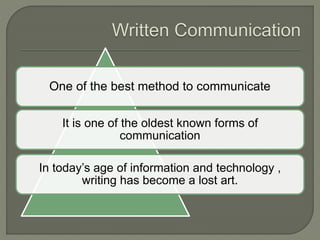
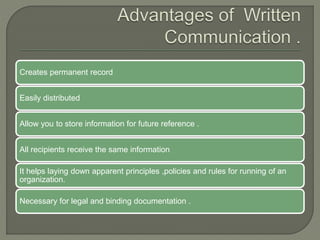
Written communication is an important skill that has evolved over thousands of years. It allows information to be stored and shared across distances and time. Effective written communication requires clarity, structure, appropriate tone and style for the intended audience. Key considerations include organization, grammar, vocabulary choice, format and ensuring the audience can easily understand the message.