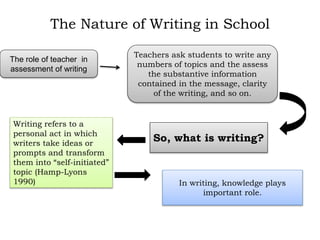
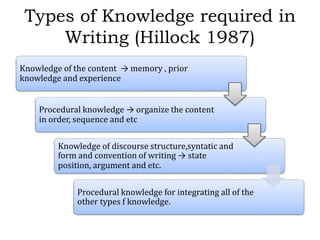
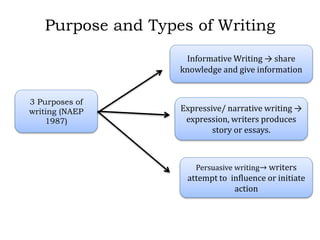
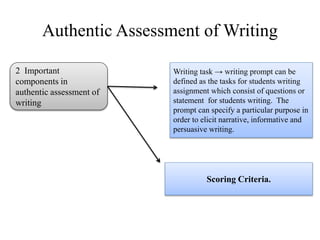
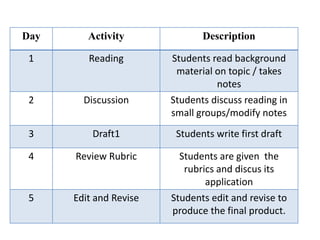
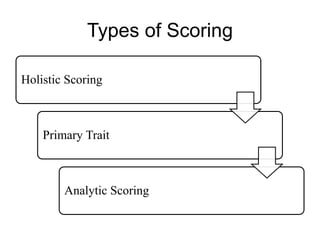
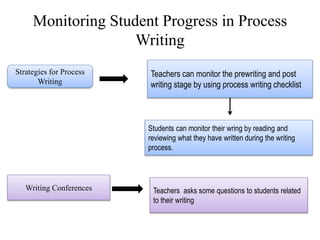
Writing assessment is used for placement, monitoring progress, and accountability of ELL students. It involves evaluating students' writing content, clarity, and mechanics. Effective writing instruction incorporates process writing, writing across curriculums, and authentic tasks. Scoring can be holistic, focusing on traits, or analytical. Monitoring student development includes checking prewriting, post-writing, and conferencing. Self and peer assessment also support writing growth.