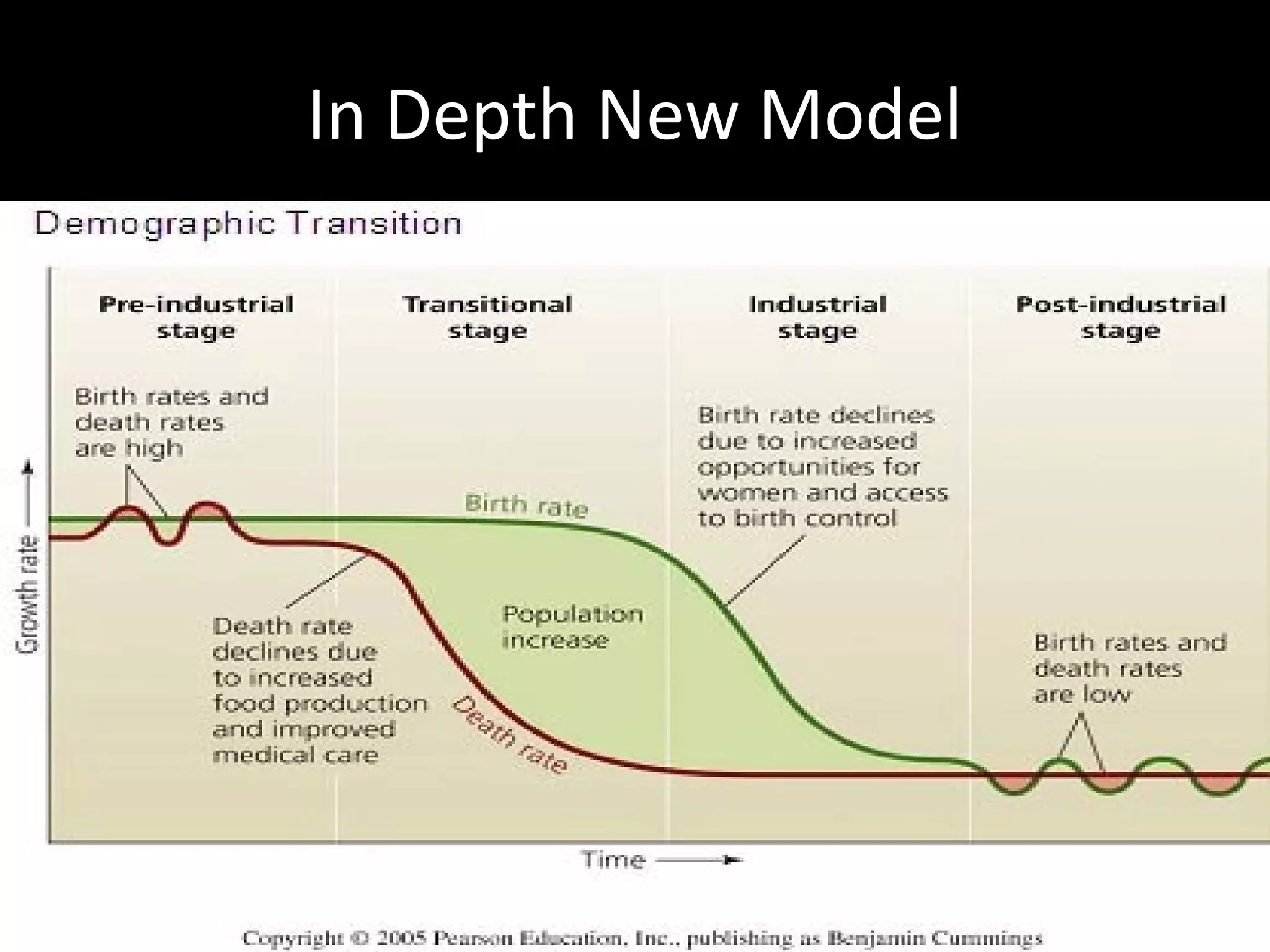
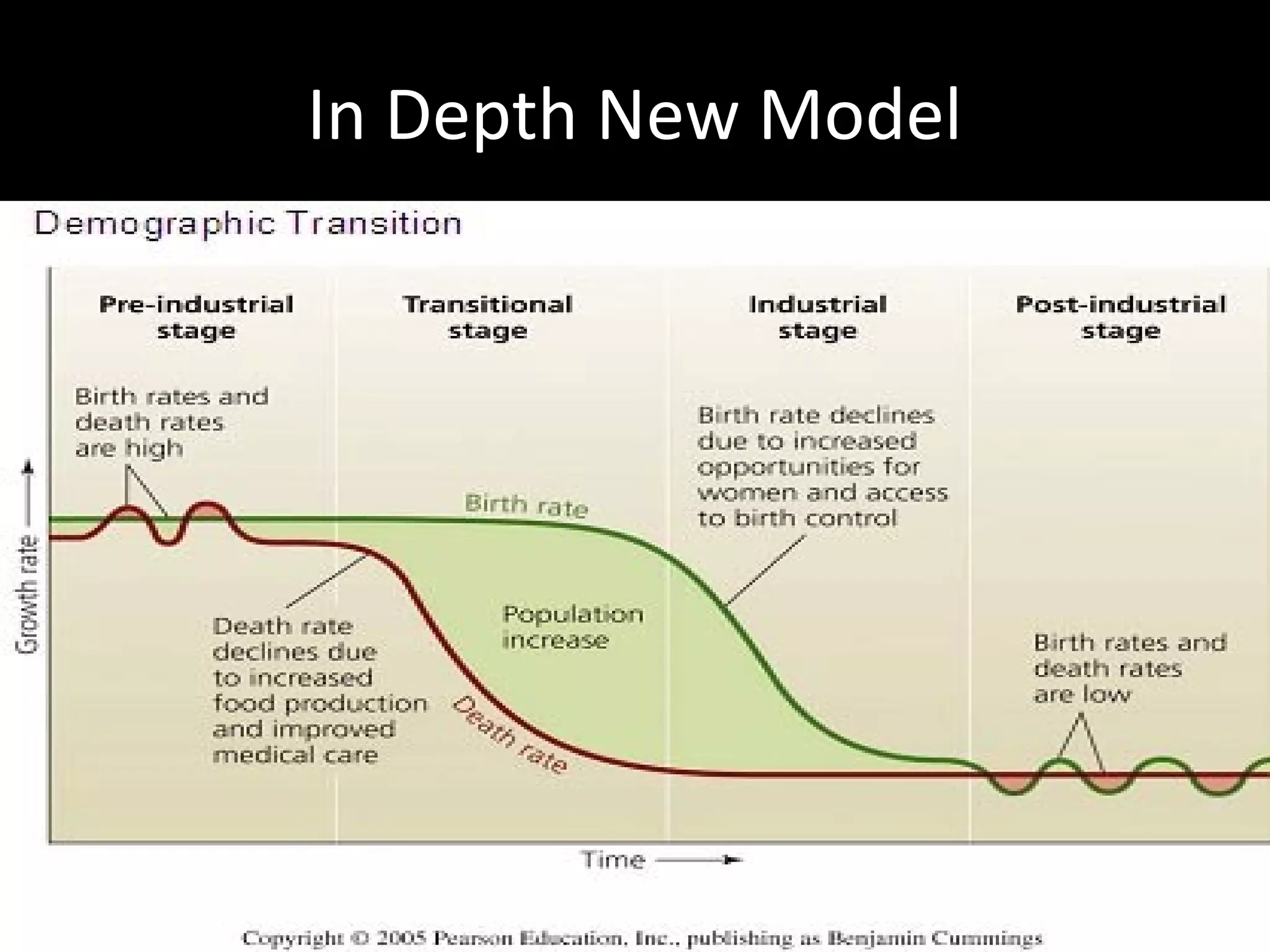
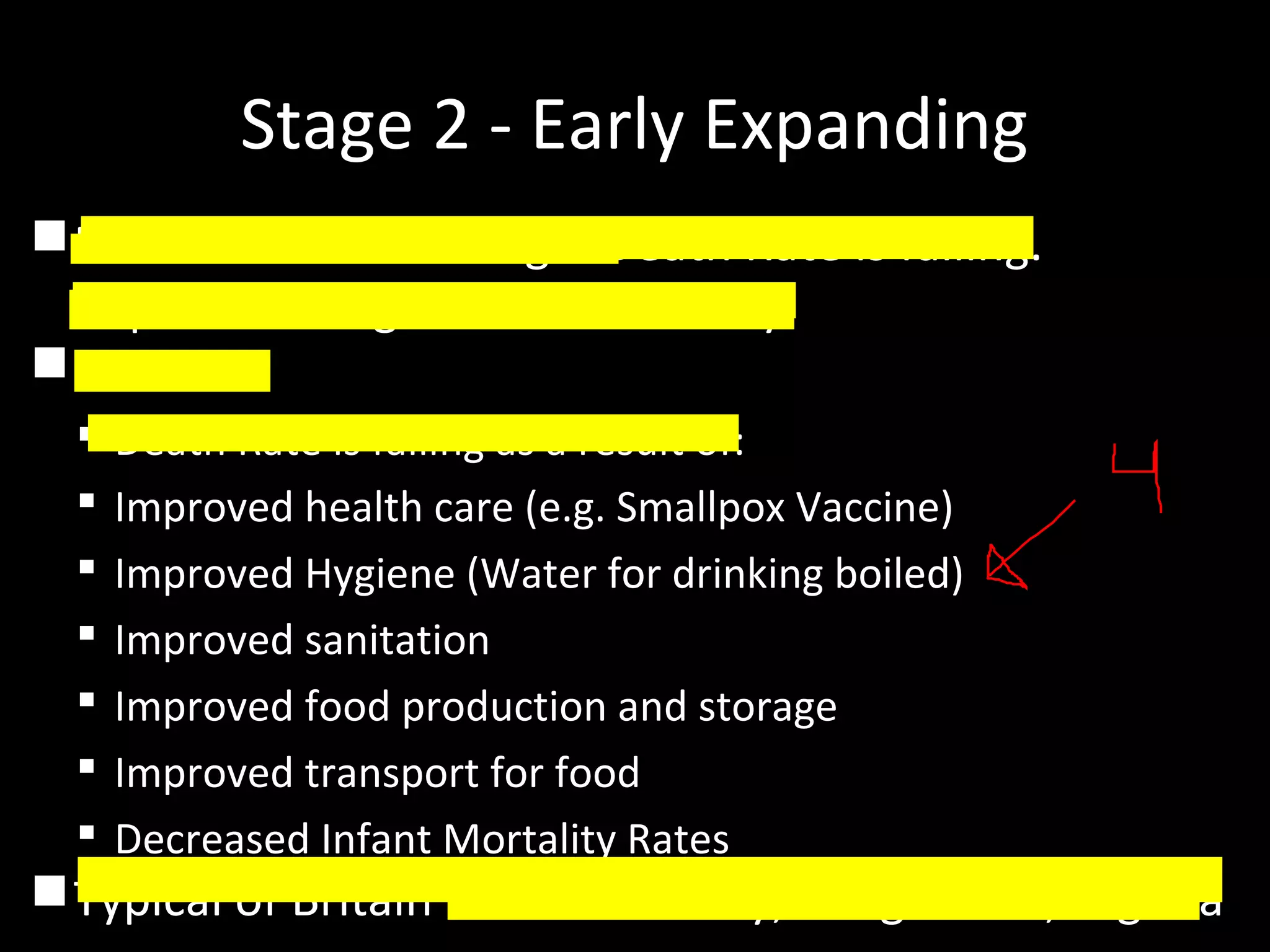
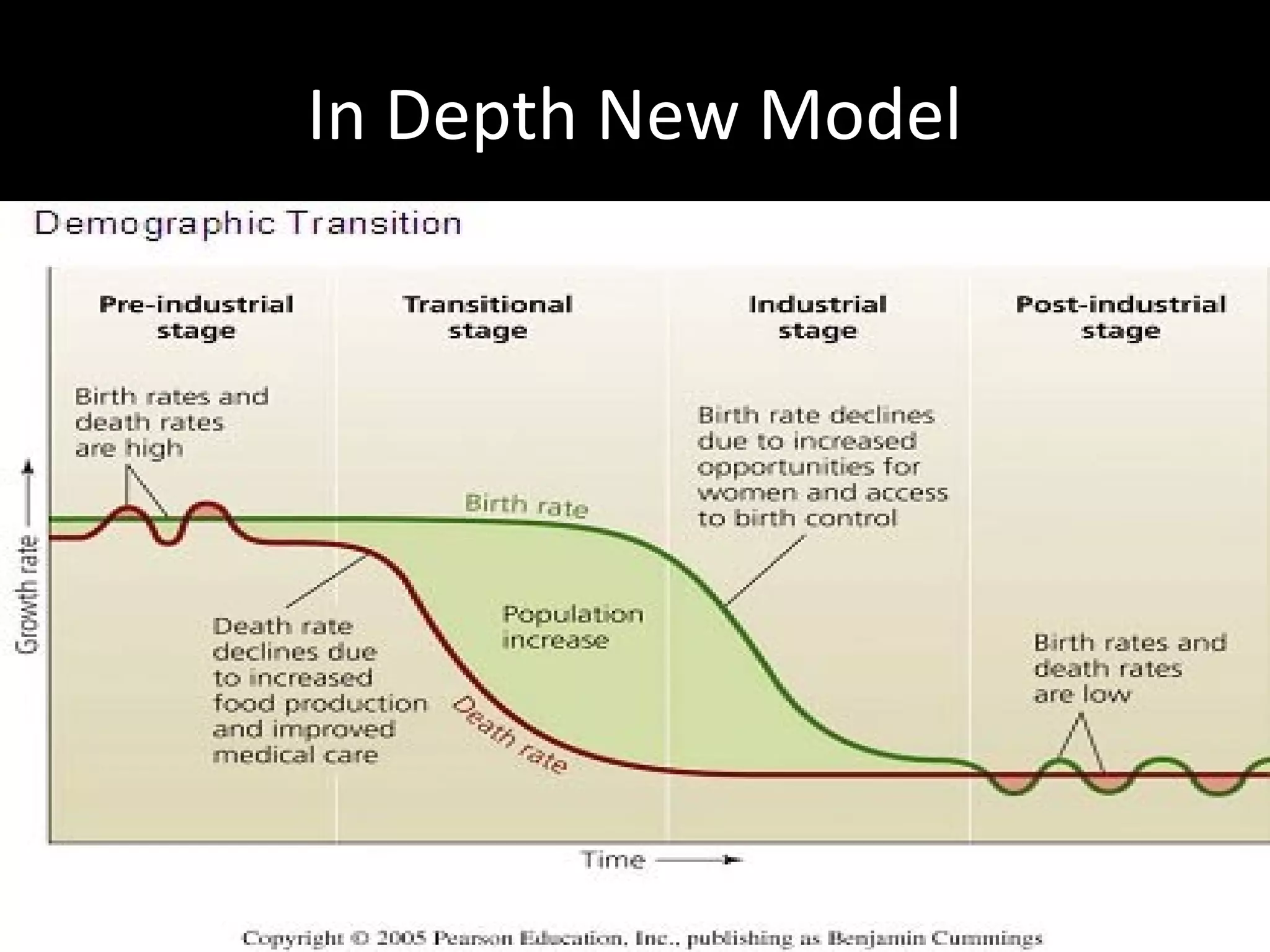
