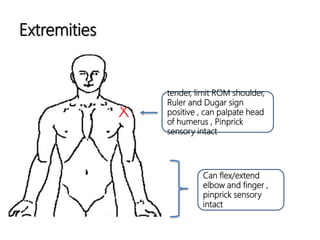
- A 67-year-old Thai female presented to the emergency department with left shoulder pain after falling from a motorcycle accident.
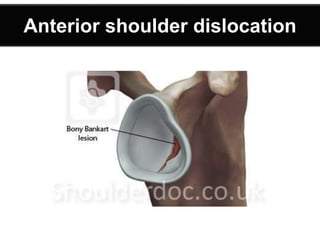
- X-rays revealed an anterior dislocation of the left shoulder with a greater tuberosity fracture.
- She underwent closed reduction under sedation and analgesia, followed by immobilization of the left arm in a sling.






























![Clinical presentation & Physical
examination
• Pain [severe]
• Hold limb with normal limb by side
of body.
• Abduction and external rotation.
• Pt can’t touch apposite shoulder
[Dugar test]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shoulderdislocation-180325073115/85/Shoulderdislocation-33-320.jpg)









