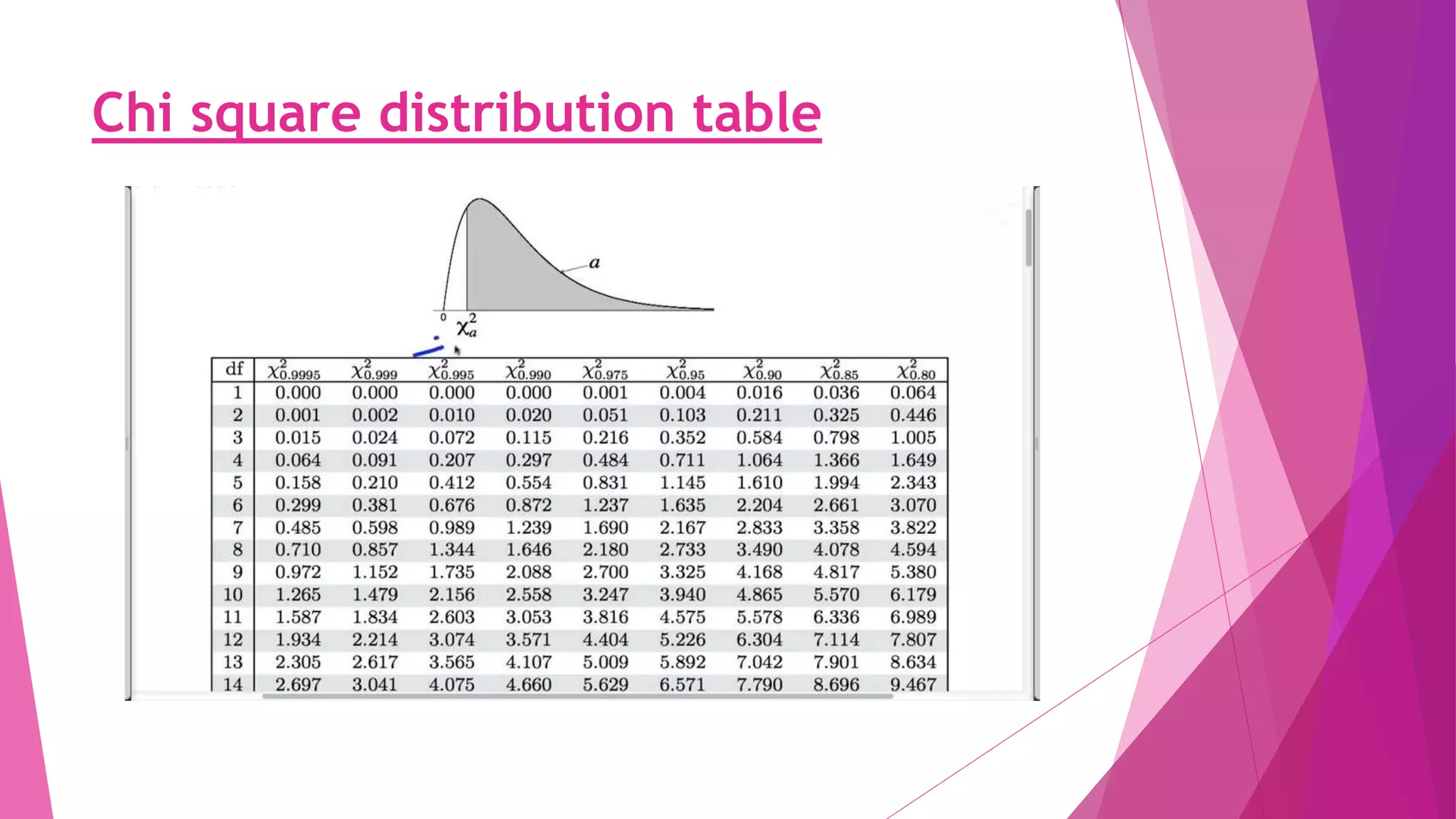
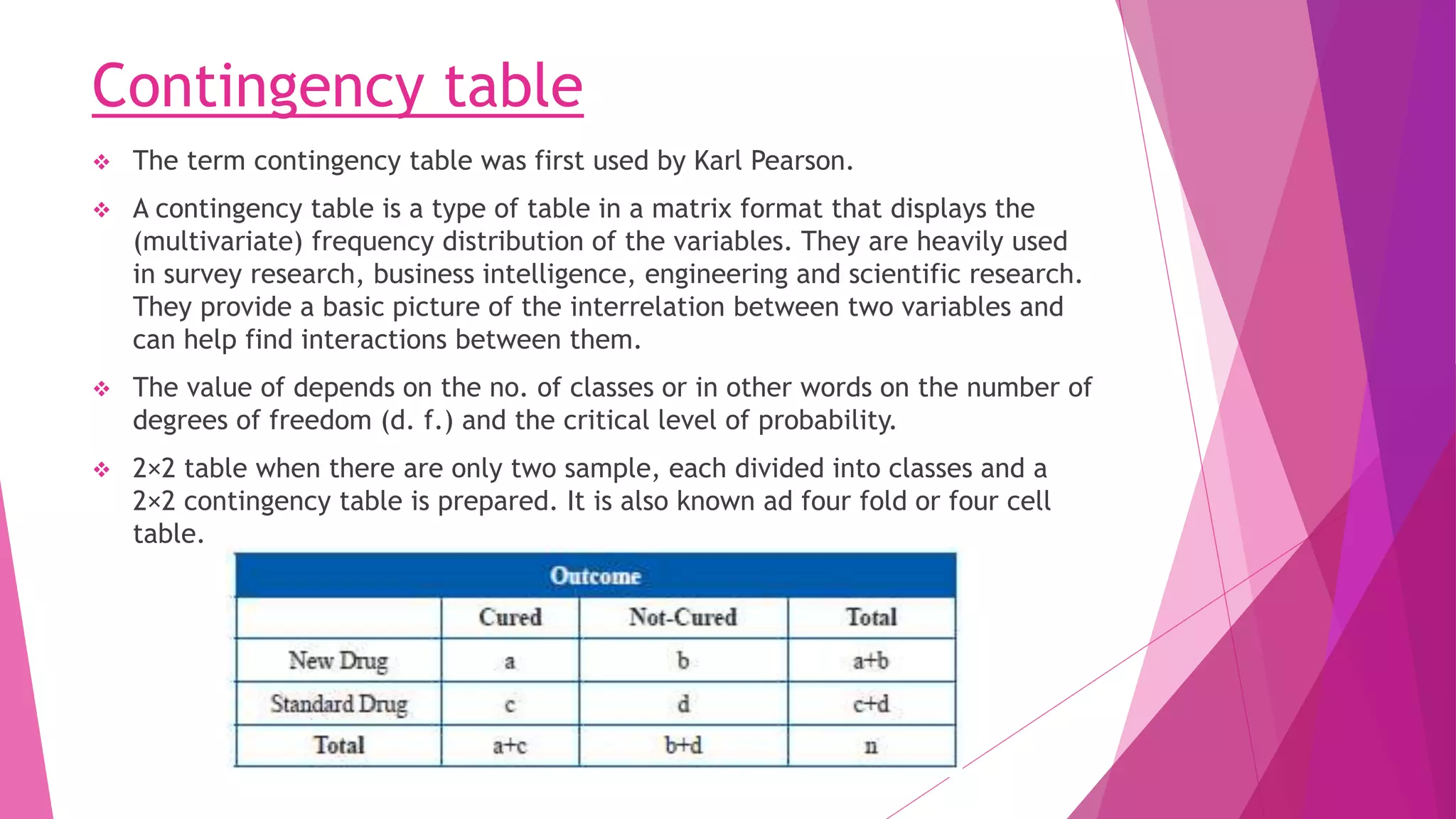
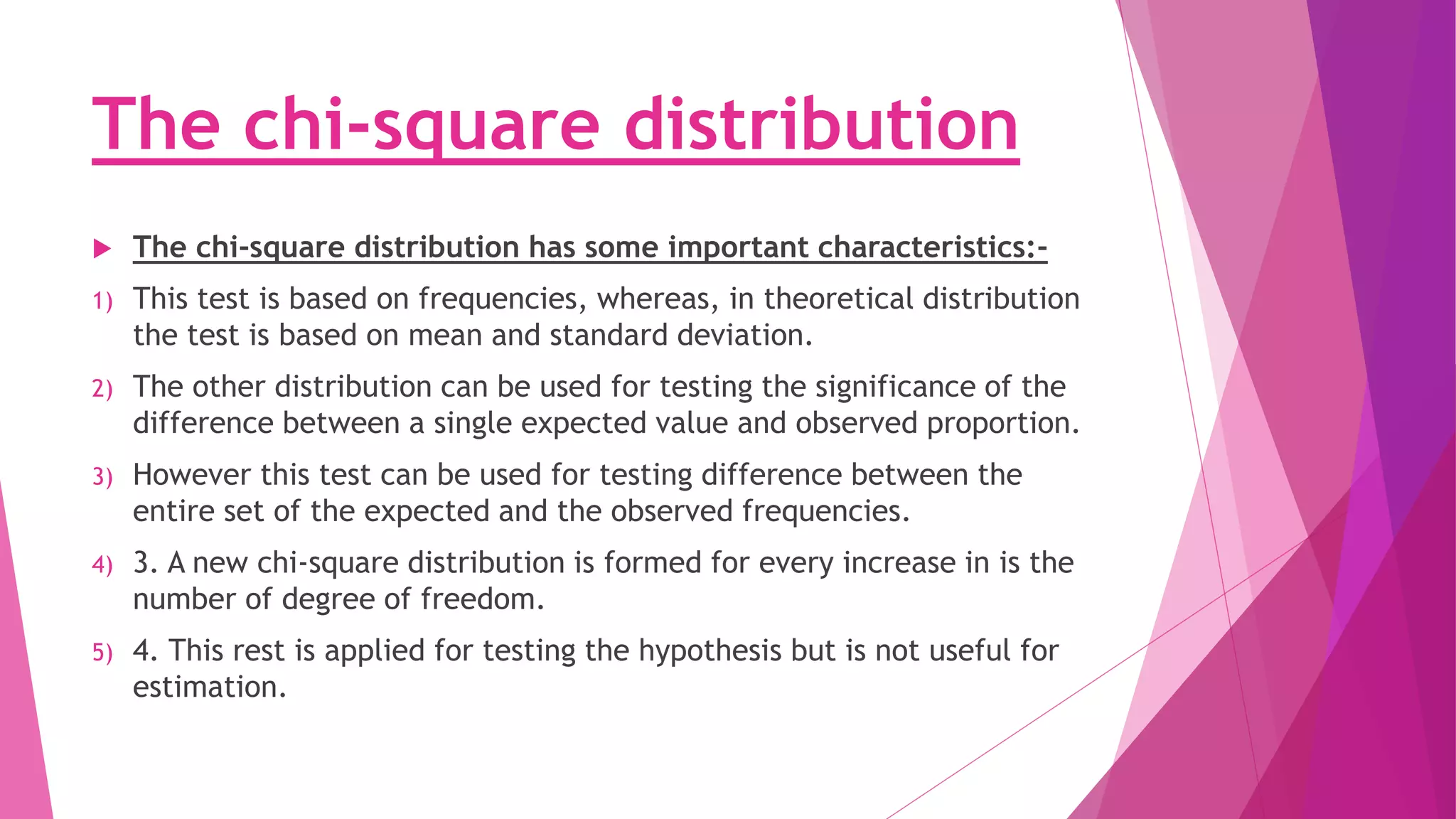
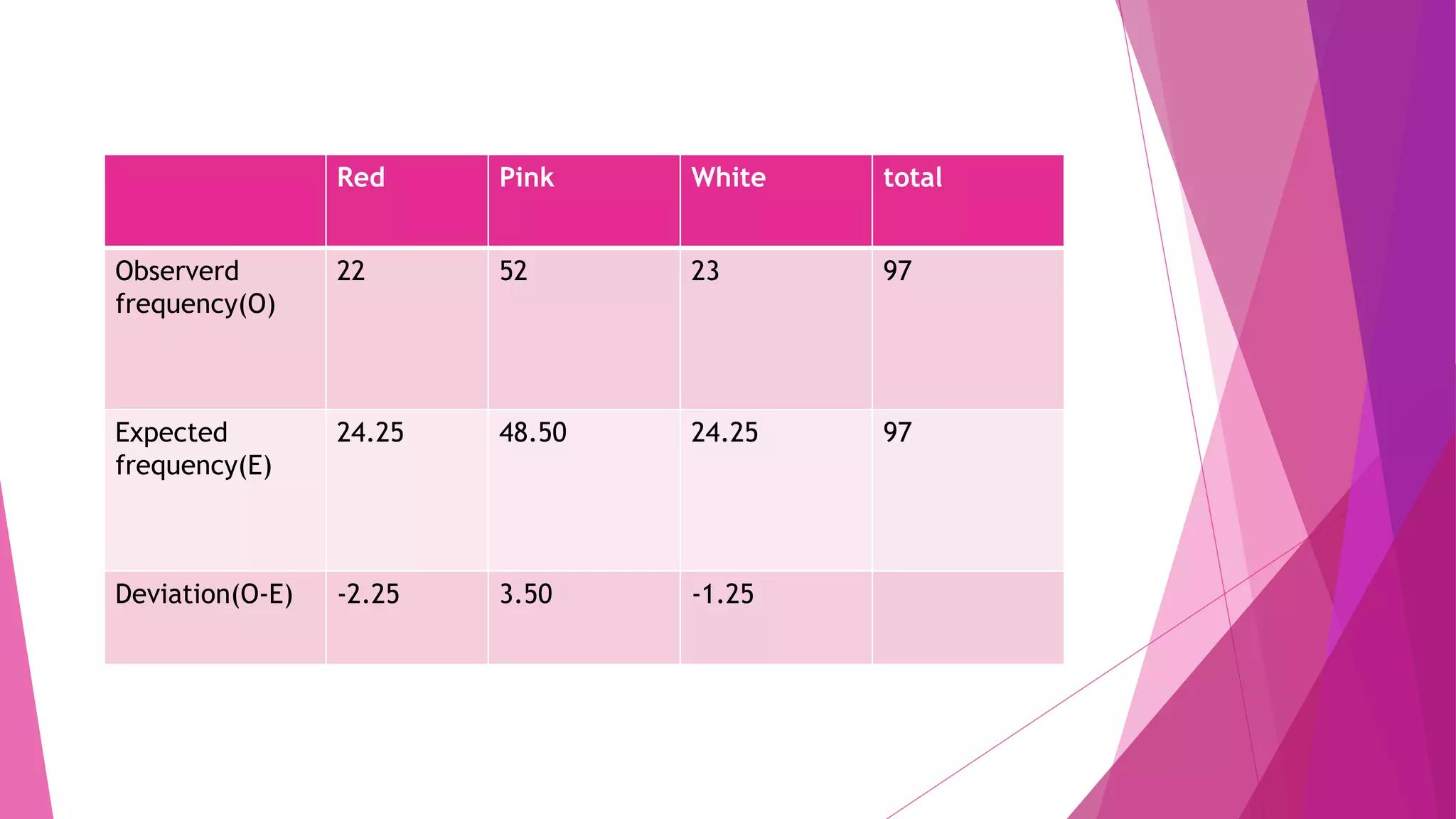
The chi-square test is used to determine if an observed distribution of data differs from the theoretical distribution. It compares observed frequencies to expected frequencies based on a hypothesis. The chi-square value is calculated by summing the squared differences between observed and expected frequencies divided by the expected frequency. The chi-square value is then compared to a critical value from the chi-square distribution table based on the degrees of freedom. If the chi-square value is greater than the critical value, the null hypothesis that the distributions are the same can be rejected.

![Chi square distrubution
In probability theory and statistics, the chi-square distribution (also chi-
squared or χ2-distribution) with k degrees of freedom is the distribution of a
sum of the squares of k independent standard normal random variables. The
chi-square distribution is a special case of the gamma distribution and is one
of the most widely used probability distributions in inferential statistics,
notably in hypothesis testing and in construction of confidence
intervals.[2][3][4][5] This distribution is sometimes called the central chi-square
distribution, a special case of the more general noncentral chi-square
distribution. The formula is](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chisquaretest-210619085848/75/Chi-square-test-3-2048.jpg)