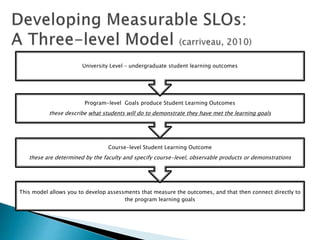
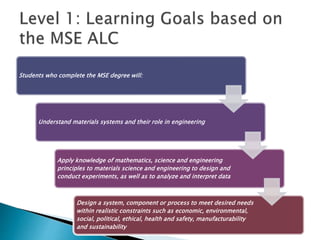
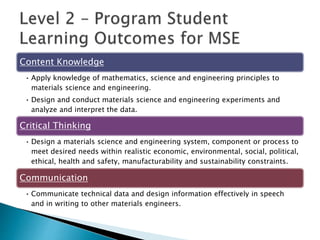
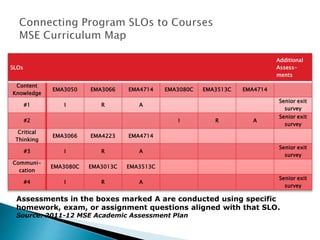
This document provides guidance on developing student learning outcomes and assessing student achievement of those outcomes. It discusses the importance of writing measurable learning outcomes using action verbs from Bloom's taxonomy. Outcomes should describe what students will know and be able to do rather than internal processes like understanding. The document also discusses the difference between outputs, outcomes and goals, and emphasizes the importance of directly assessing student learning through exams, assignments or other demonstrations of knowledge and skills. University, program and course-level outcomes are interrelated and assessments should be aligned across levels. Both direct and indirect assessment methods are recommended.