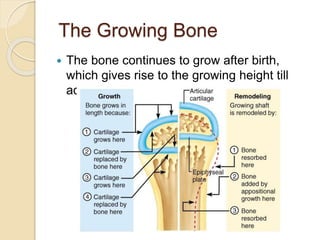
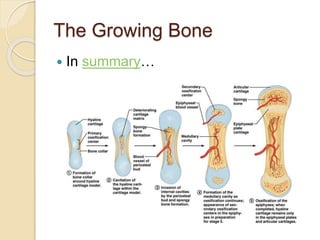
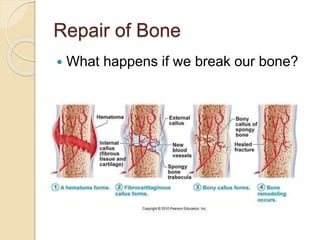
Bones grow through the process of bone cells forming in the growth plates located at the ends of bones. Growth plates allow bones to lengthen until late teens when they fuse shut. Several factors influence bone growth and height, including genes, diet, exercise, lifestyle and sleep. In adulthood, bones continue remodeling through the balanced actions of osteoblasts which build new bone and osteoclasts which break down old bone. Maintaining strong bones requires sufficient calcium, vitamin D, weight-bearing exercise and adequate sleep.