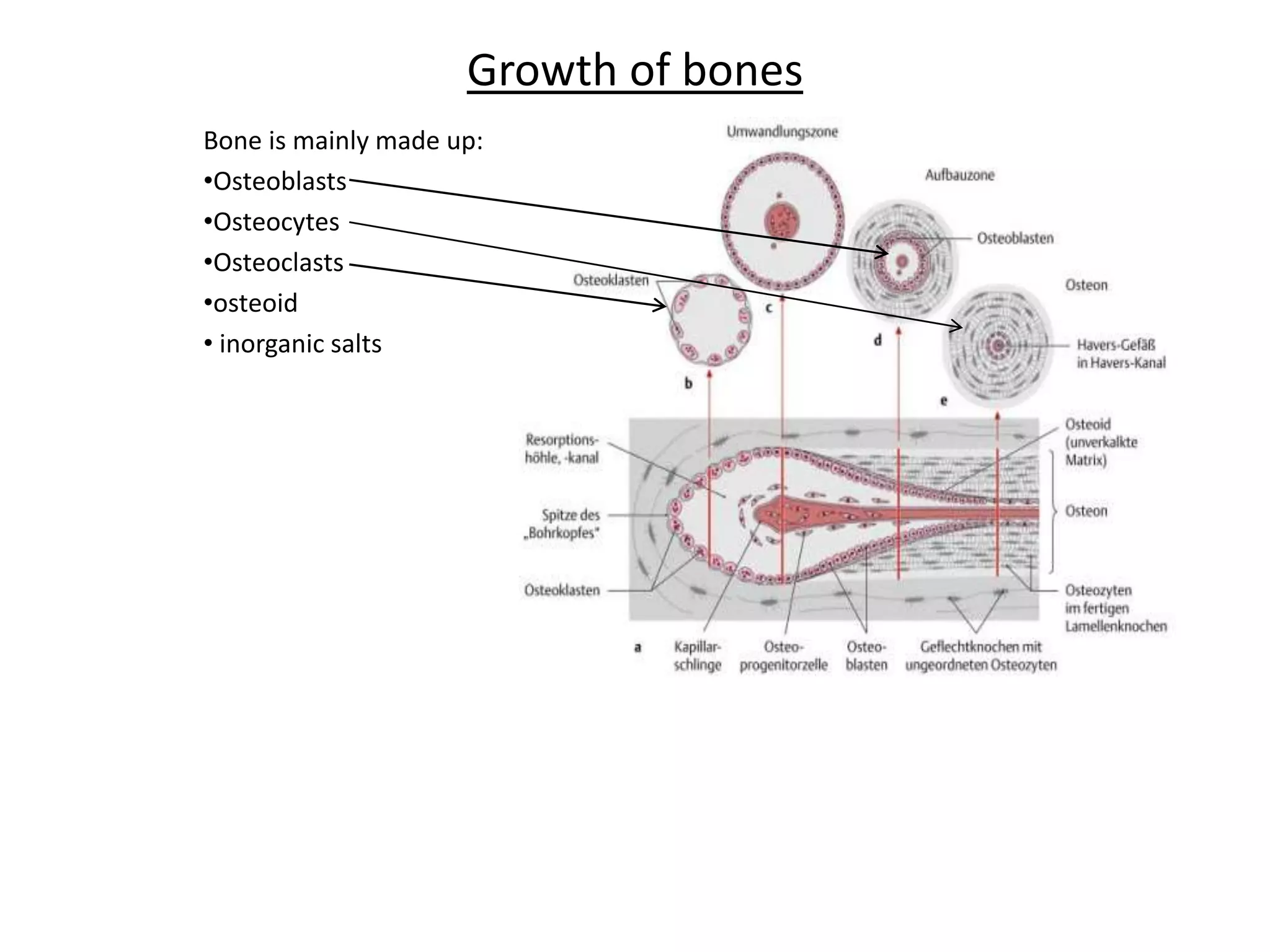
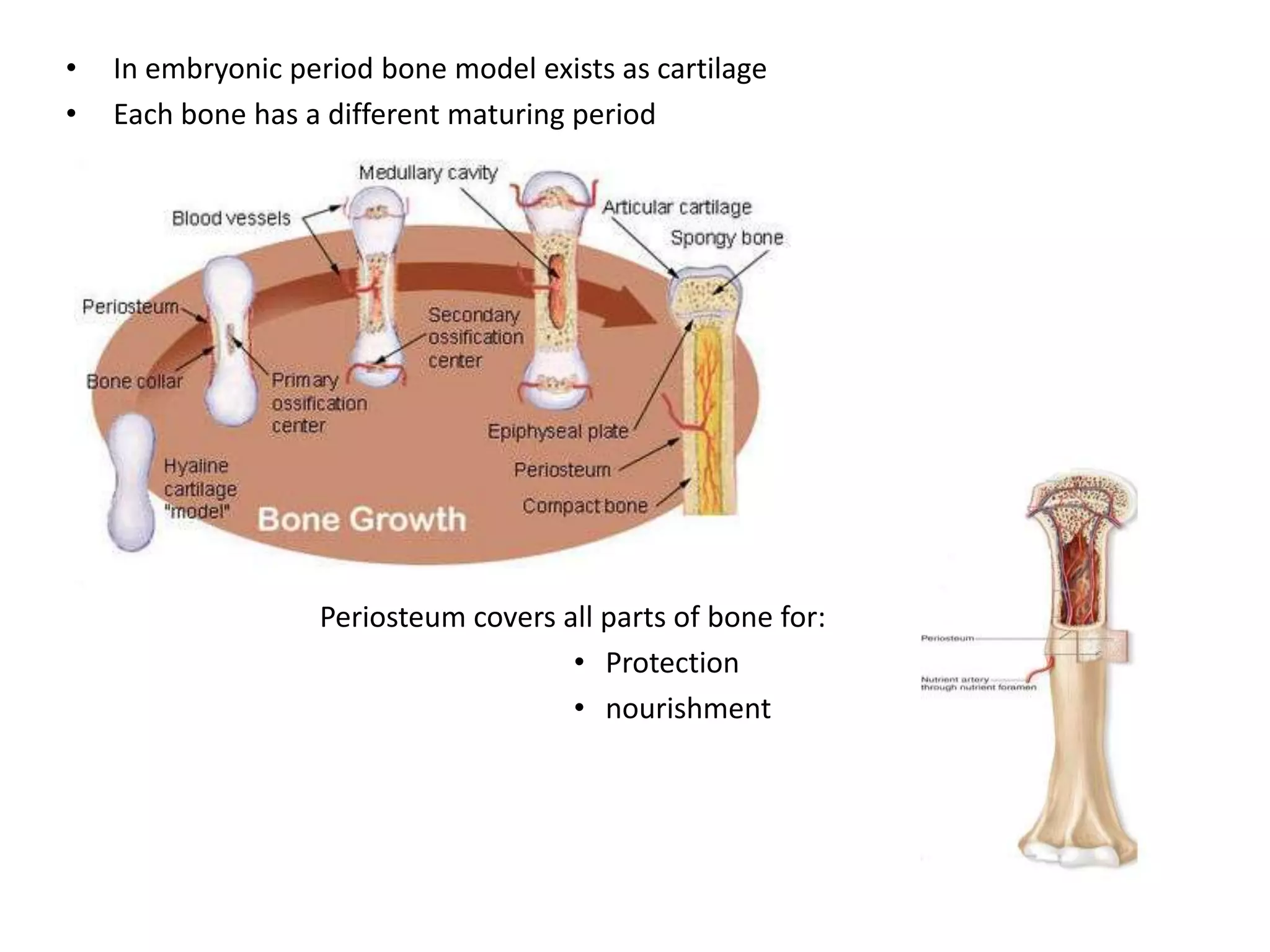
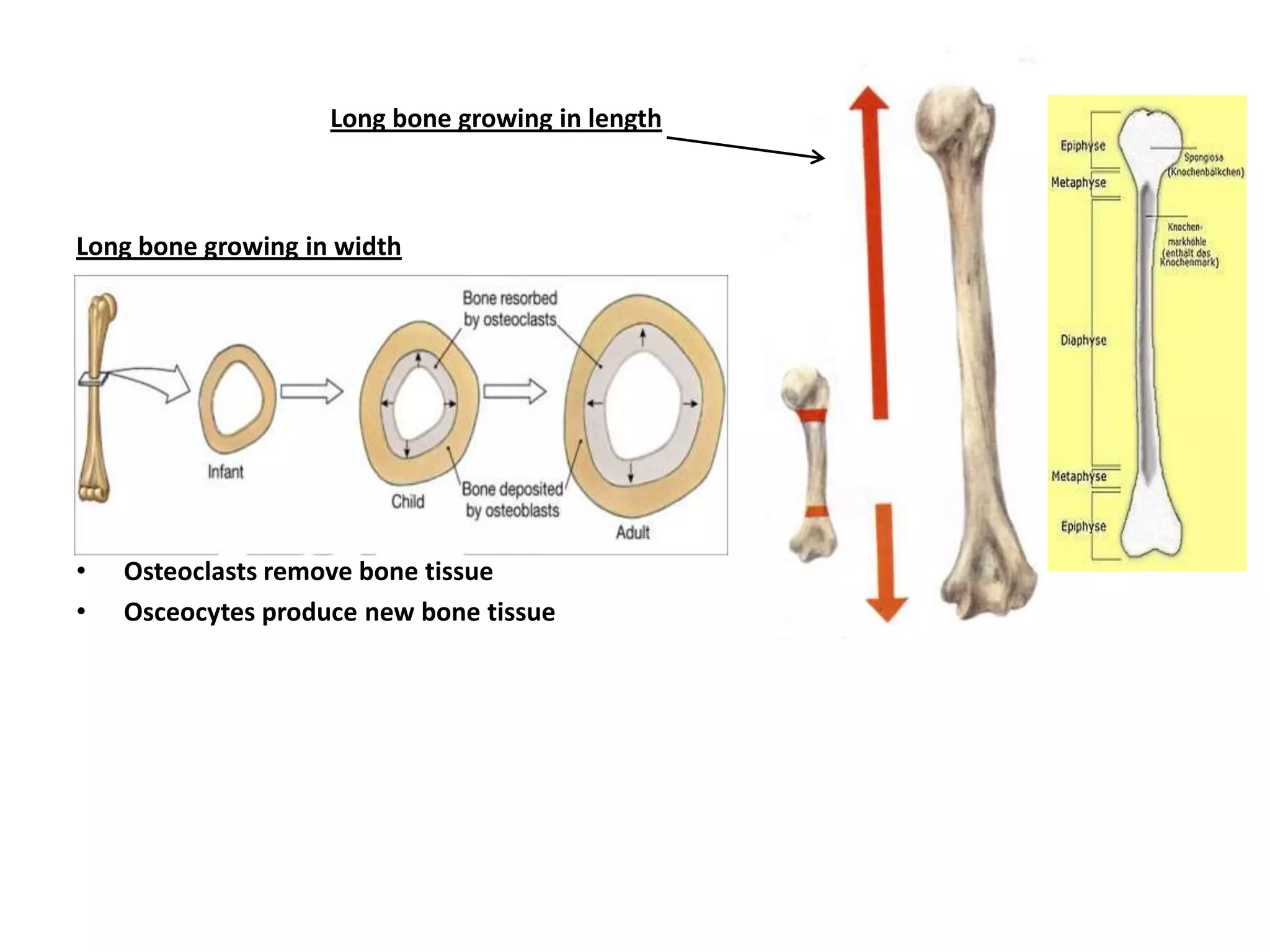
