This document discusses different arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication in binary. It covers:
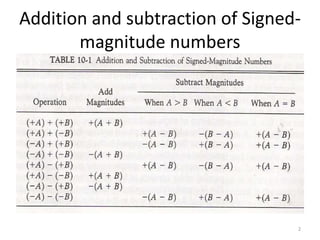
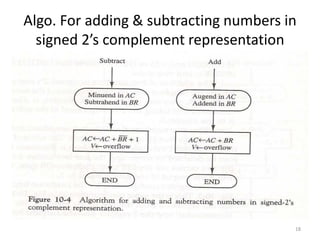
1) Representing negative numbers in signed magnitude and two's complement notation. Subtraction is performed by adding the number to the two's complement of the subtrahend.
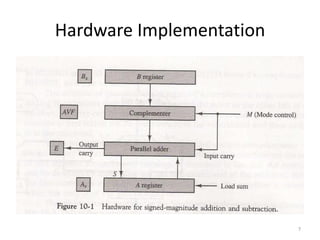
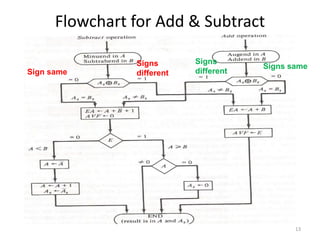
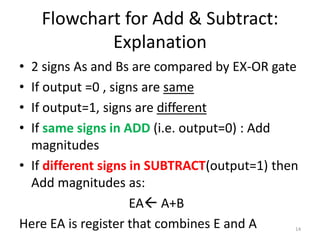
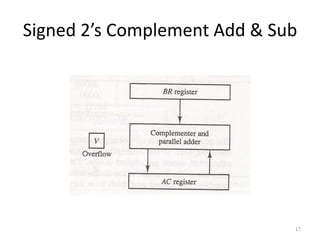
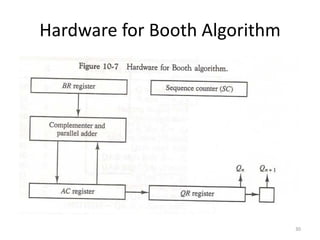
2) Hardware implementation of addition and subtraction using registers, sign flip flops, and a parallel adder. Subtraction is achieved by adding the number to the two's complement using a mode control signal.
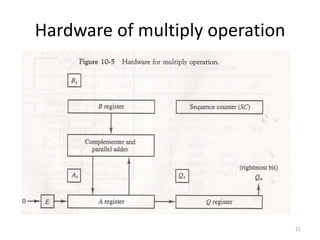
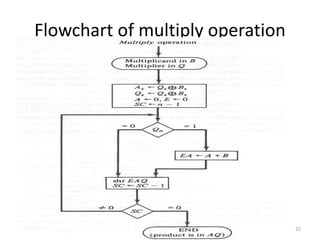
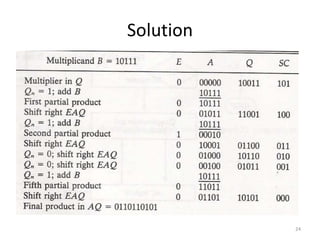
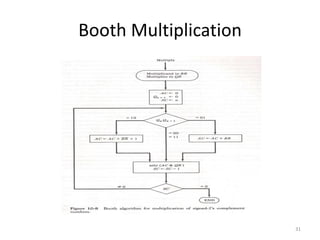
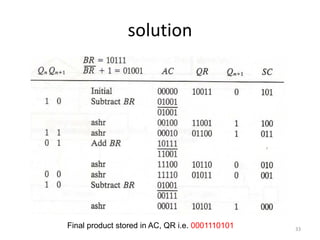
3) The Booth algorithm for multiplying signed two's complement numbers, which involves conditionally adding or subtracting the multiplicand from the partial product based on the multiplier bits.