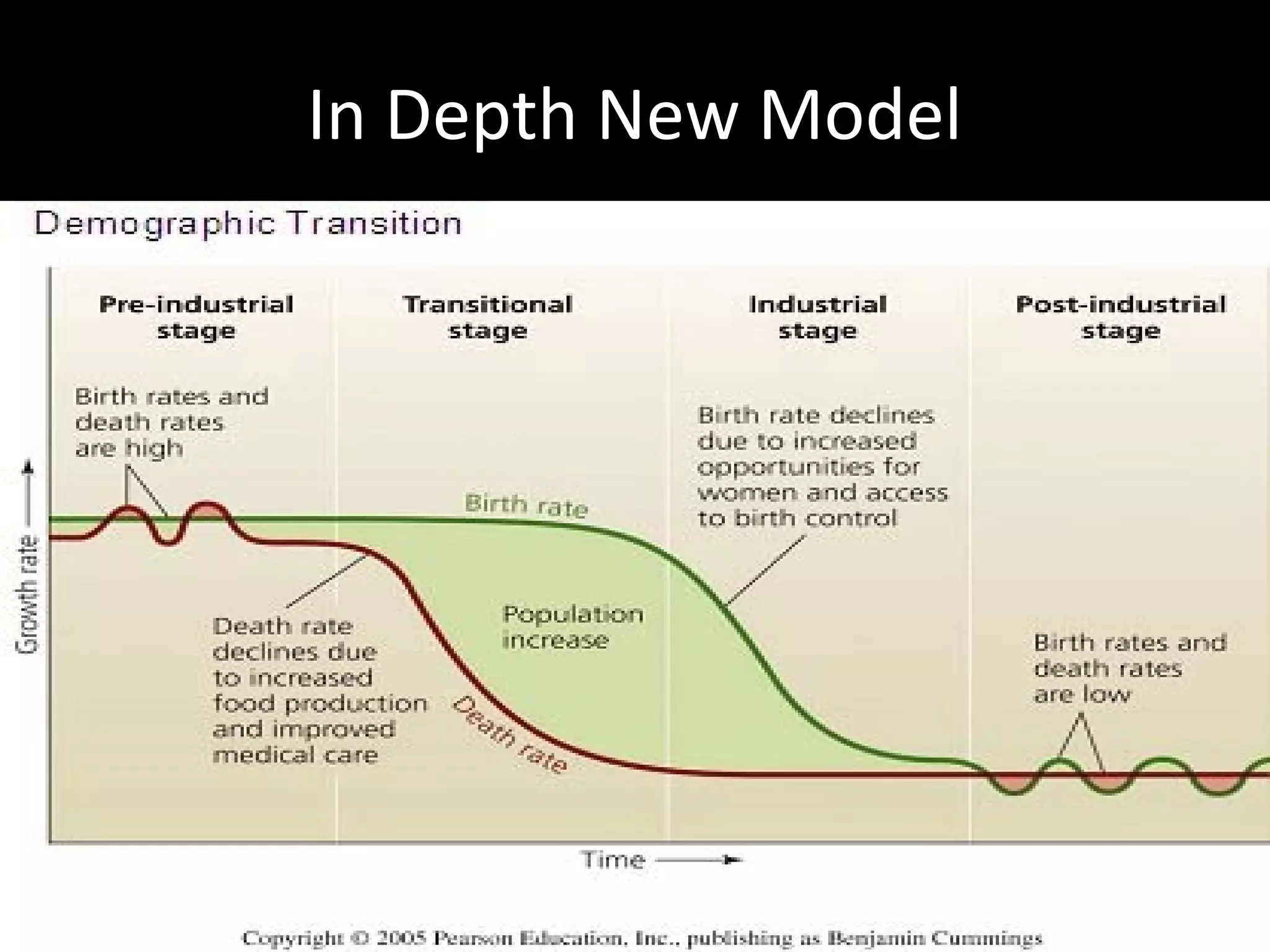
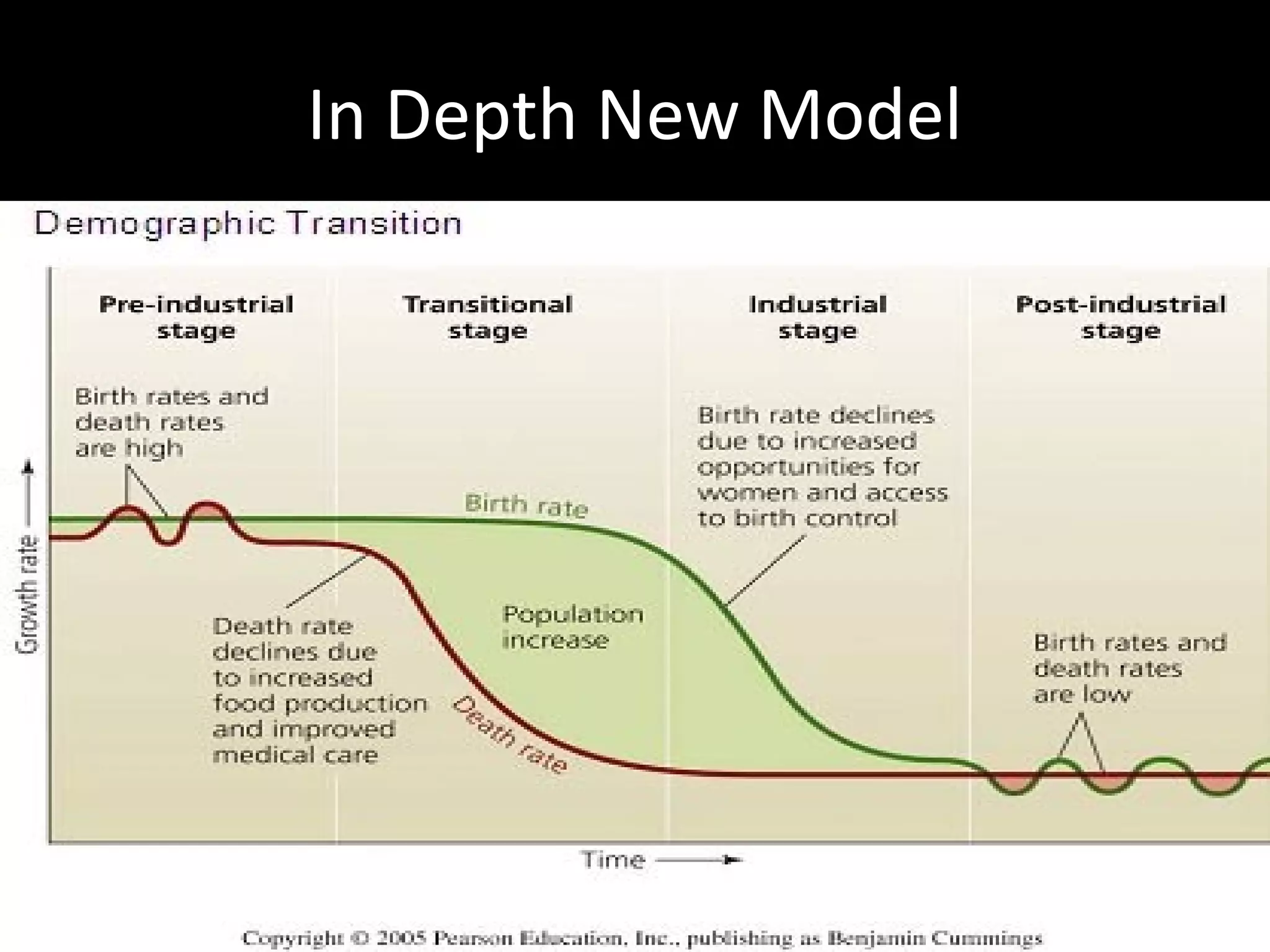
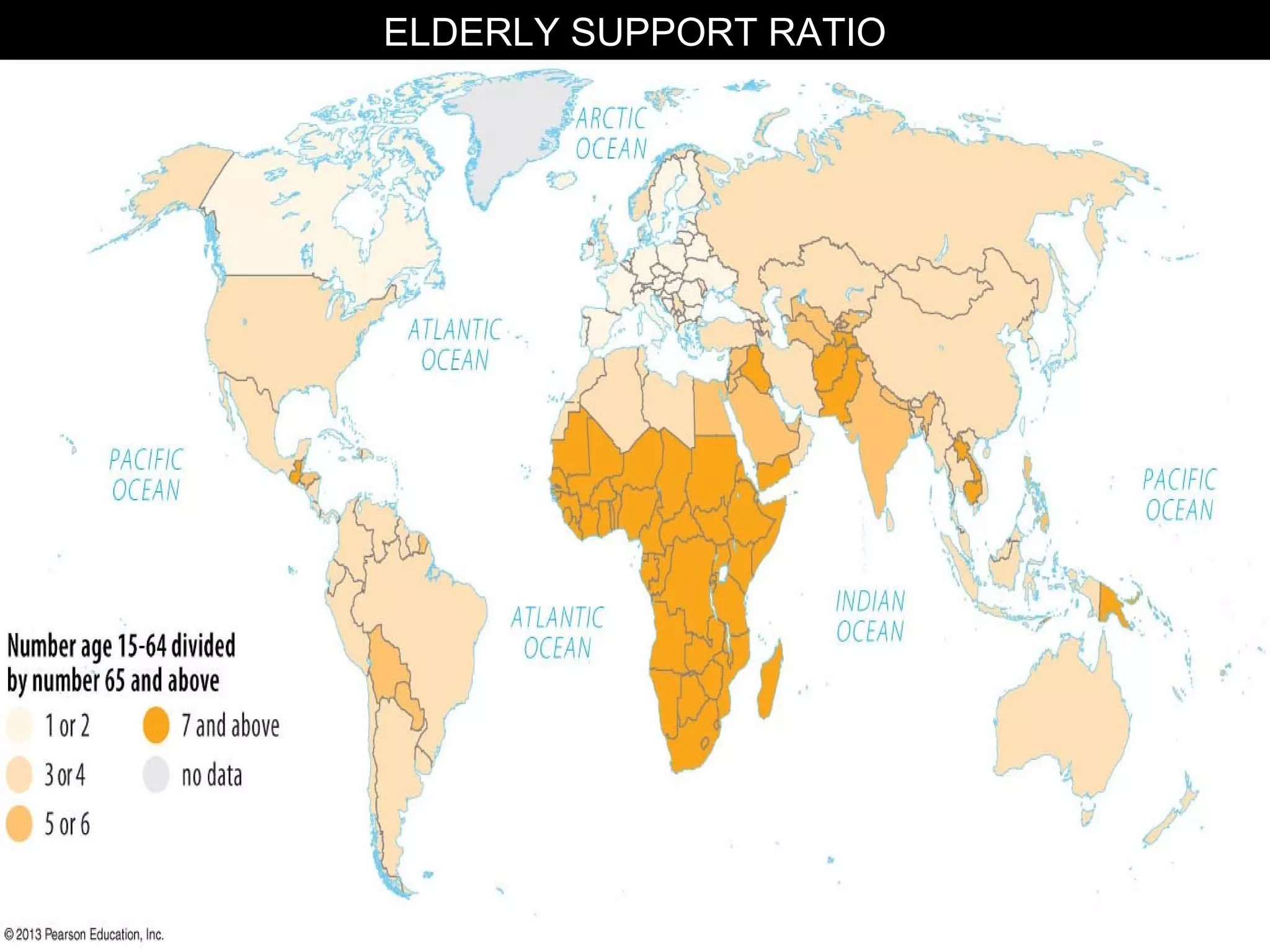