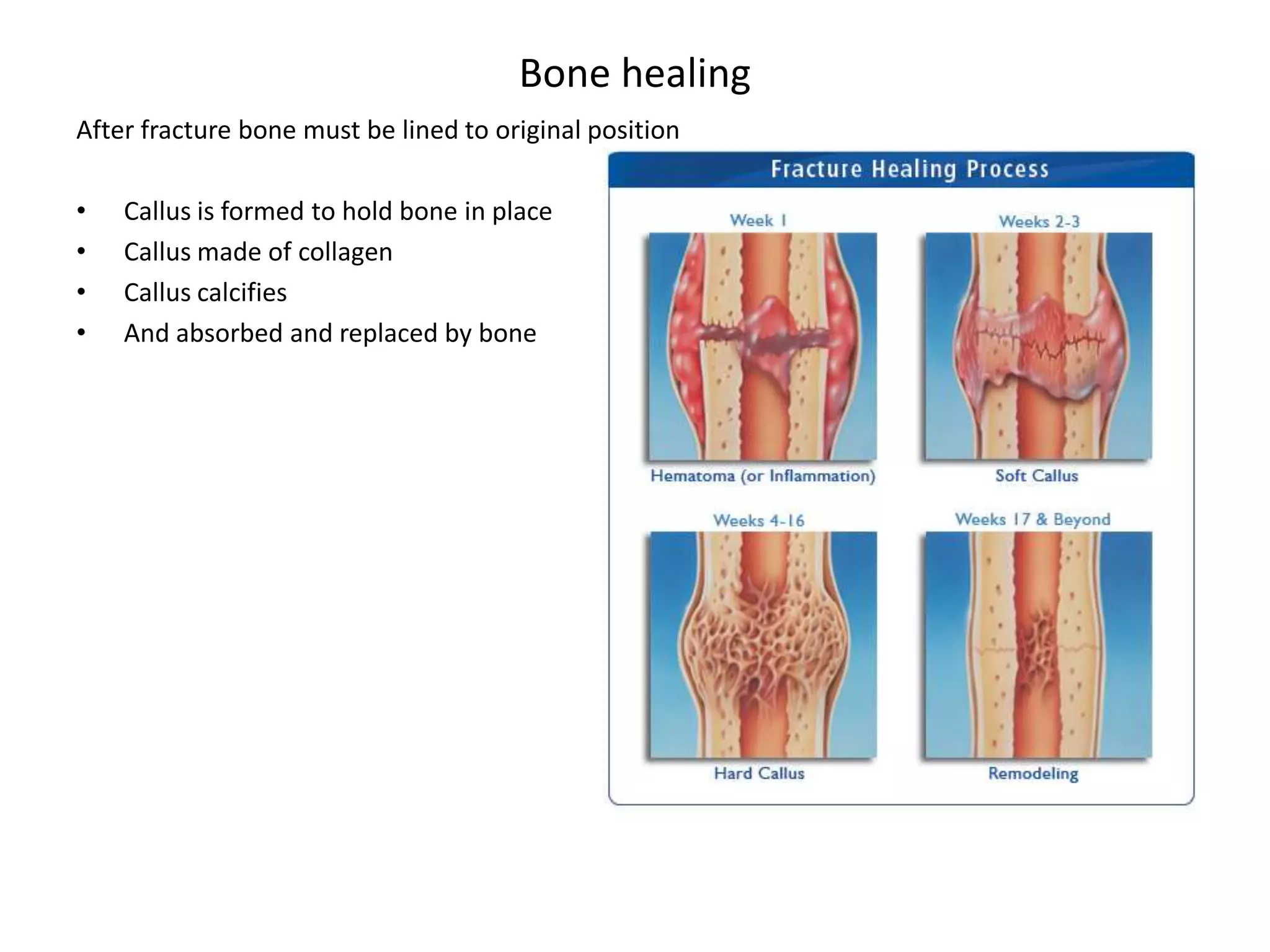
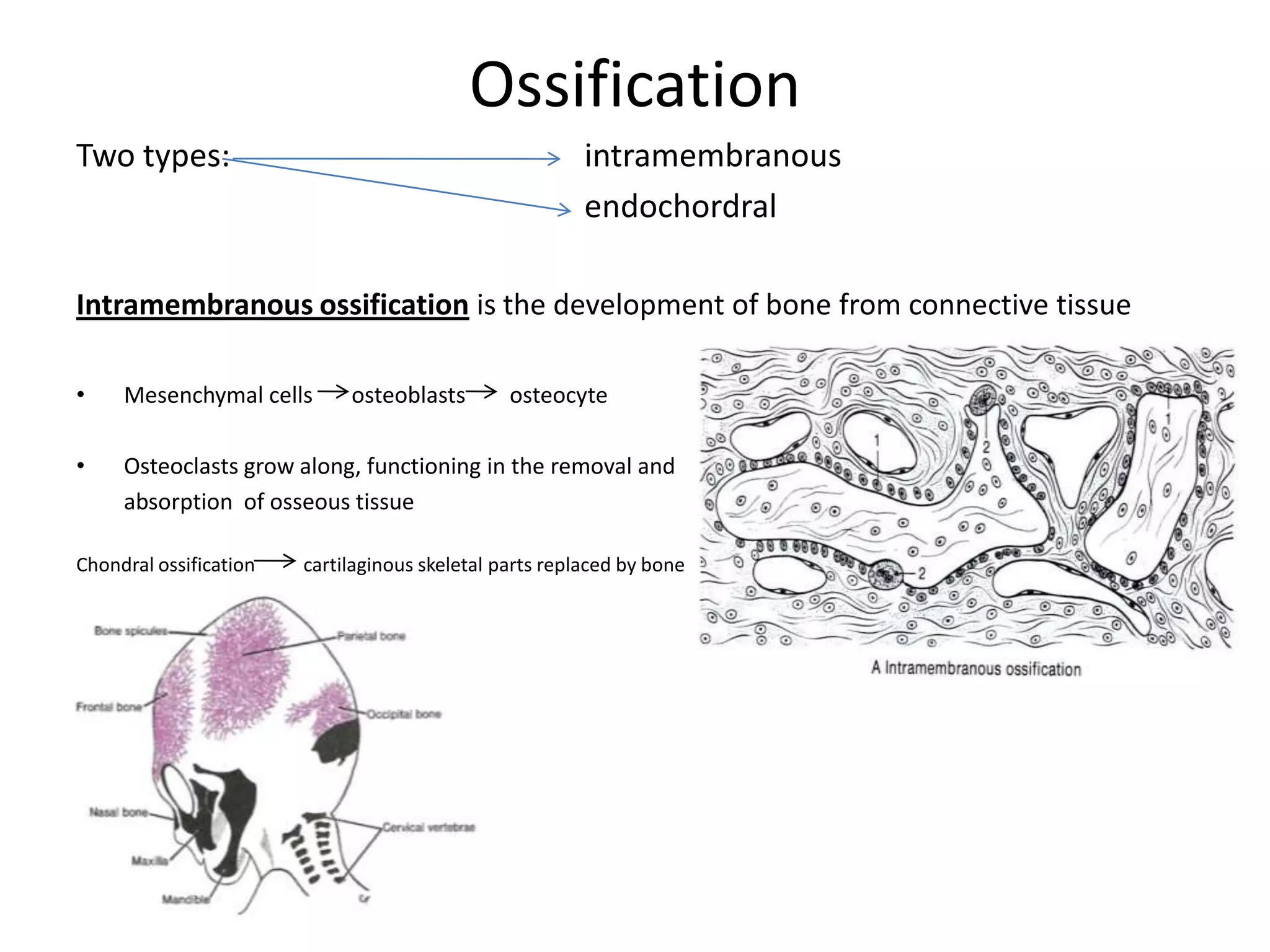
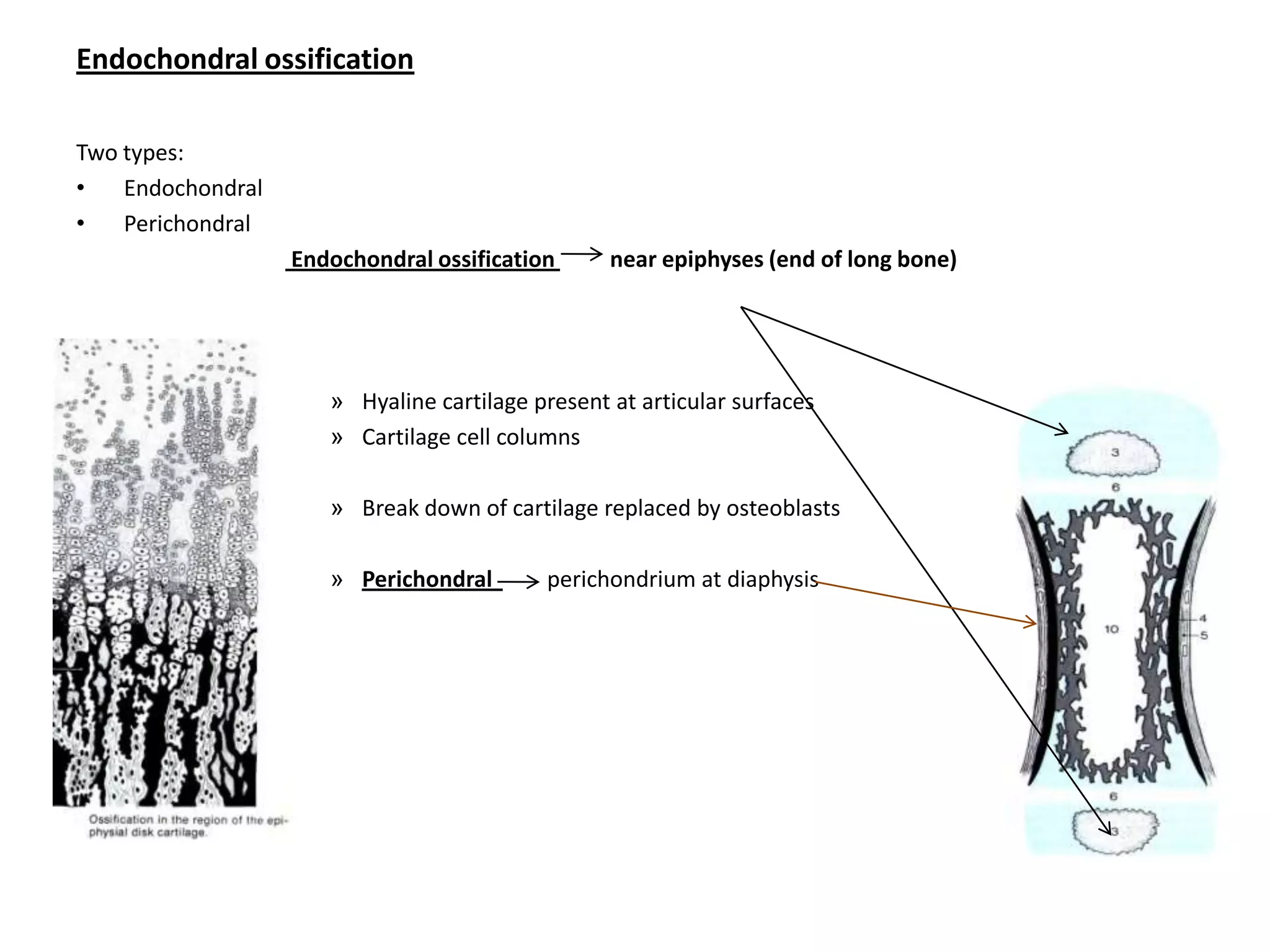
