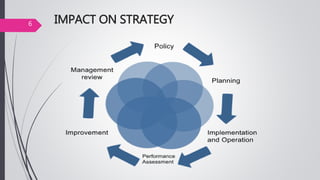
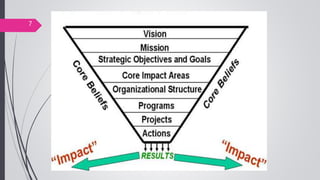
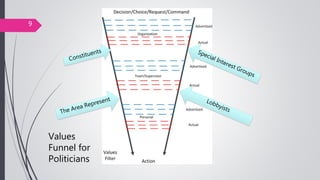
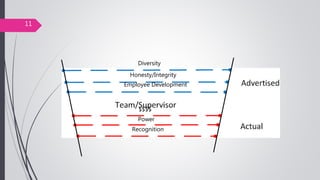
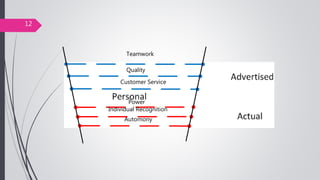
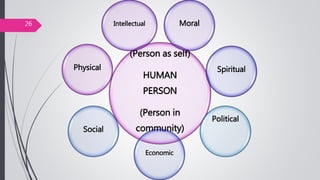
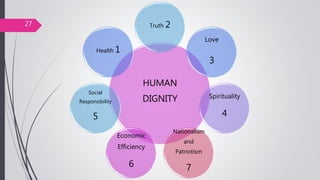
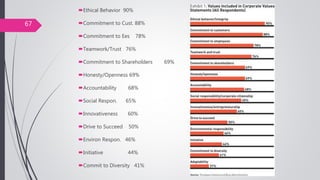
This document discusses organizational core values. It defines values as beliefs, missions or philosophies that are meaningful. Core values represent fundamental principles that guide an organization in determining right from wrong and good from bad. Values impact all aspects of a company from products to employee treatment. They form the foundation for decision making and relationships. Establishing clear core values helps align personal values with an organization's values, guide strategy and improve productivity, decision making and employee morale.