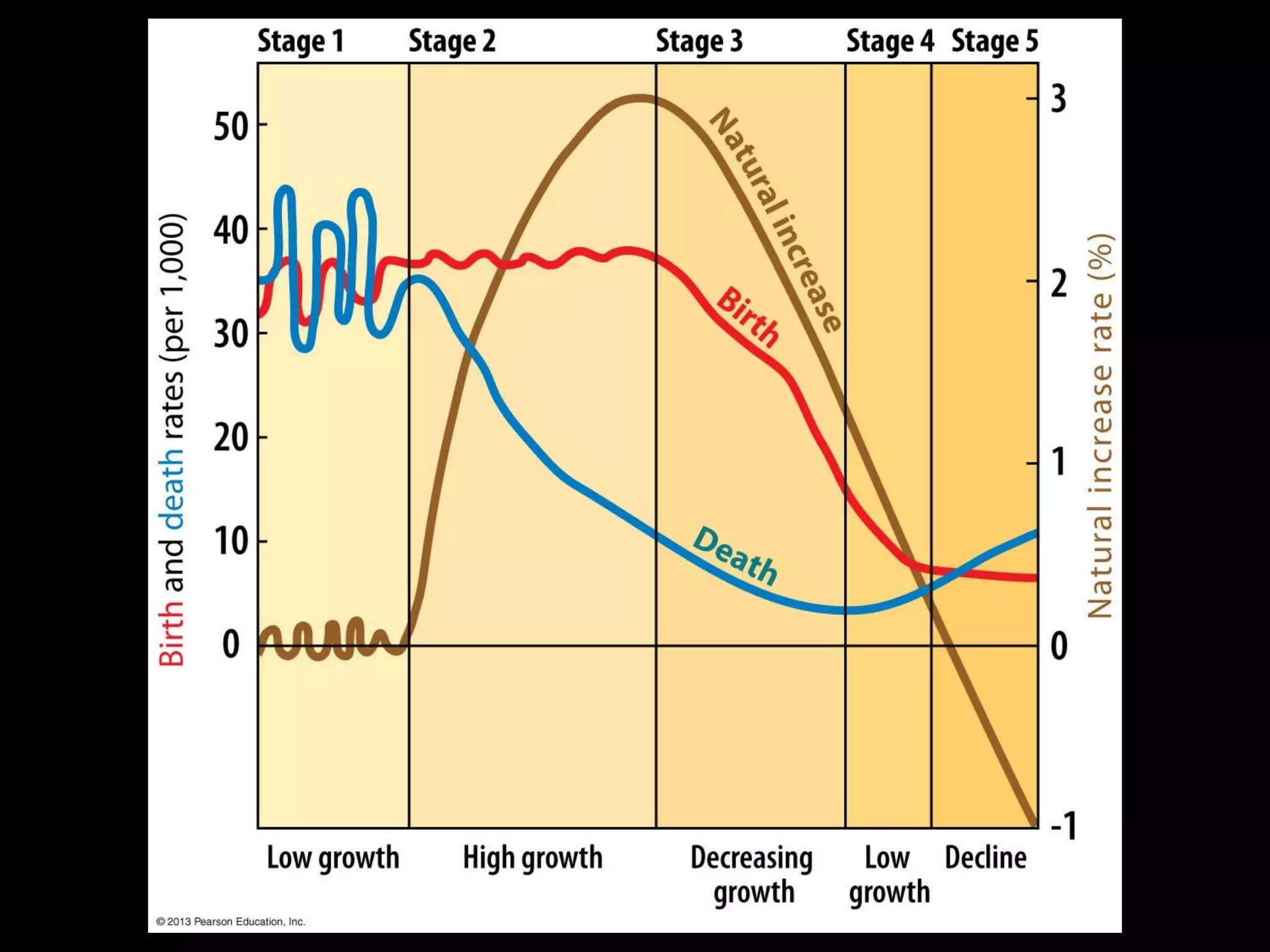
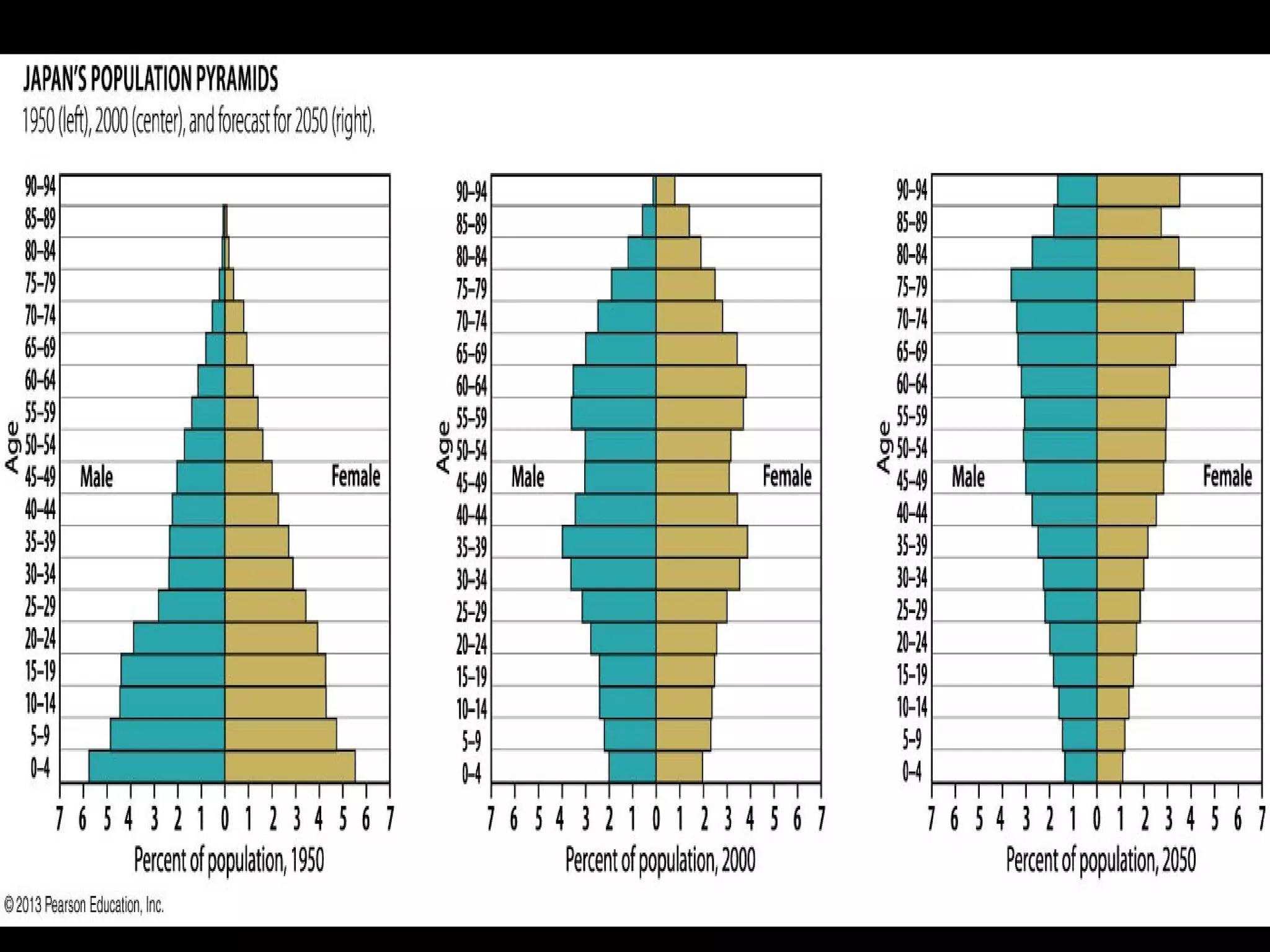
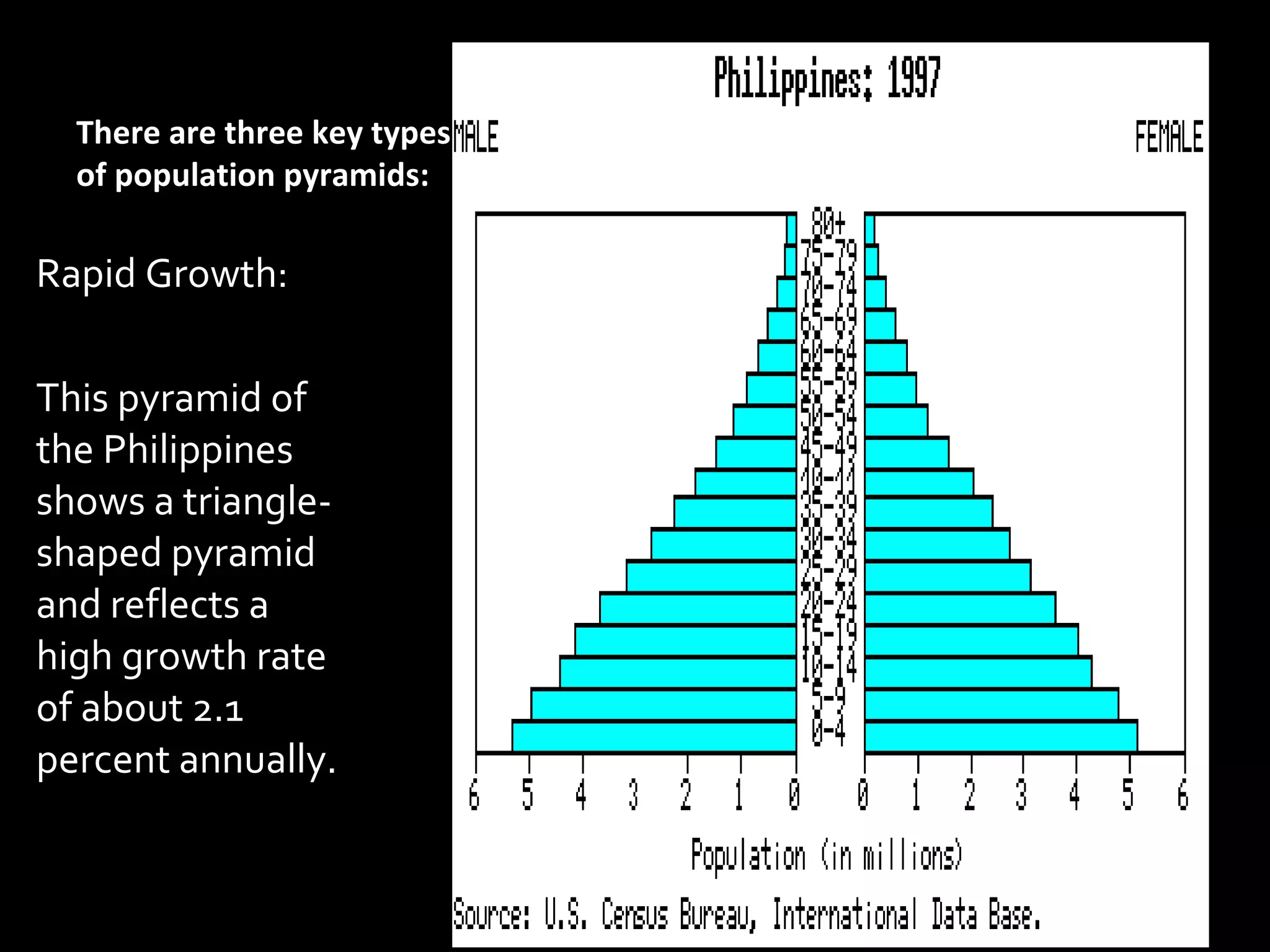
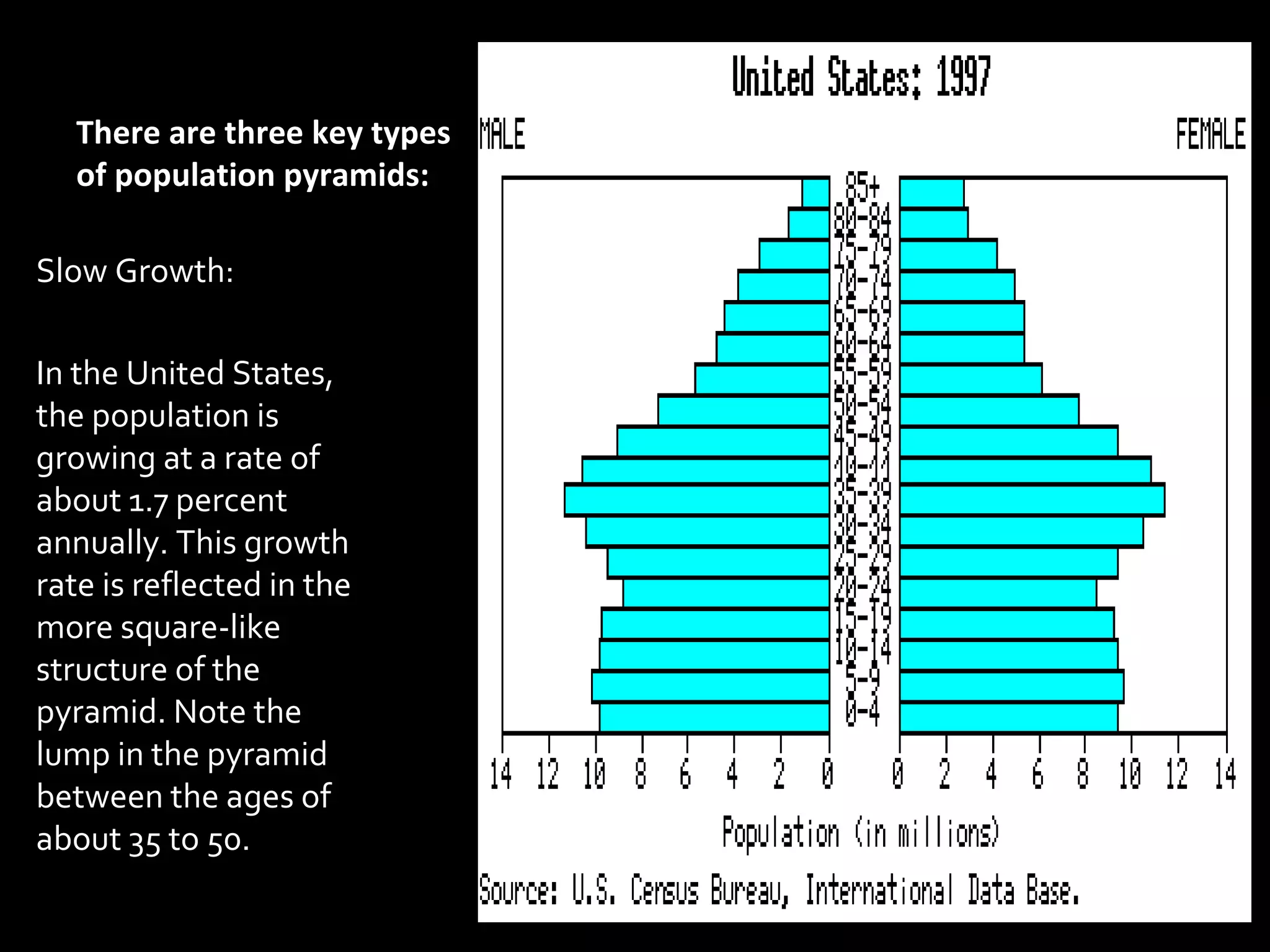