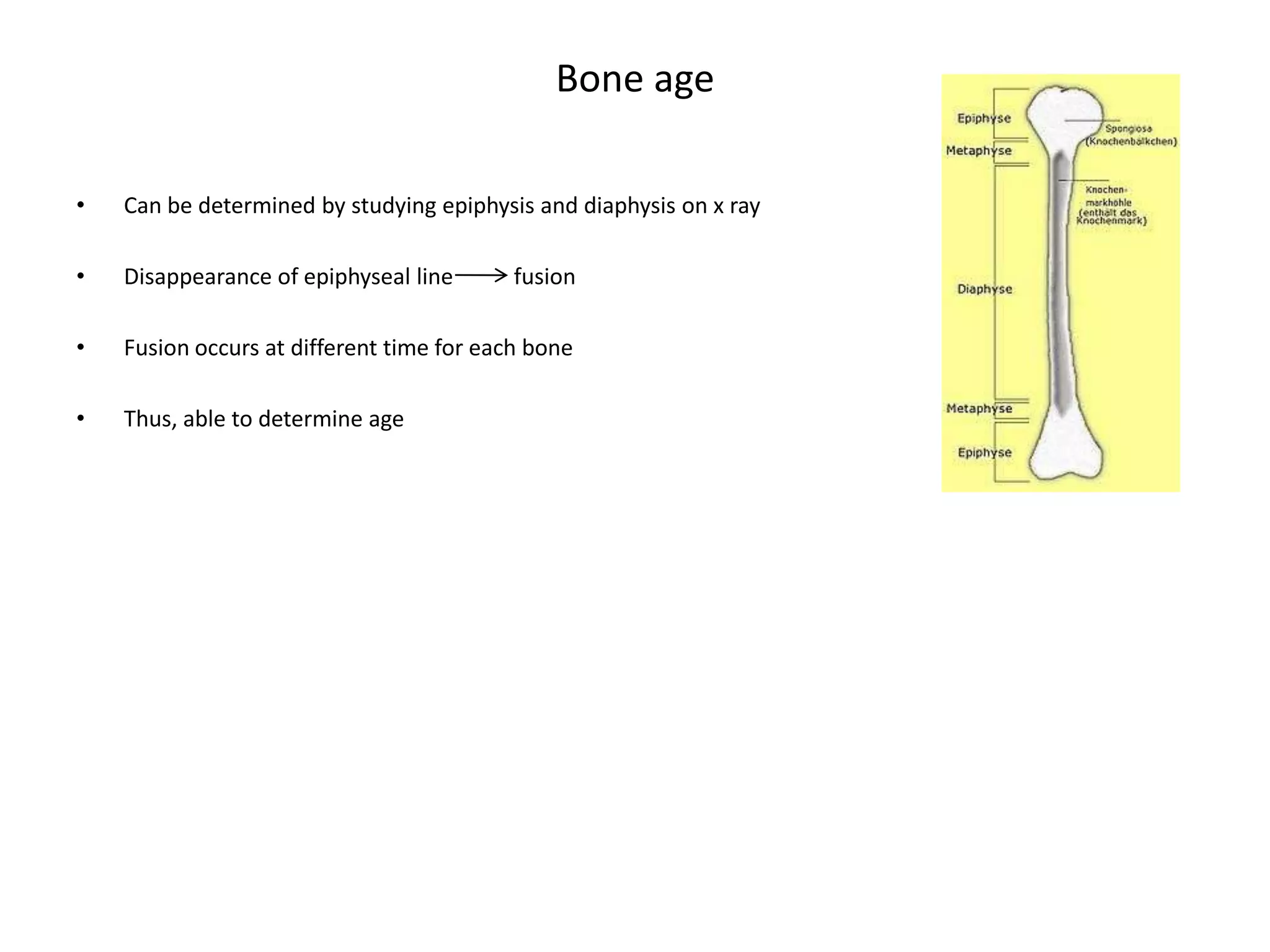
Bone grows through the processes of intramembranous and endochondral ossification. Intramembranous ossification develops bone directly from connective tissue, while endochondral ossification replaces cartilaginous skeletal parts with bone. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is present near the epiphyses of long bones and breaks down as cartilage cell columns are replaced by osteoblasts depositing new bone tissue. Bone age can be determined by examining an x-ray of the epiphyseal plates and timing of their fusion with the diaphyses, which occurs at different ages for each bone.