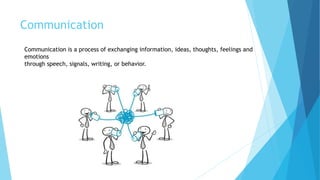
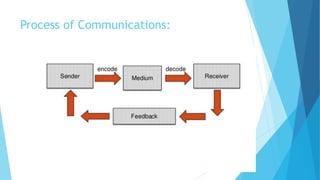
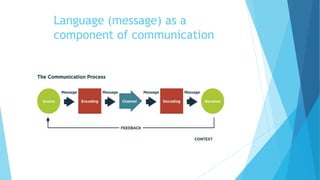
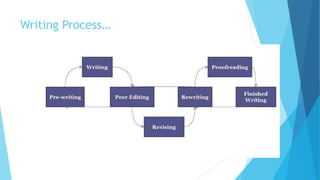
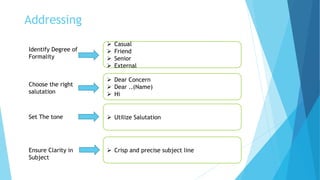
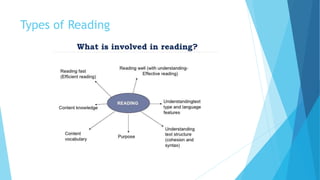
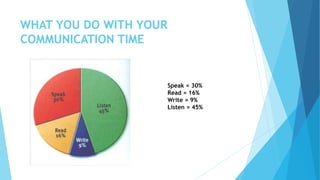
The document outlines various types of communication, including verbal, nonverbal, internal, and external communication, emphasizing their importance in organizational contexts. It describes effective writing, reading, listening, and speaking skills, providing guidelines for improving these skills and making impactful presentations. Additionally, it highlights the significance of choosing the right medium and language in business communication.