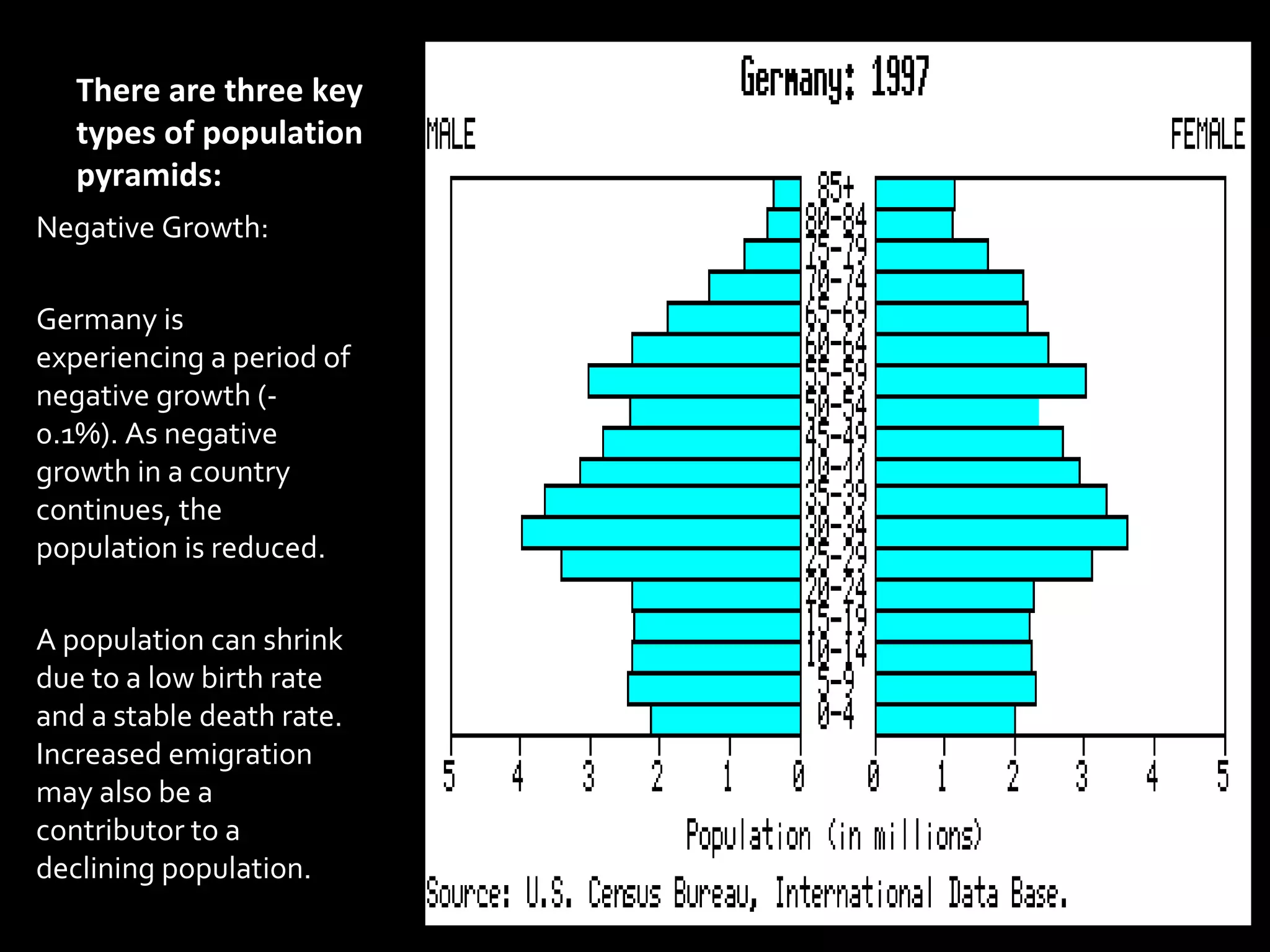
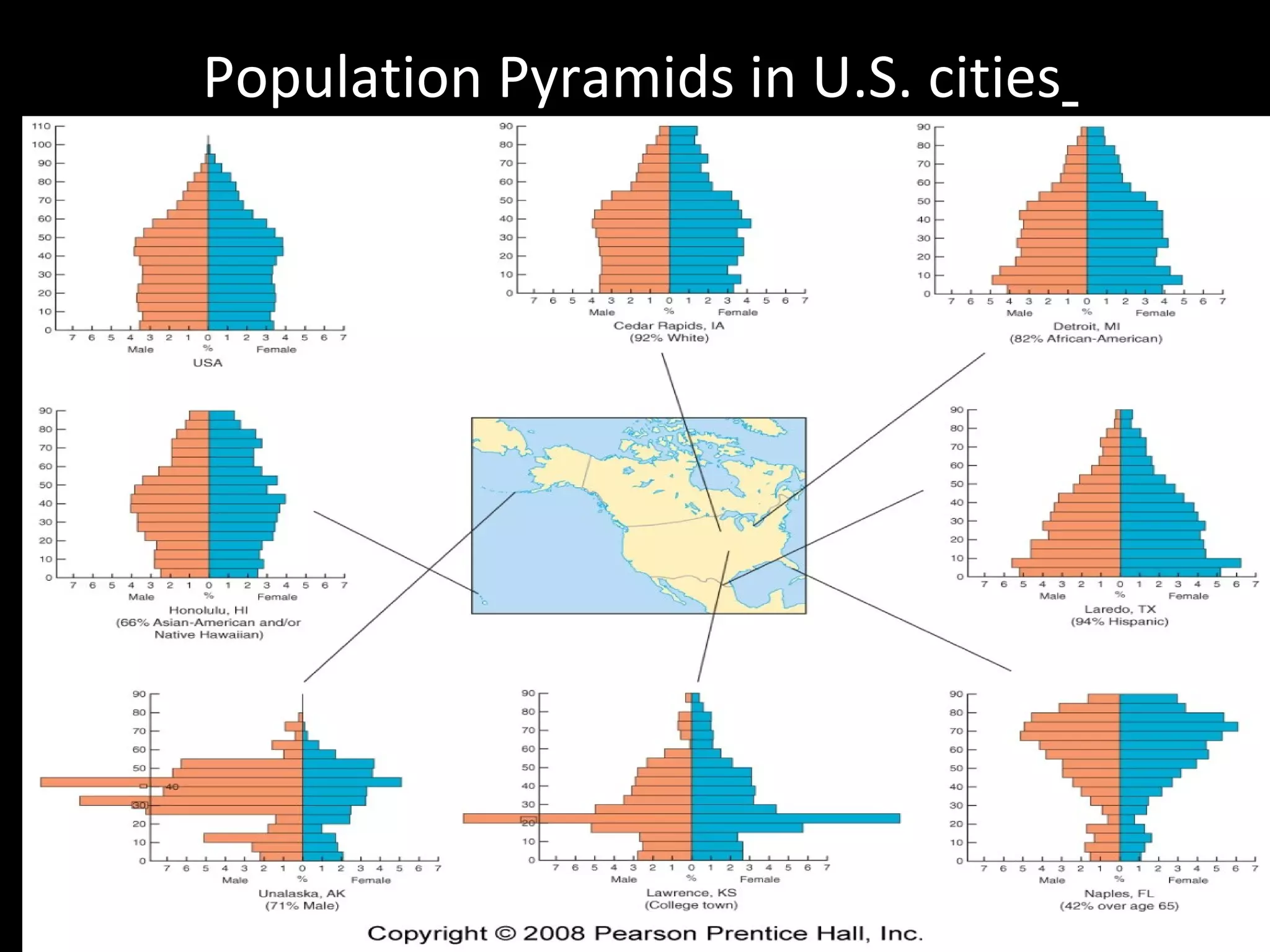
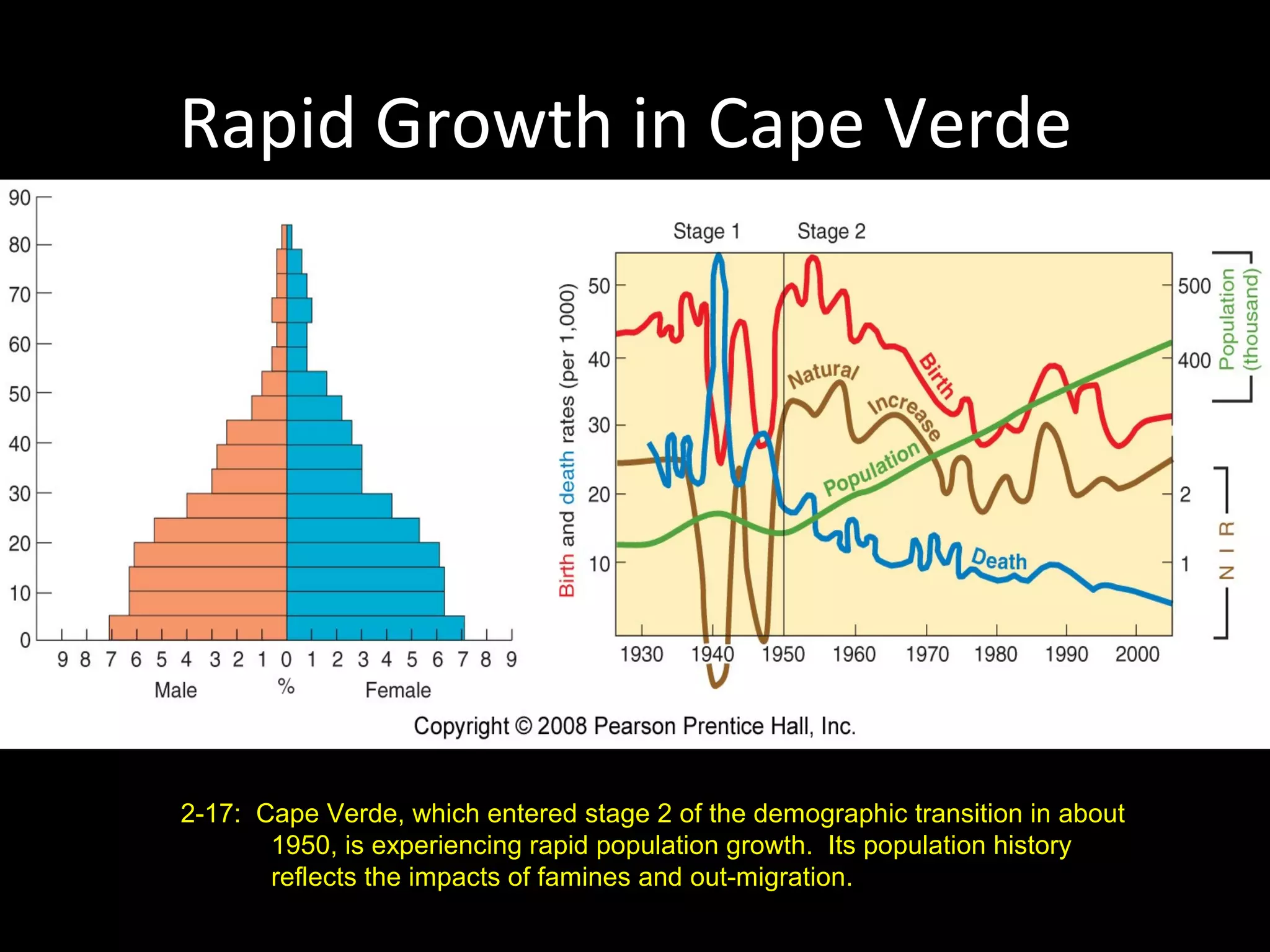
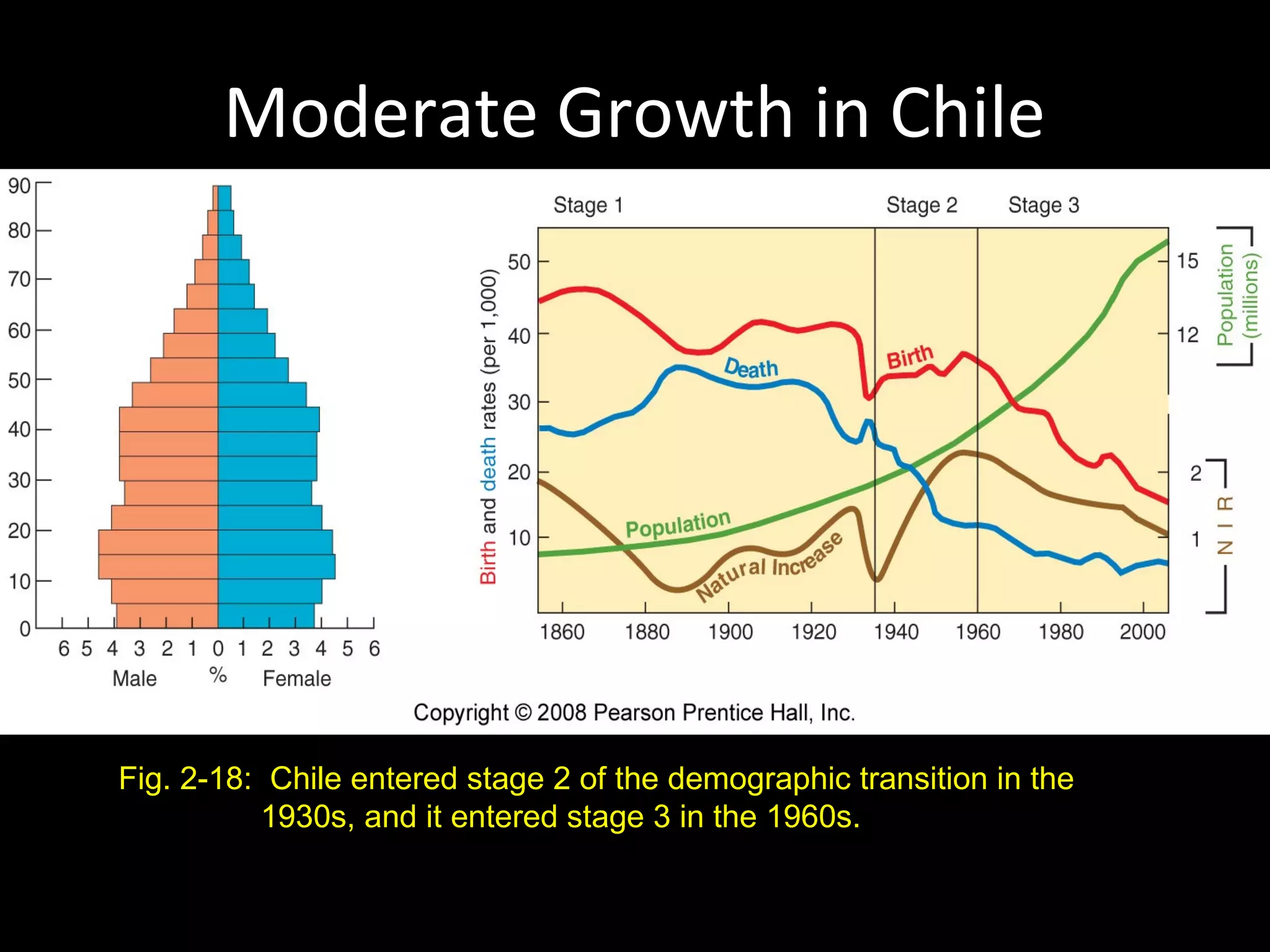
