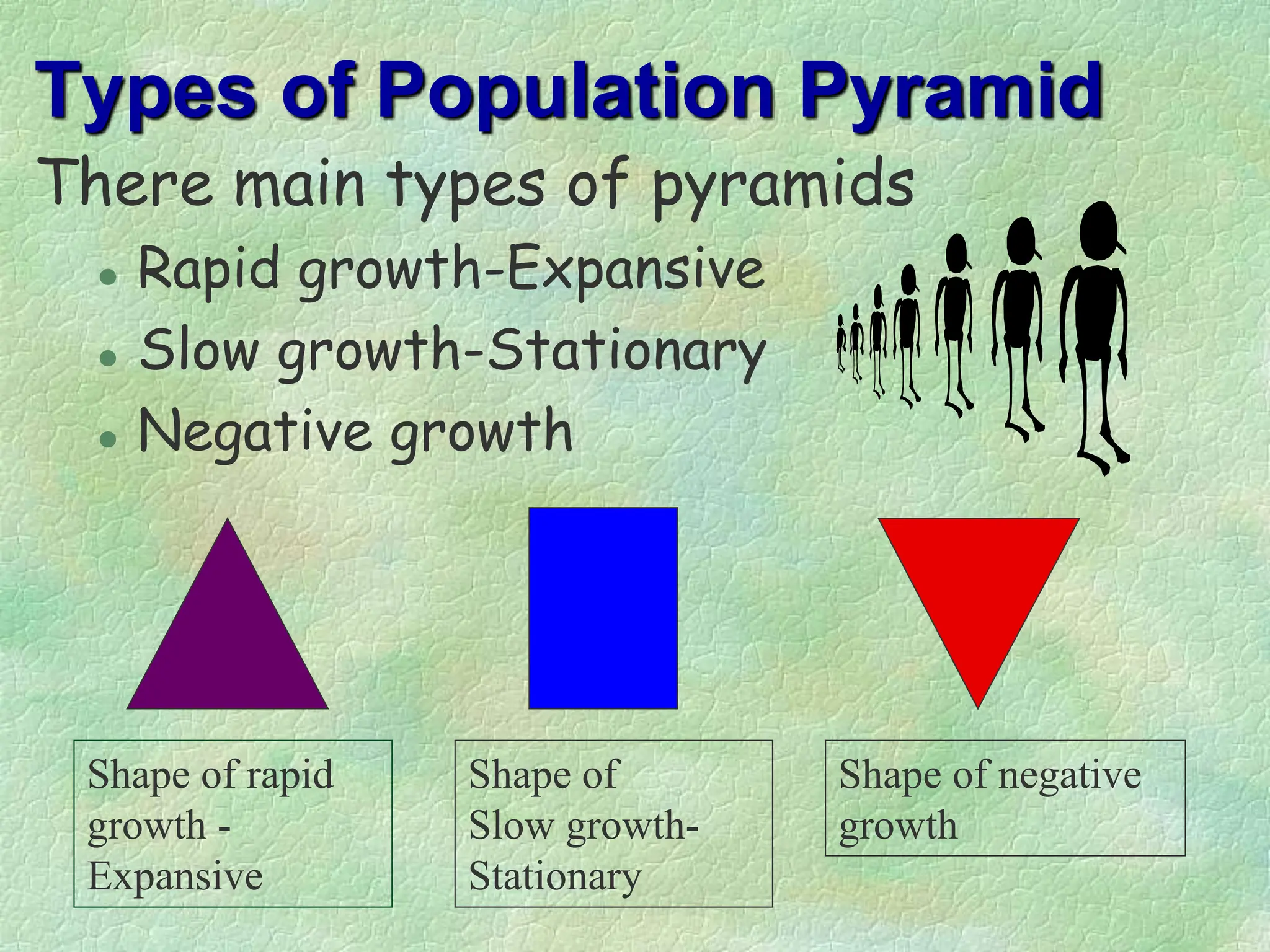
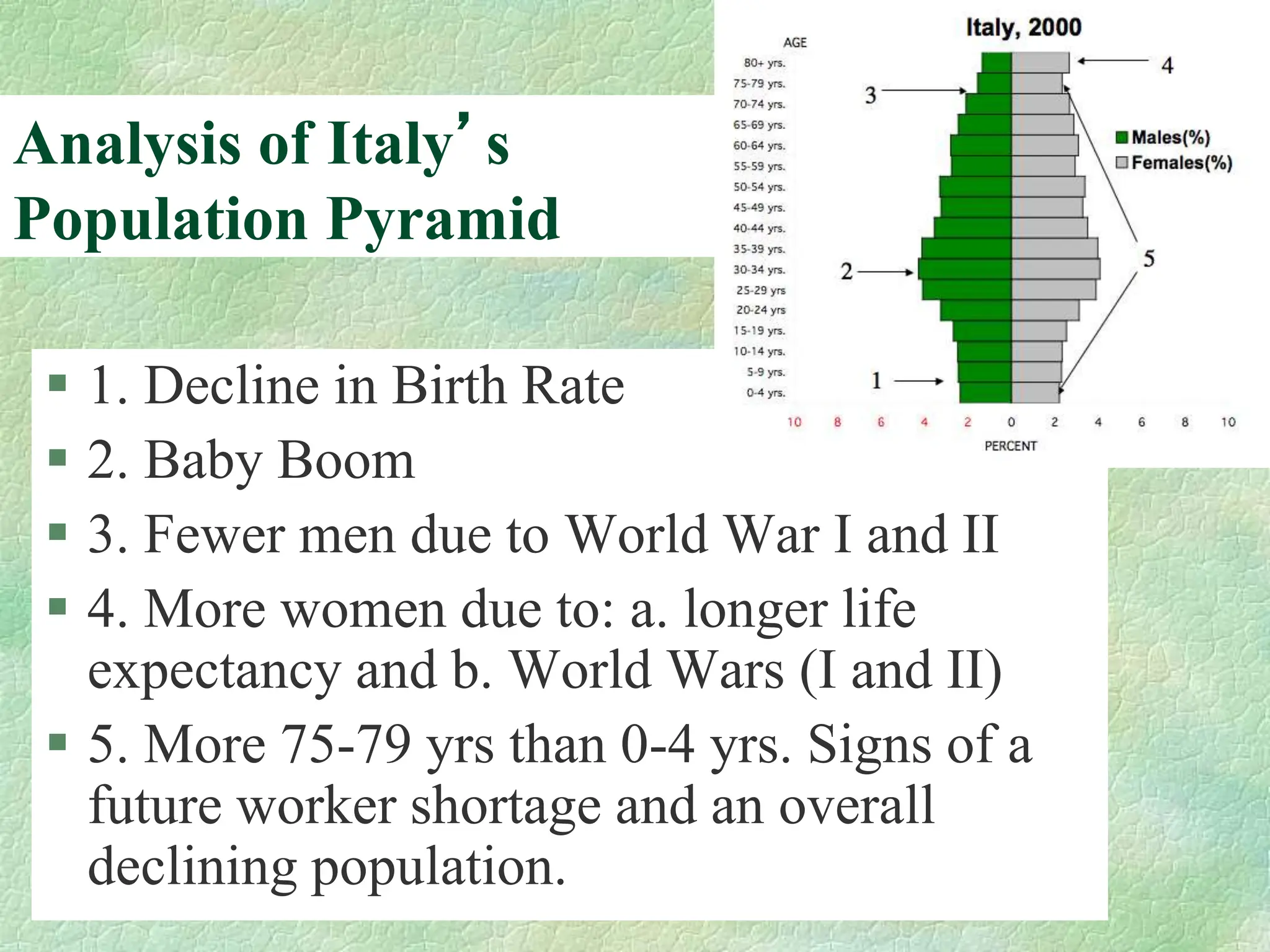
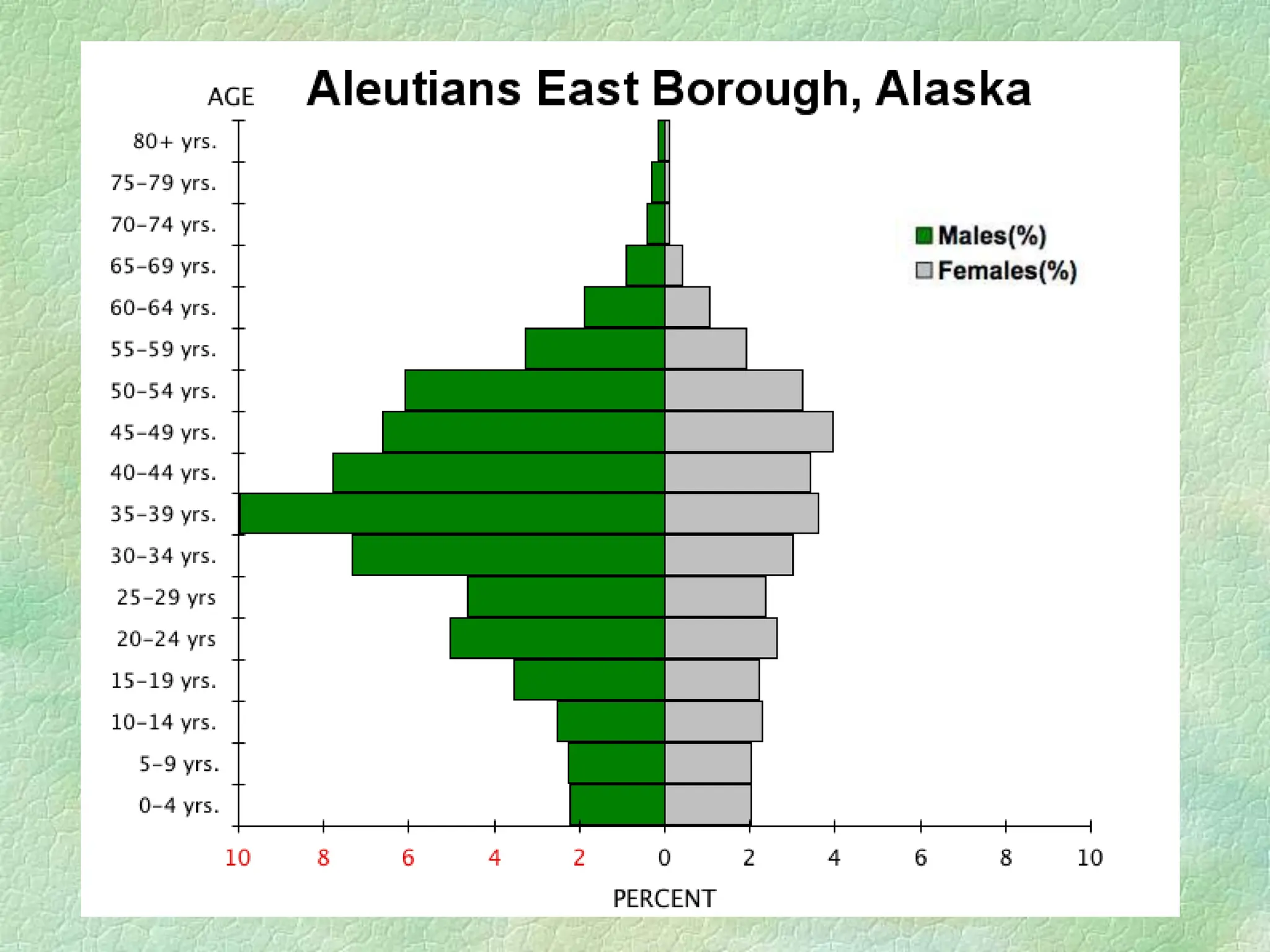
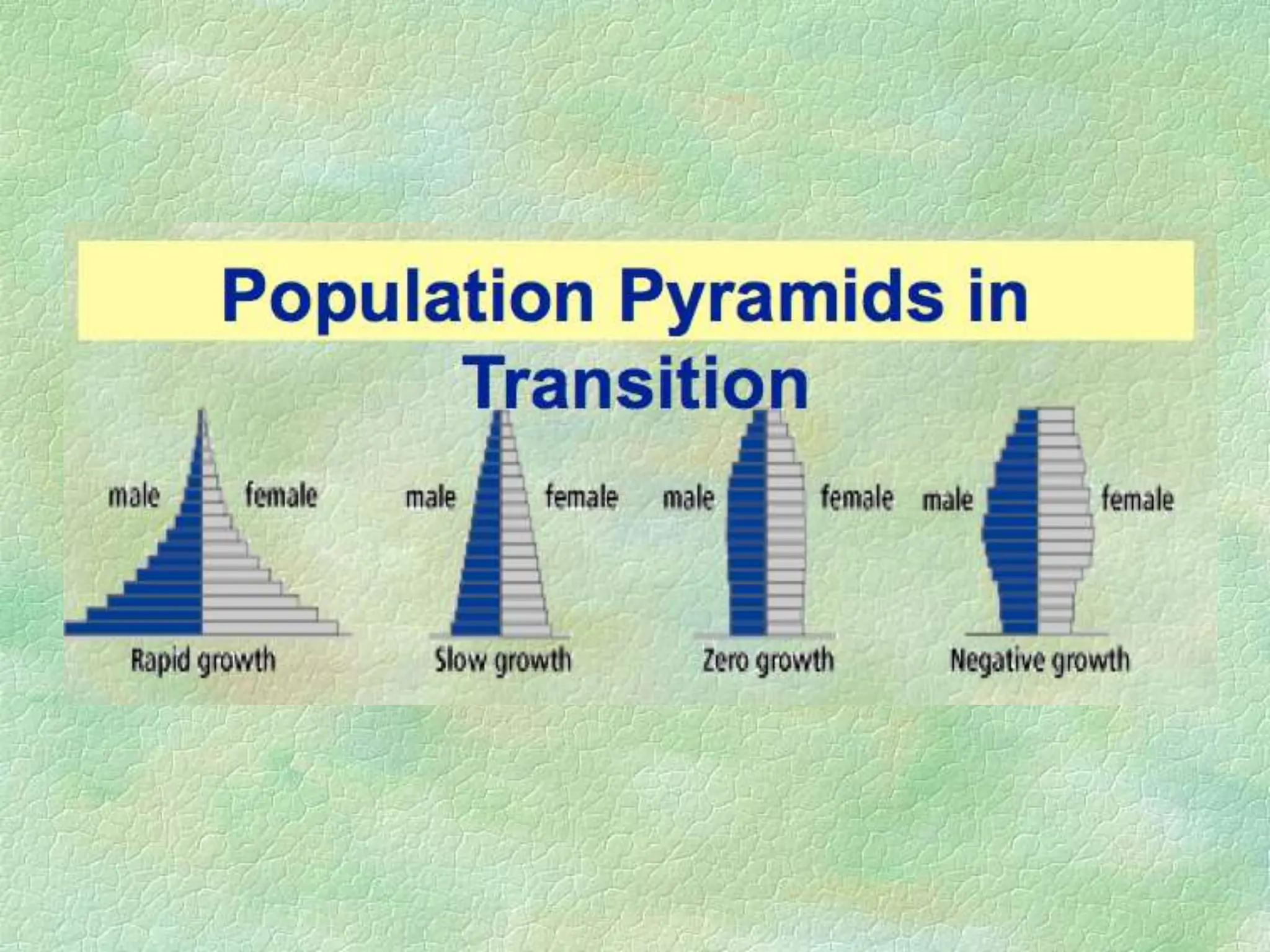
The document discusses population pyramids, including their definitions, types, and significance in understanding demographic trends. It explains how to read these pyramids and highlights their importance for planning future services based on birth and death rates, as well as migration patterns. Different shapes of population pyramids represent varying growth trends, including expanding, stable, and contracting populations.