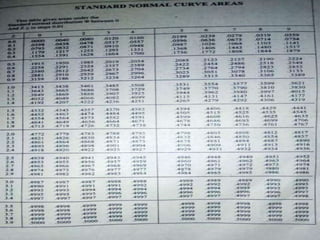
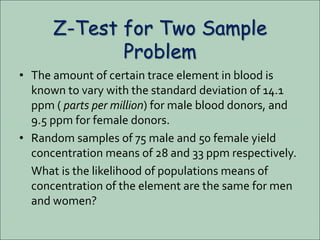
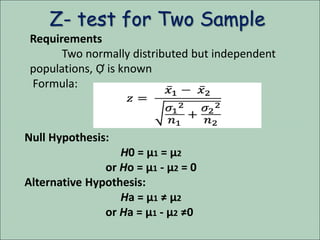
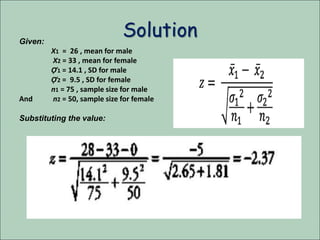
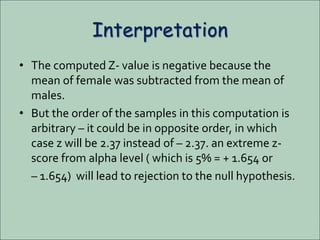
The document discusses the z-test, a statistical procedure used to test the difference between two population means. It provides the formulas and steps to conduct a z-test, including stating the null and alternative hypotheses, finding the z-score, and interpreting the results. An example problem is shown where a z-test is used to determine if the mean IQ scores of students at a school are above average. A second example tests if the mean concentration of a trace element is the same between male and female blood donors.