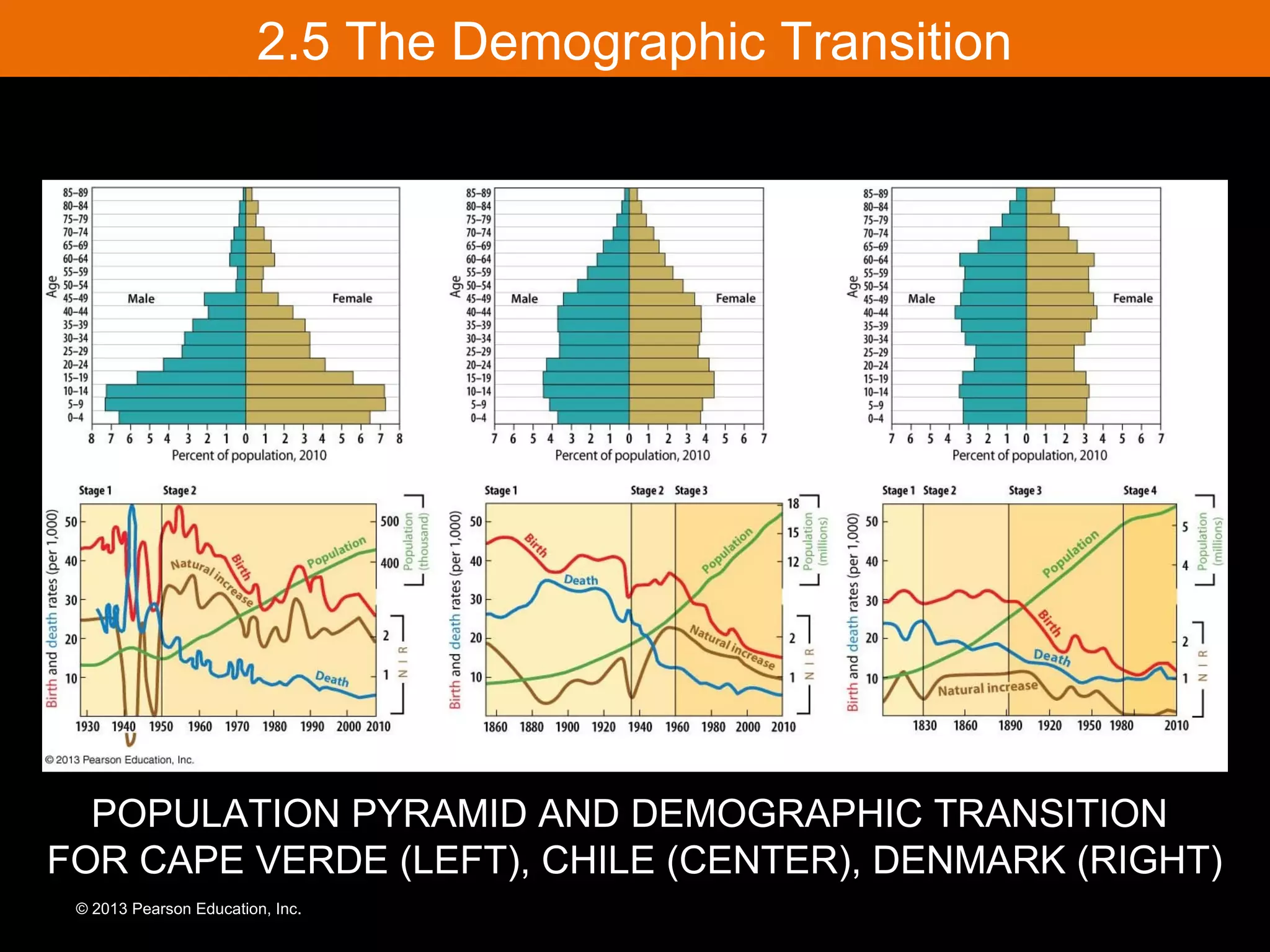
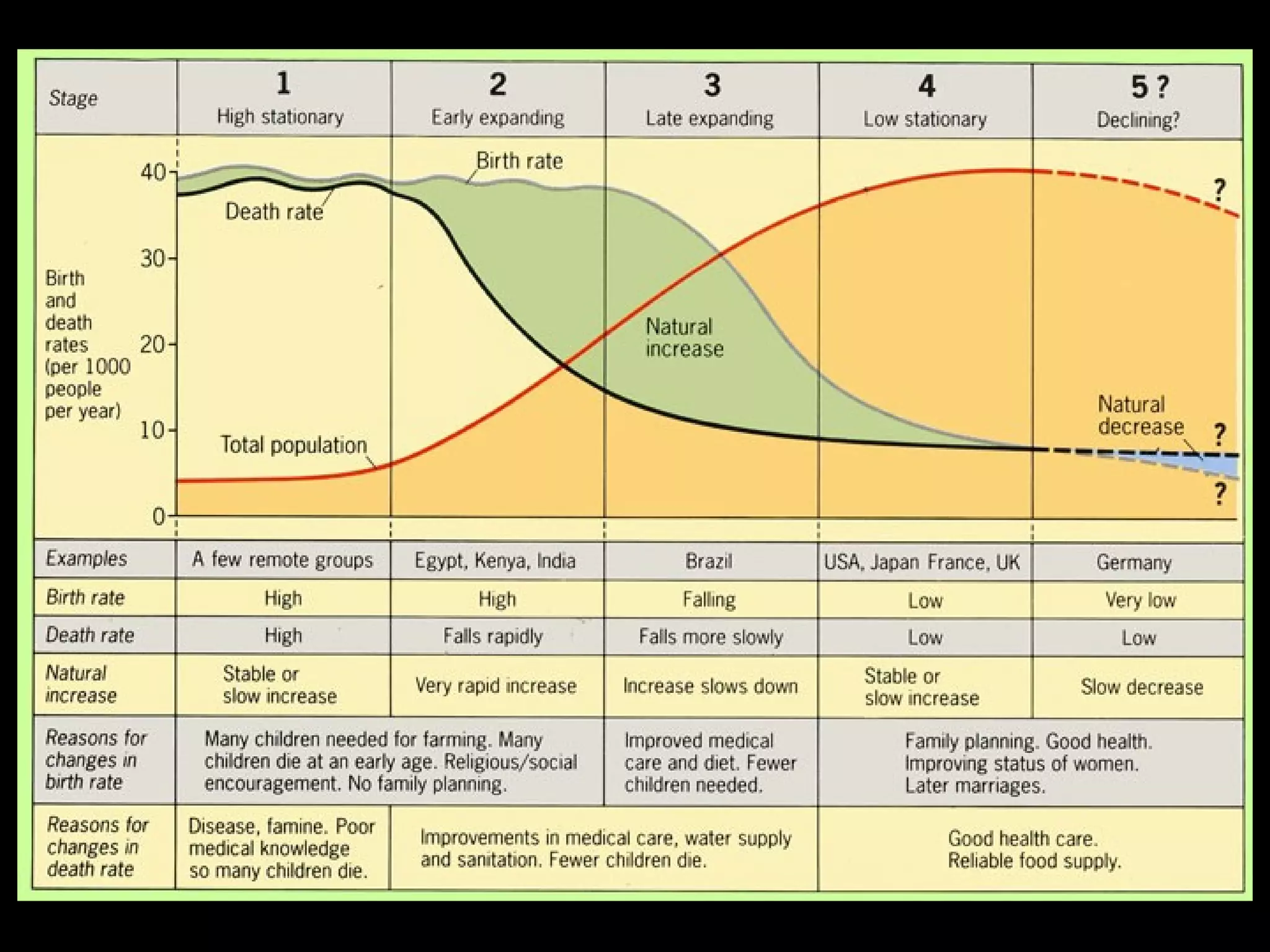
The document discusses the demographic transition model and how it explains variations in population growth rates between countries. It describes the four stages of the demographic transition from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates, and notes that most developing countries are currently in stages 2-3 with rapid population growth. Population pyramids are introduced as a way to visualize a country's age and sex structure and compare demographics between places in different transition stages.