Embed presentation
Downloaded 33 times















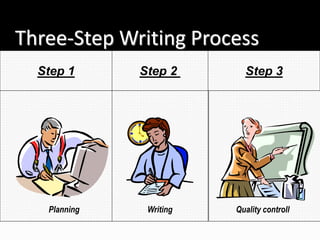



The document outlines various types of written communication, including internal and external formats, and emphasizes key etiquettes such as structuring content and awareness of the audience. It also discusses the advantages of written communication, such as creating permanent records and enhancing organizational image, as well as its disadvantages like being time-consuming and requiring strong language skills. Additionally, it introduces different writing styles and a three-step writing process focused on planning, writing, and quality control.


















