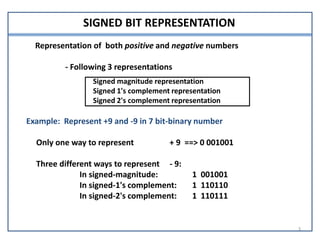
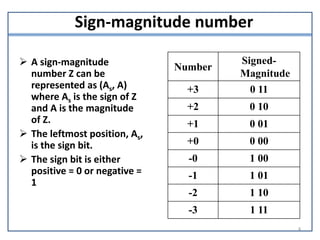
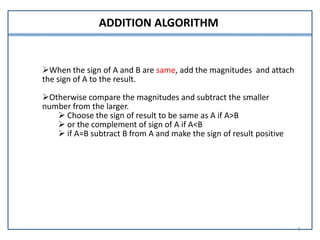
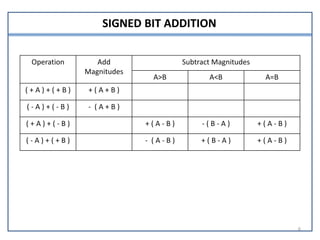
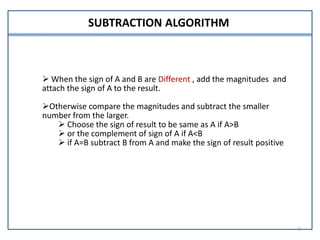
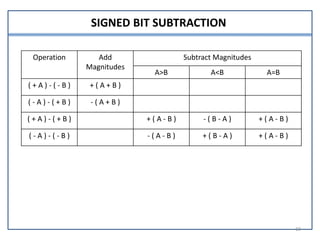
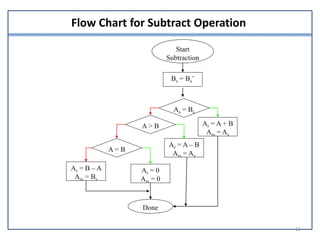
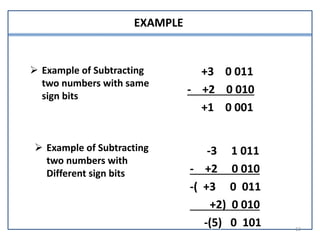
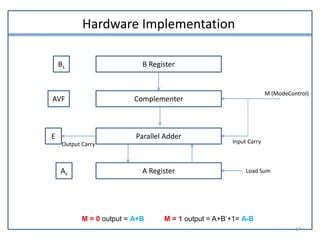
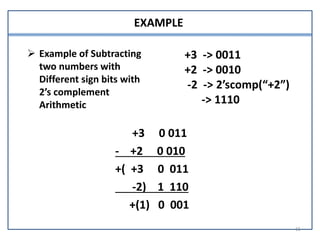
This document presents information on signed number representation and algorithms for signed addition and subtraction. It discusses signed magnitude, 1's complement, and 2's complement representations. It provides examples and flowcharts for the addition and subtraction algorithms in signed magnitude representation. The algorithms treat the signs and magnitudes separately. For hardware implementation, it shows how a parallel adder, complementer, and mode control can be used to perform signed addition and subtraction.